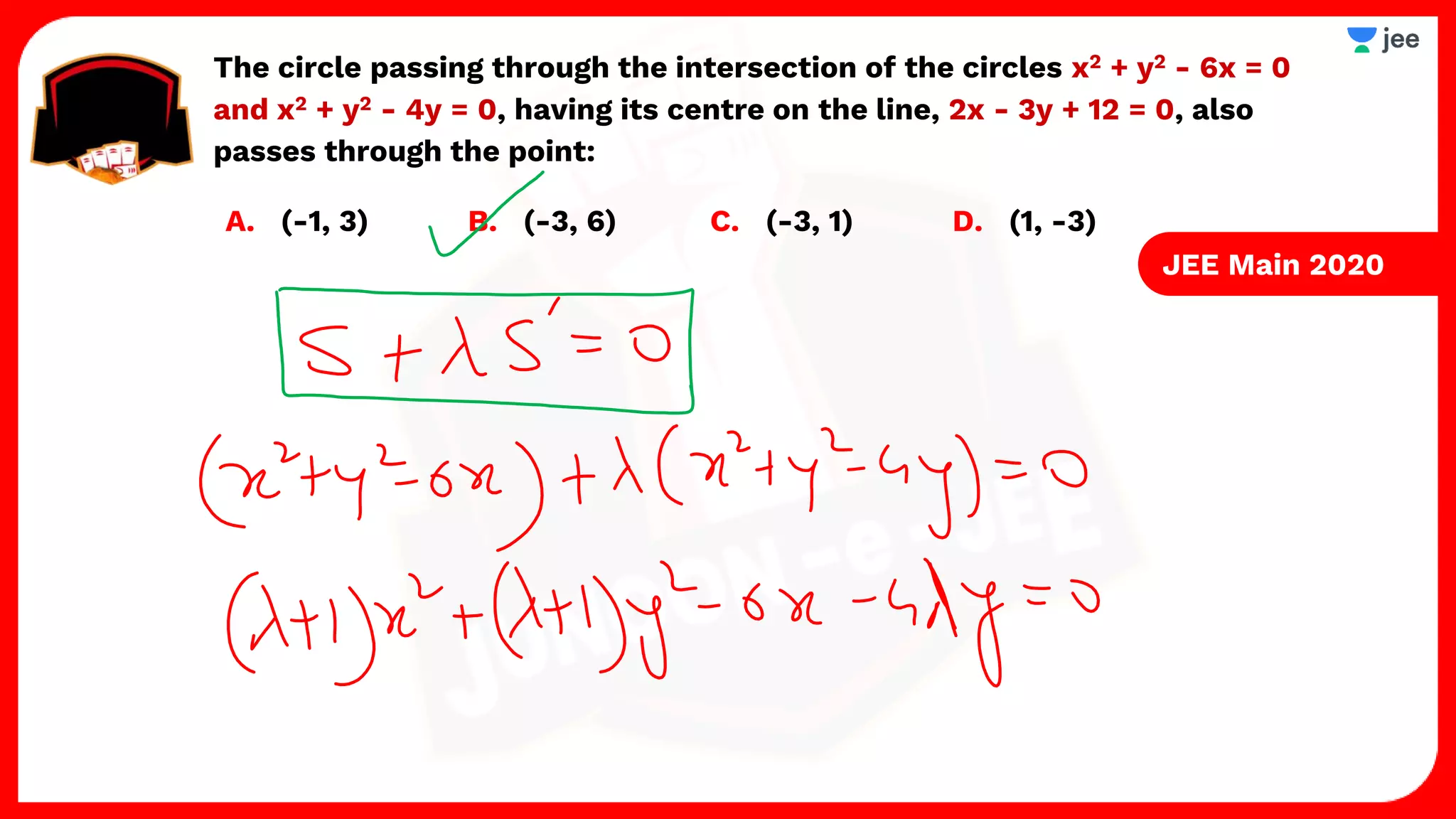
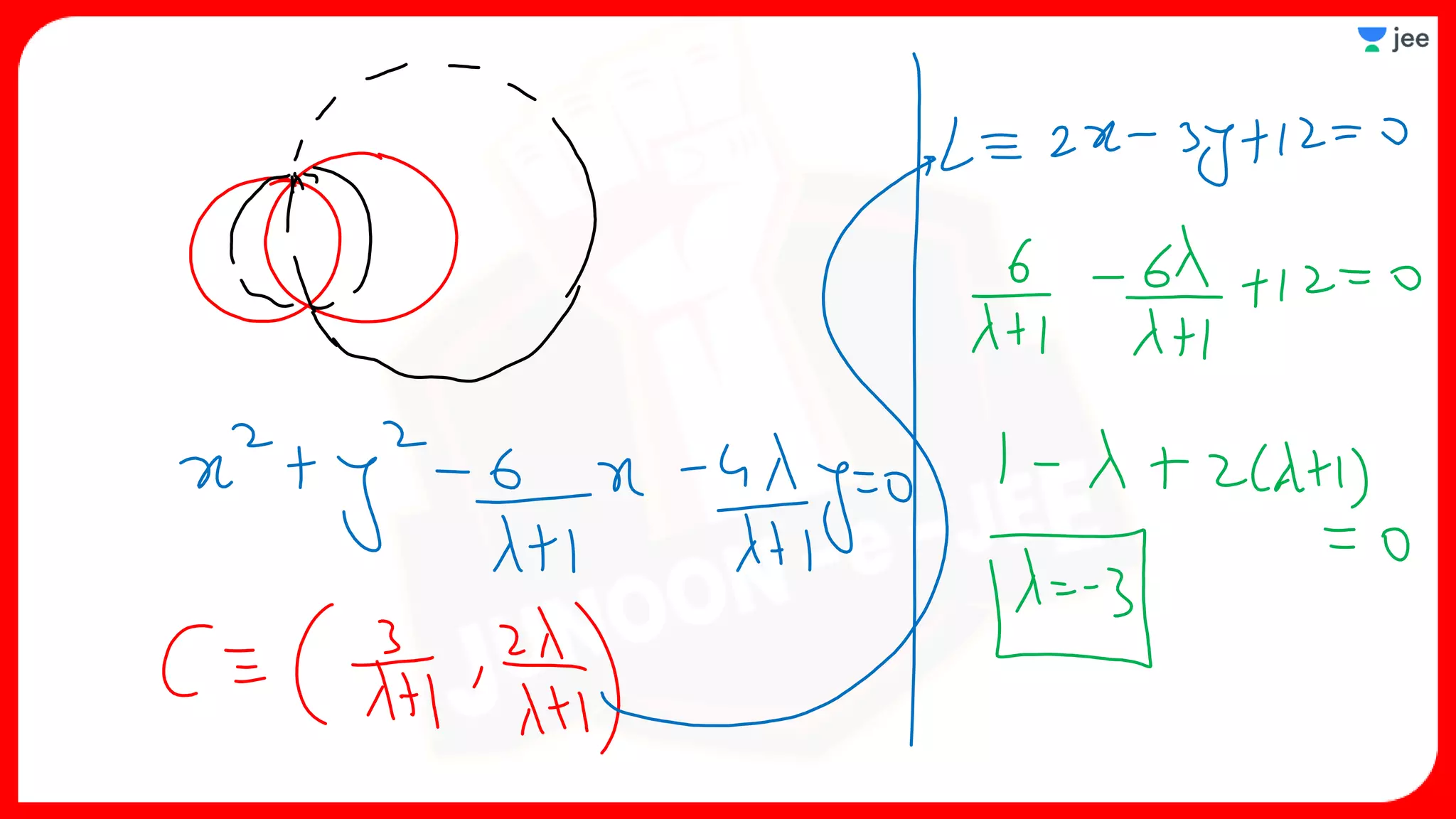
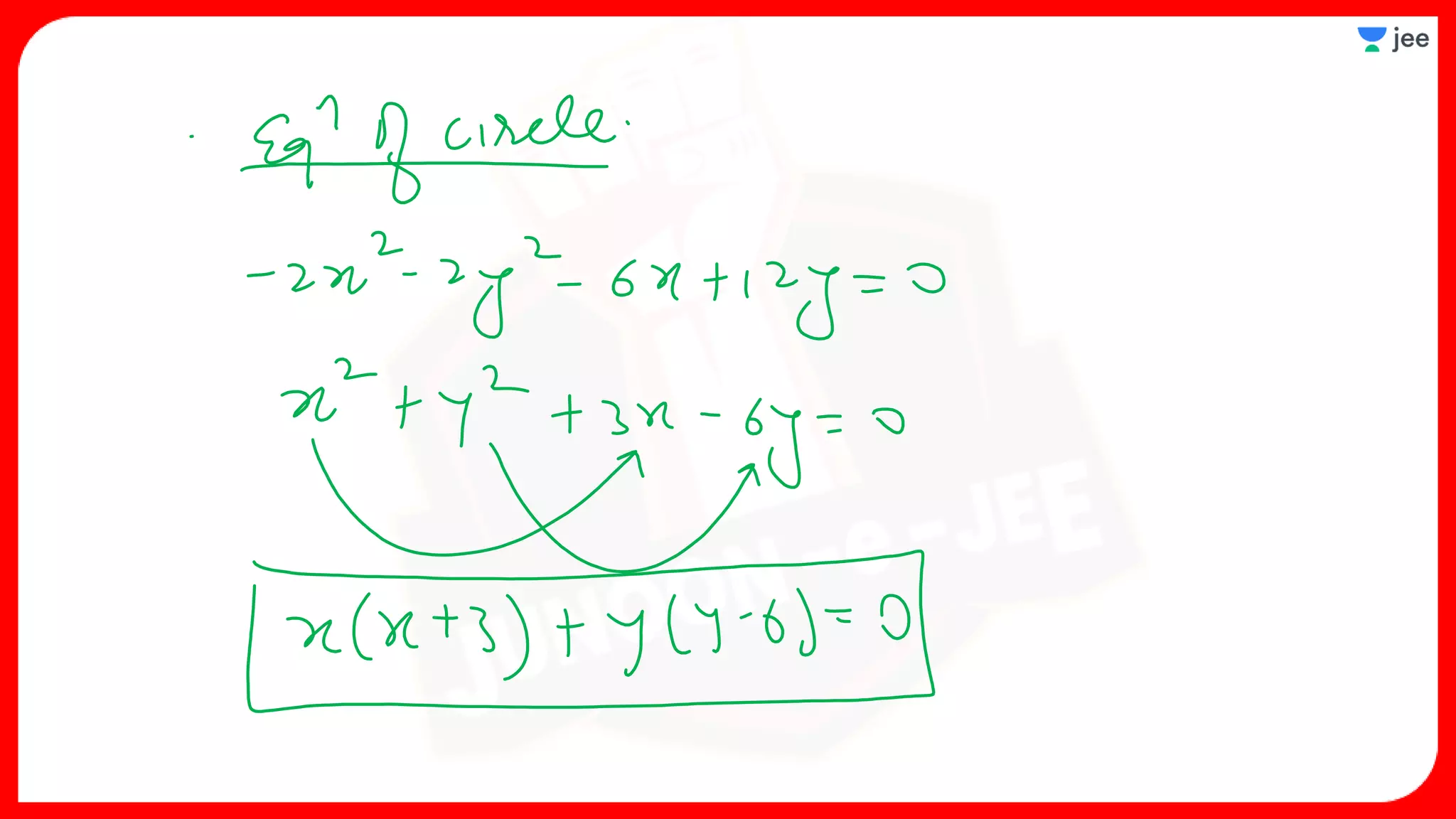
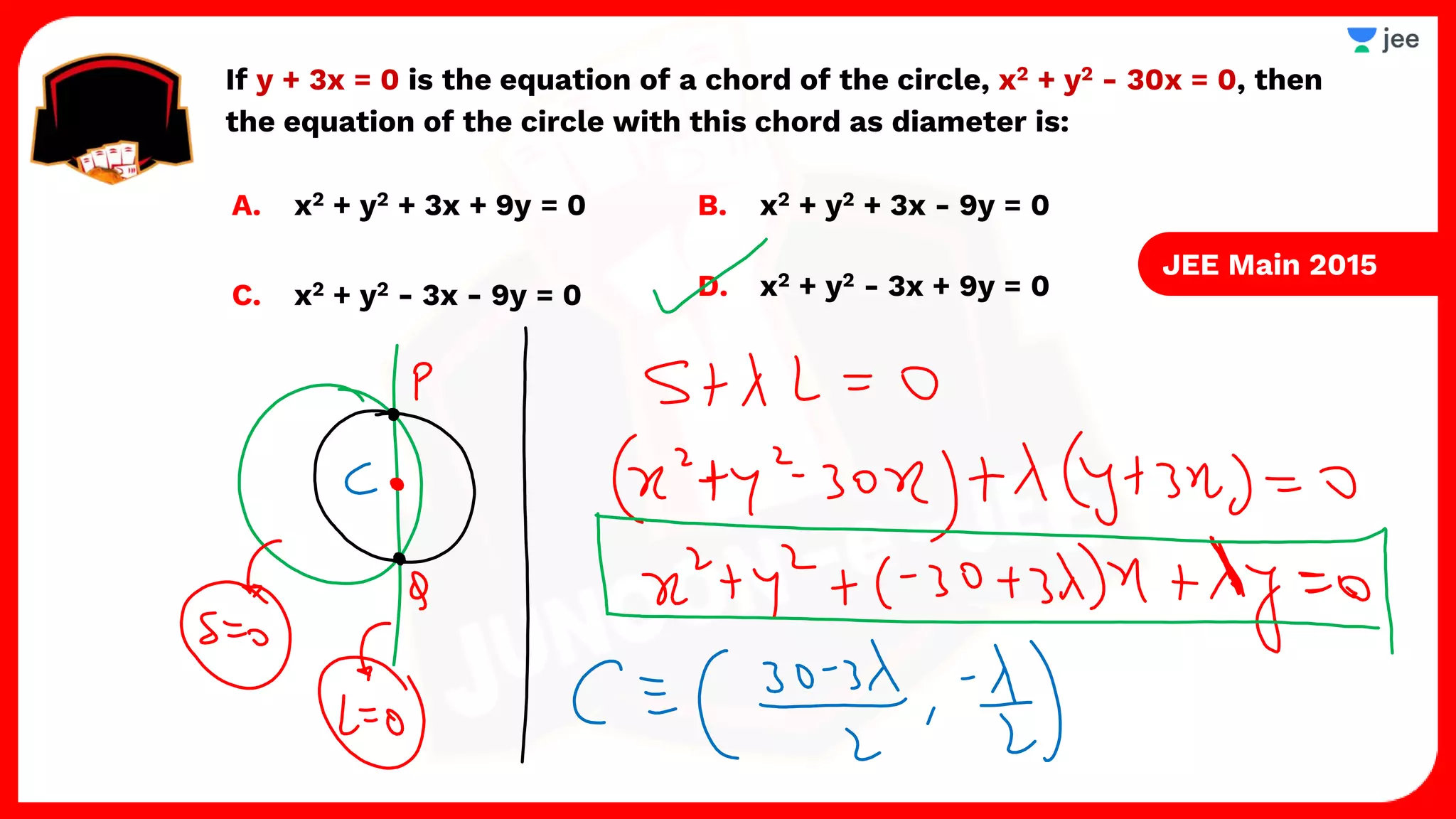
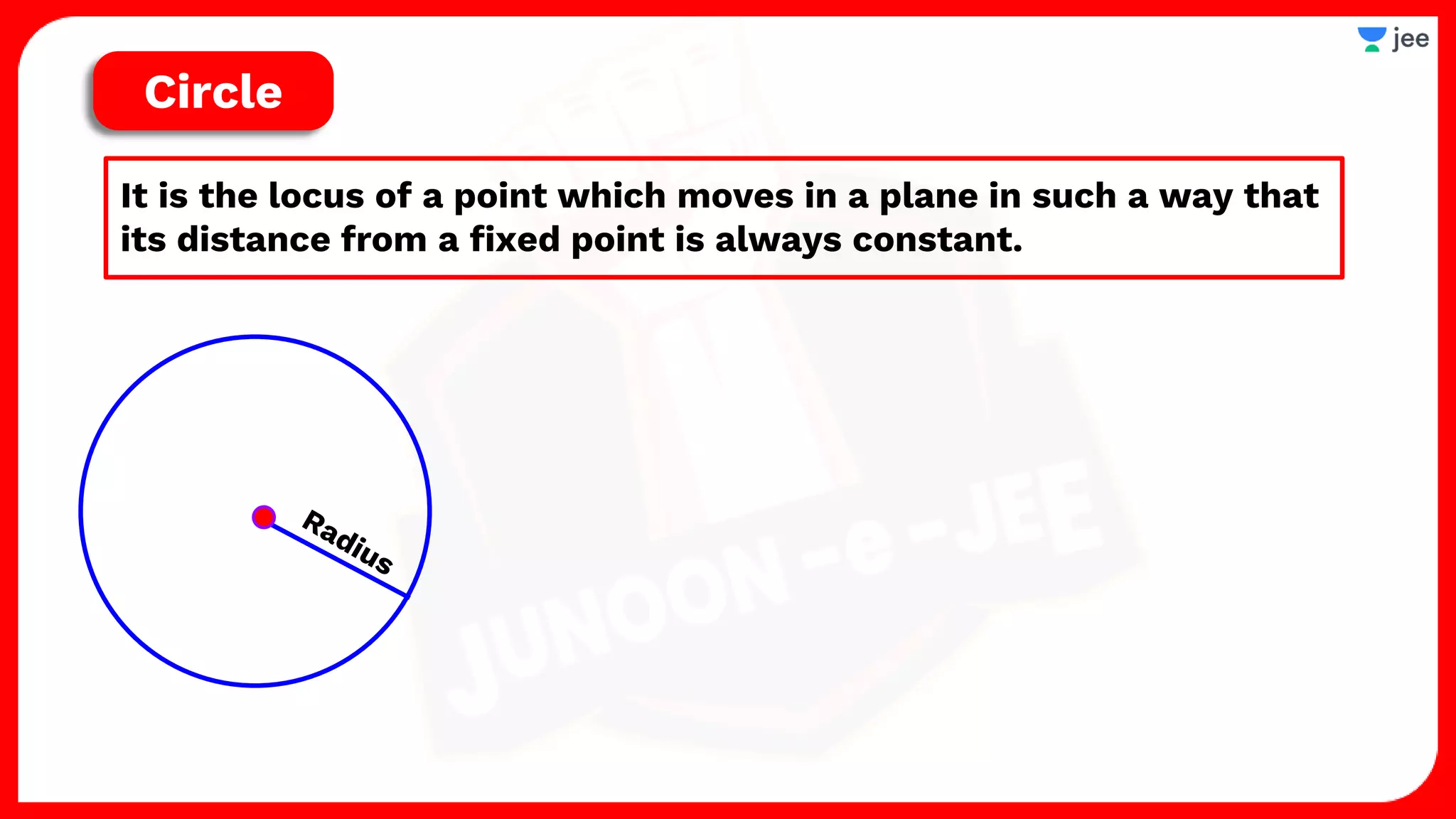
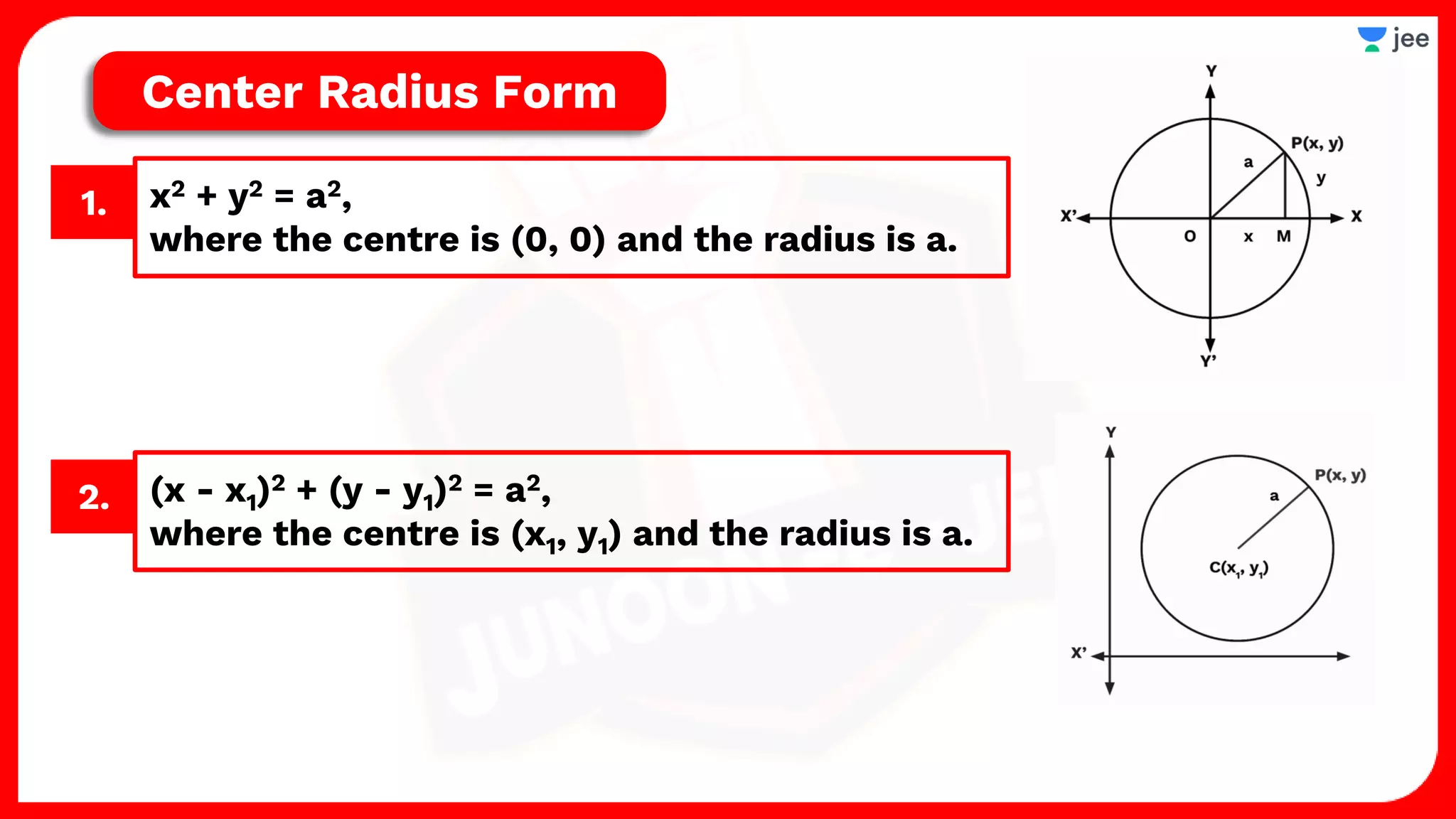
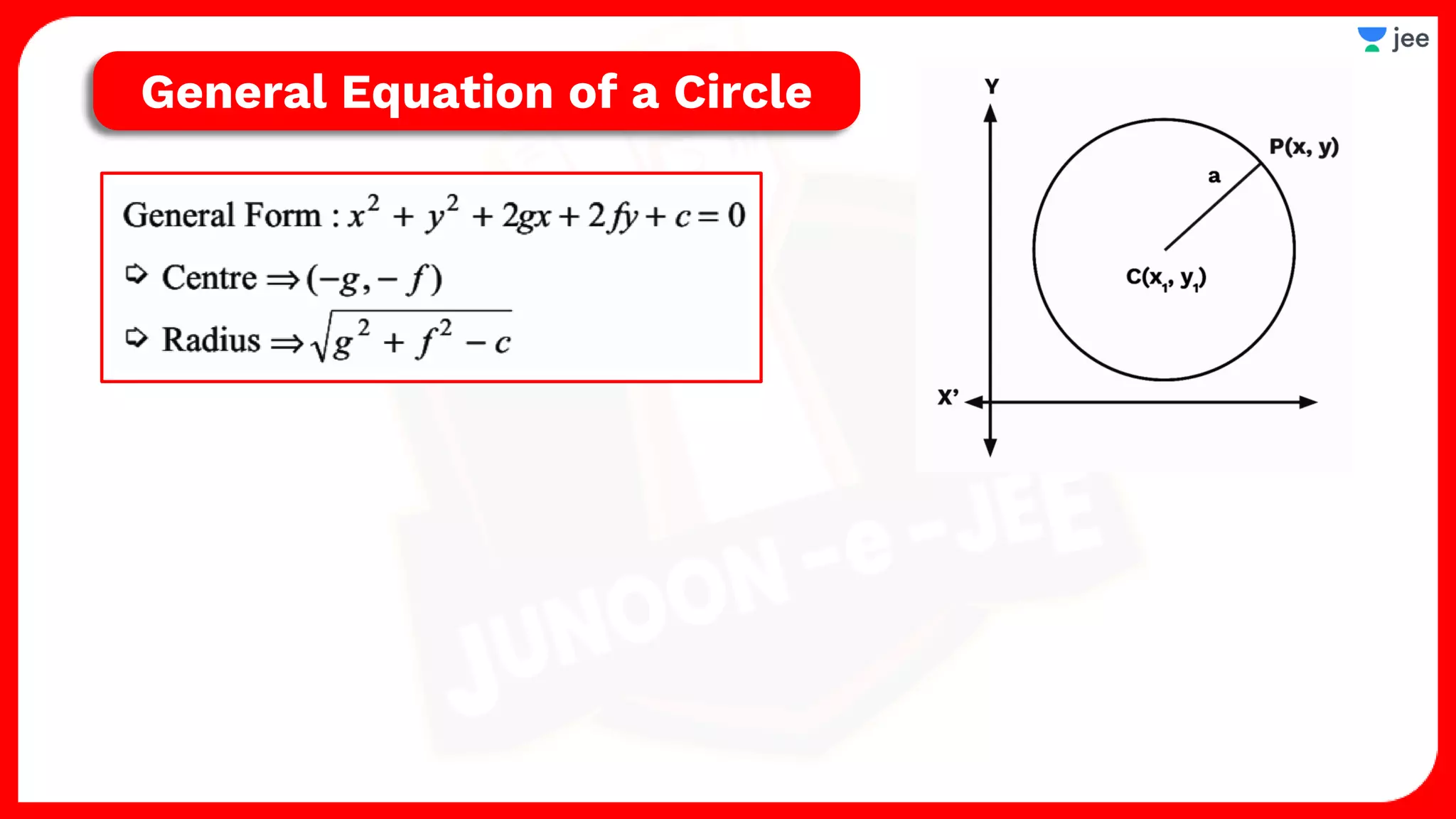
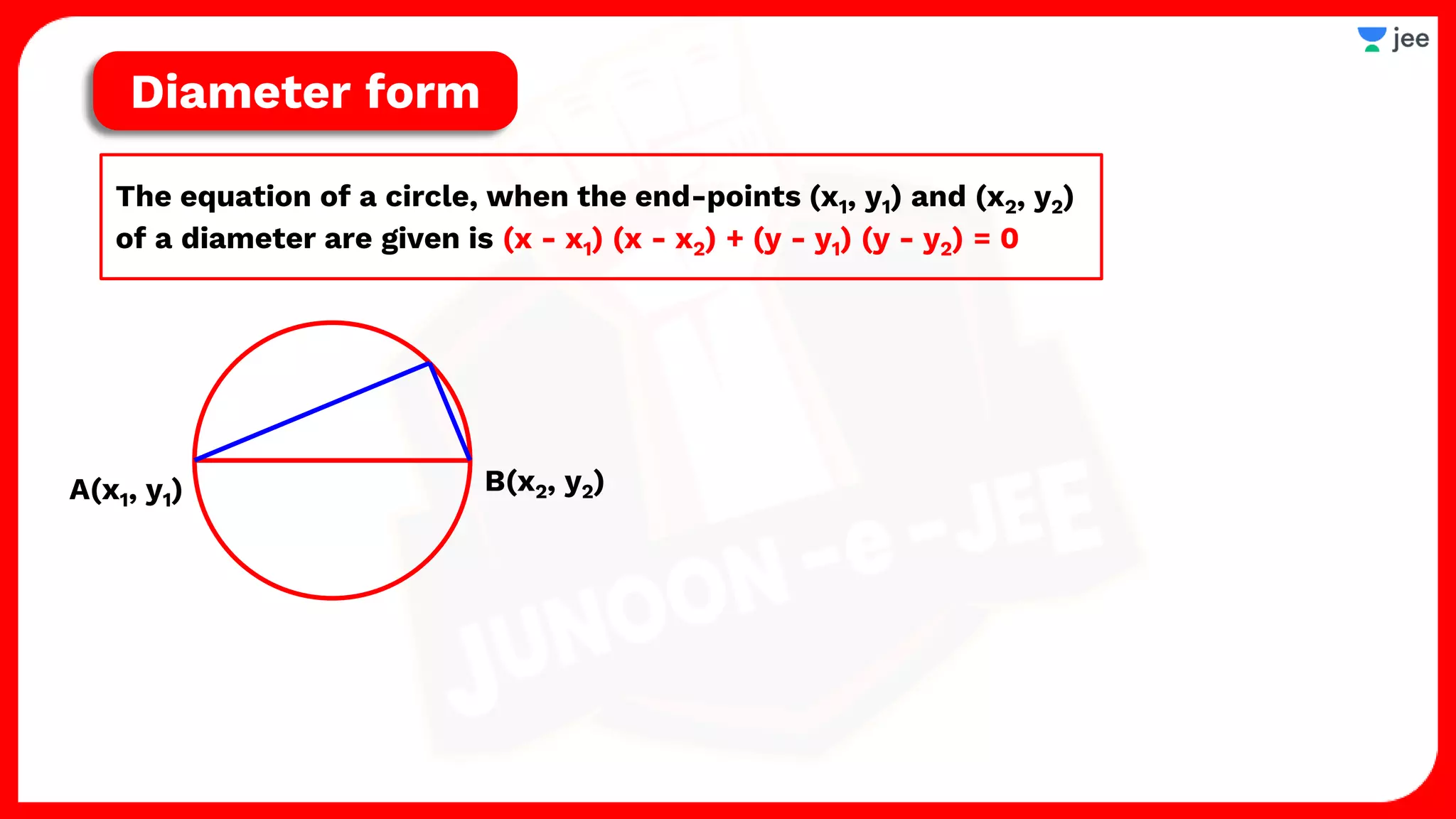
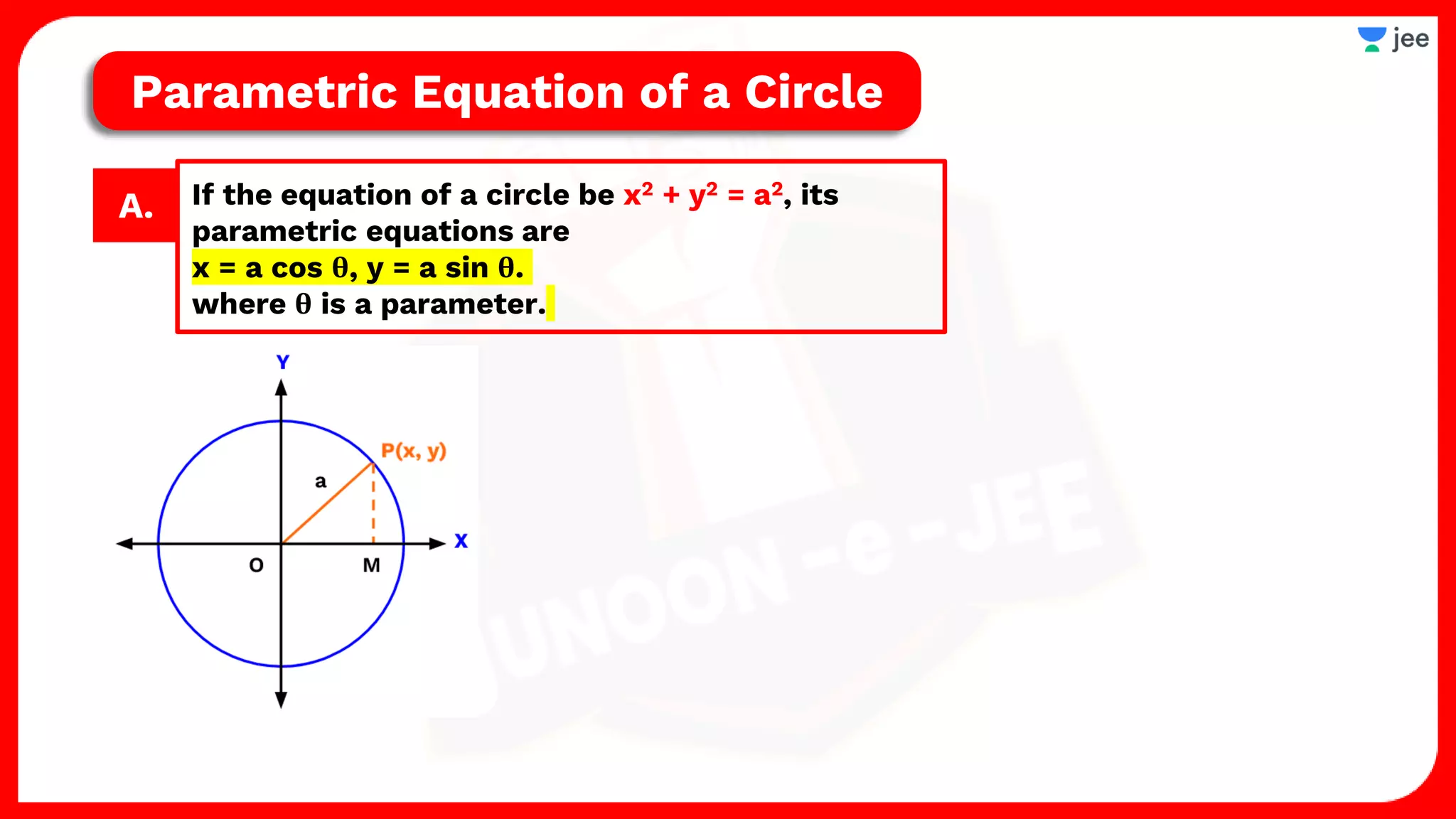
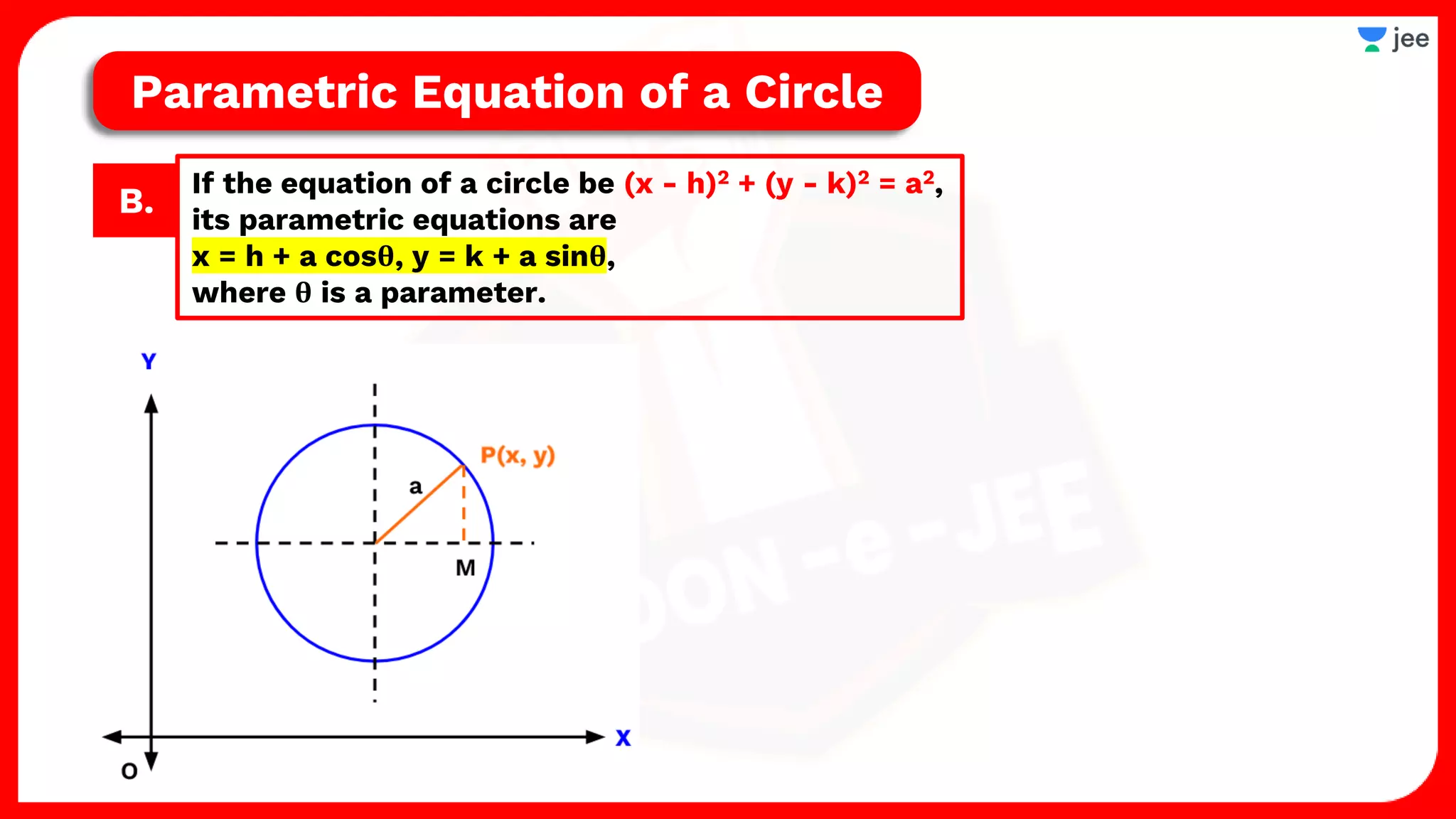
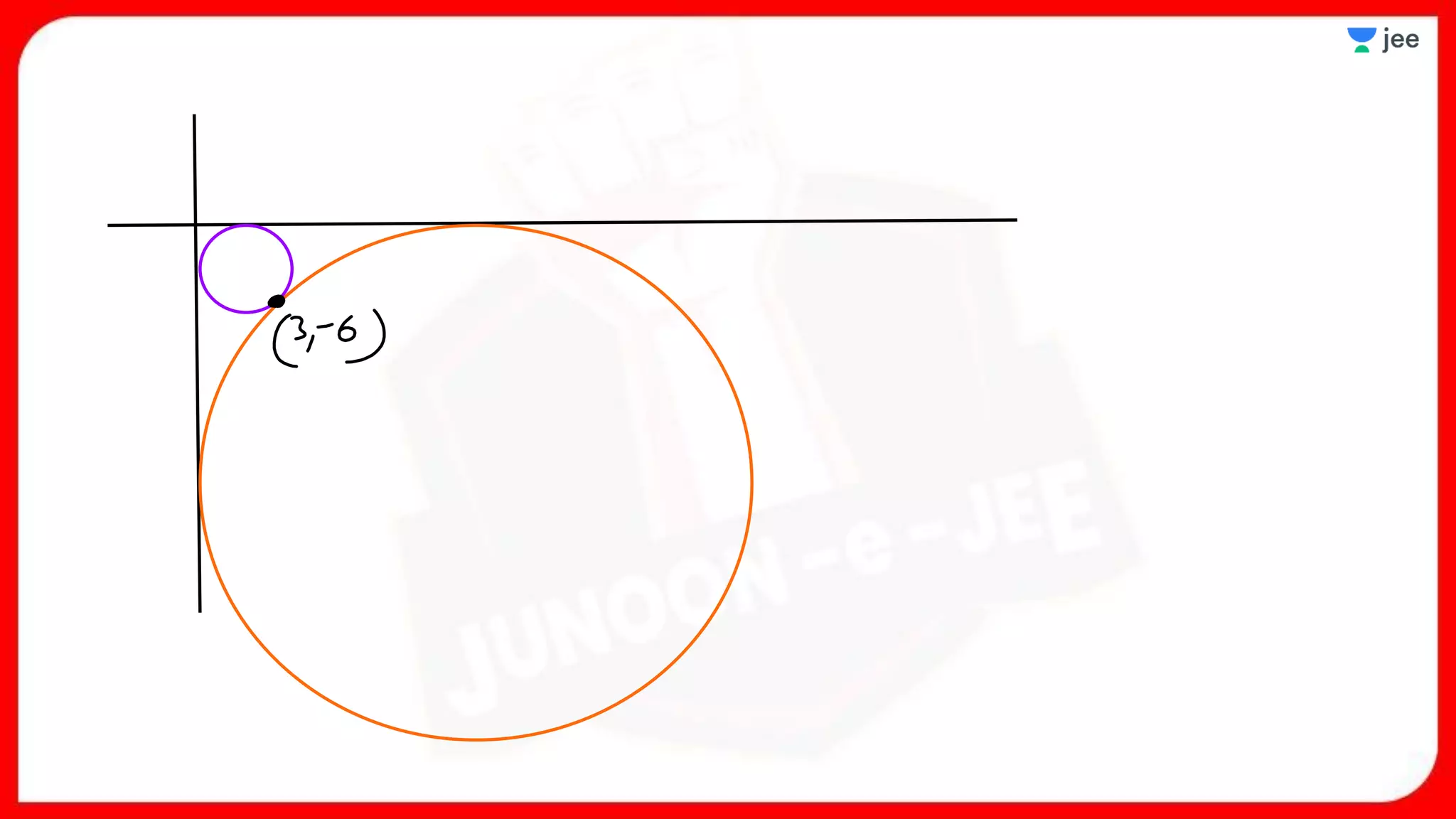
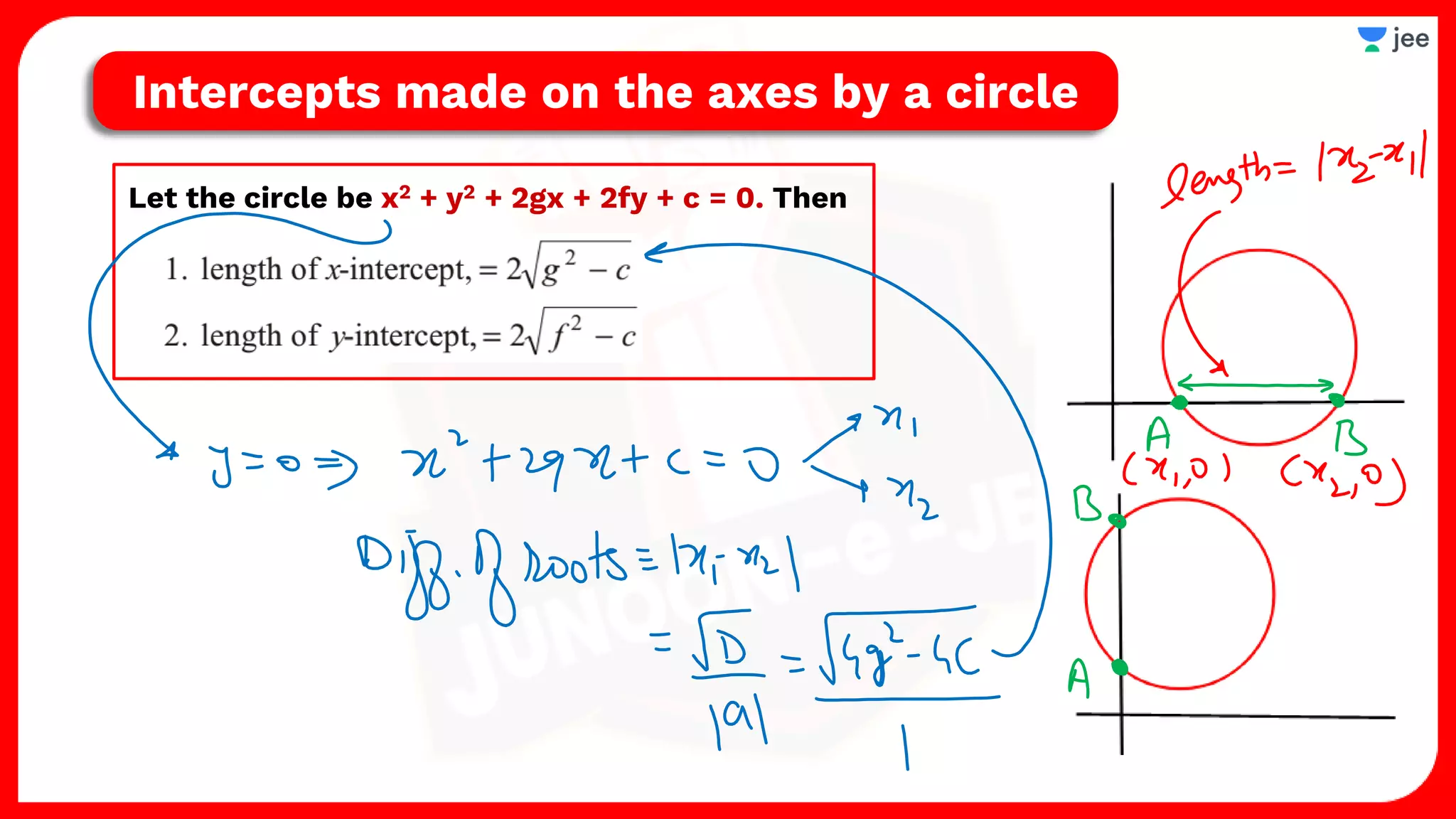
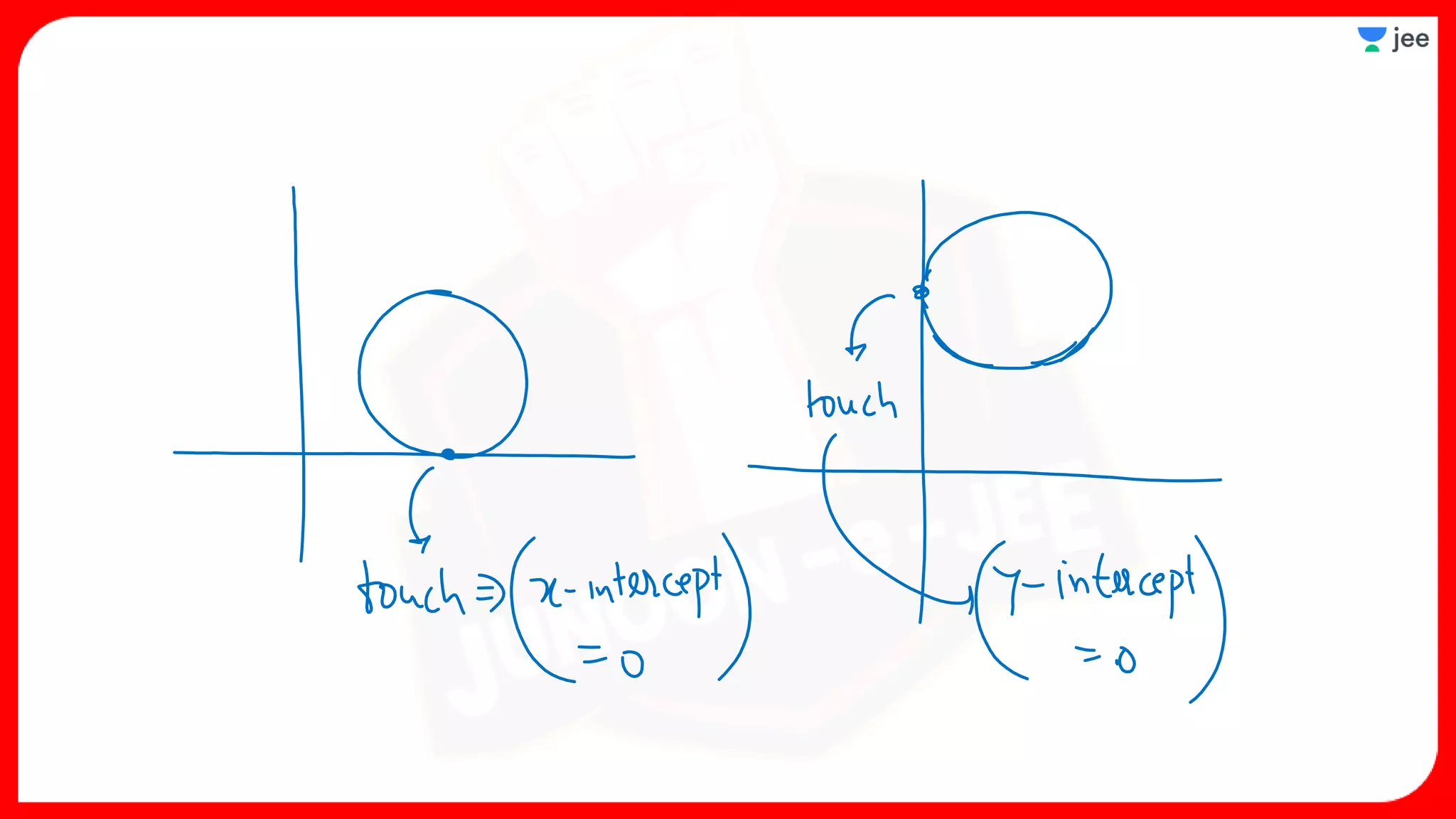
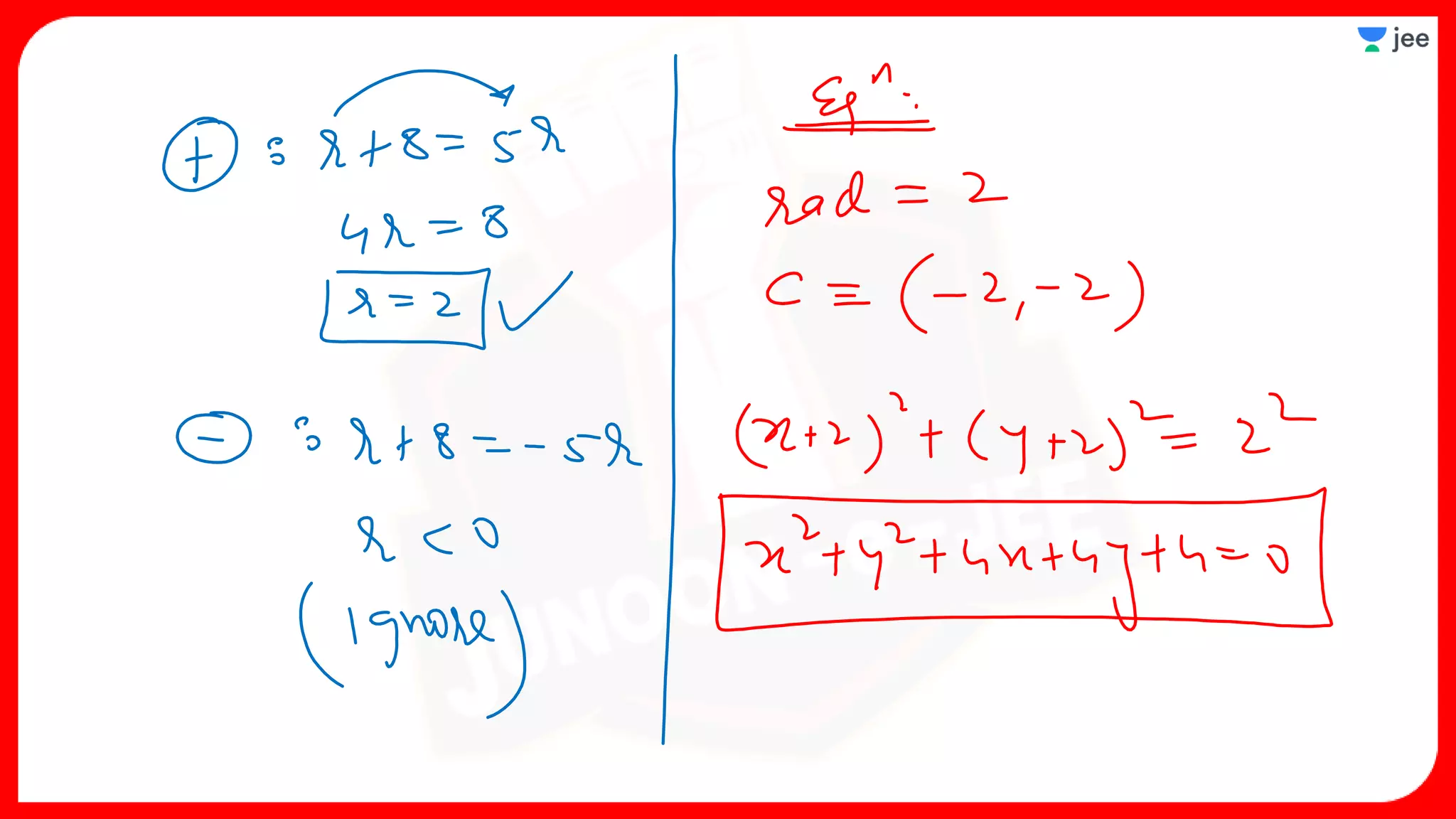
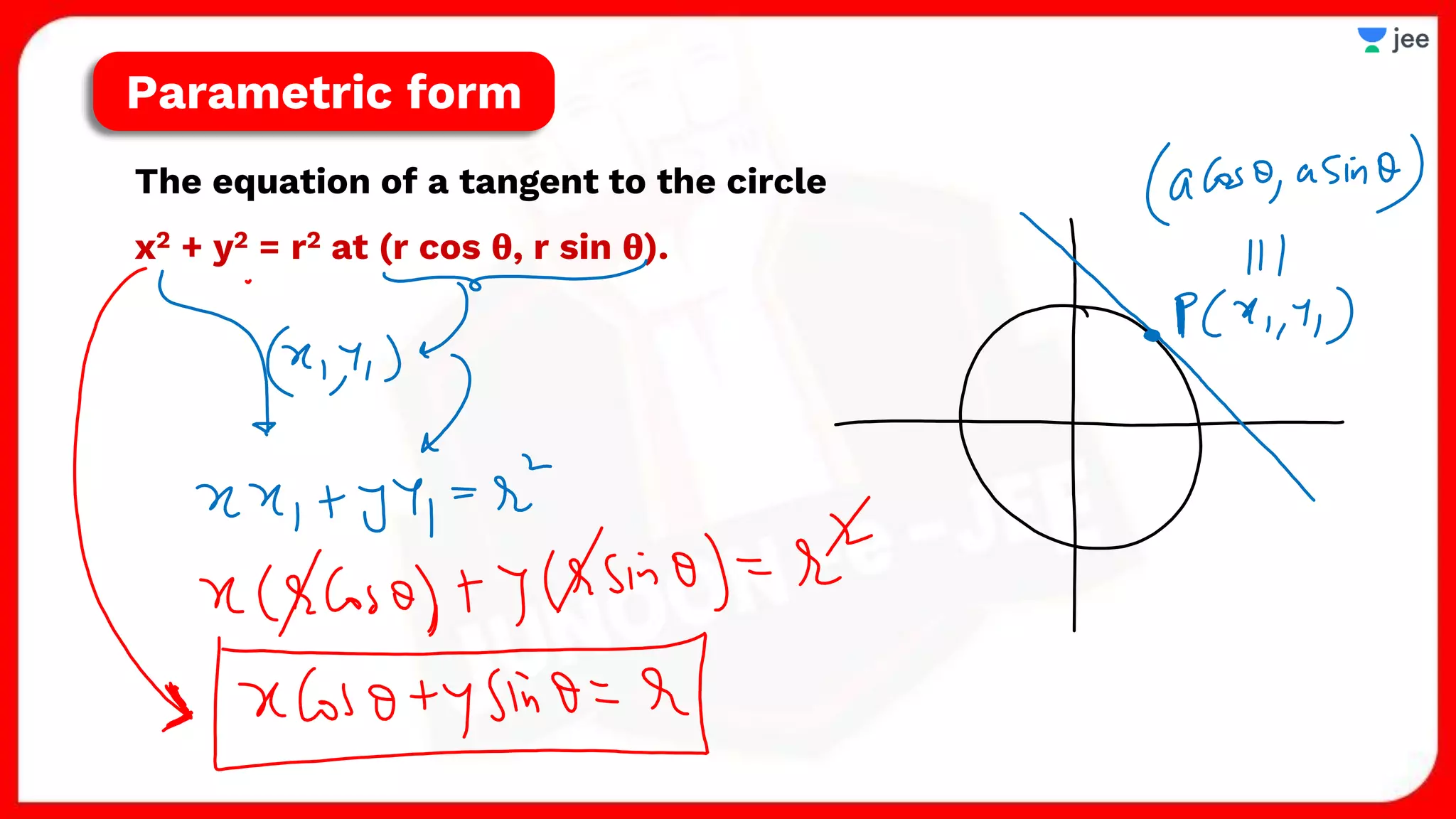
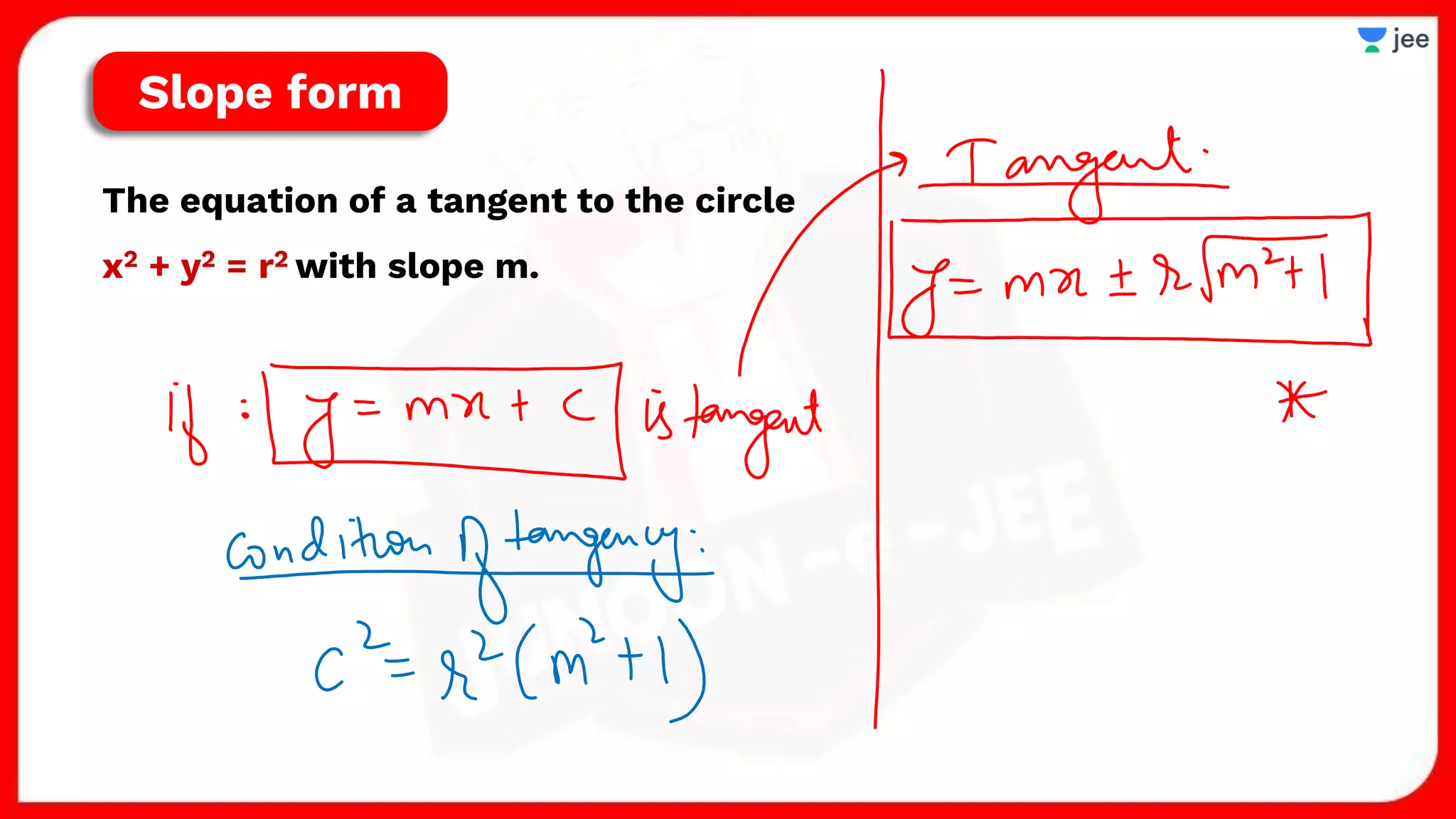
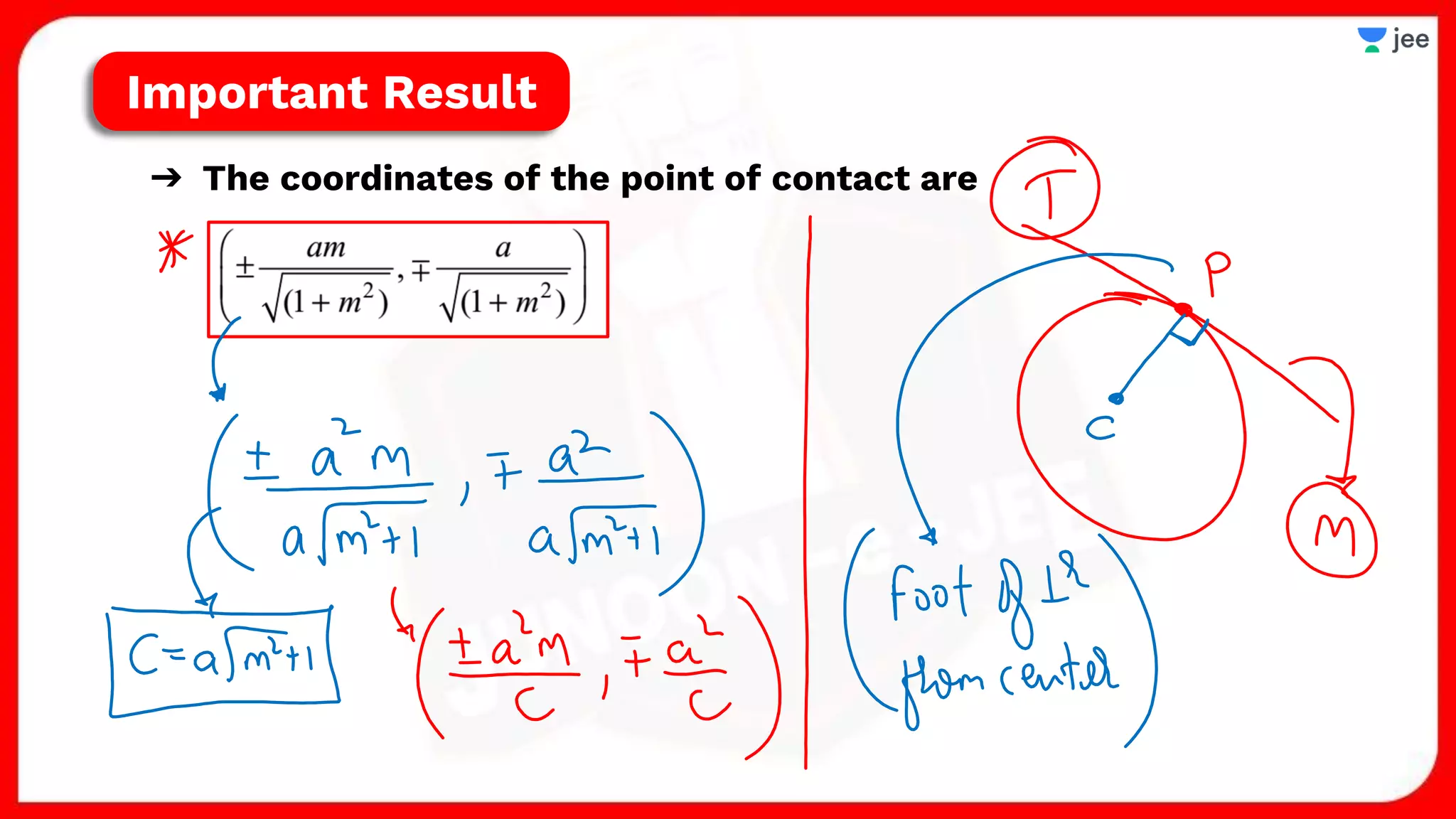
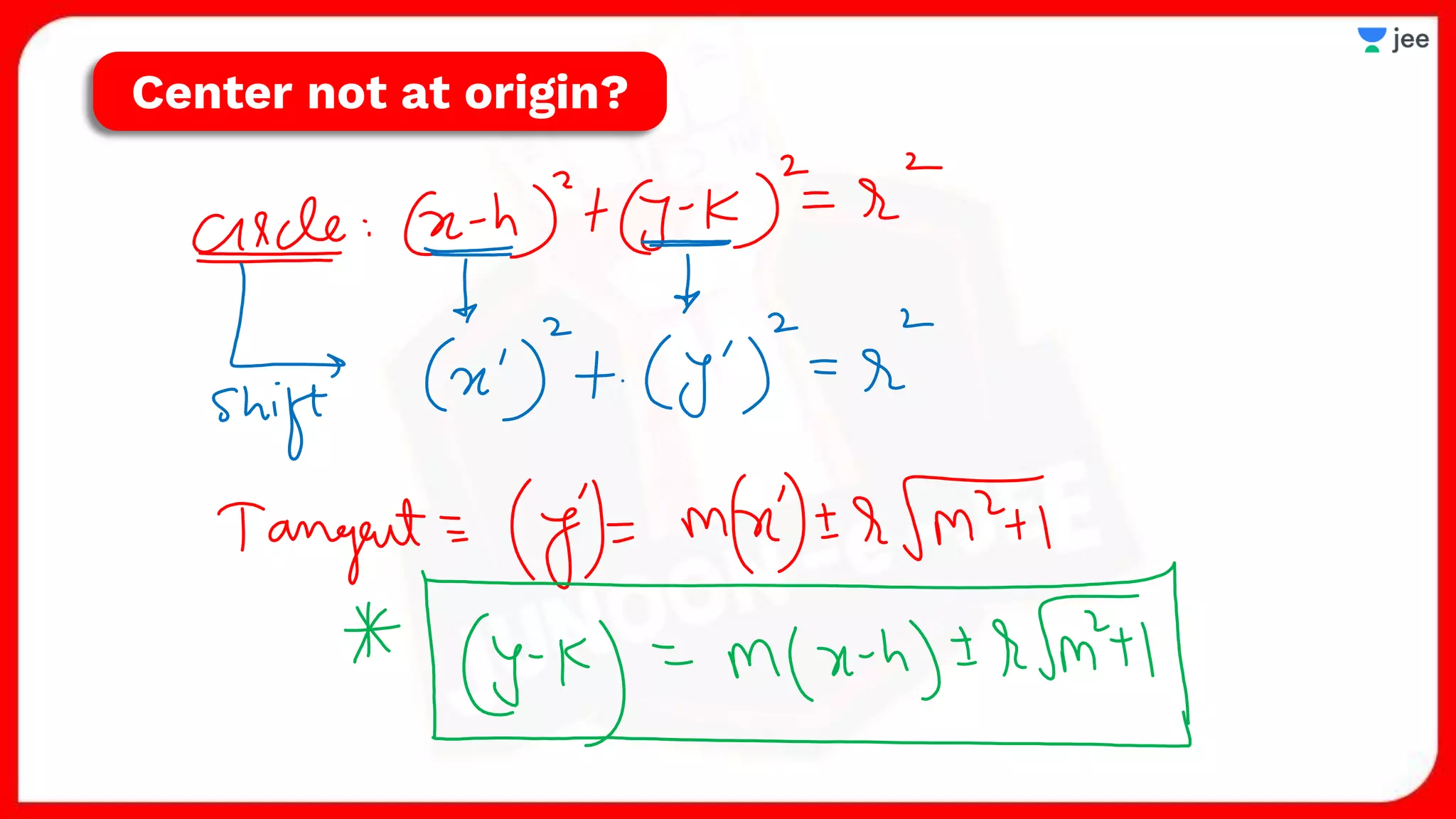
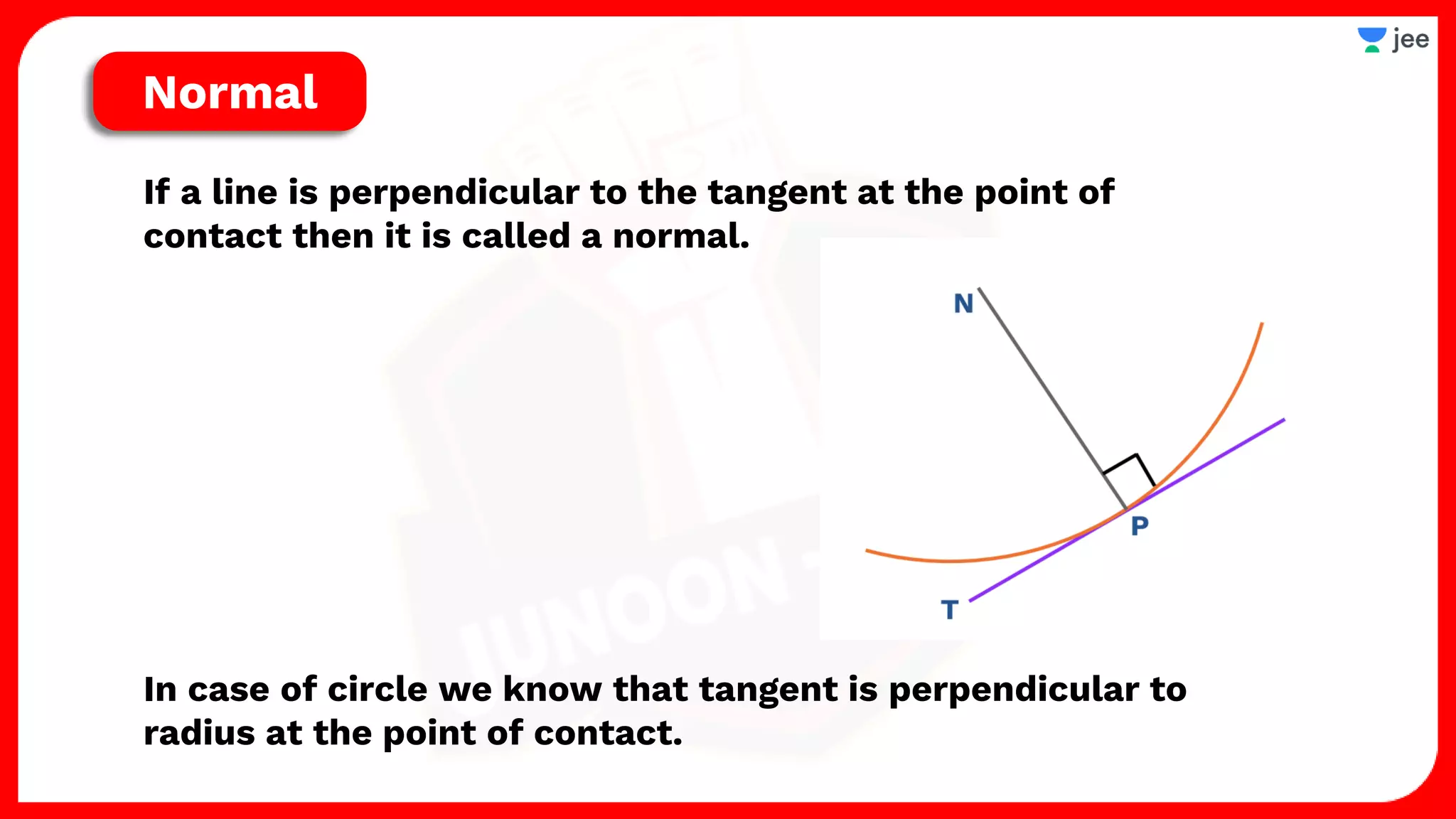
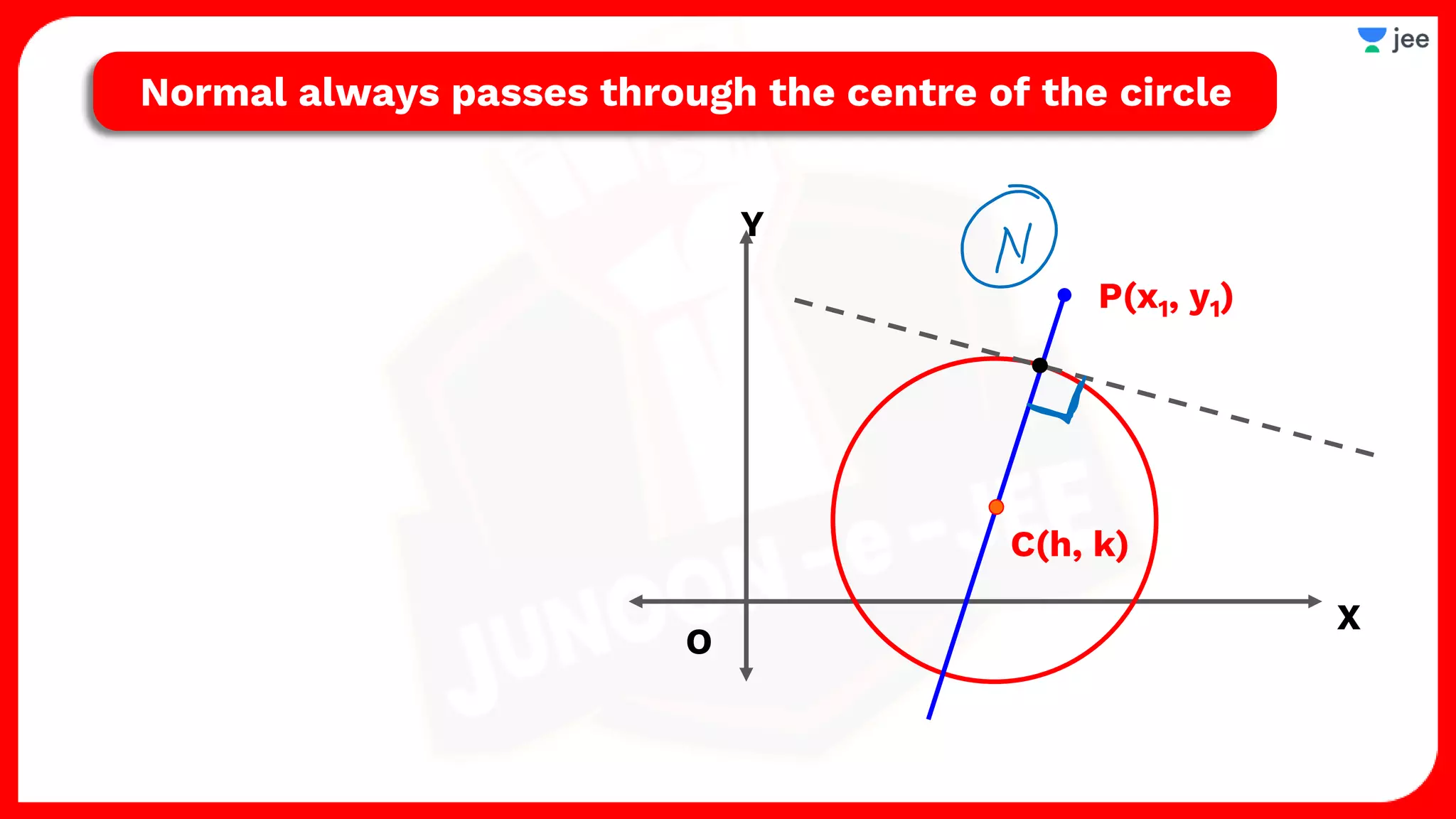
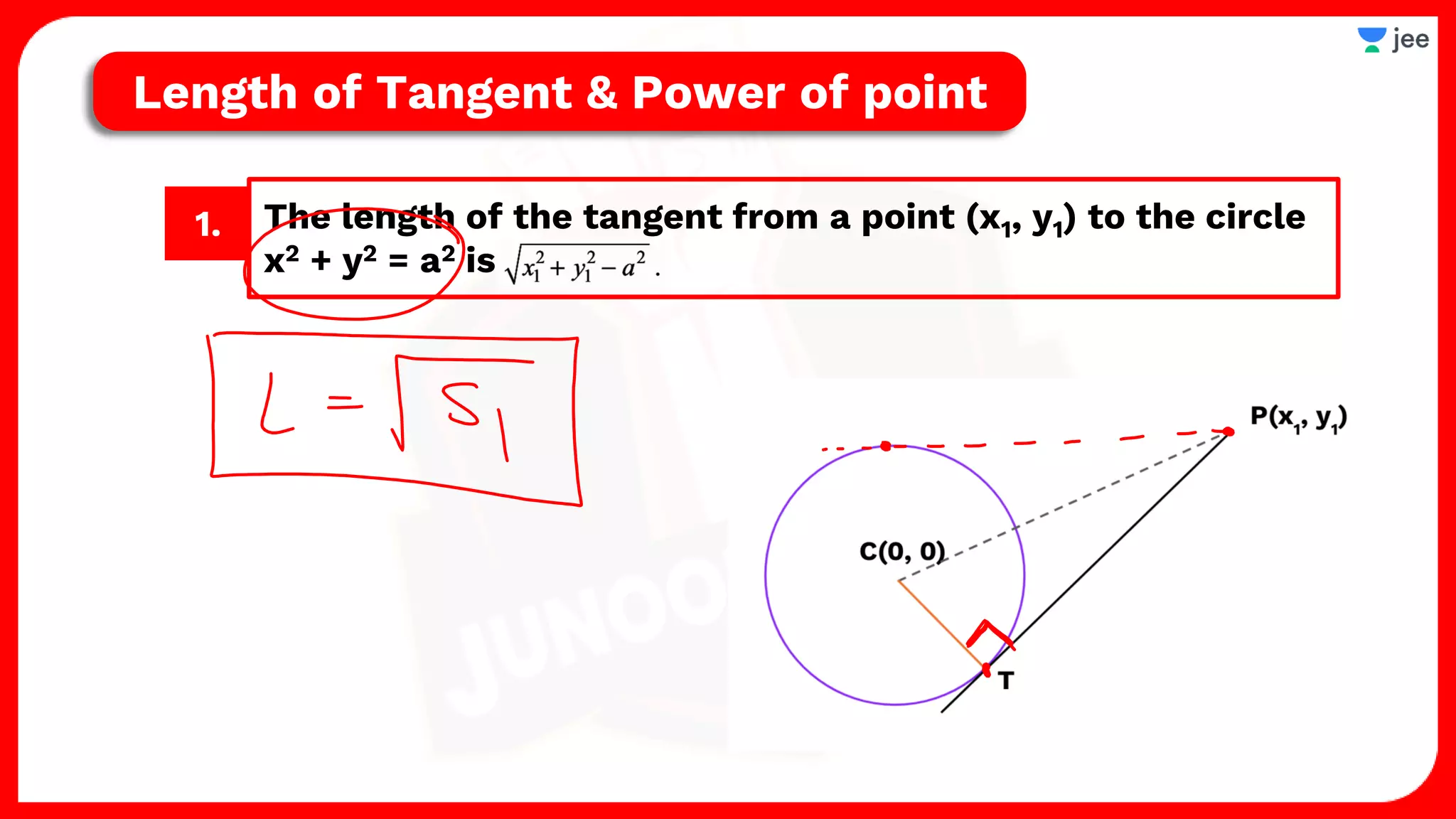
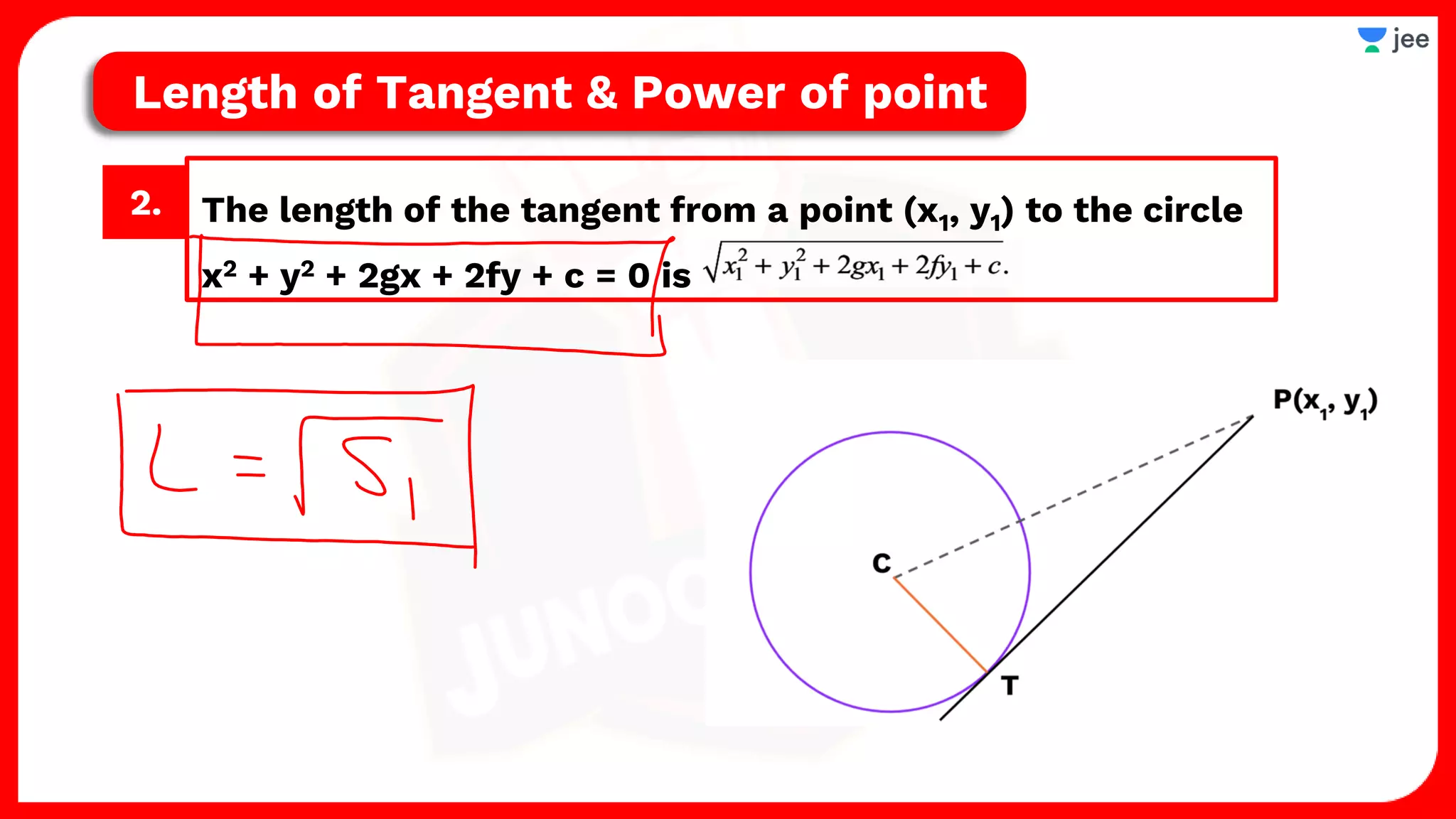
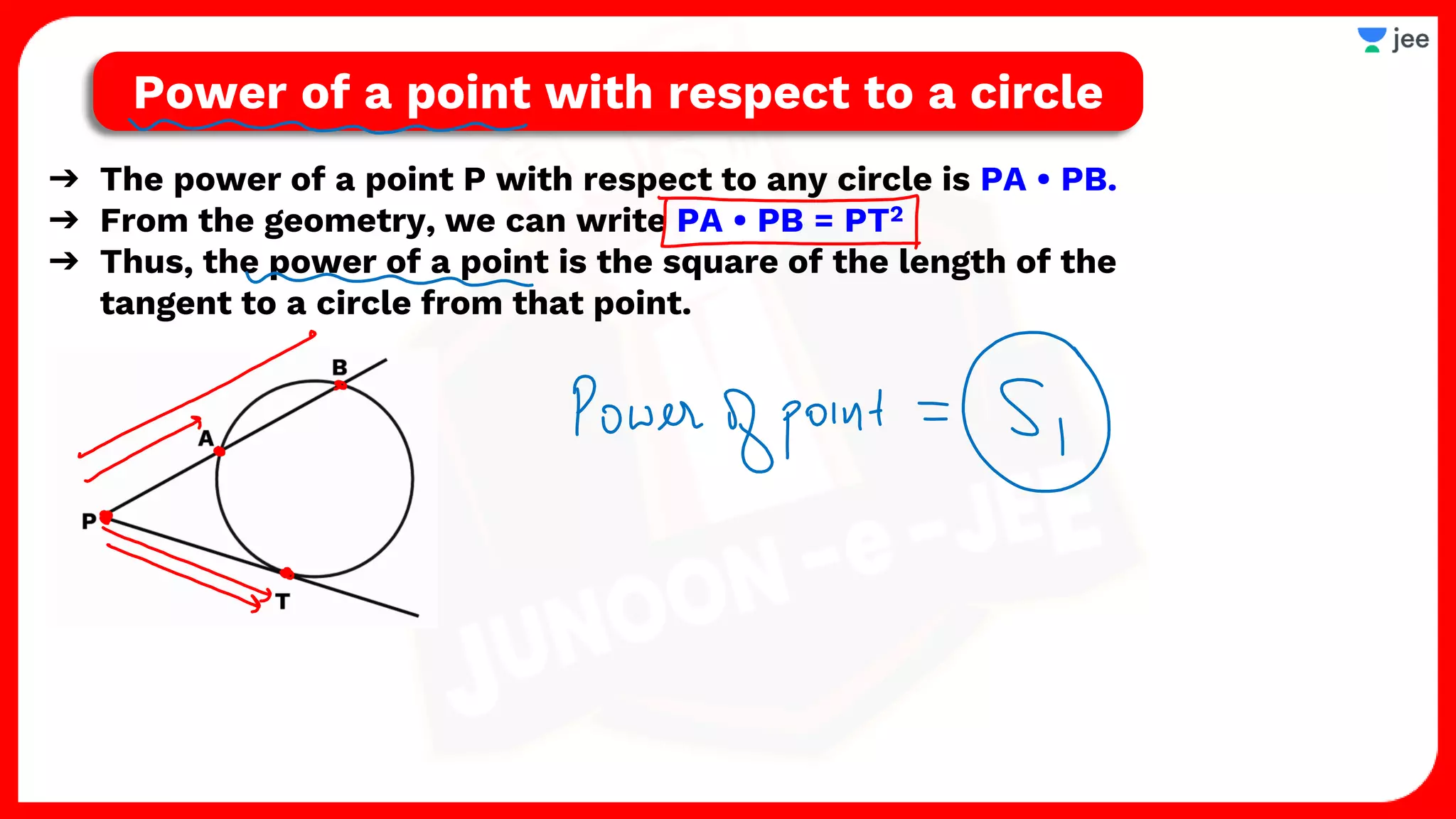
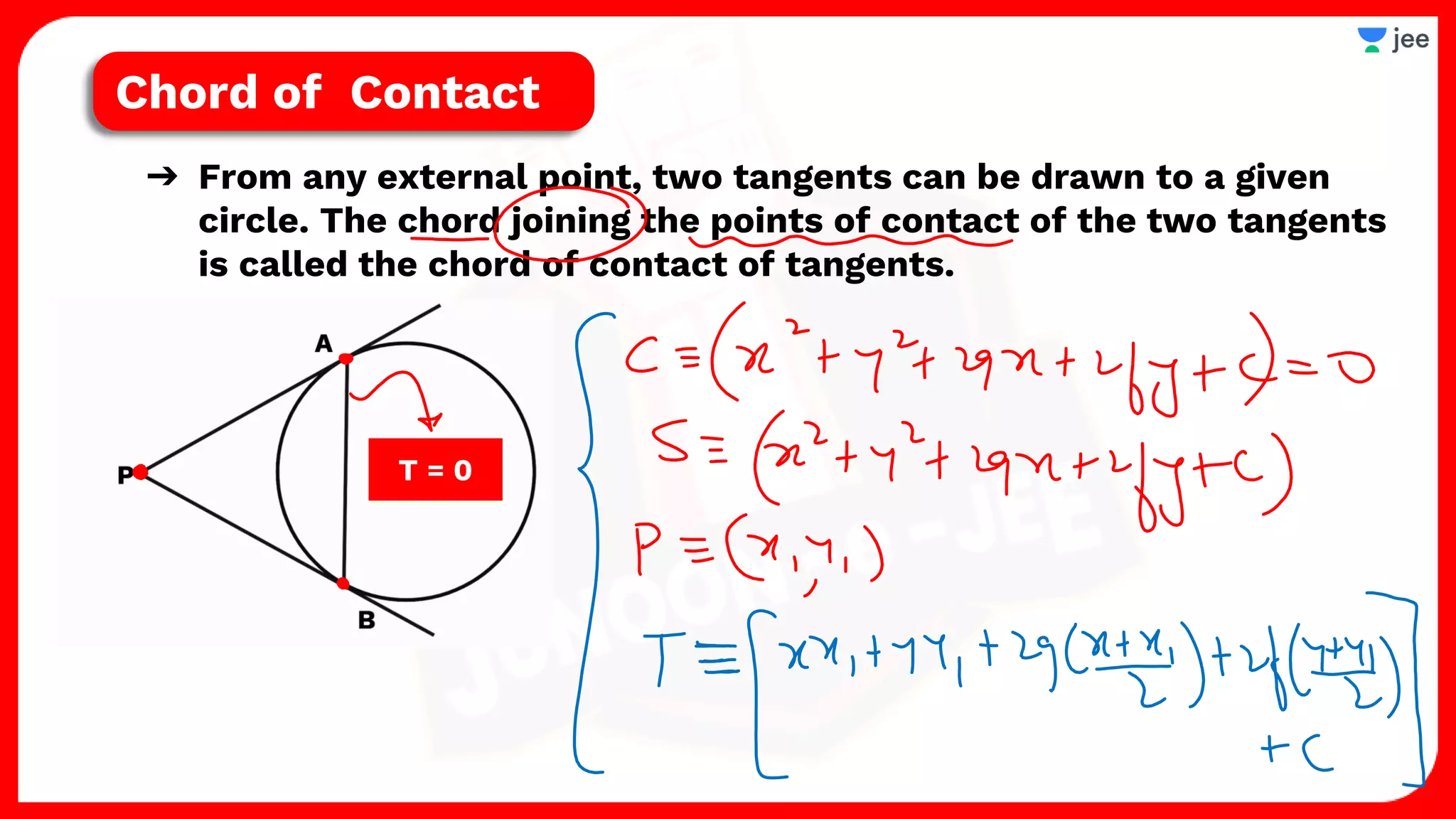
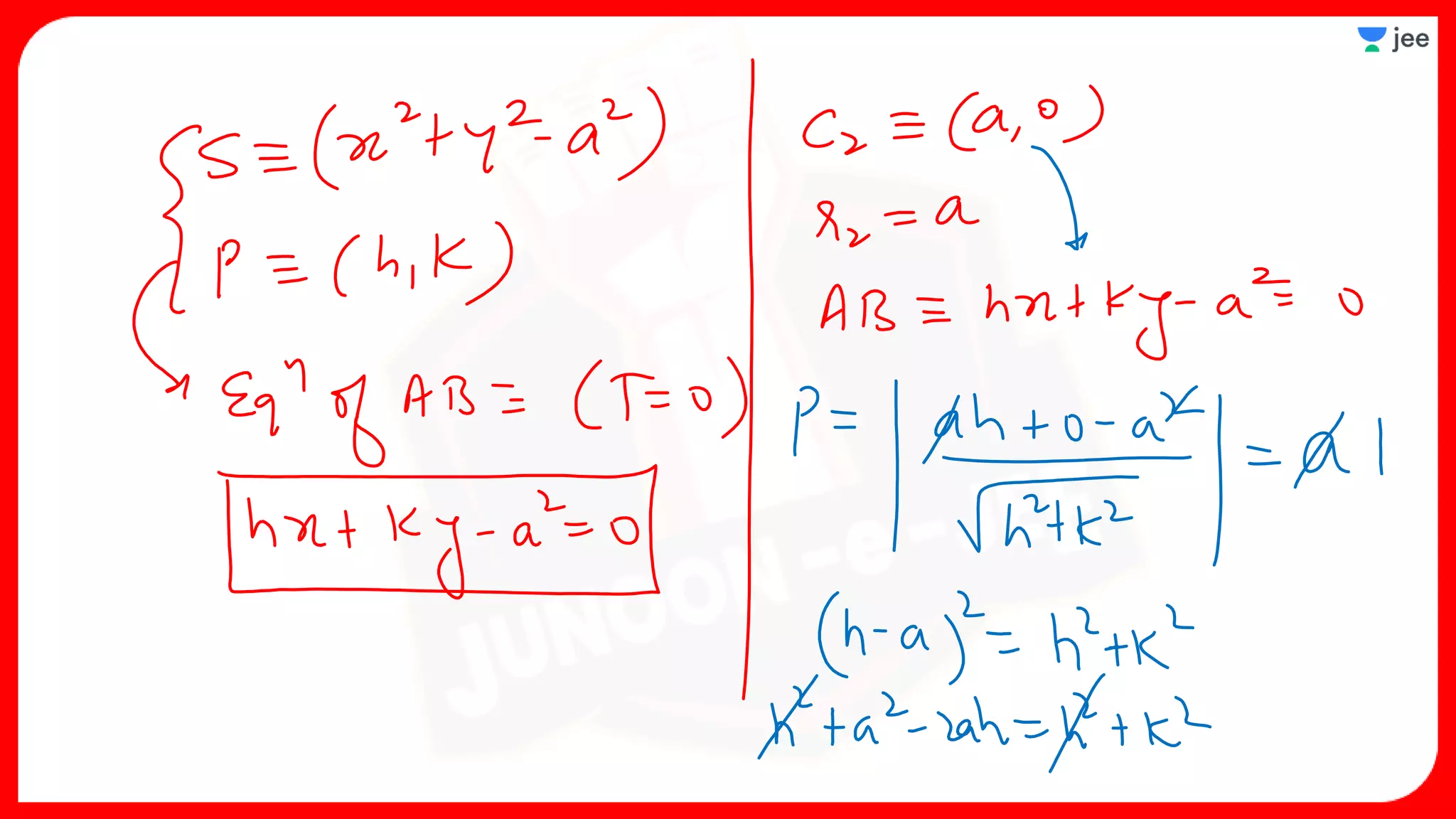
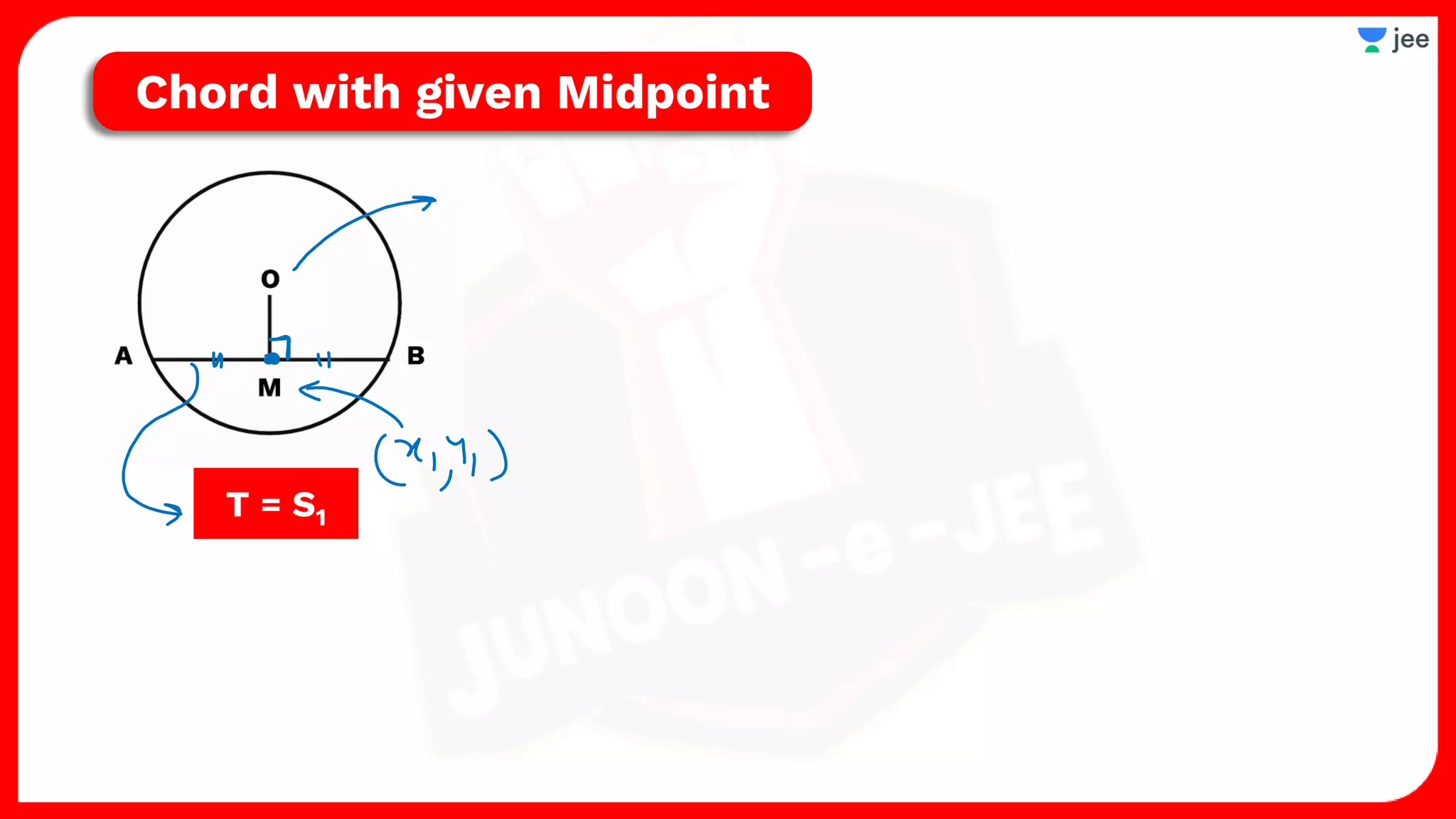
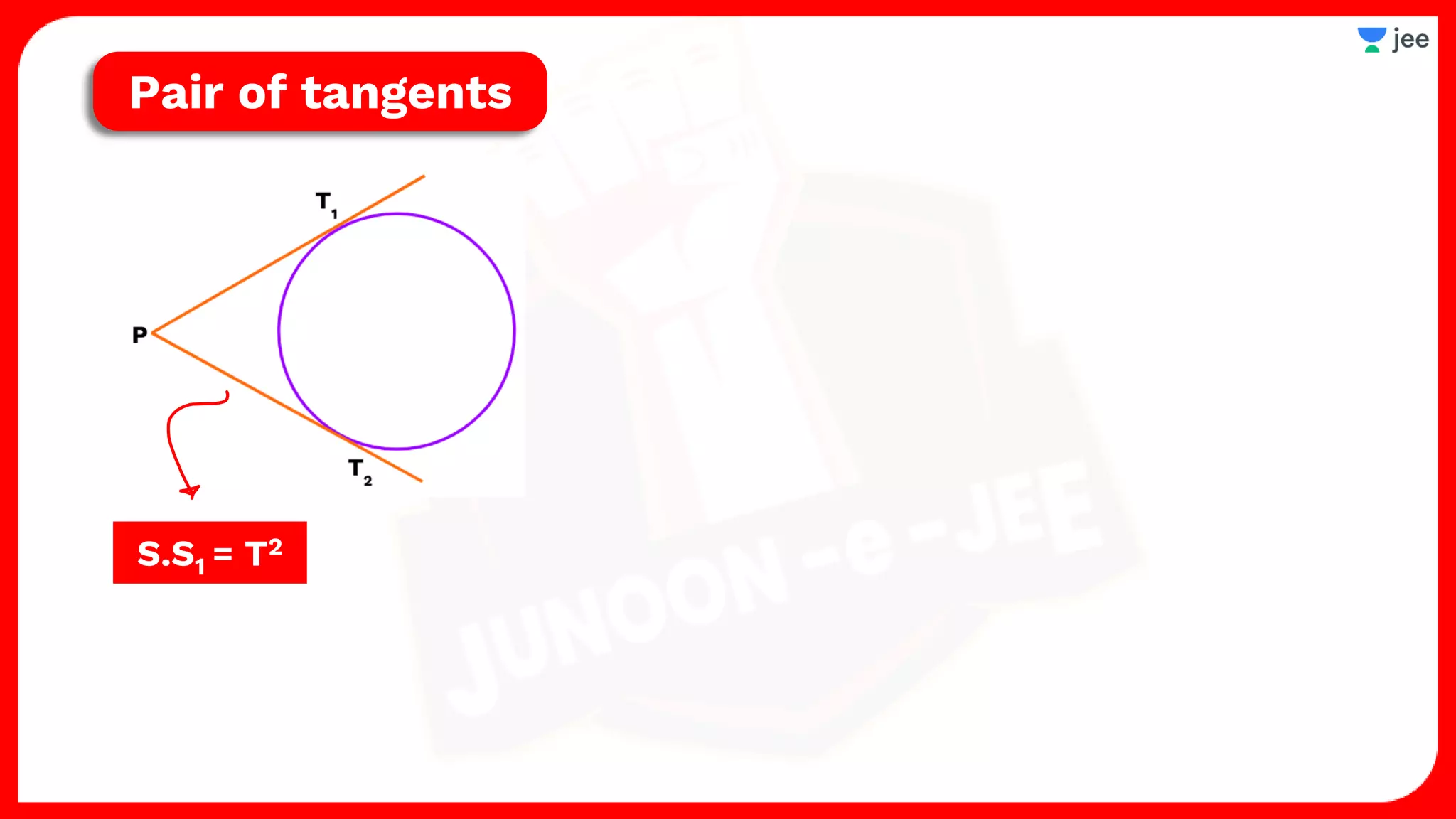
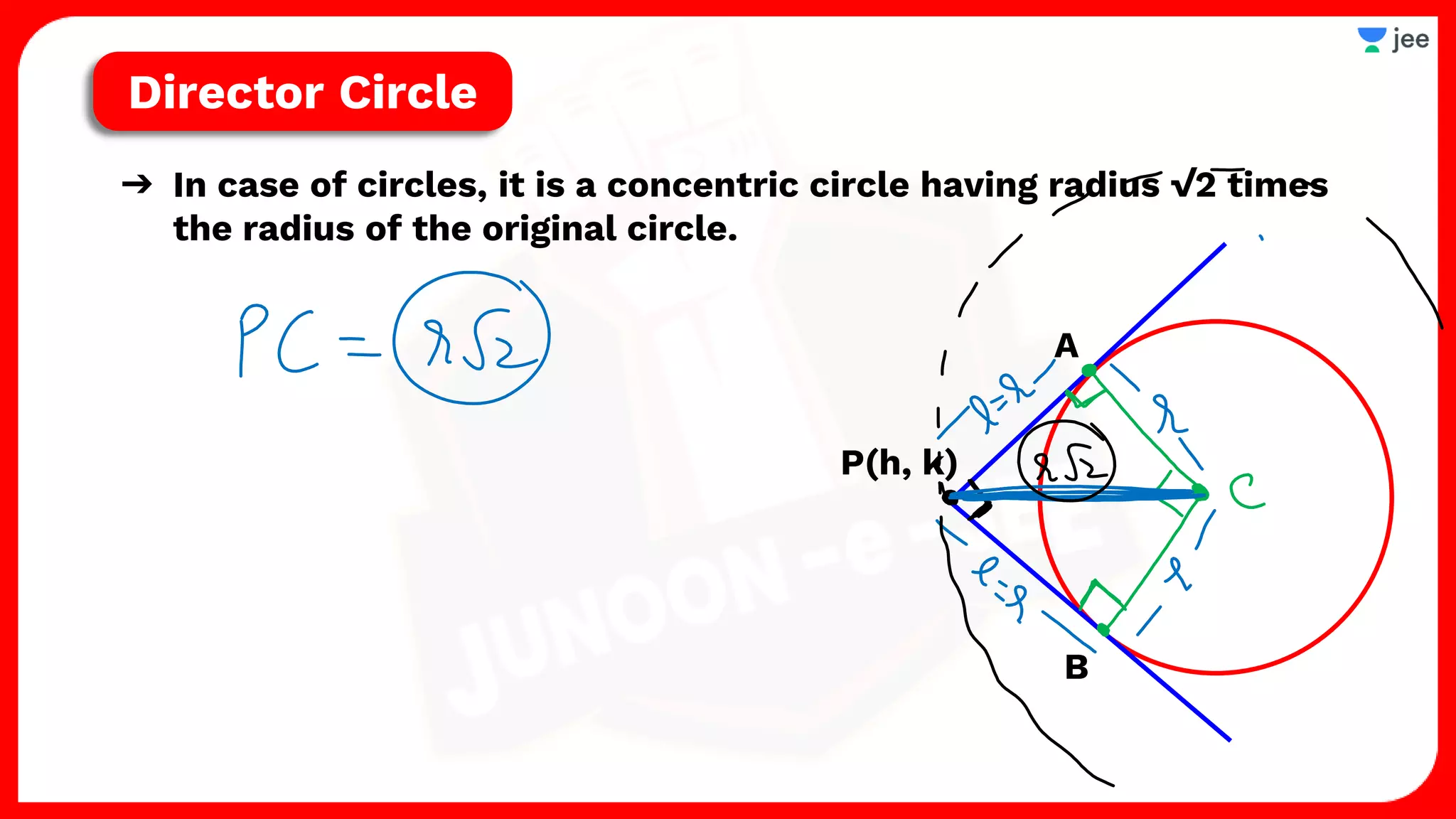
1. The document discusses various properties and equations related to circles such as the standard equation of a circle, parametric equations of a circle, equations of circles under special conditions like touching axes, and equations of tangents, normals, and chords related to circles.
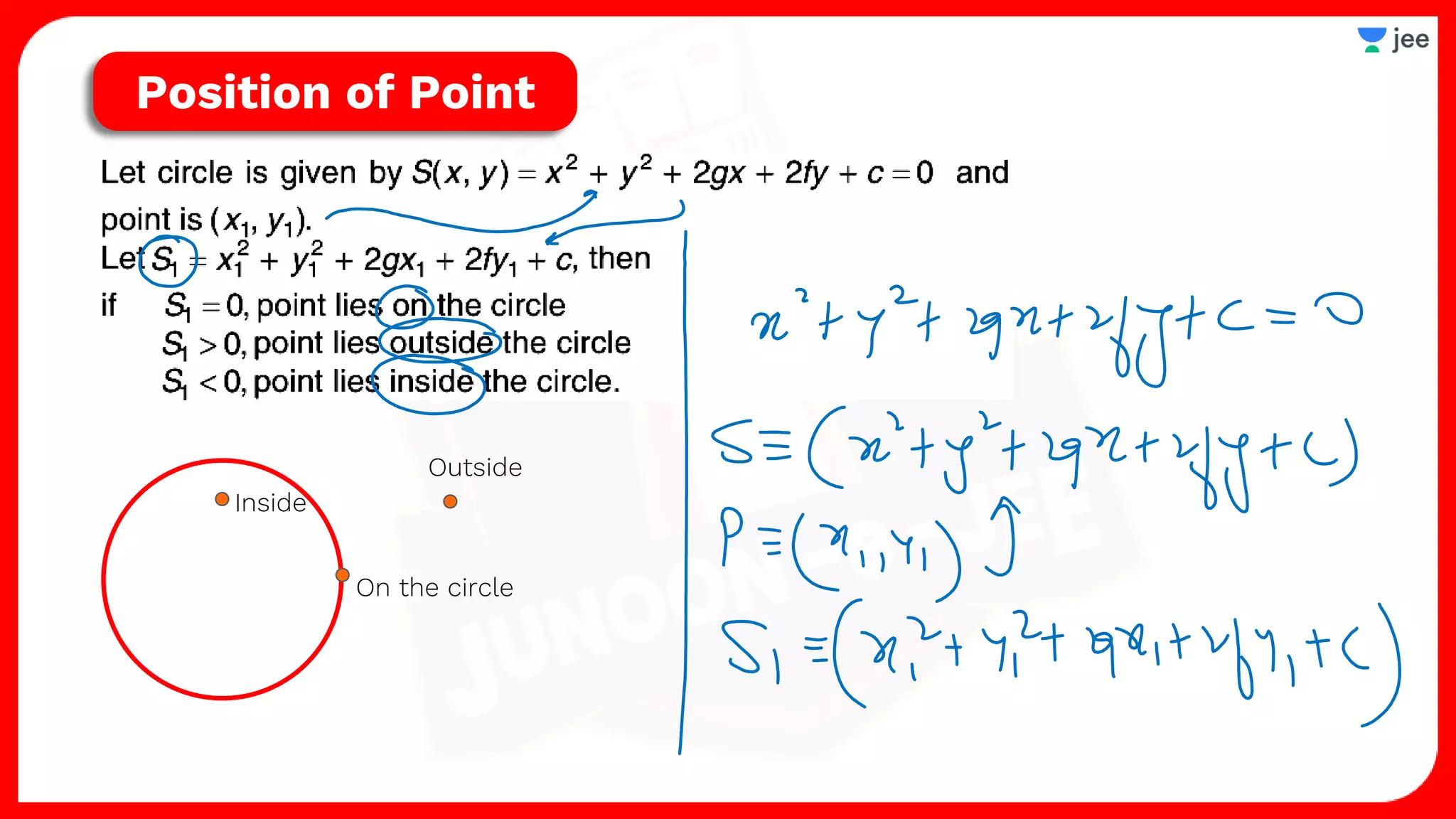
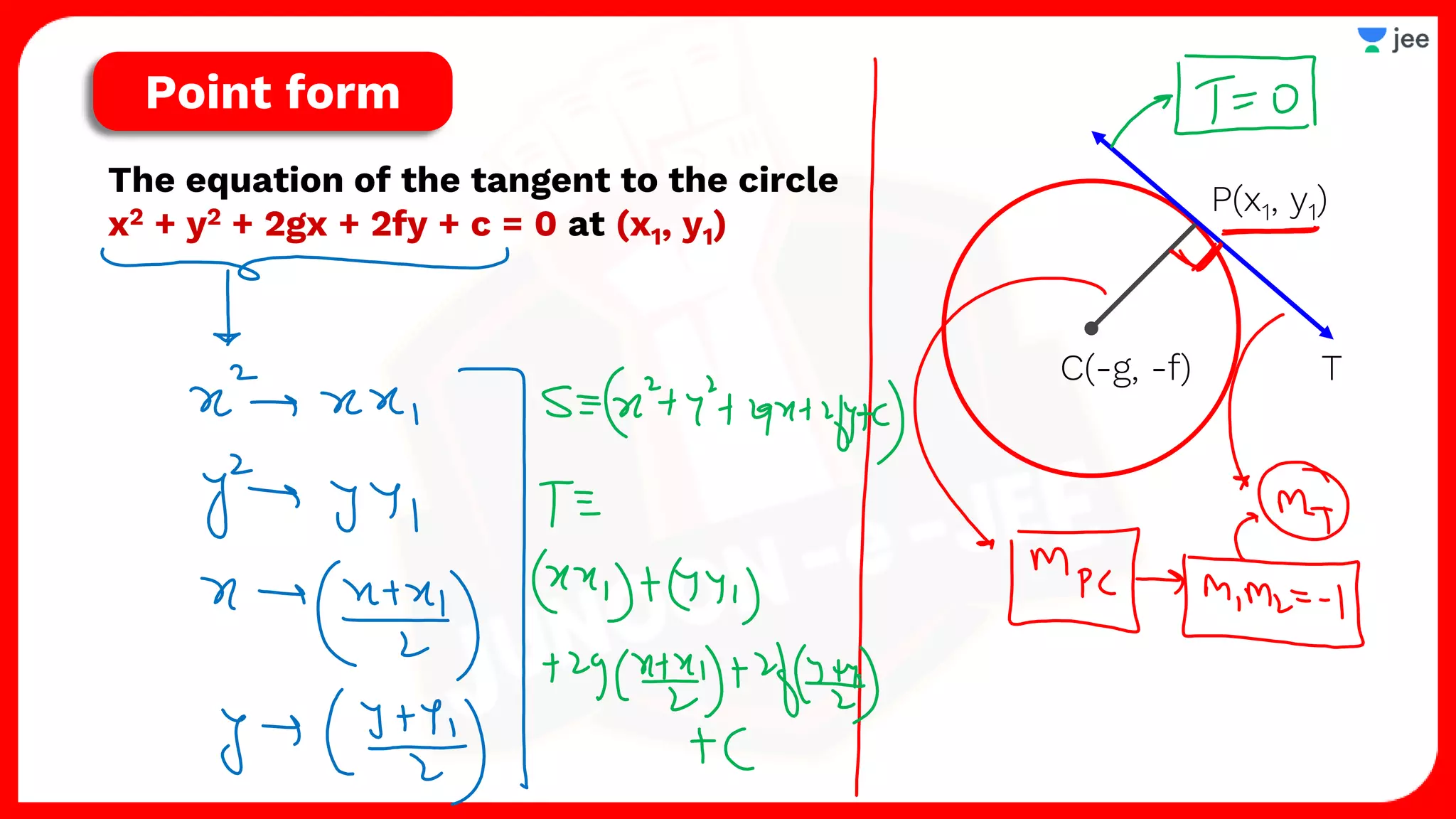
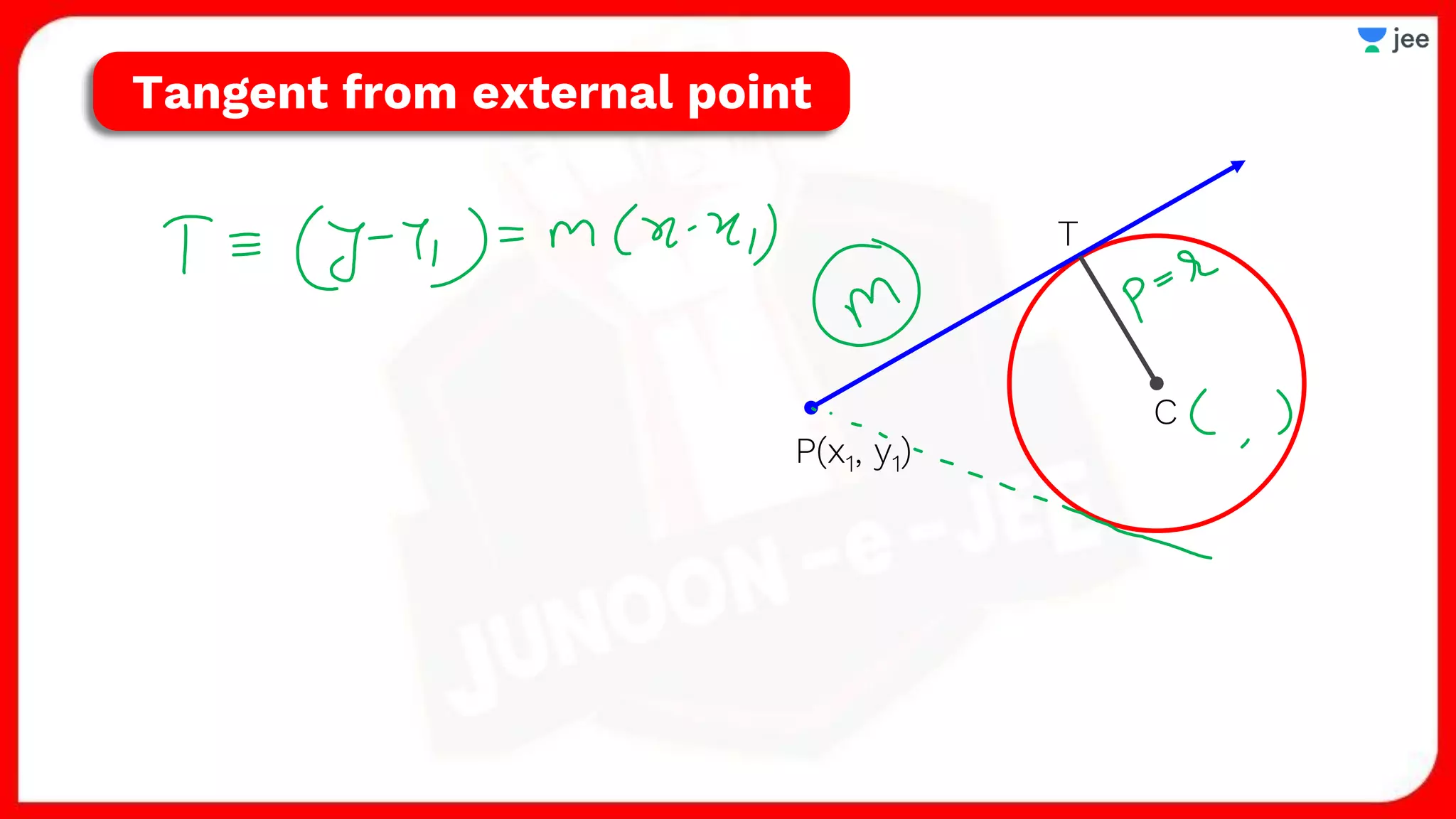
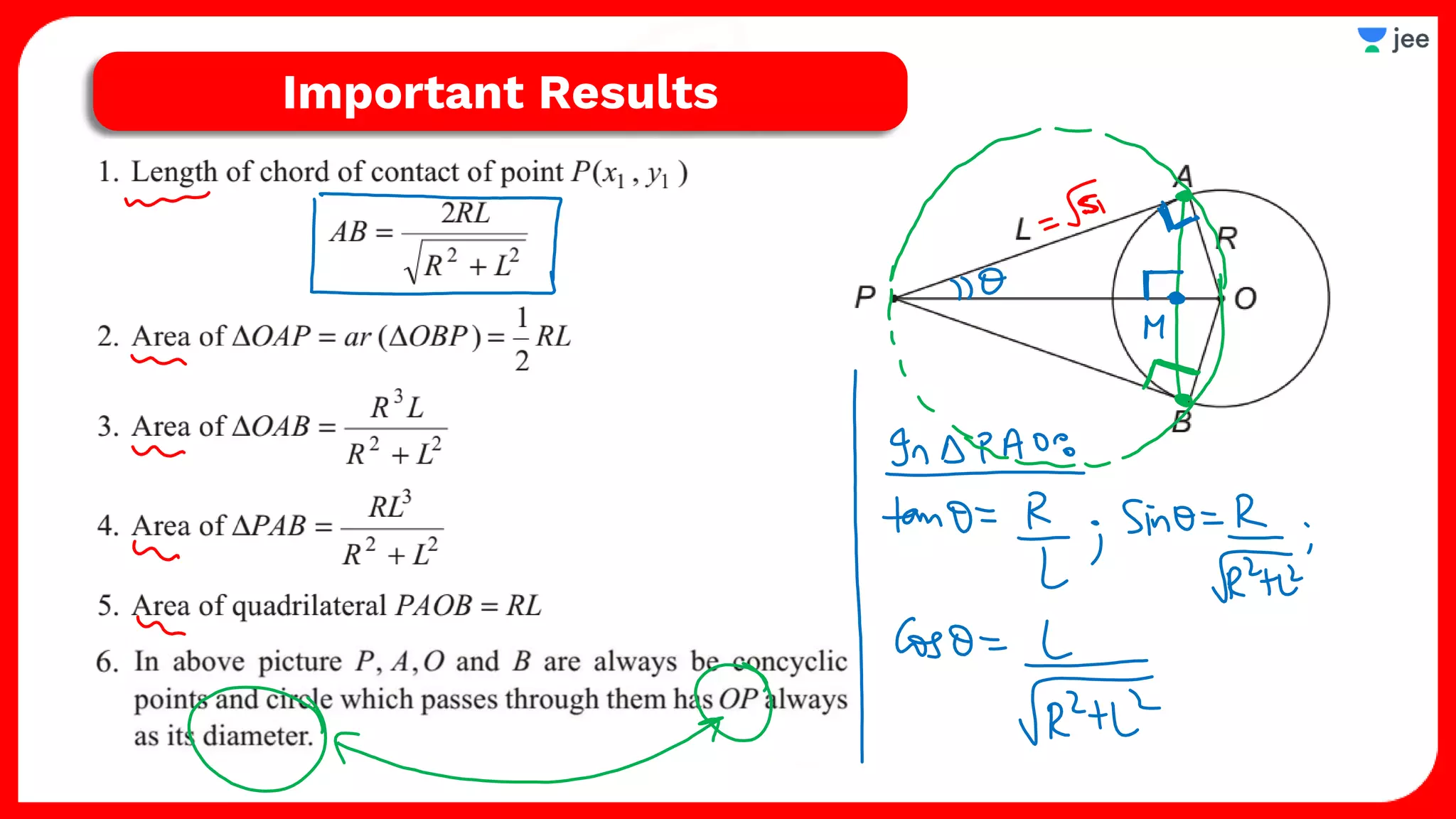
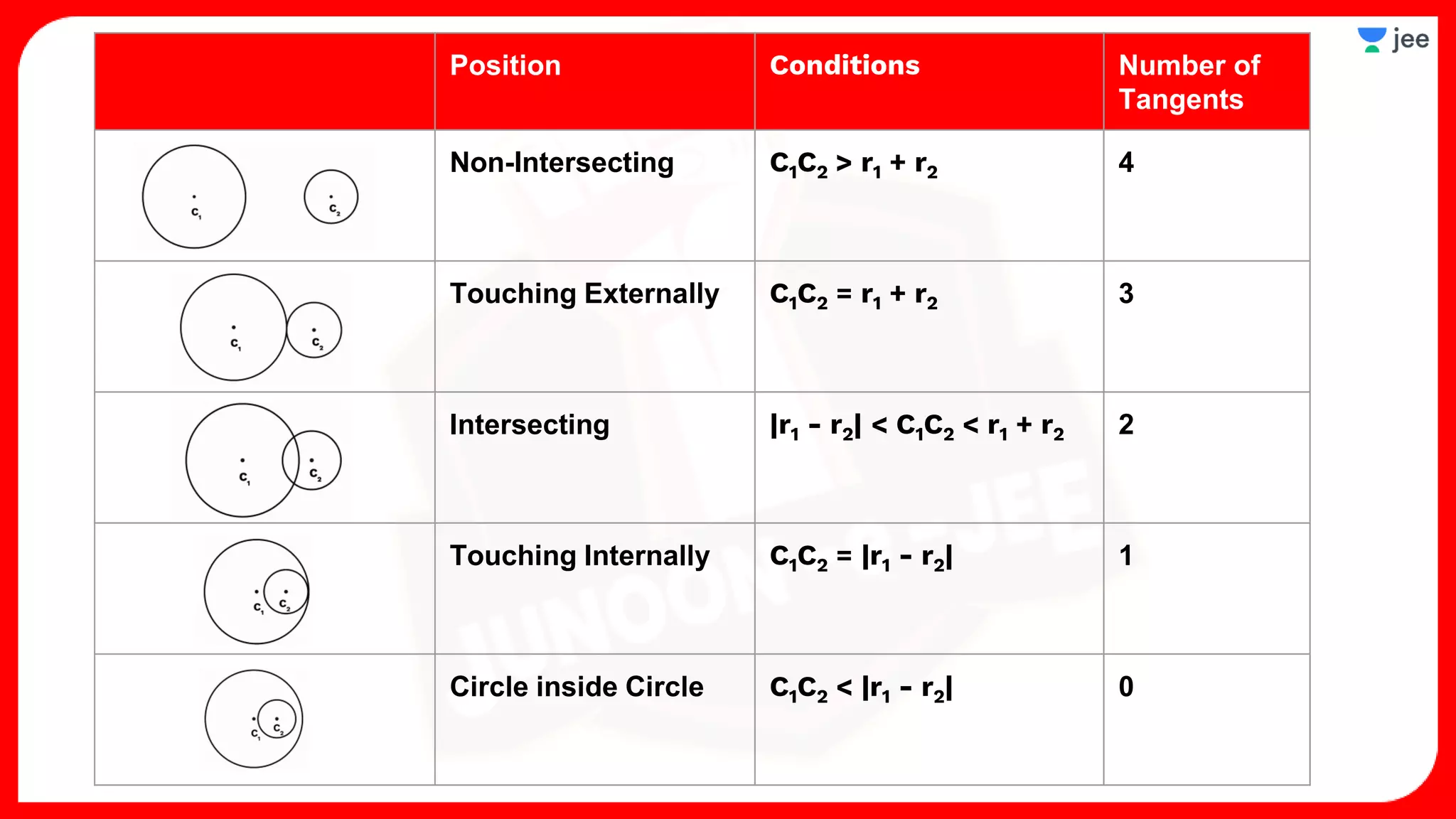
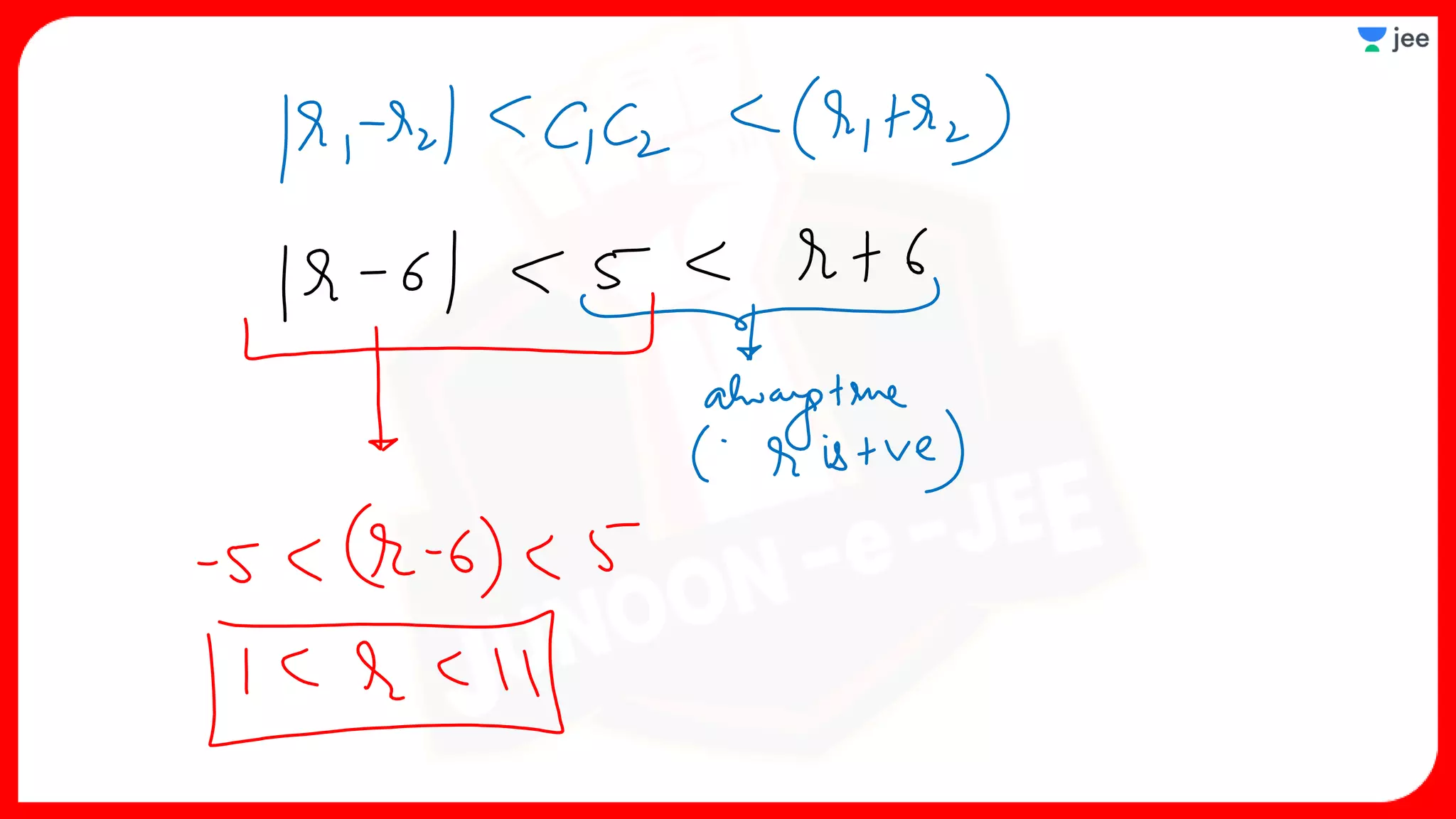
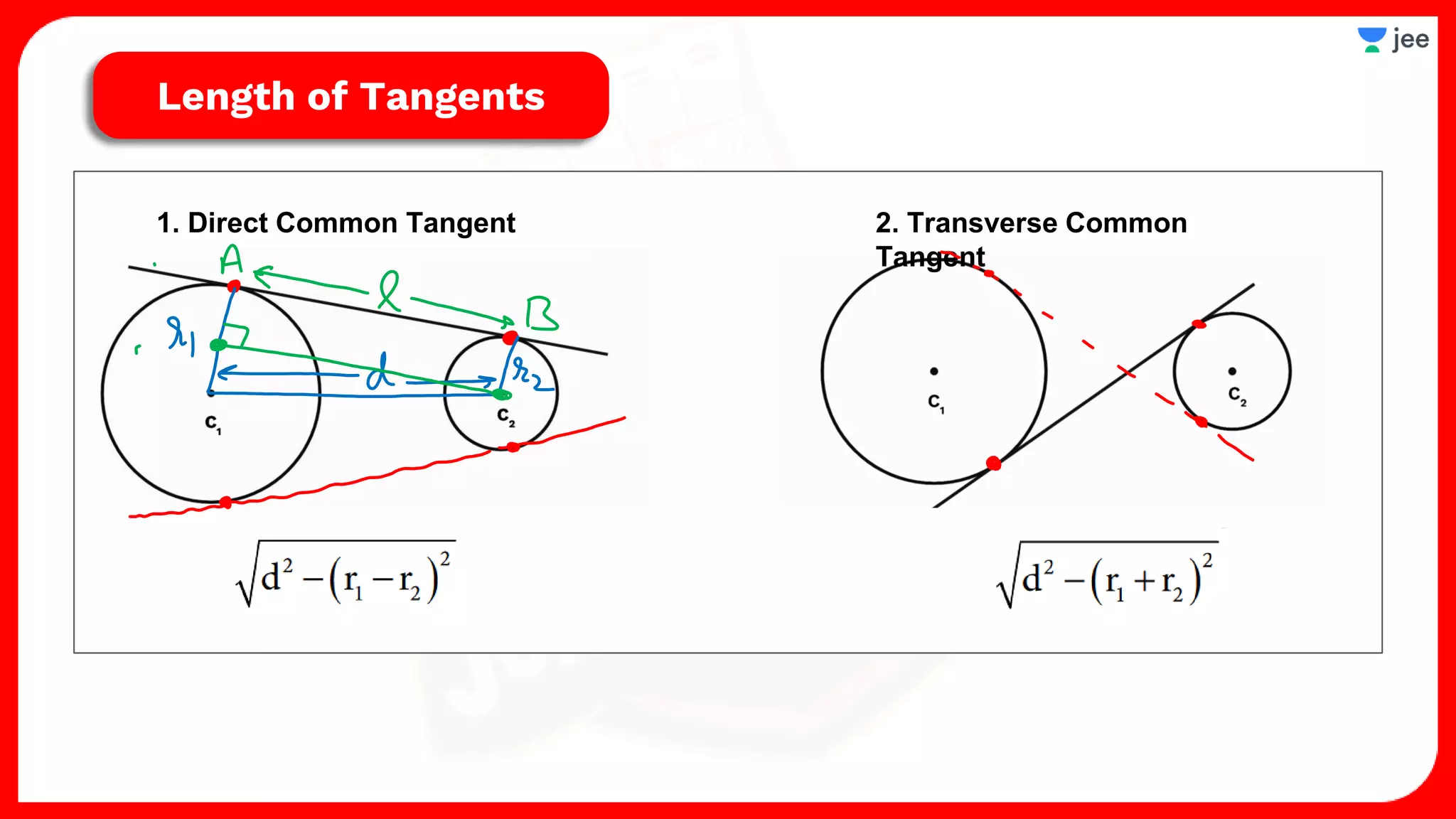
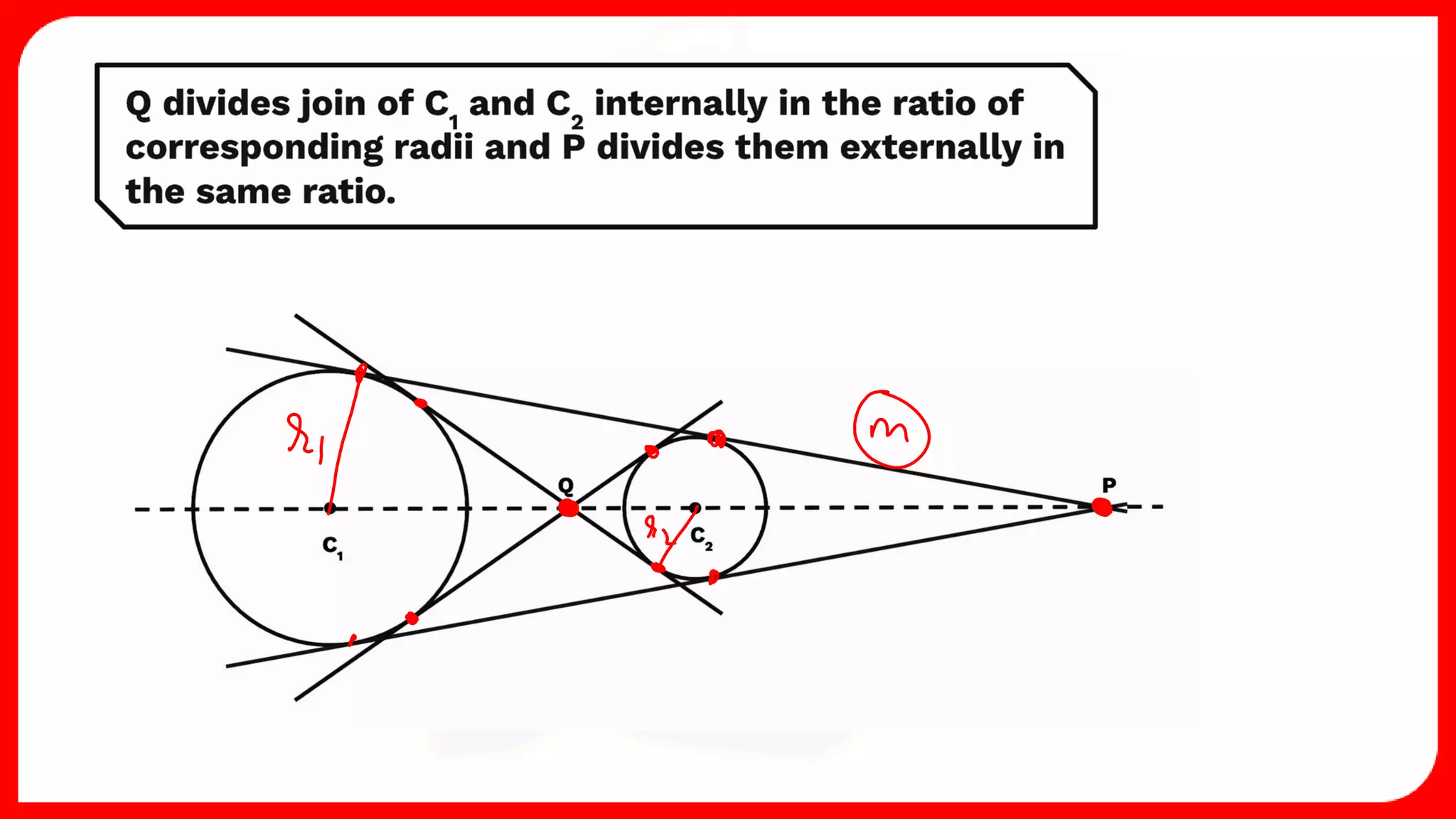
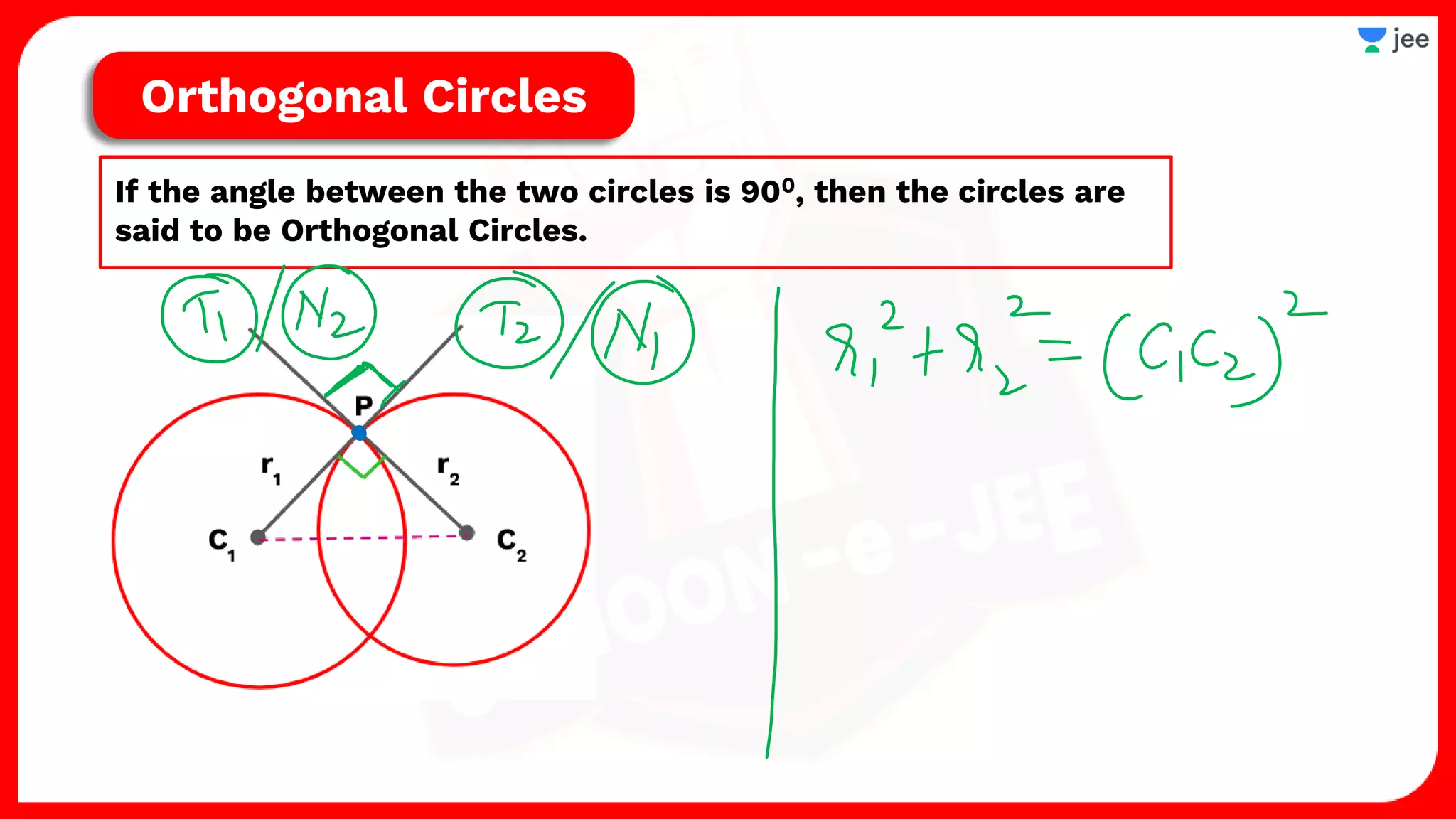
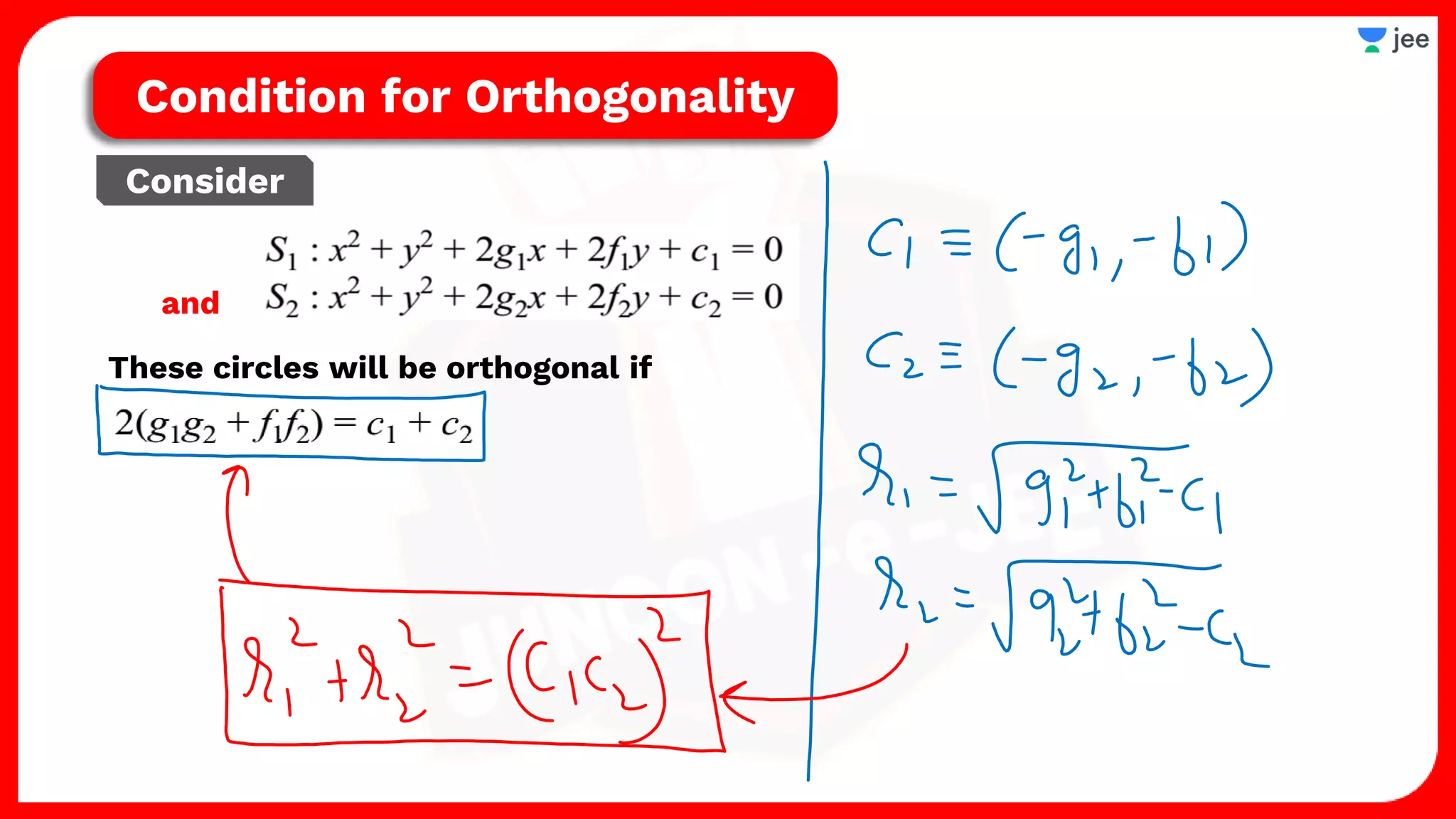
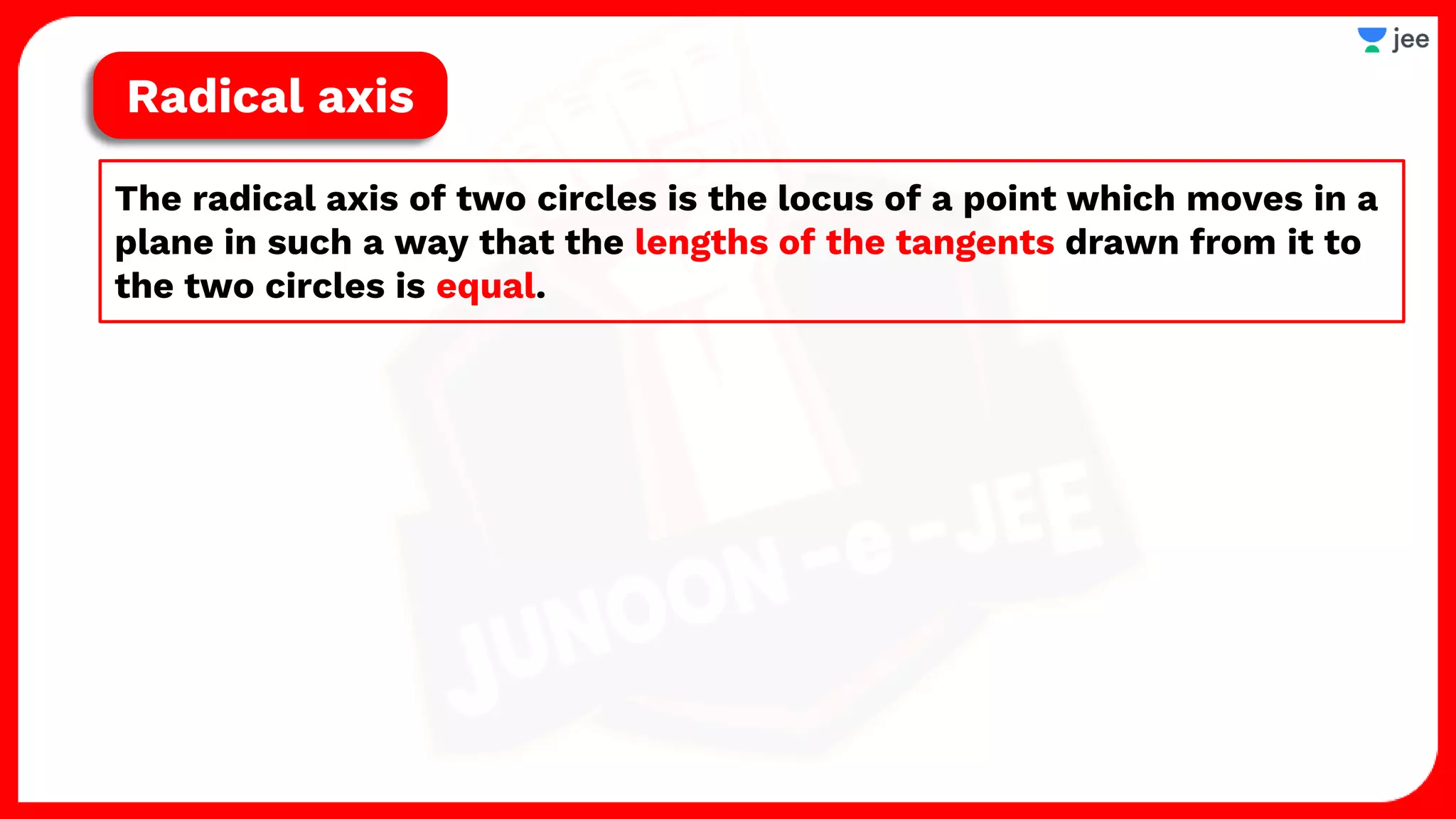
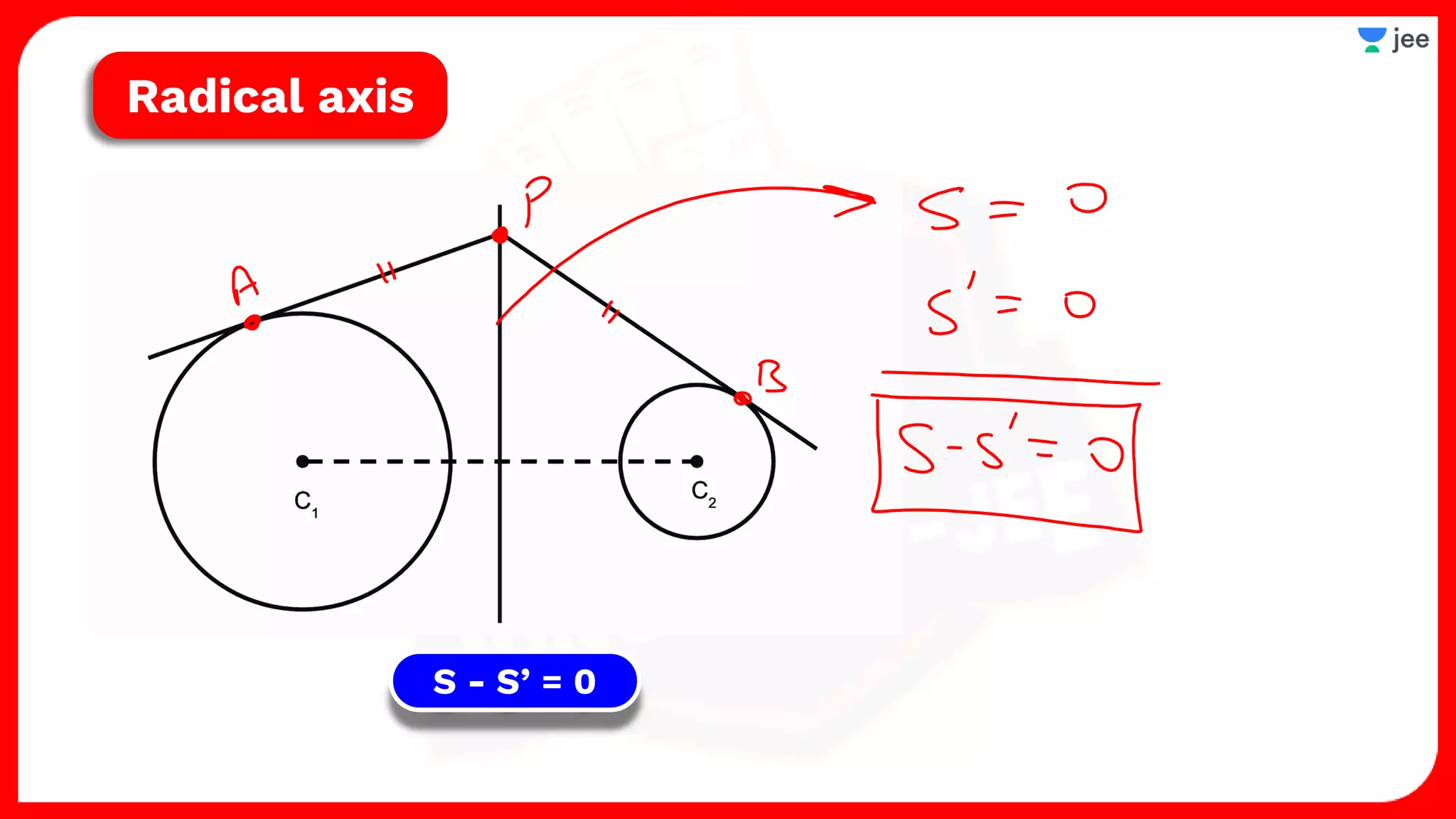
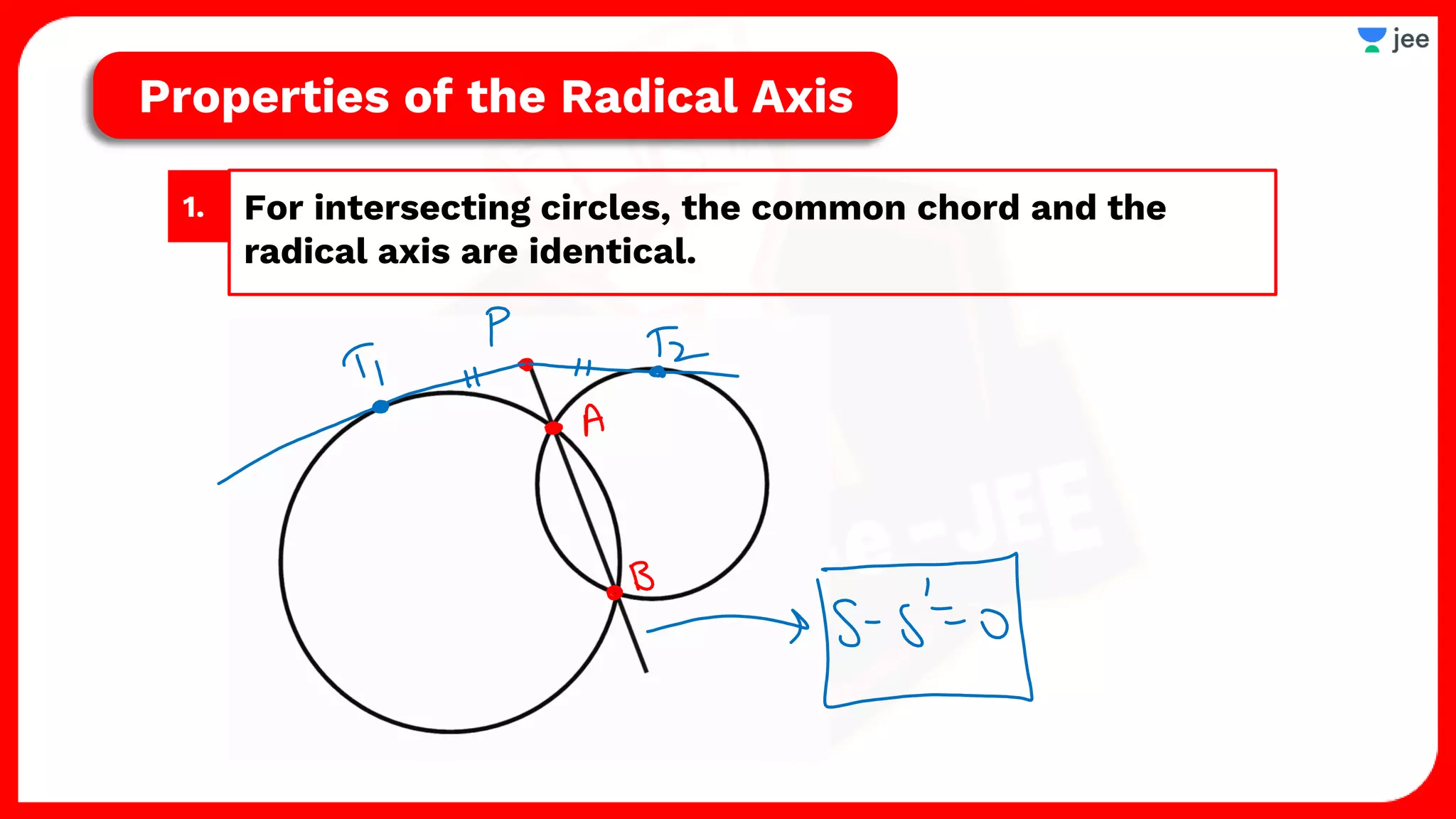
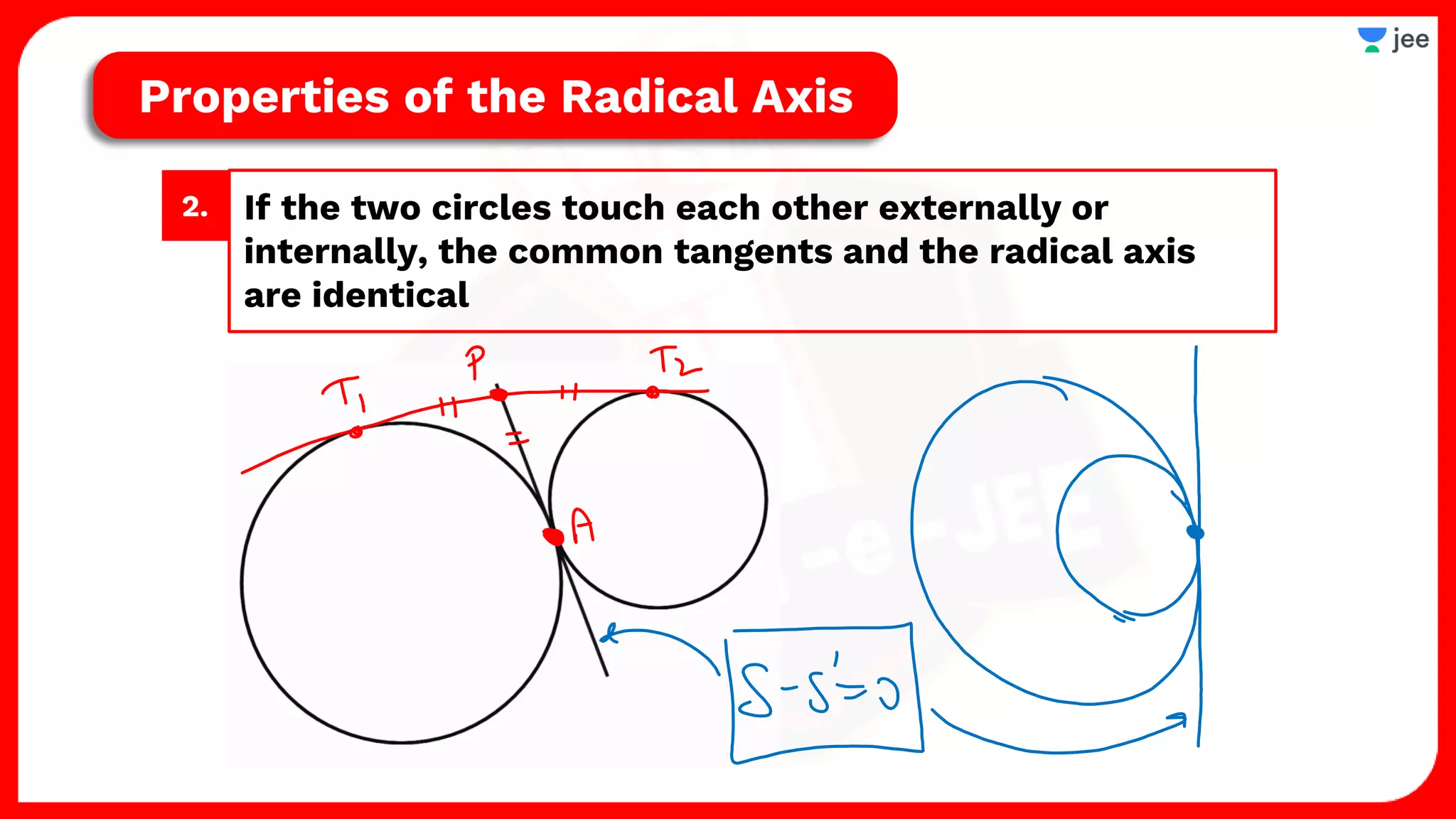
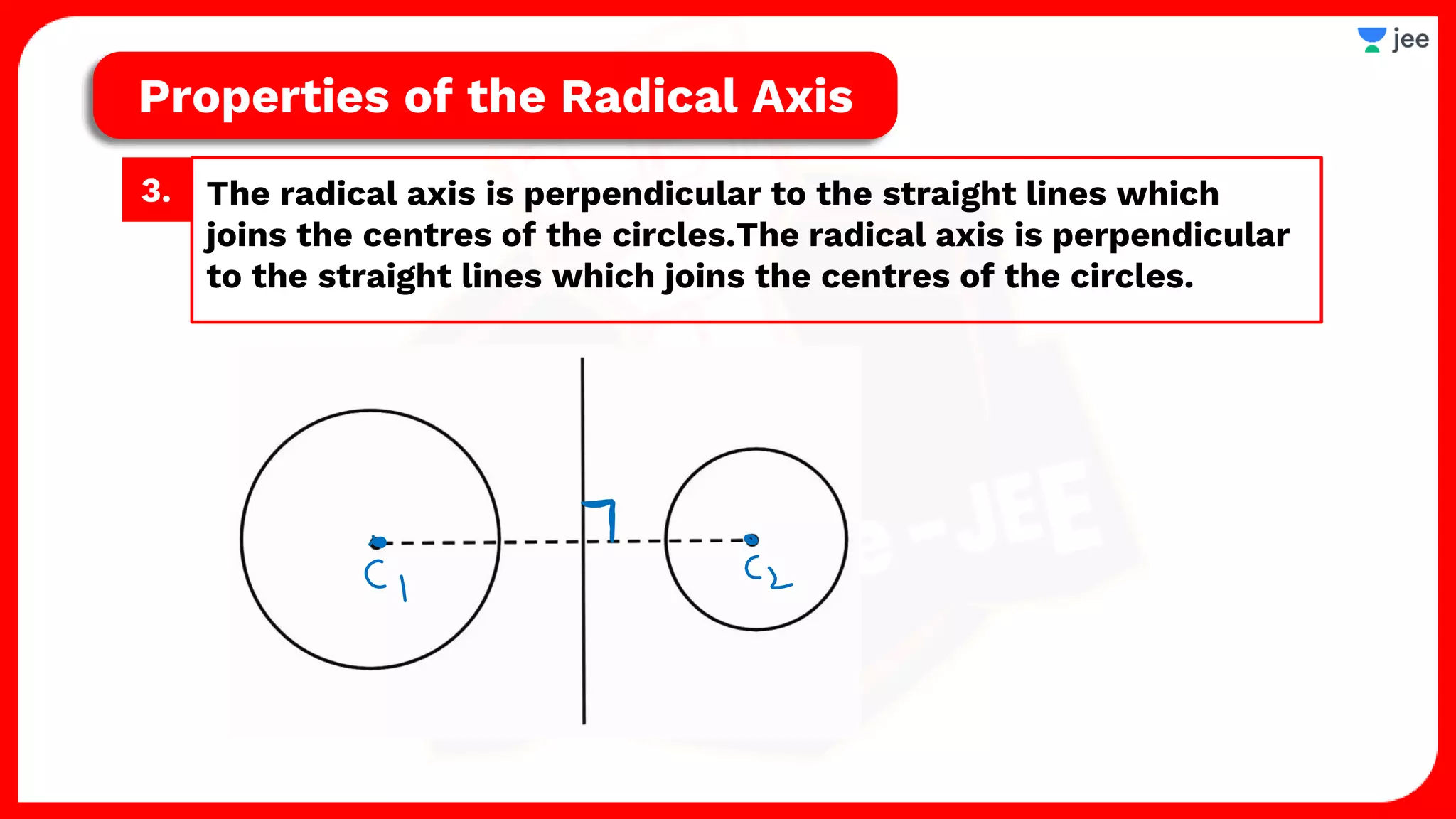
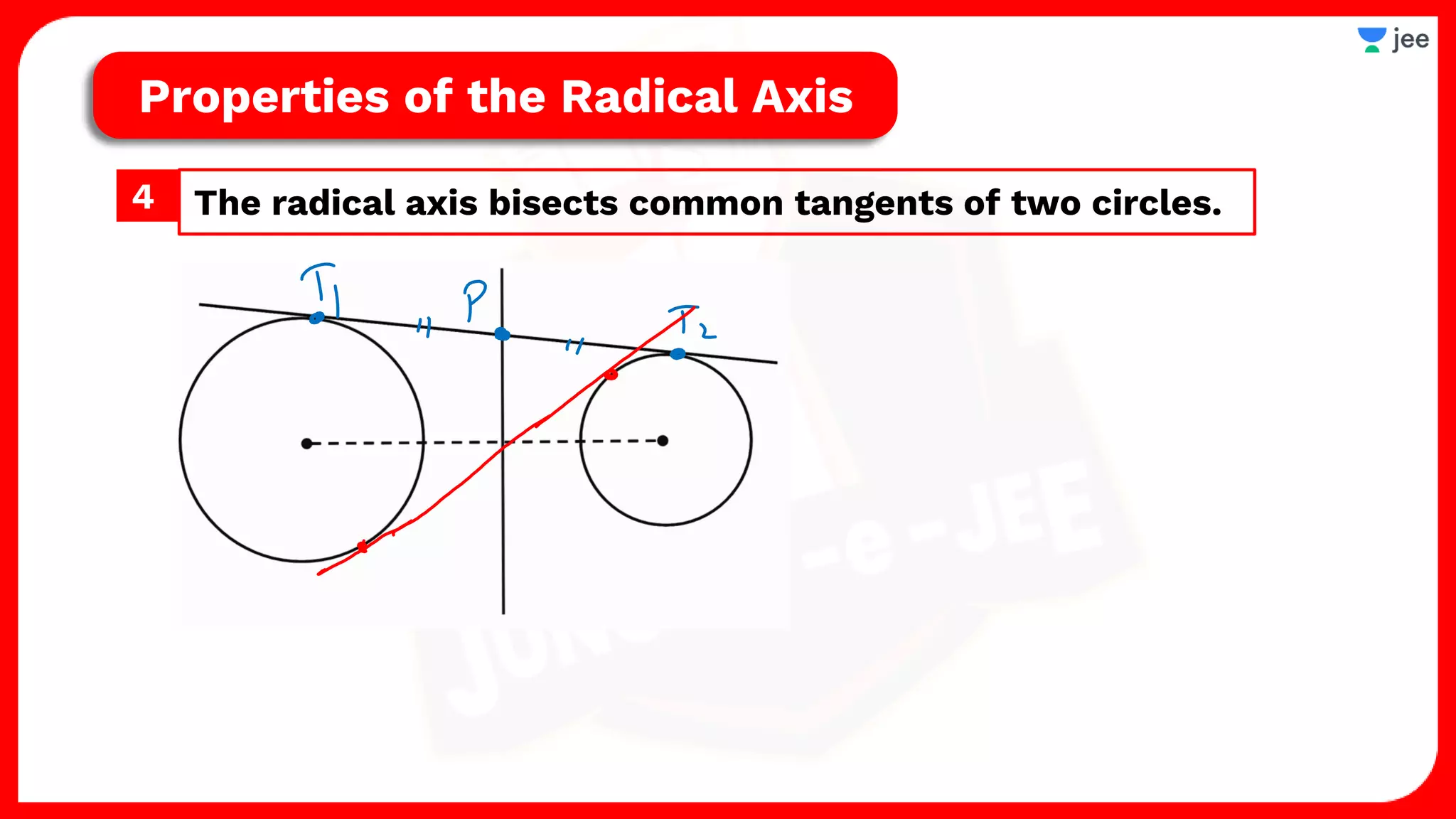
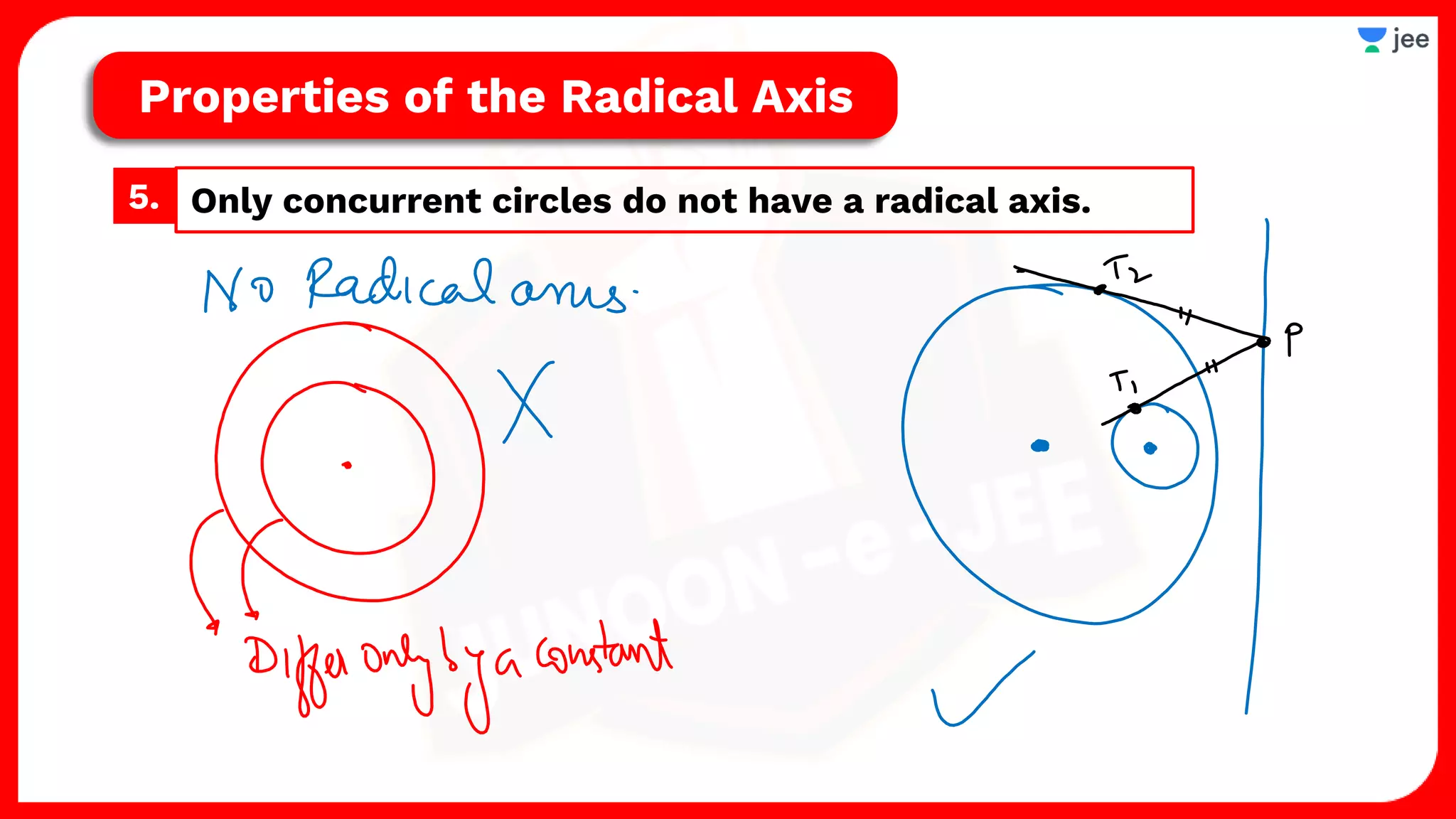
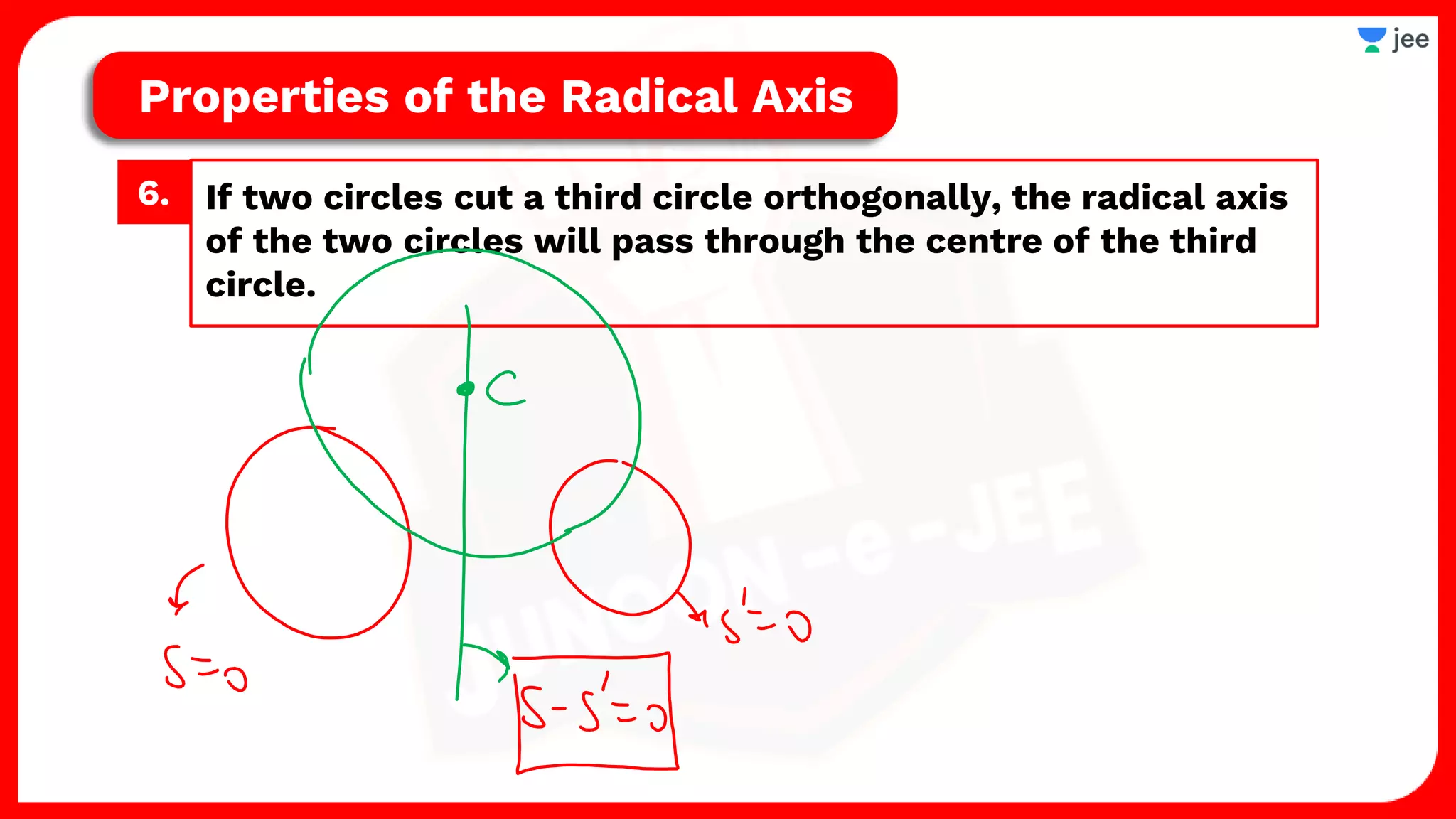
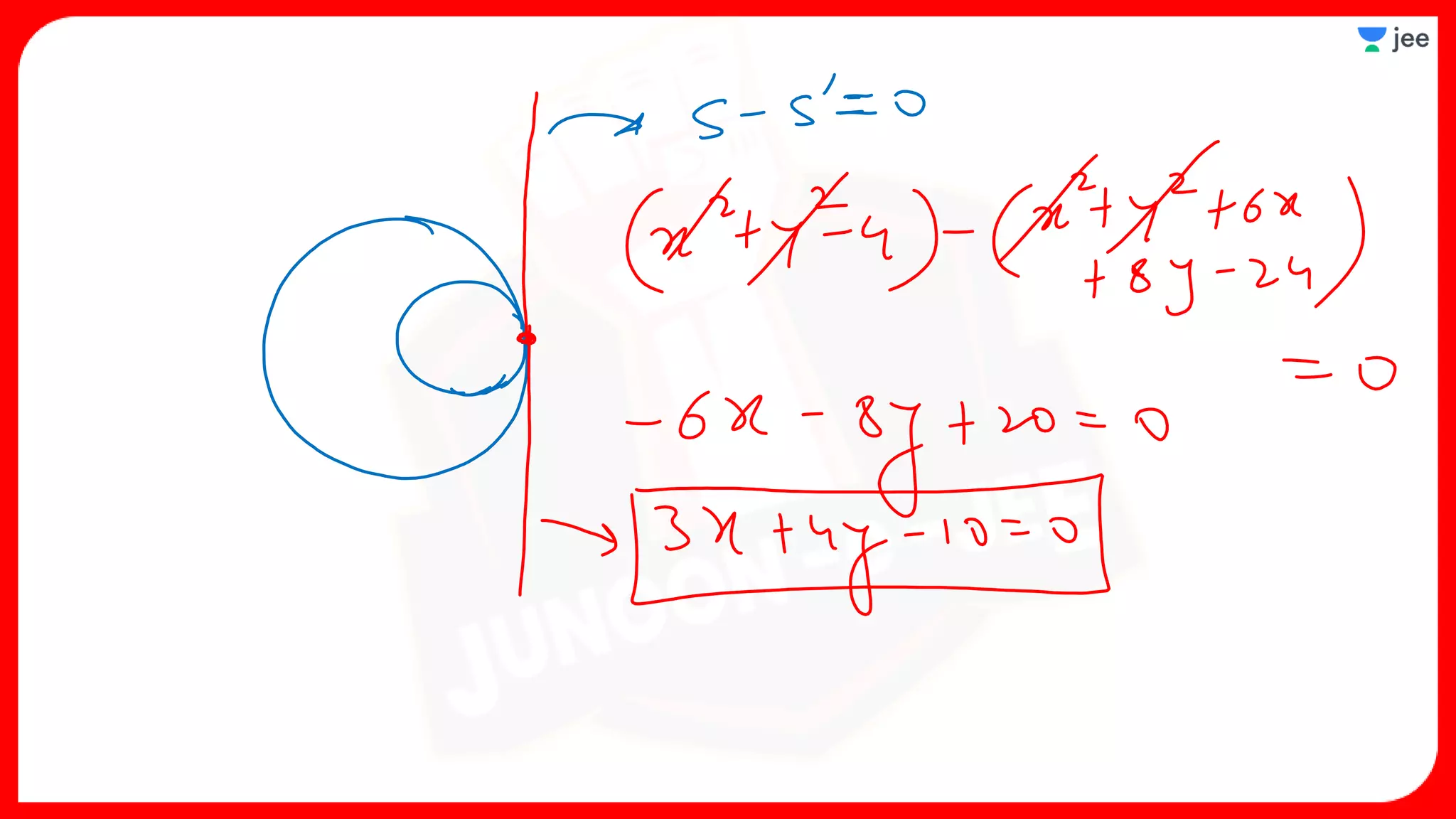
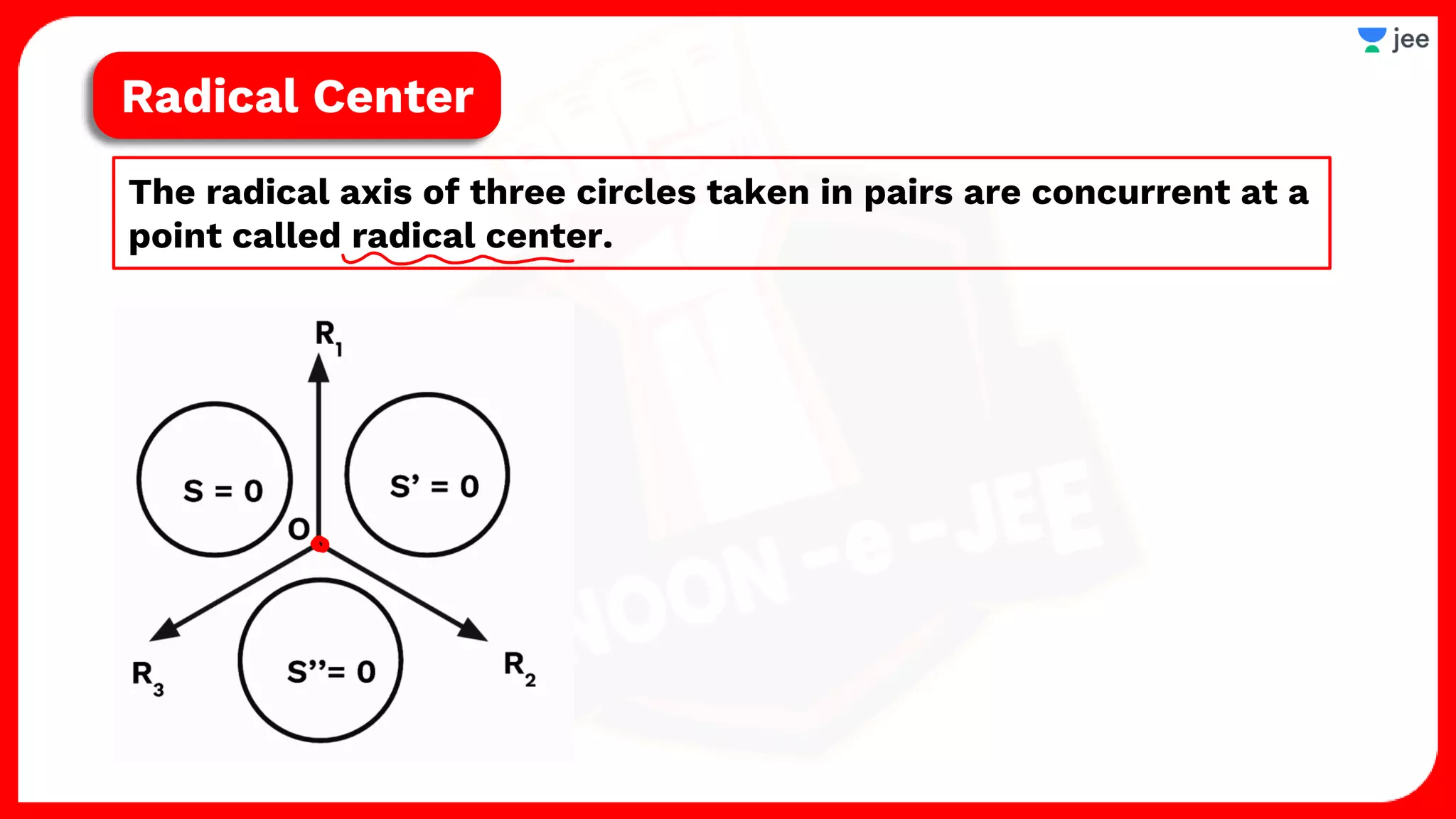
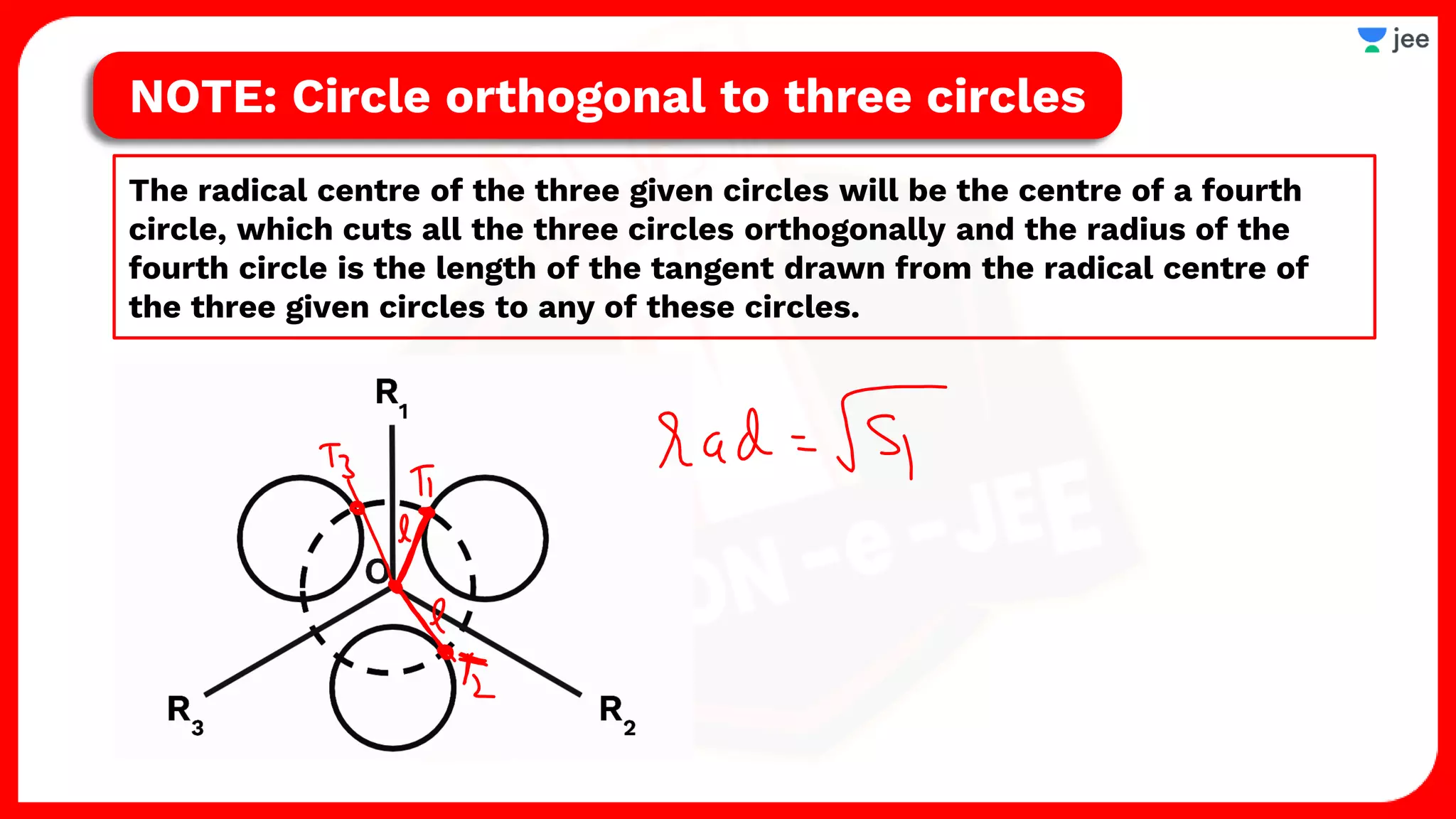
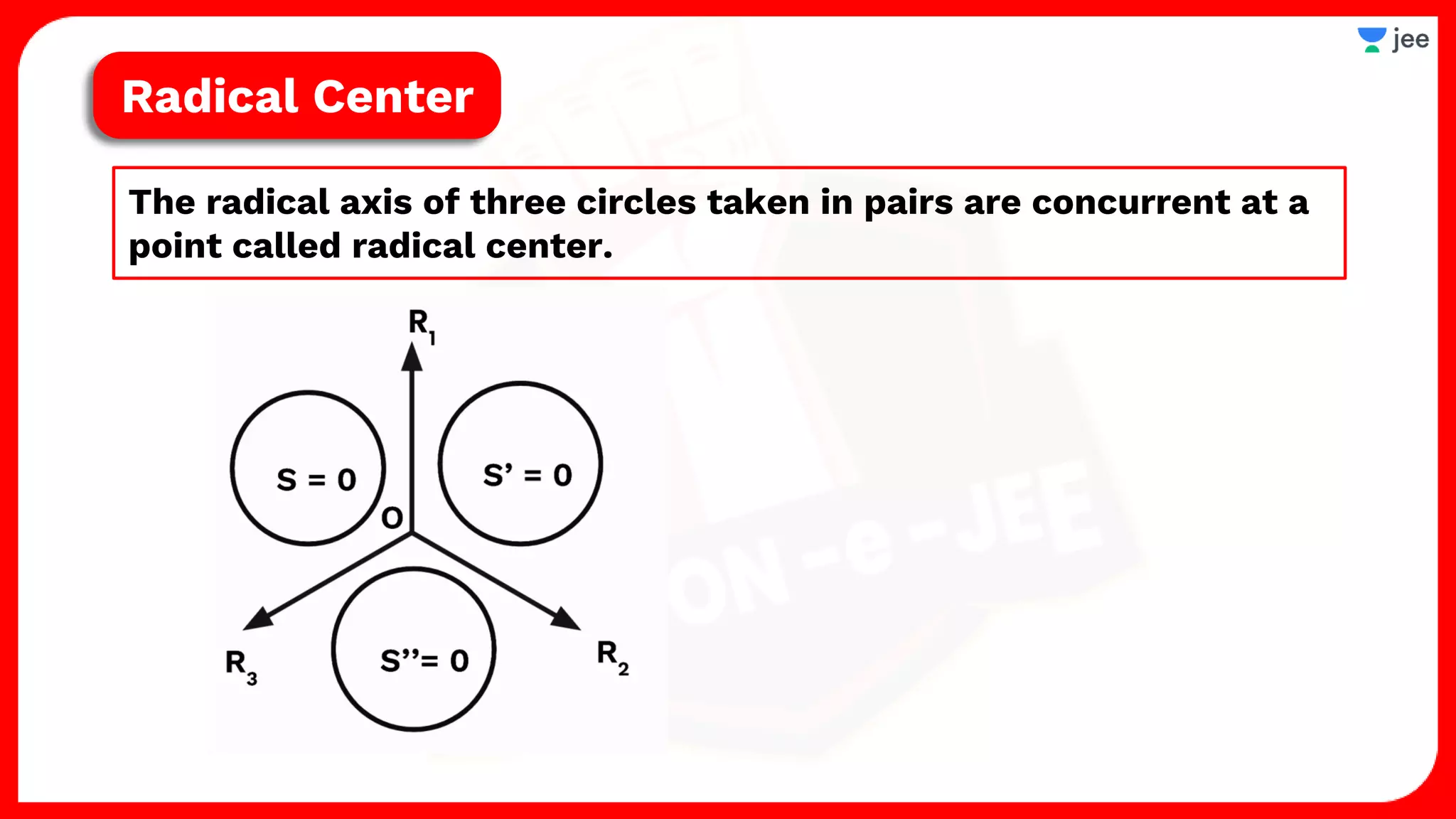
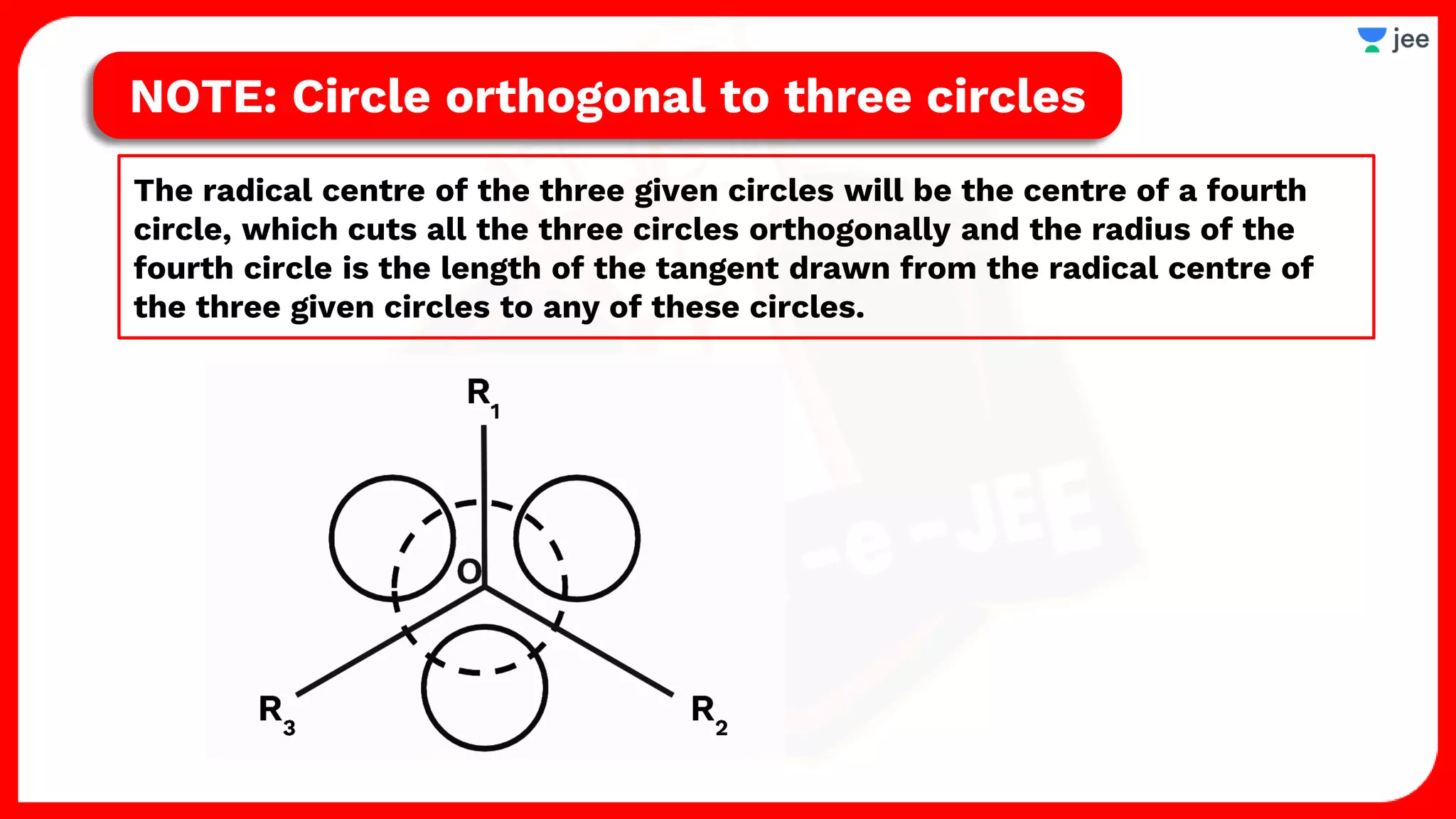
2. It also covers topics like the position of a point or line with respect to a circle, equations for common tangents between two circles, conditions for orthogonality of circles, properties of the radical axis, and the radical center.
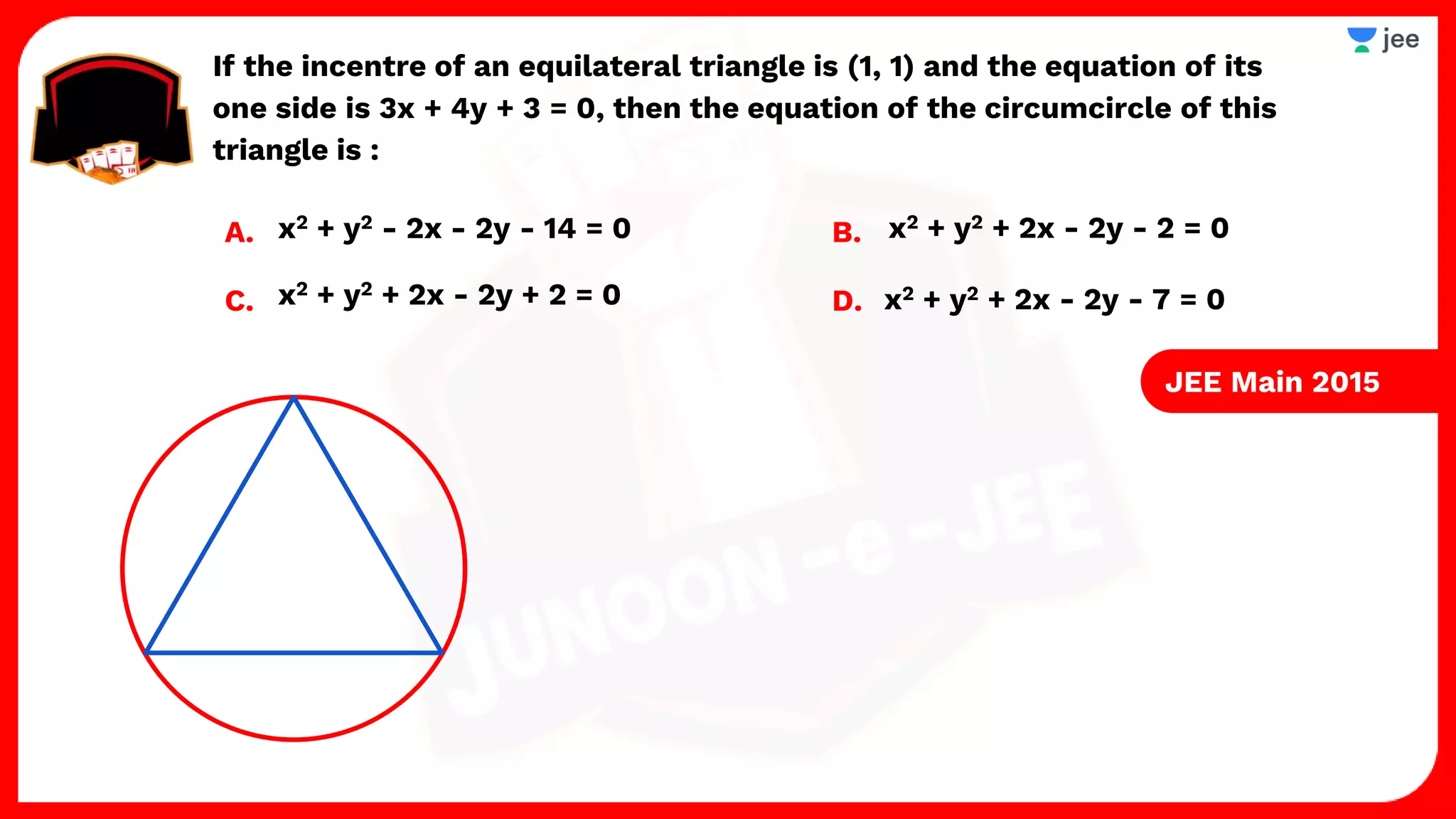
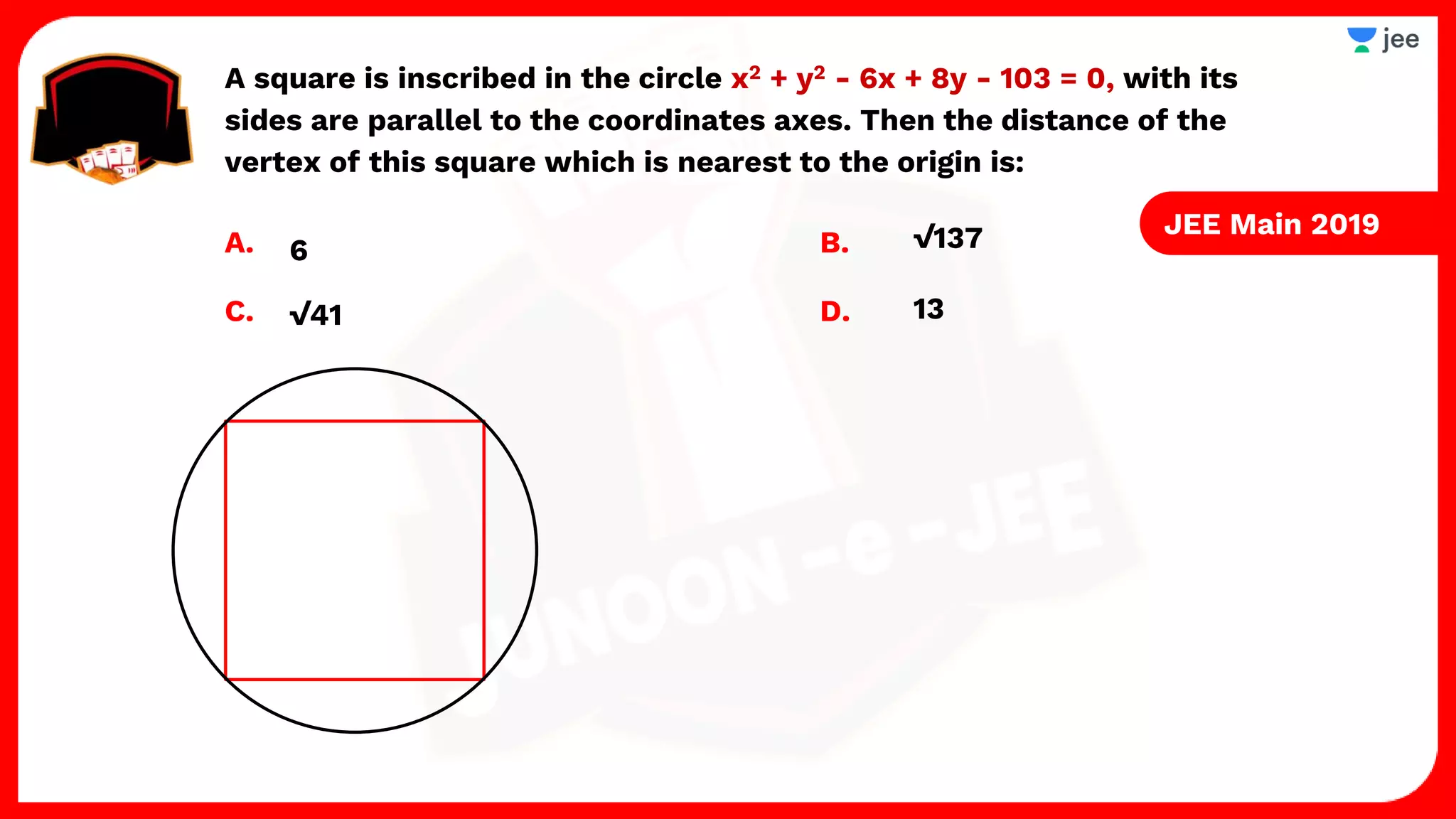
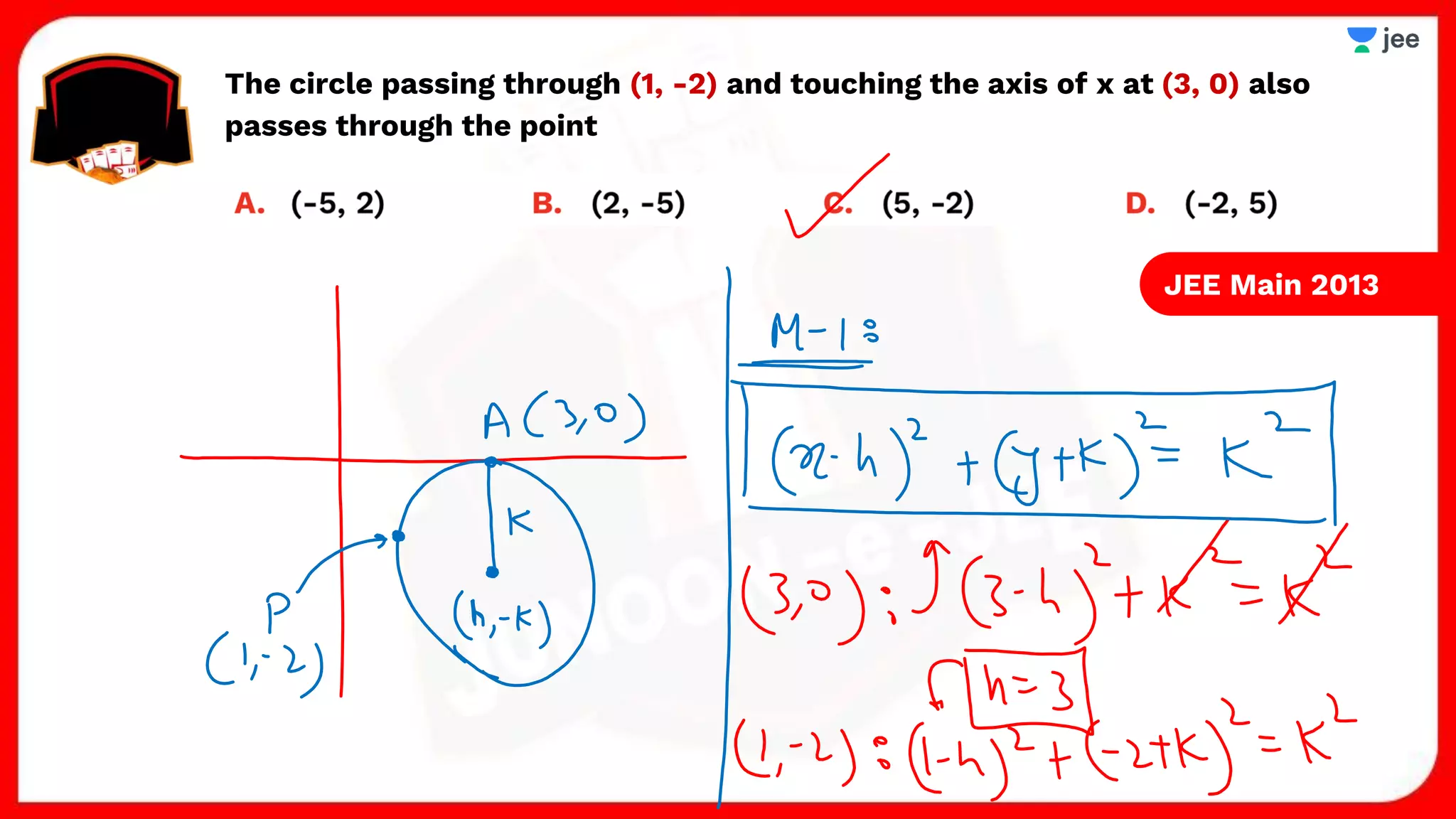
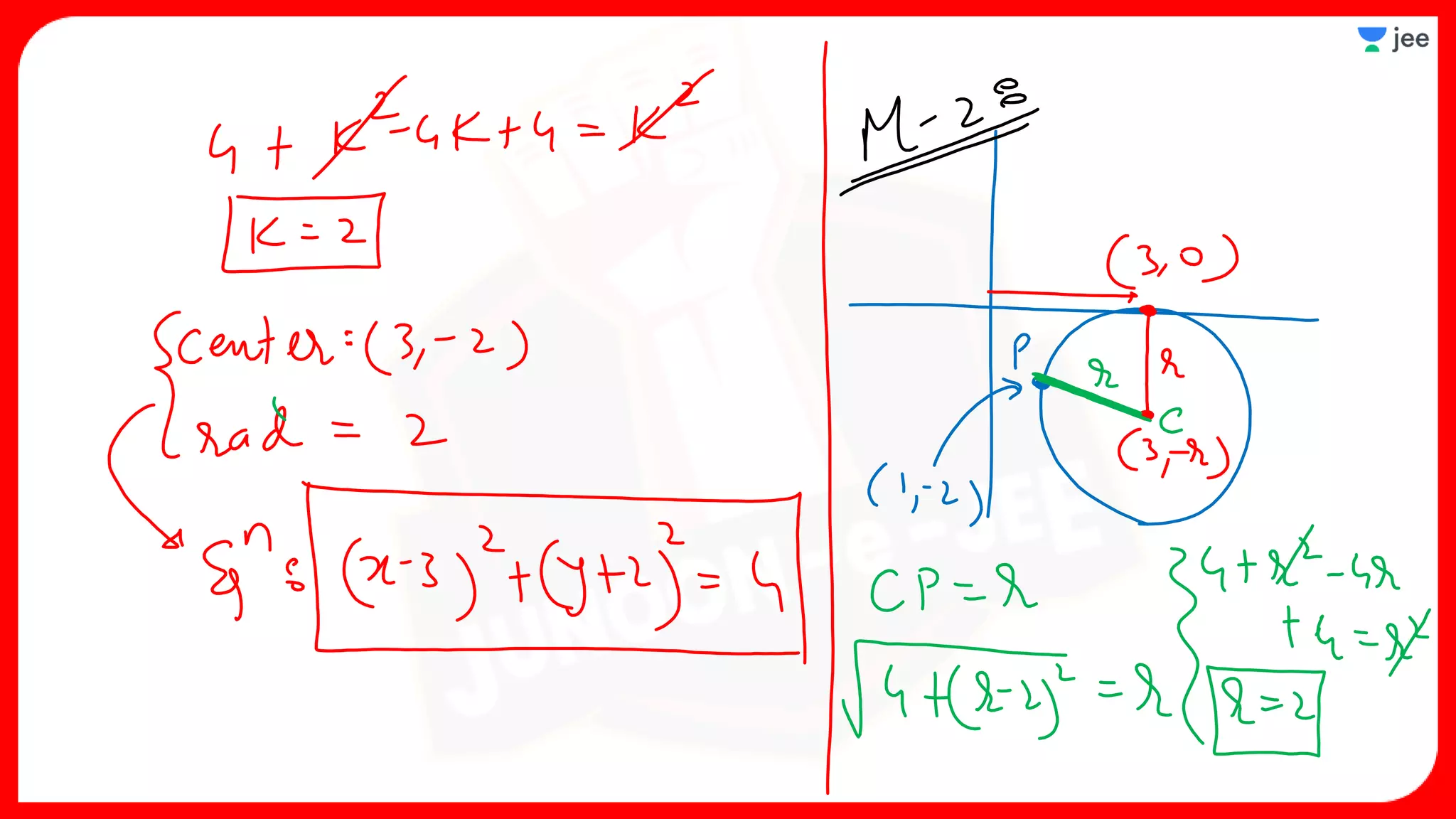
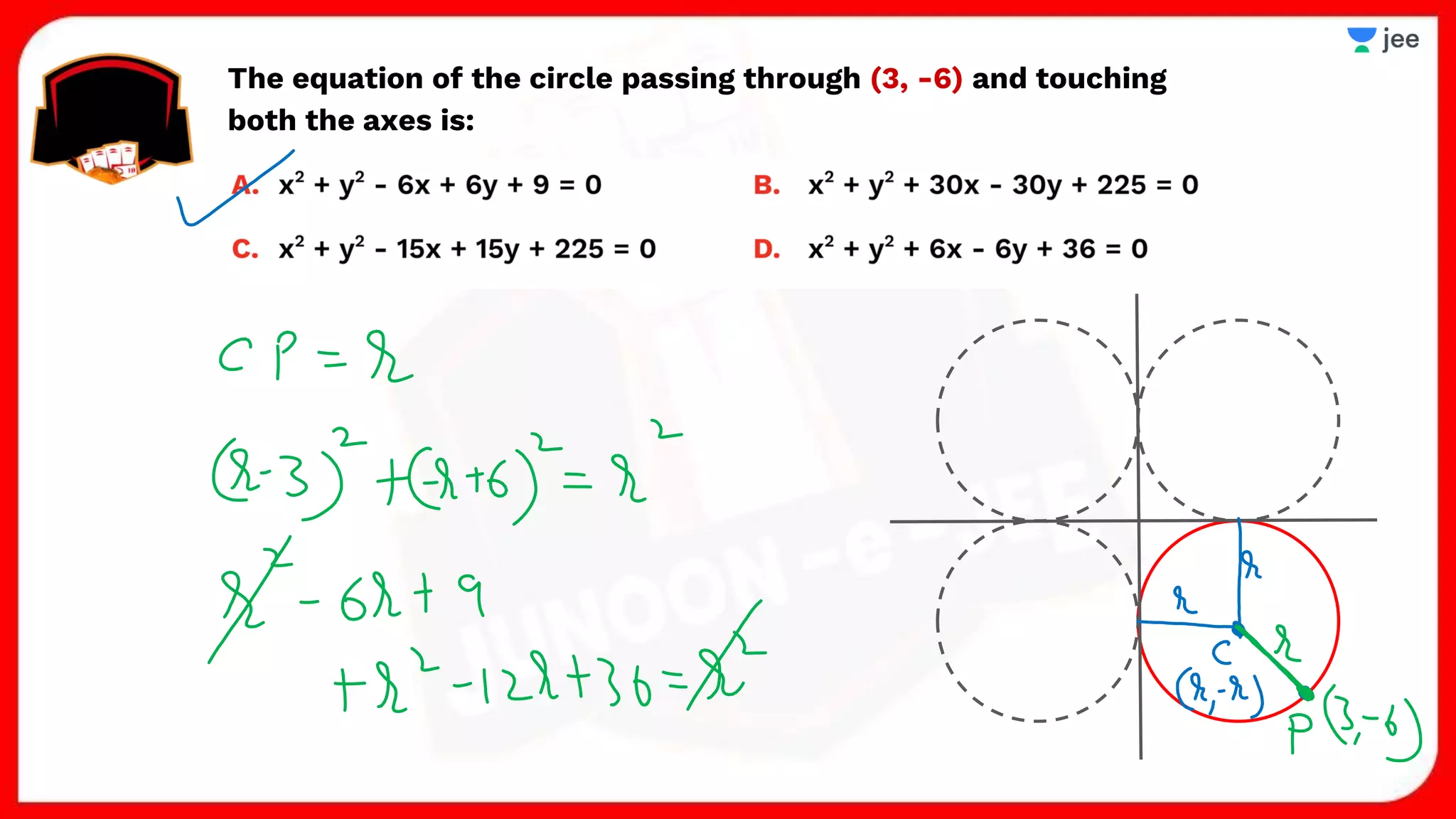
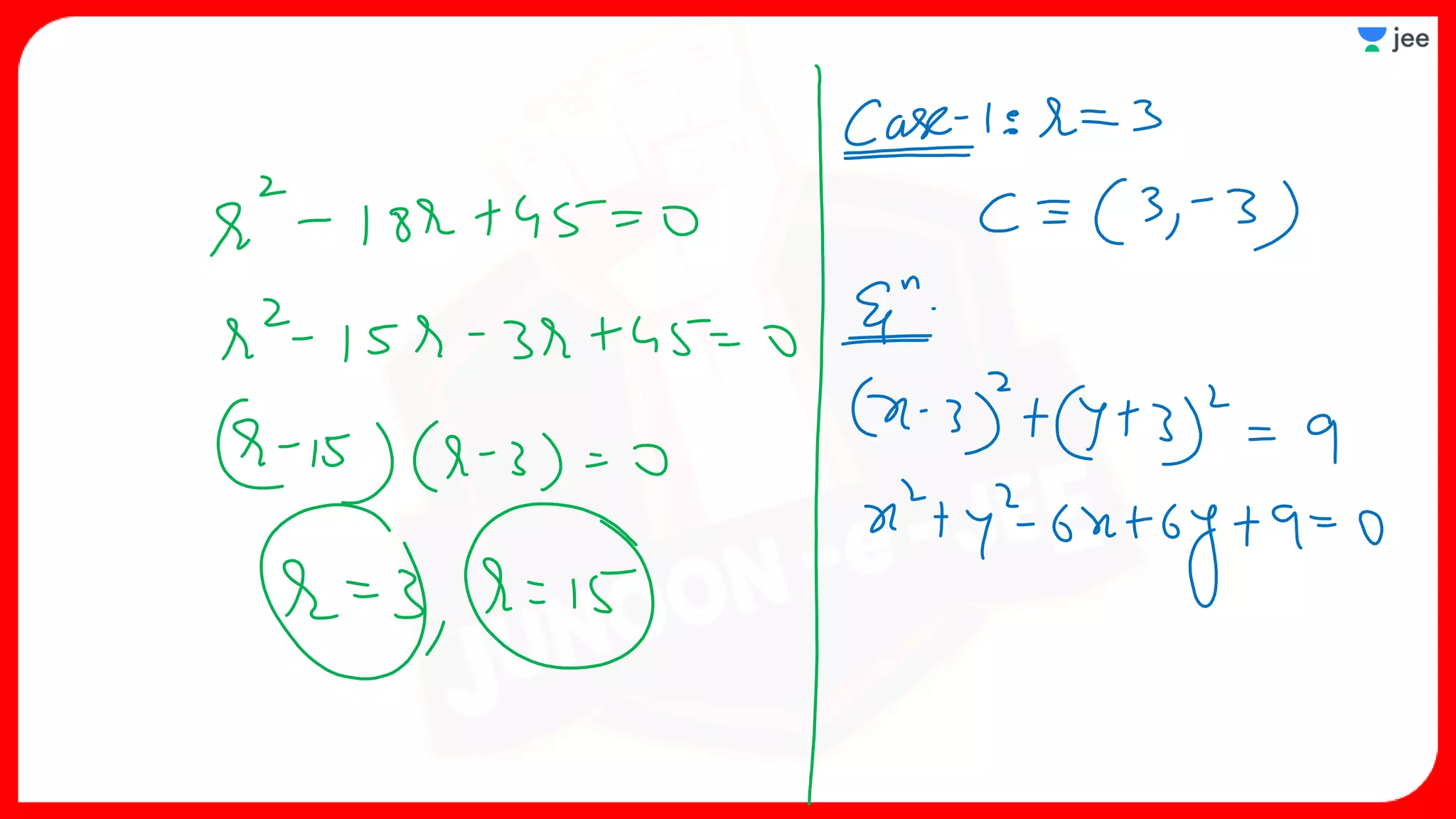
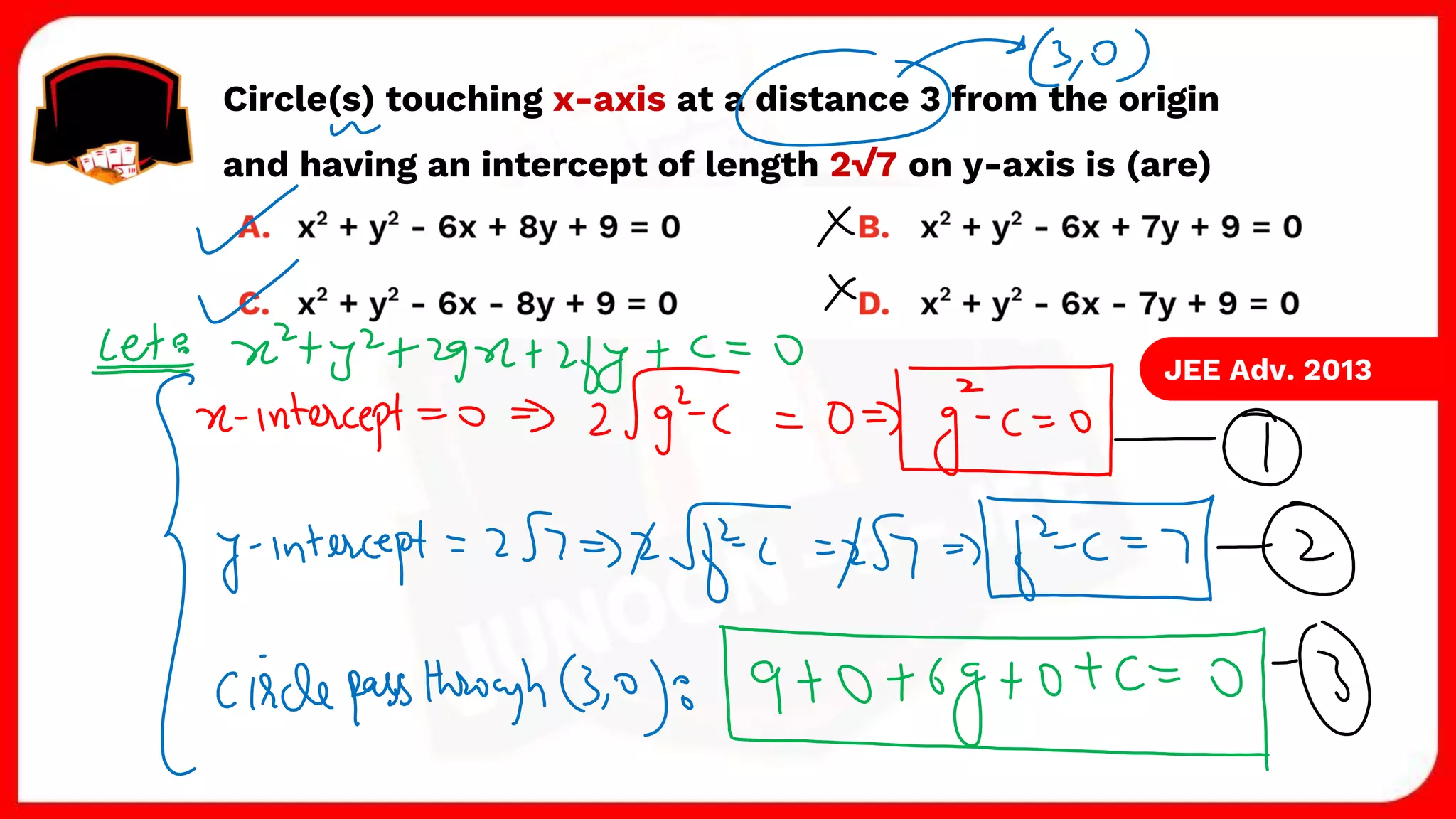
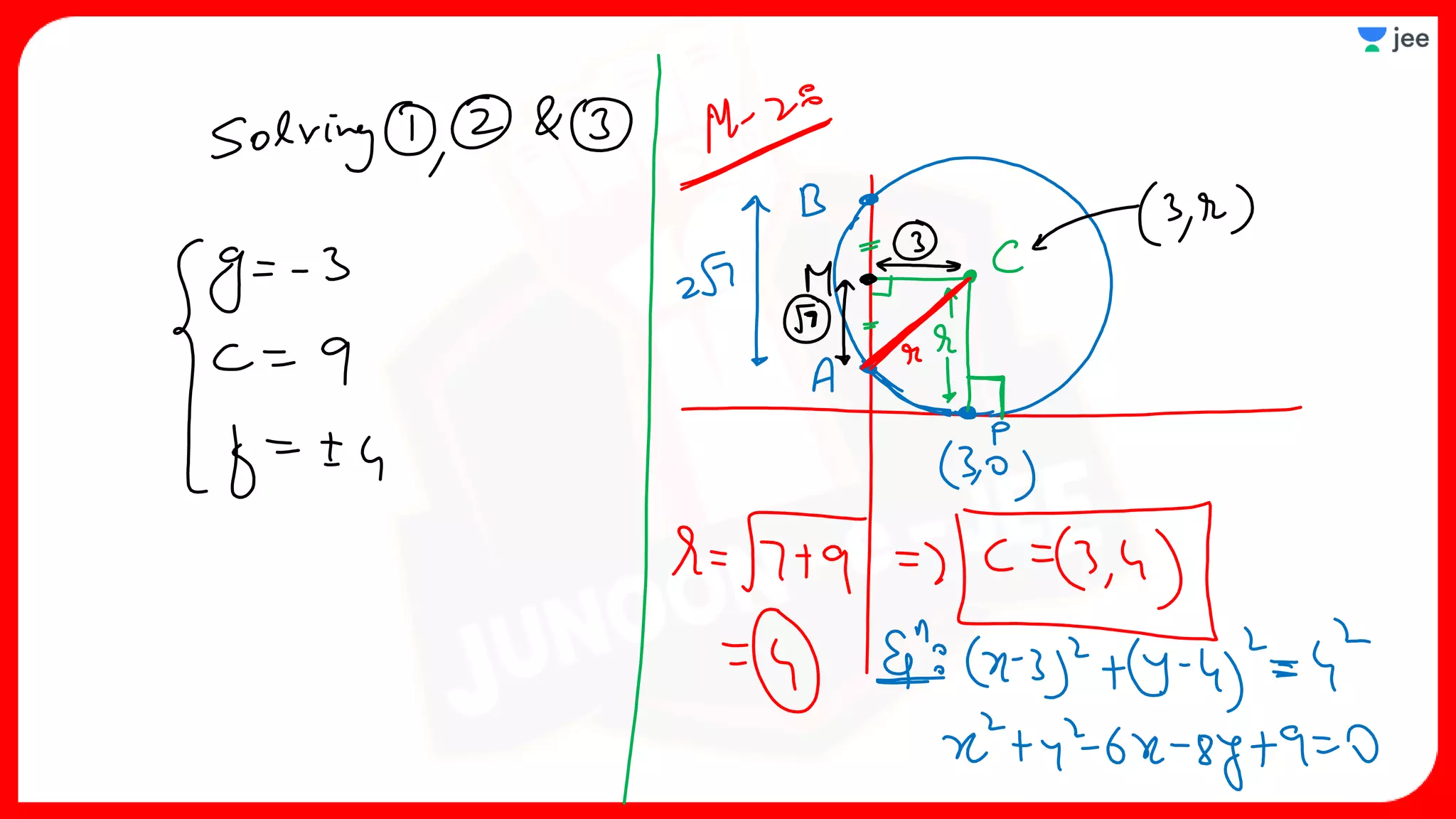
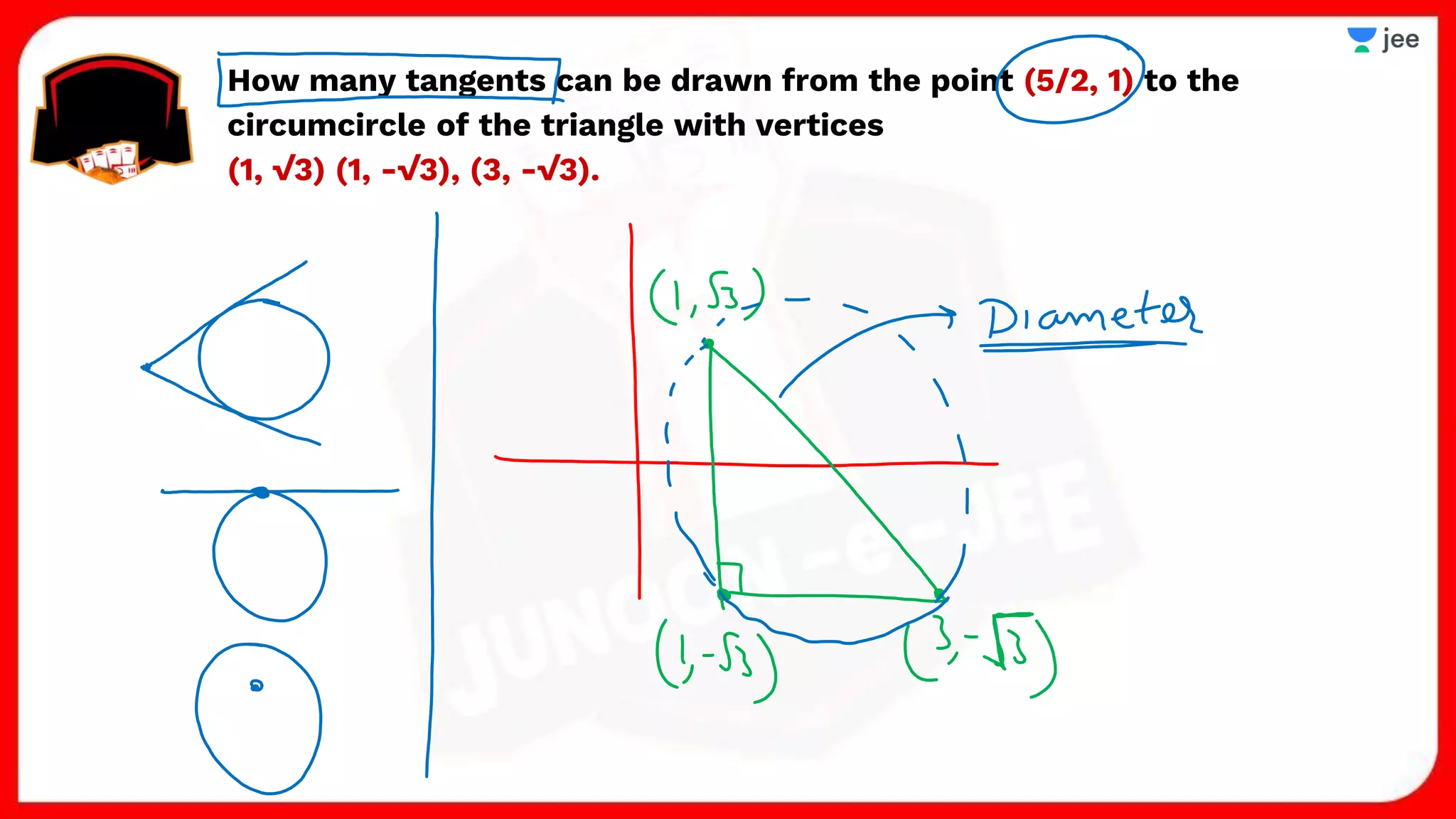
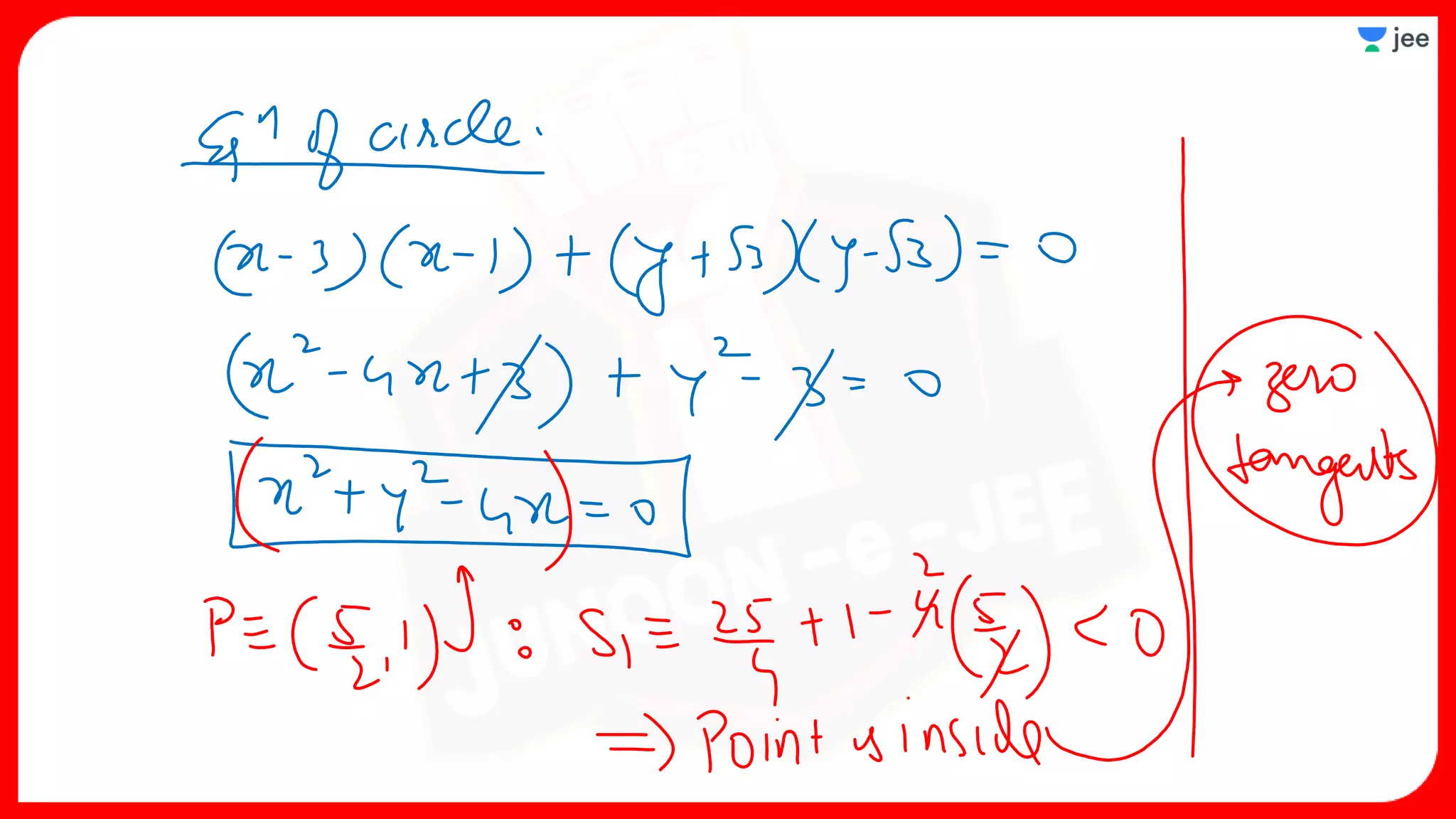
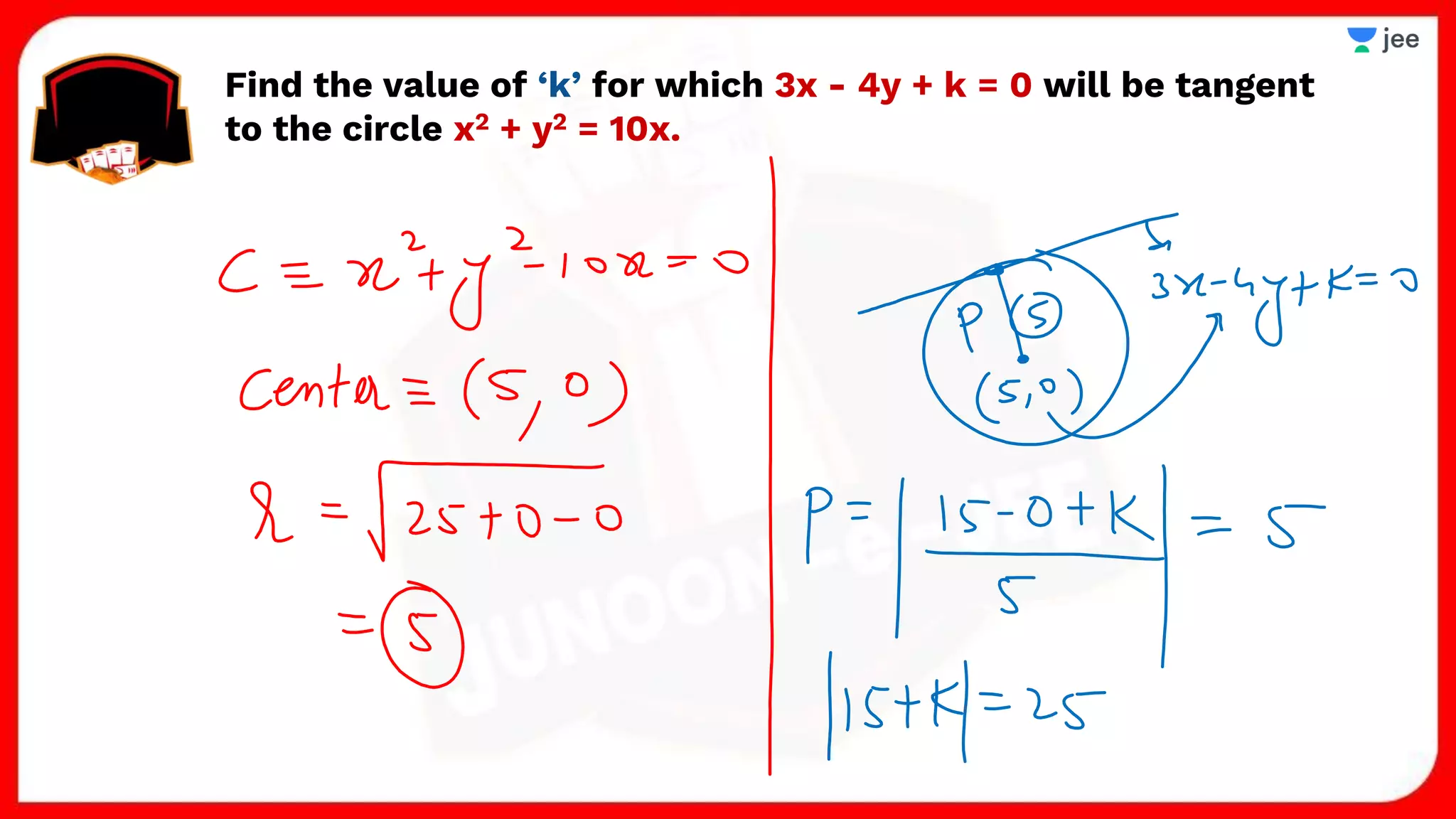
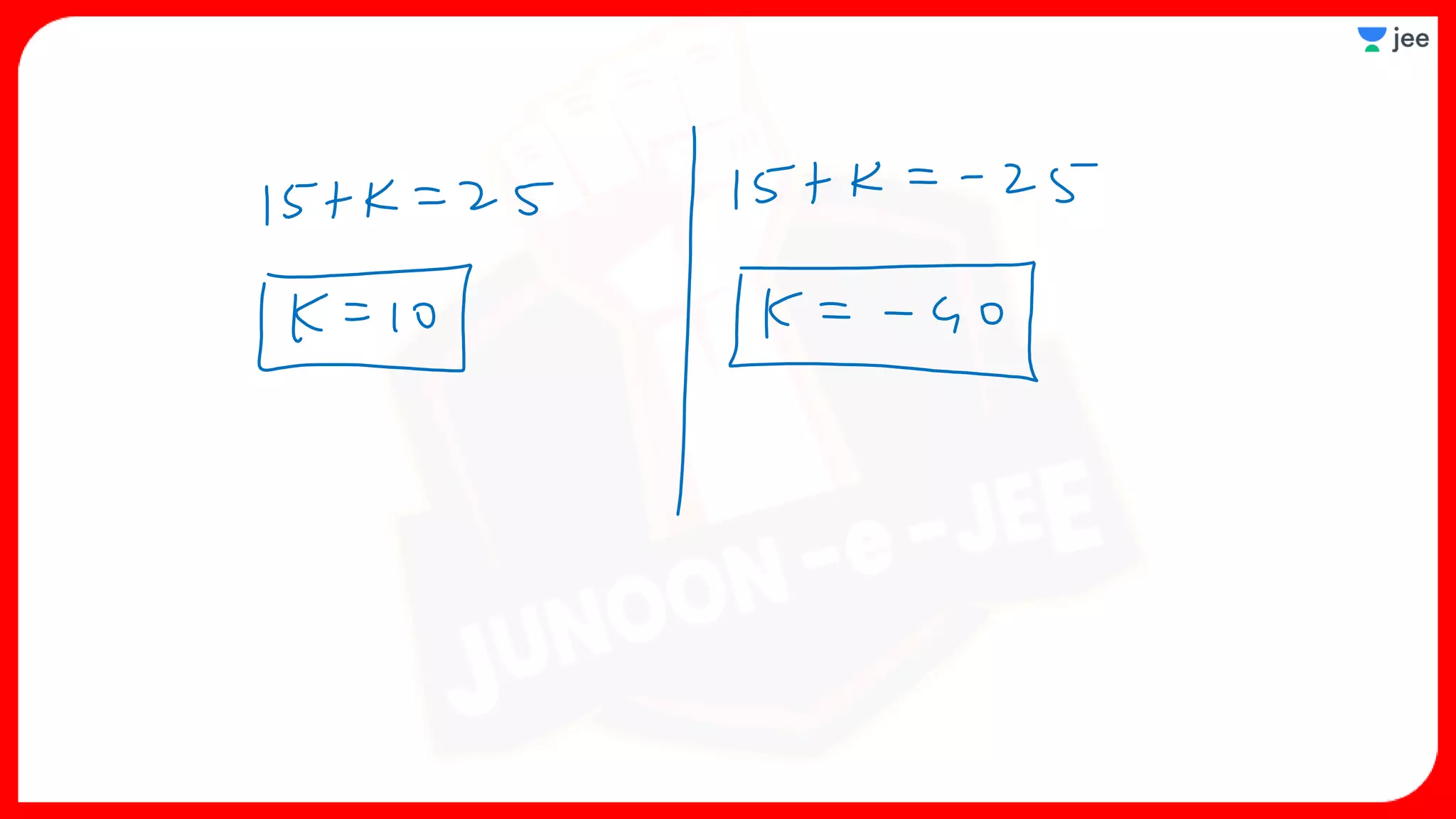
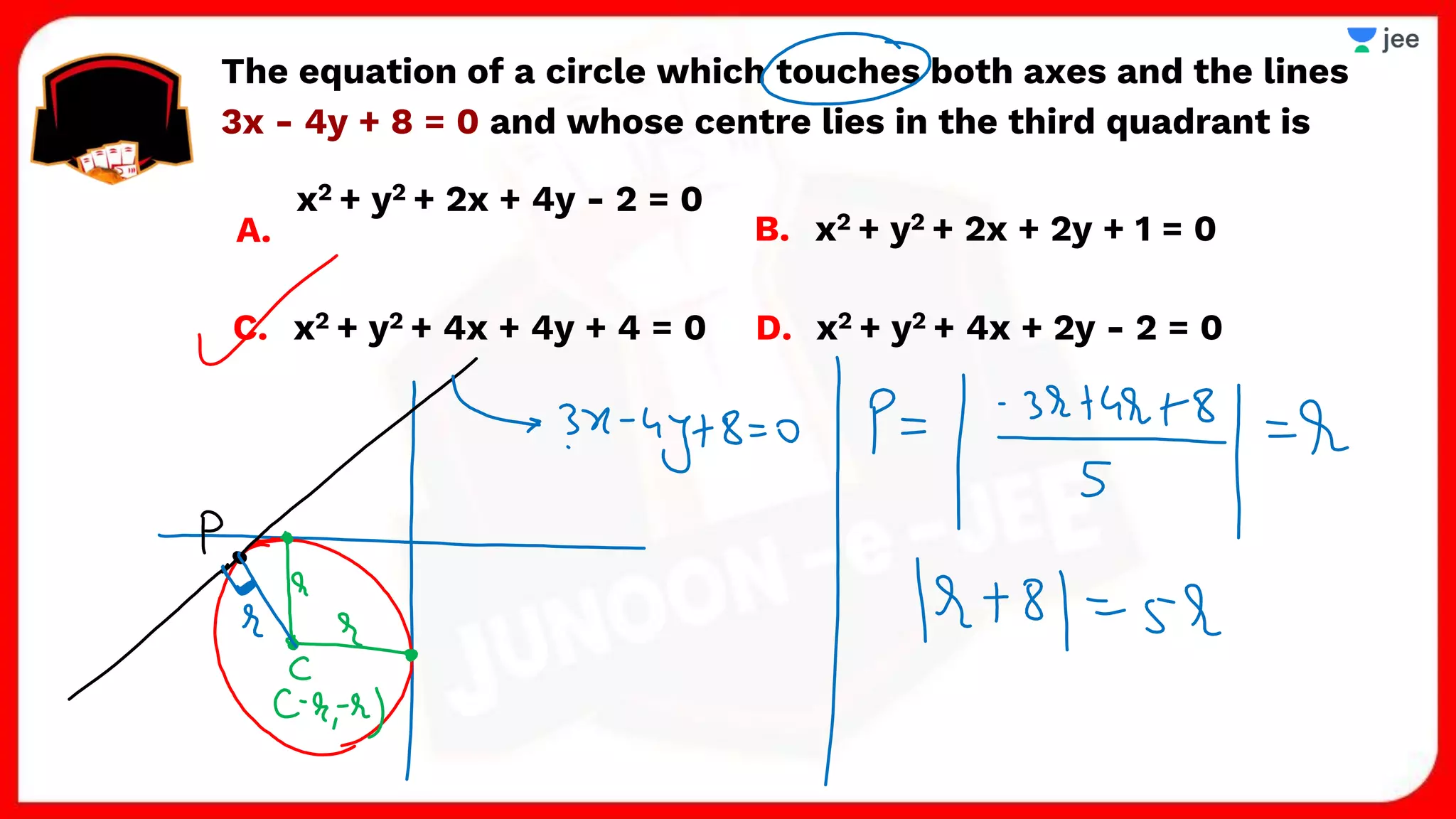
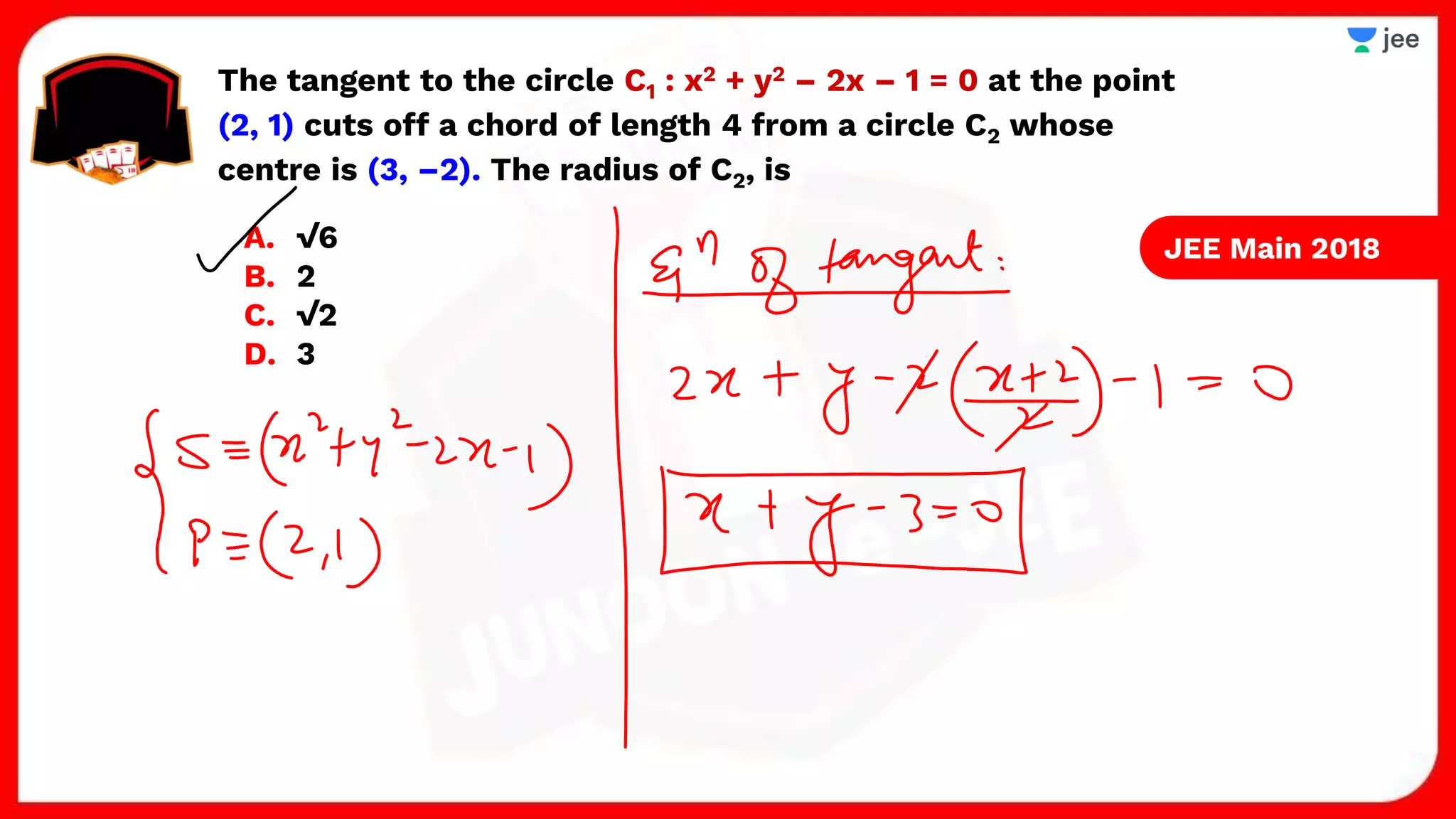
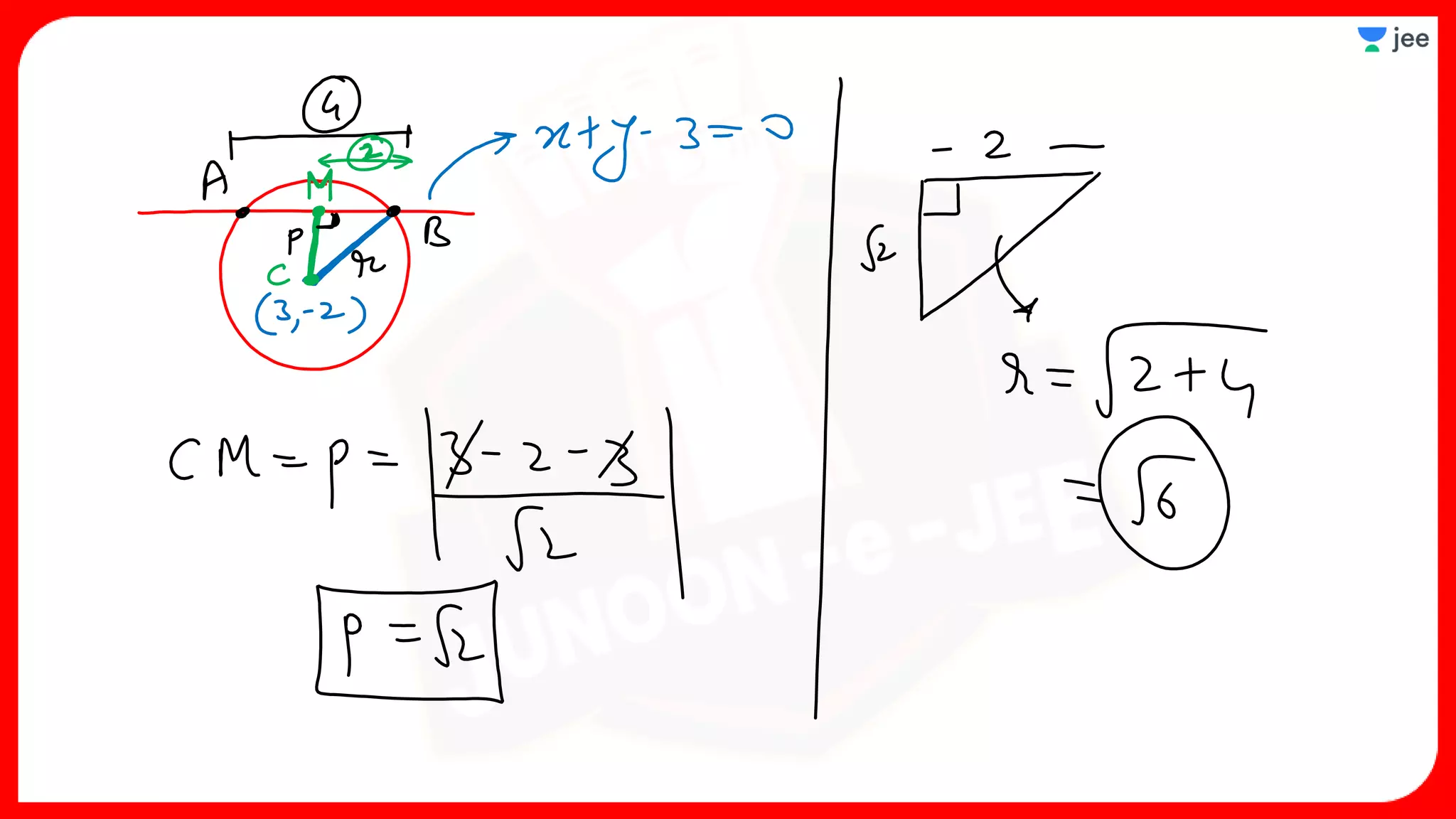
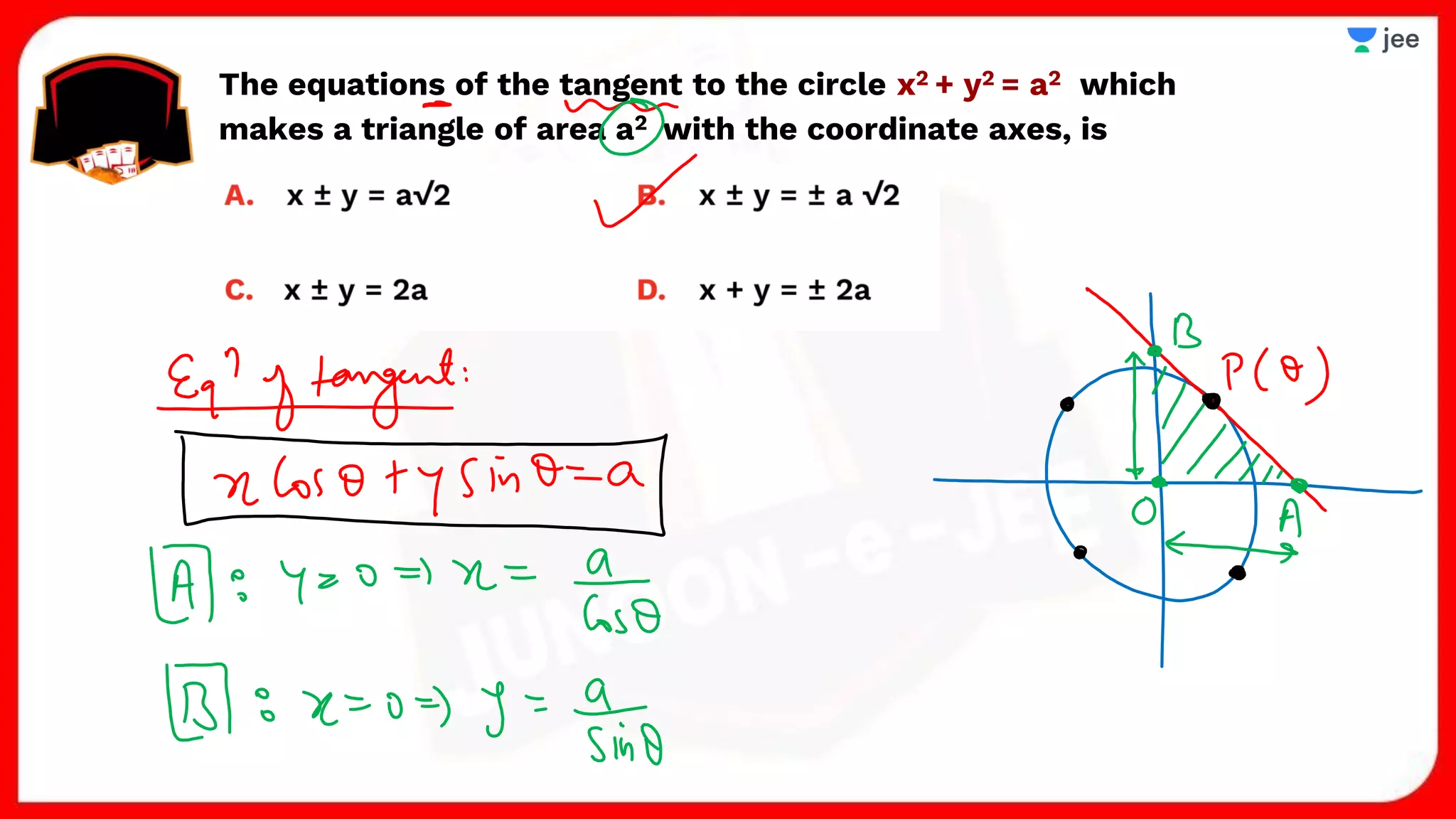
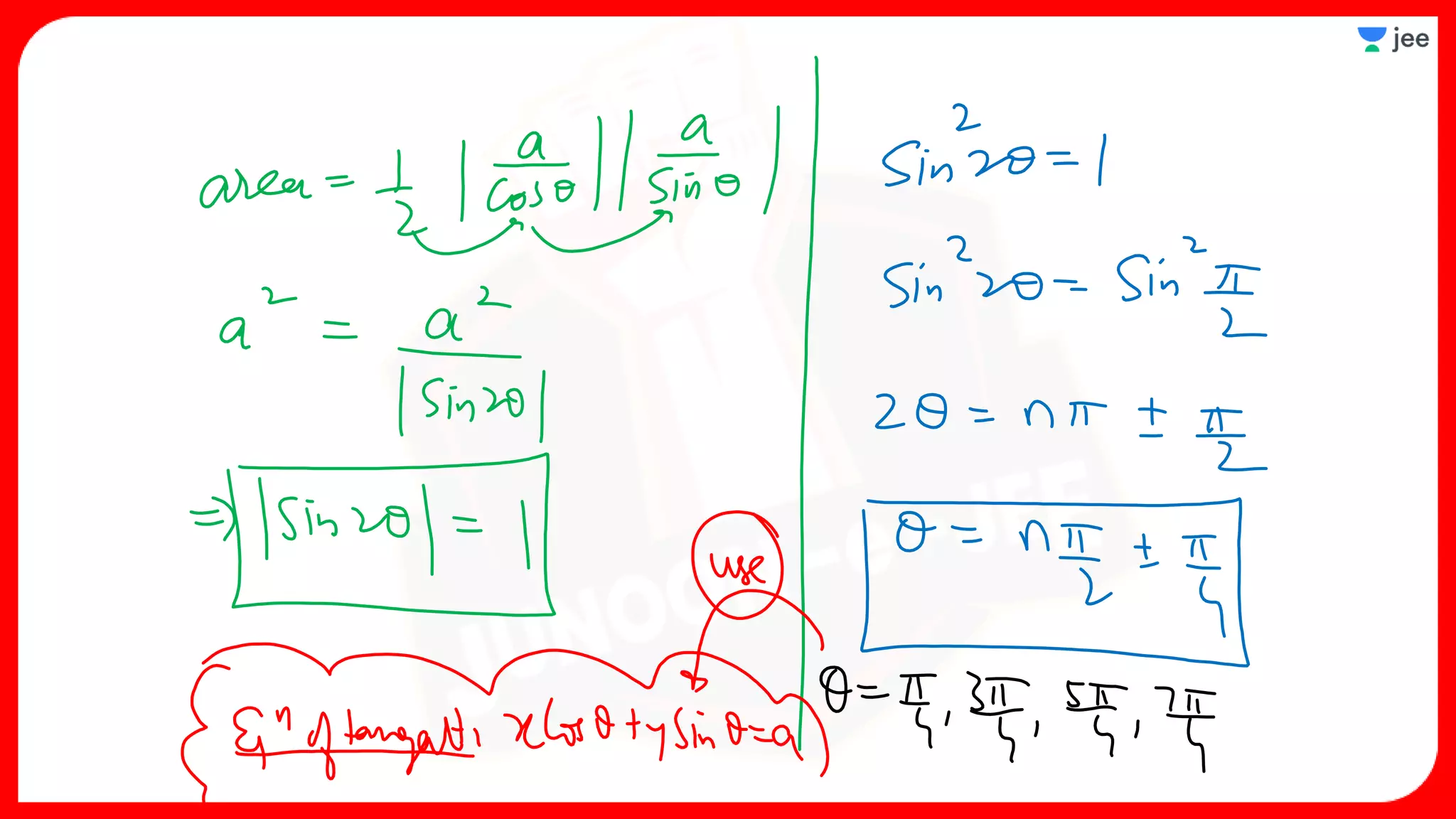
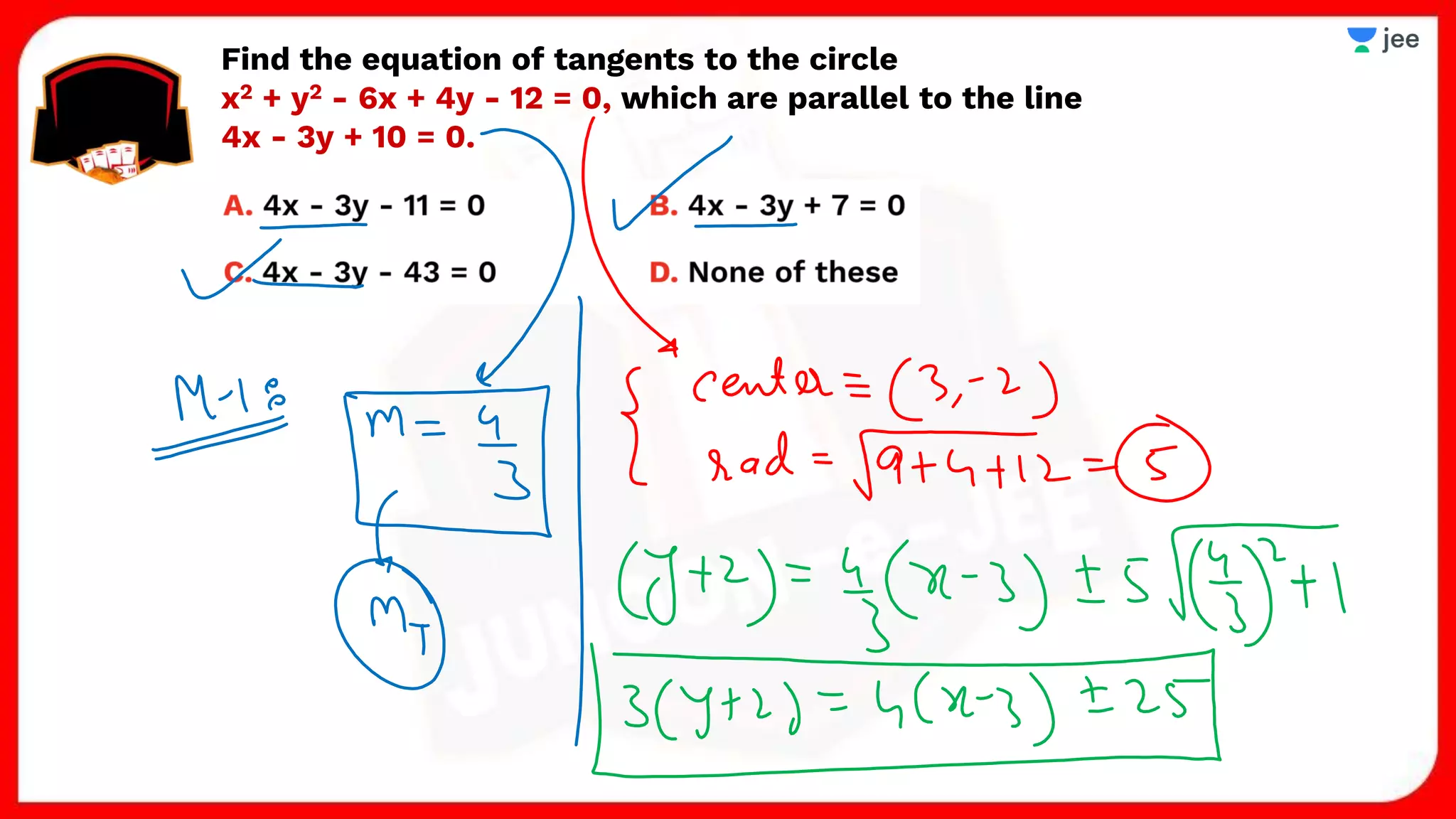
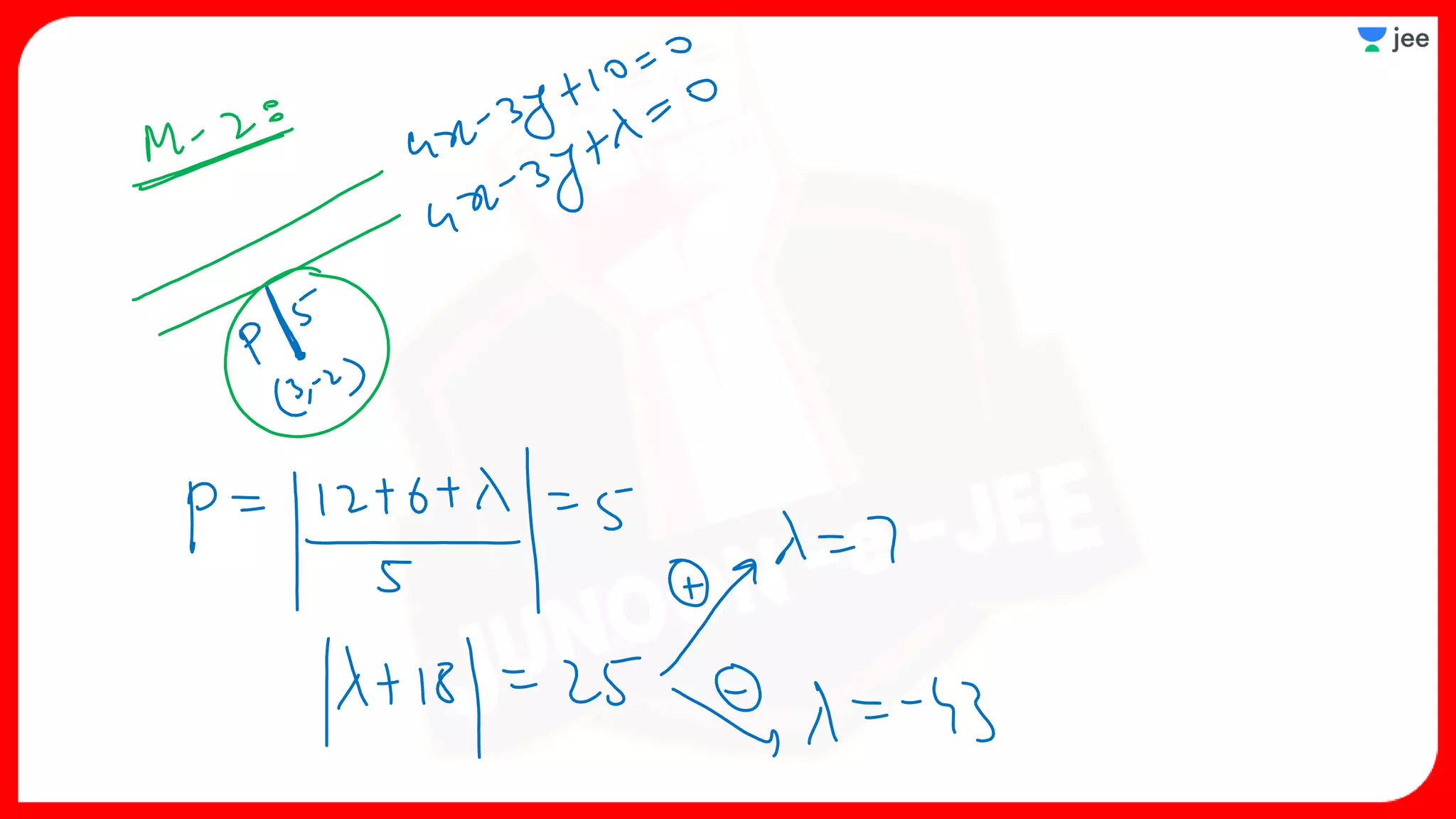
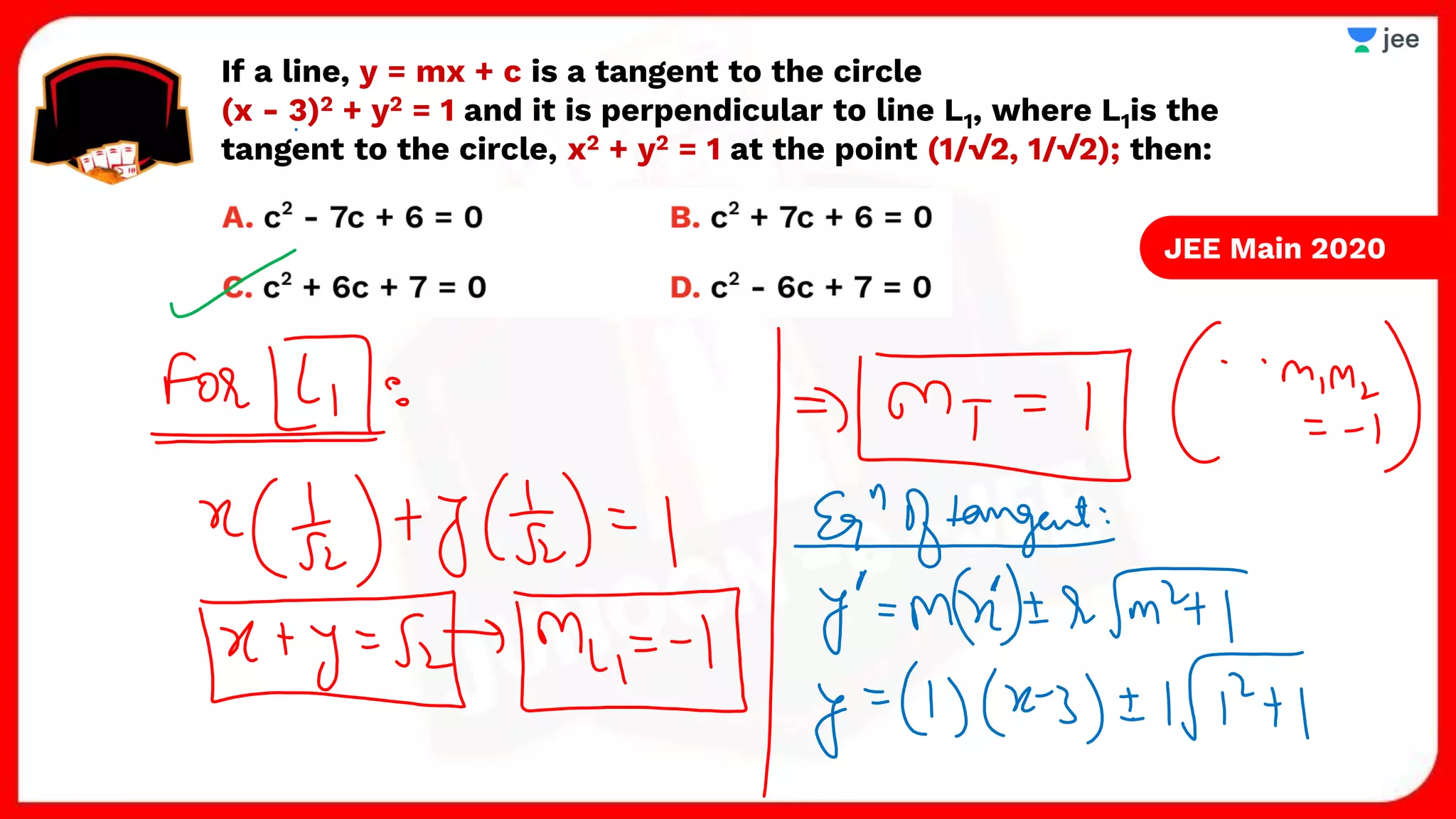
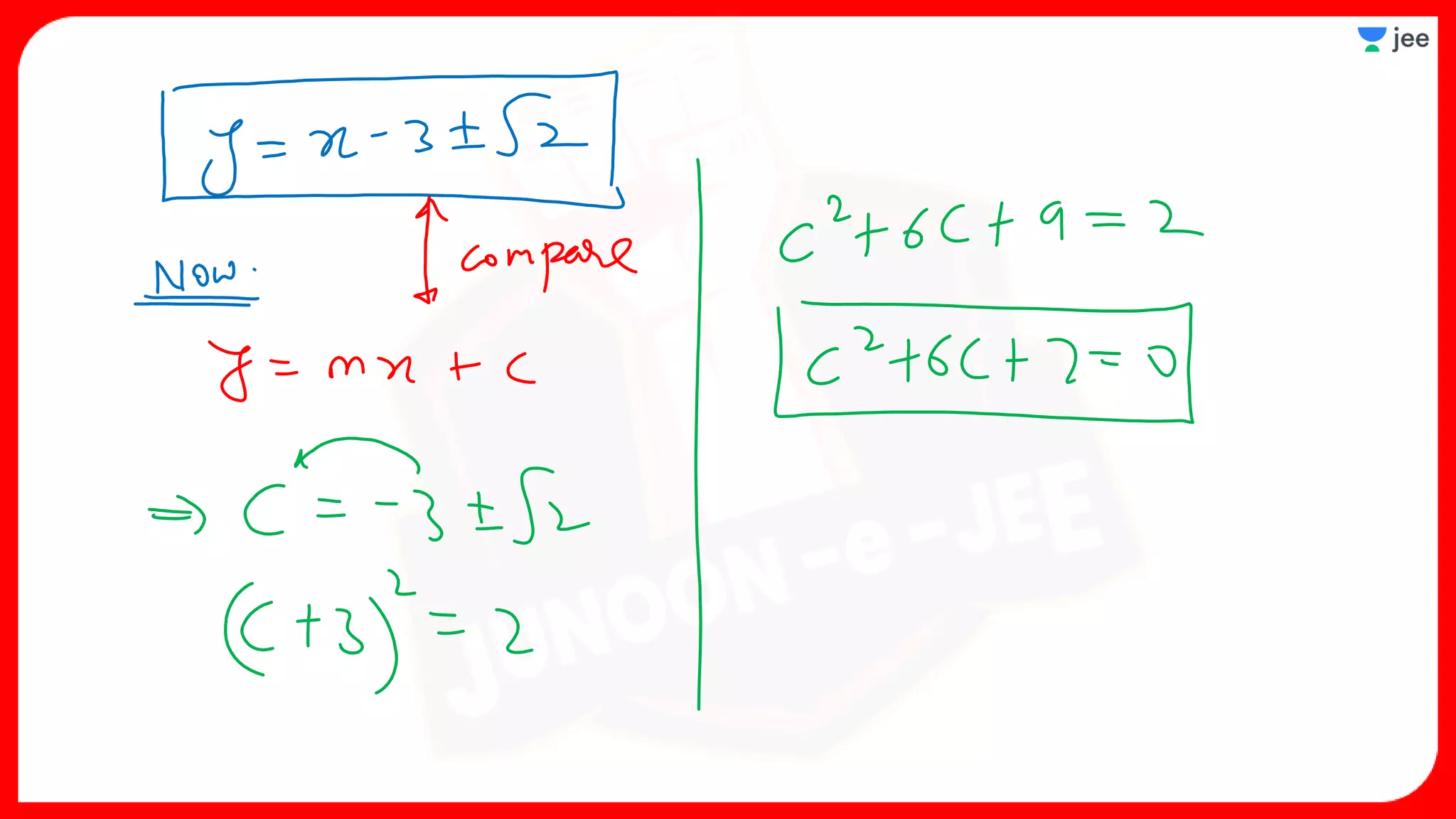
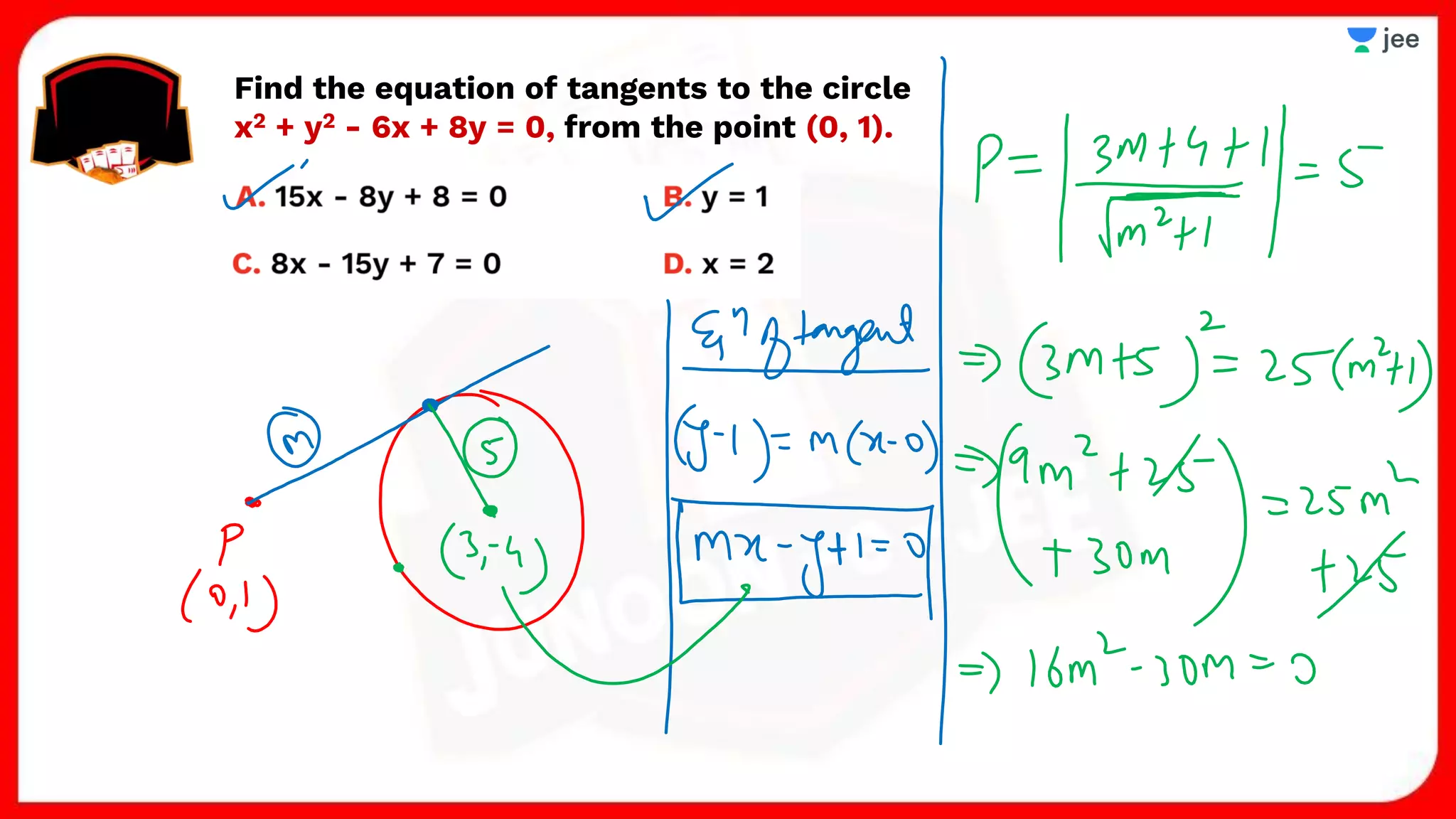
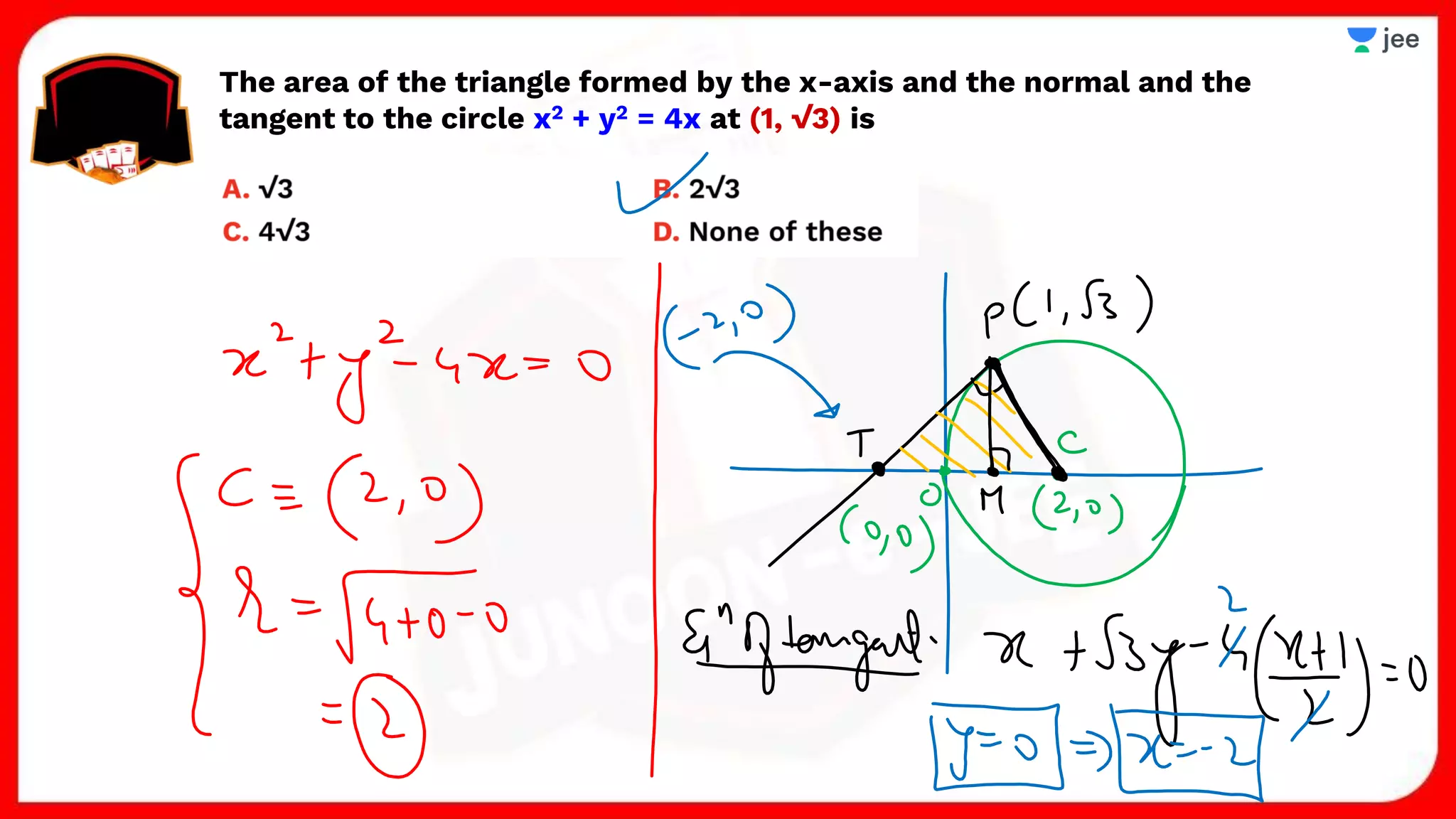
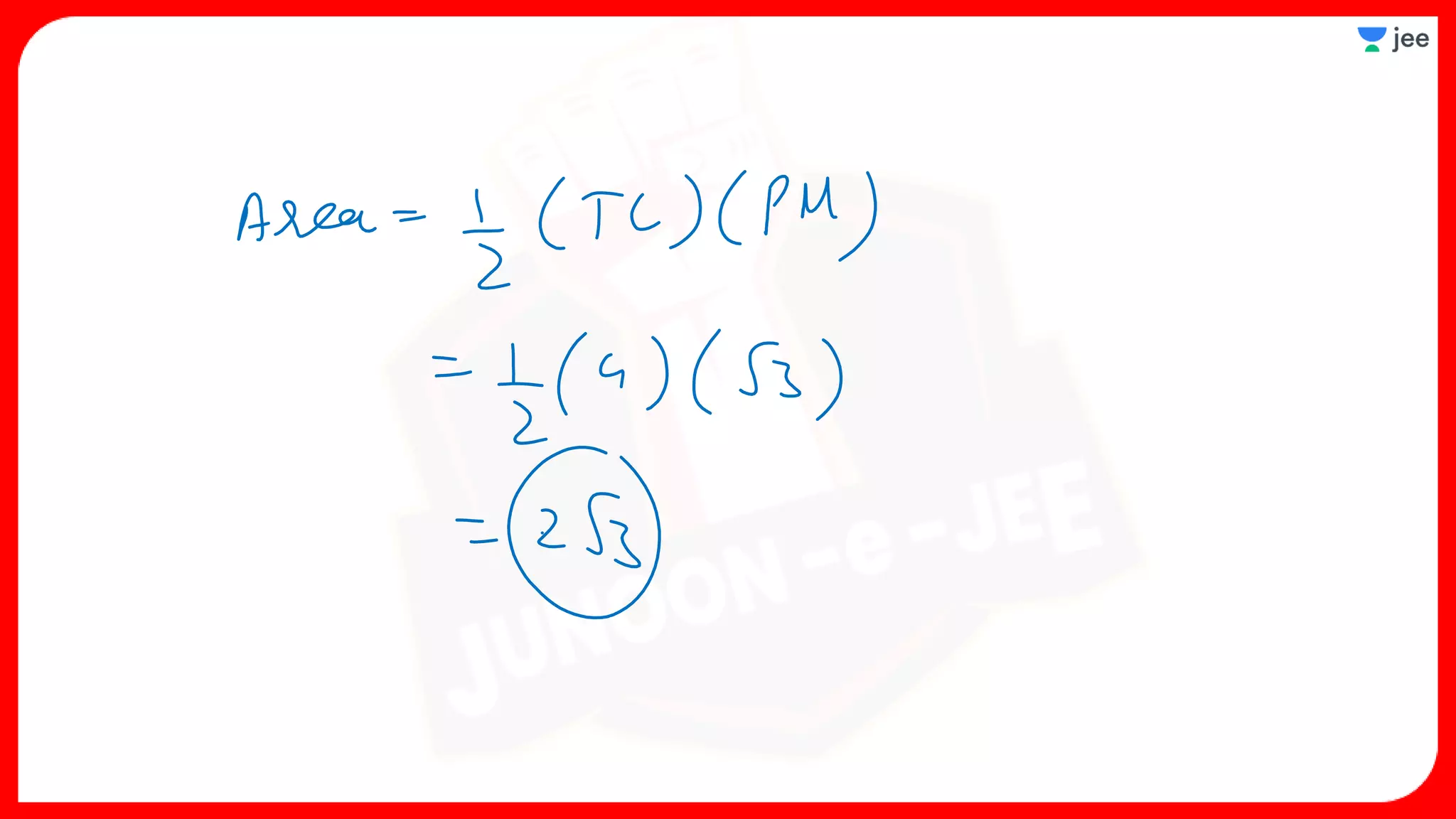
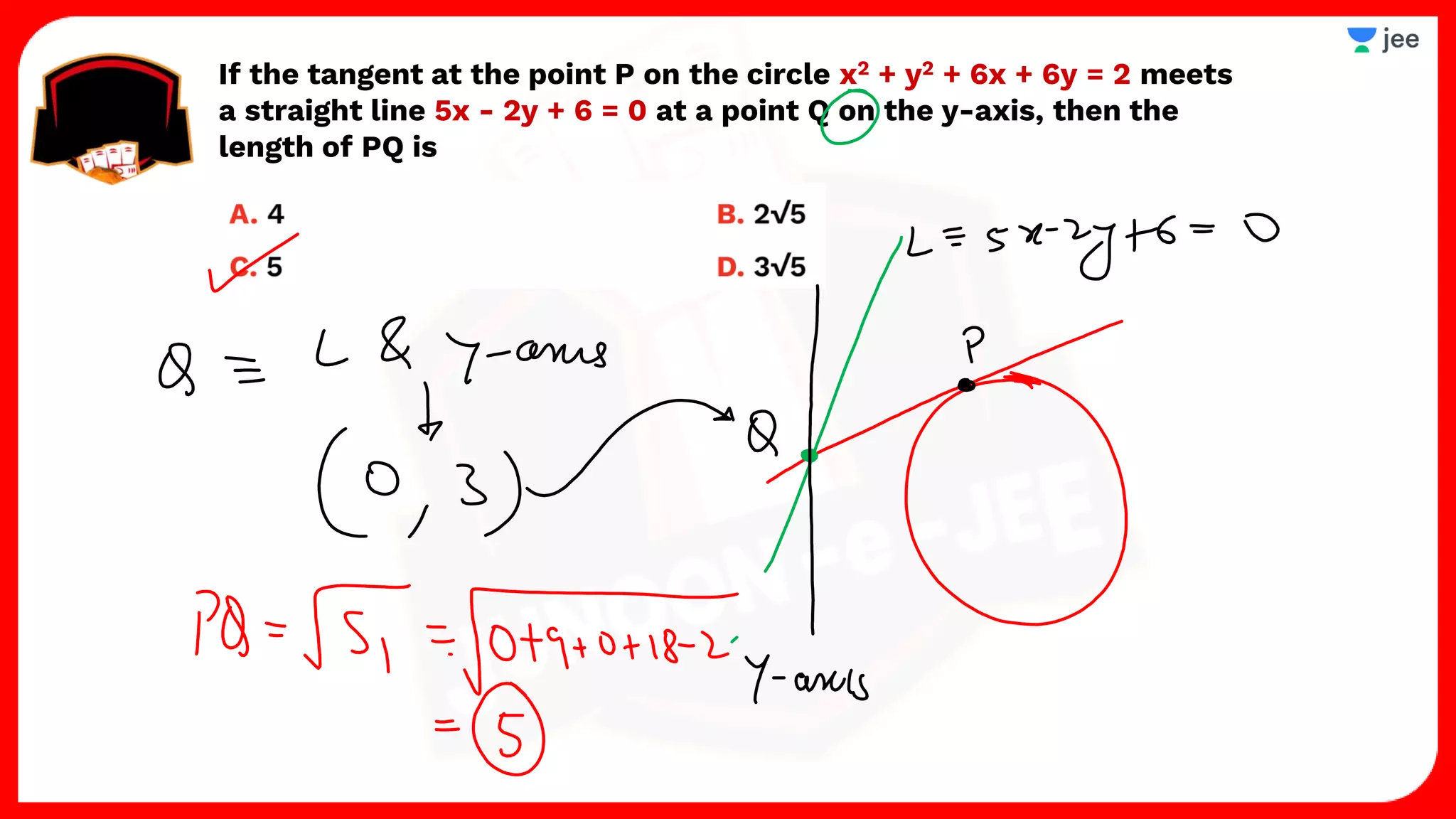
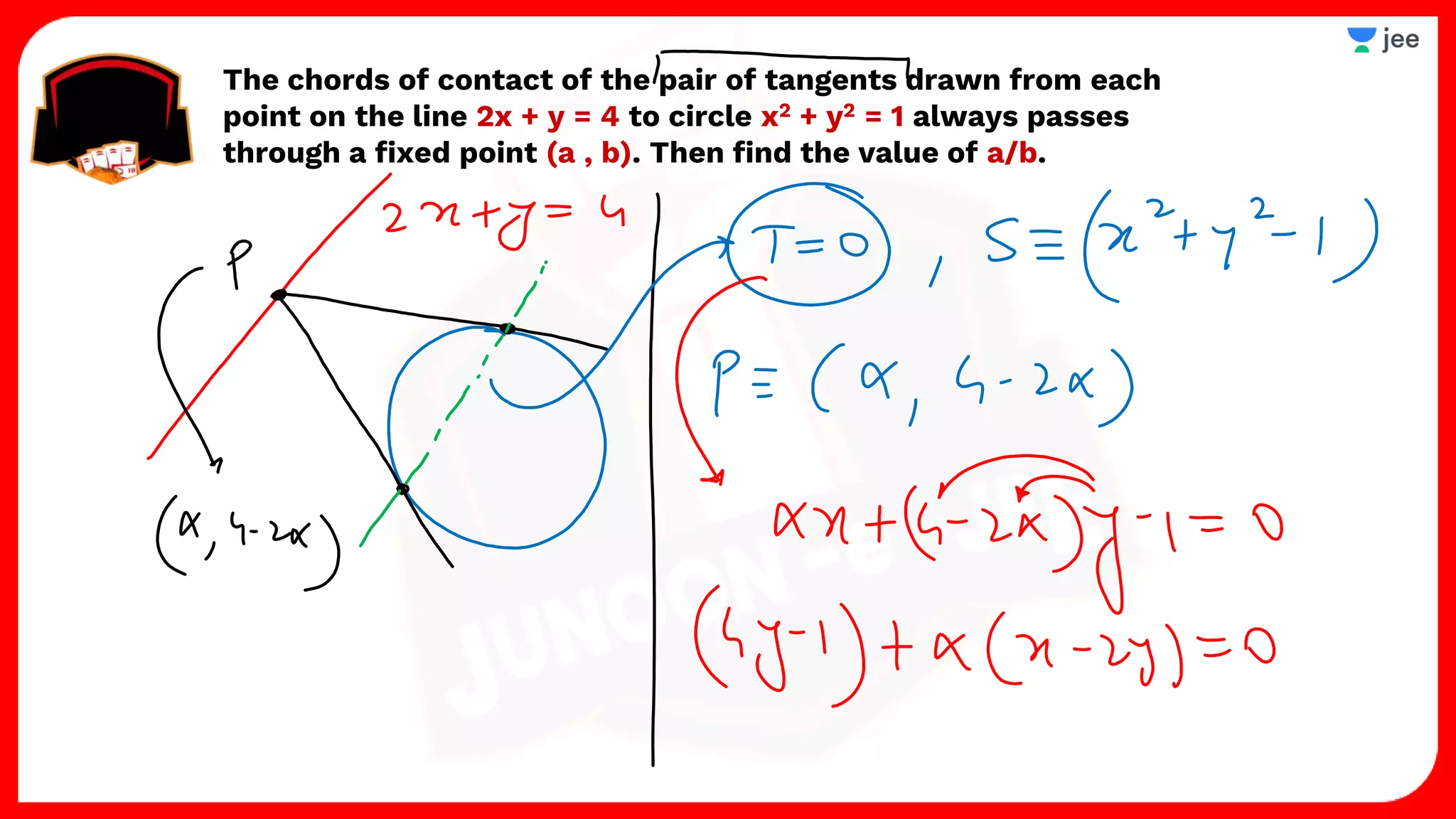
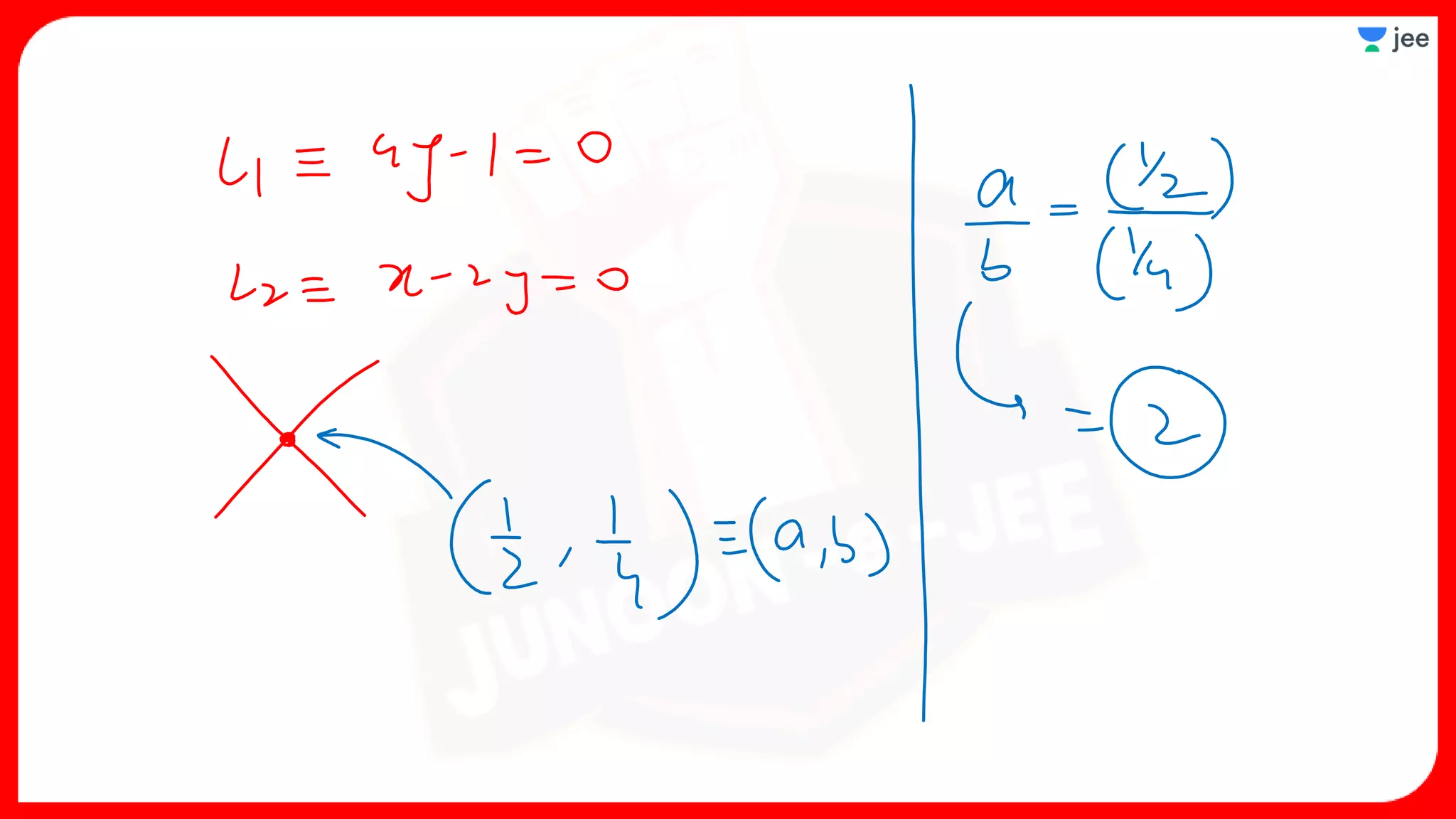
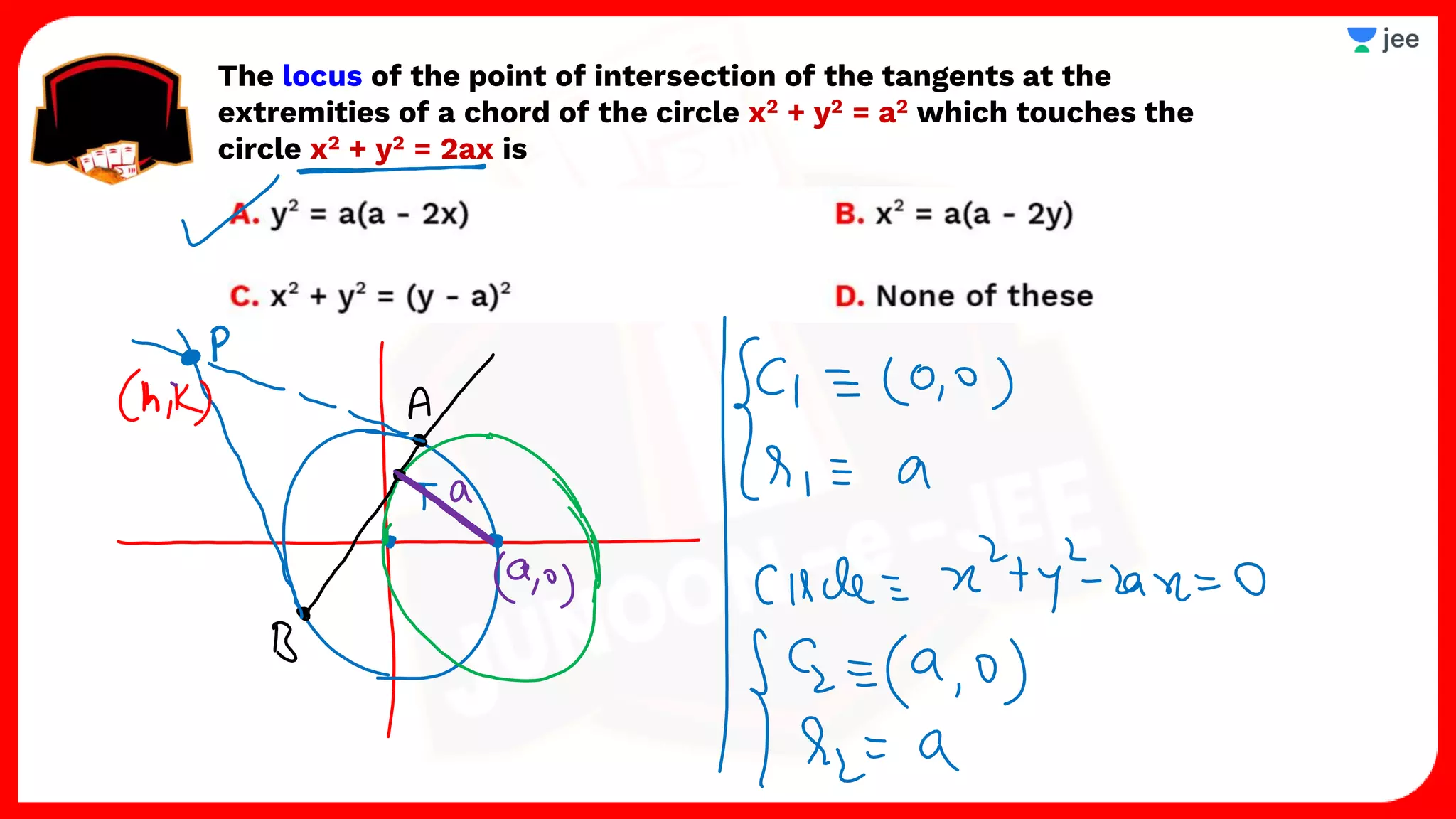
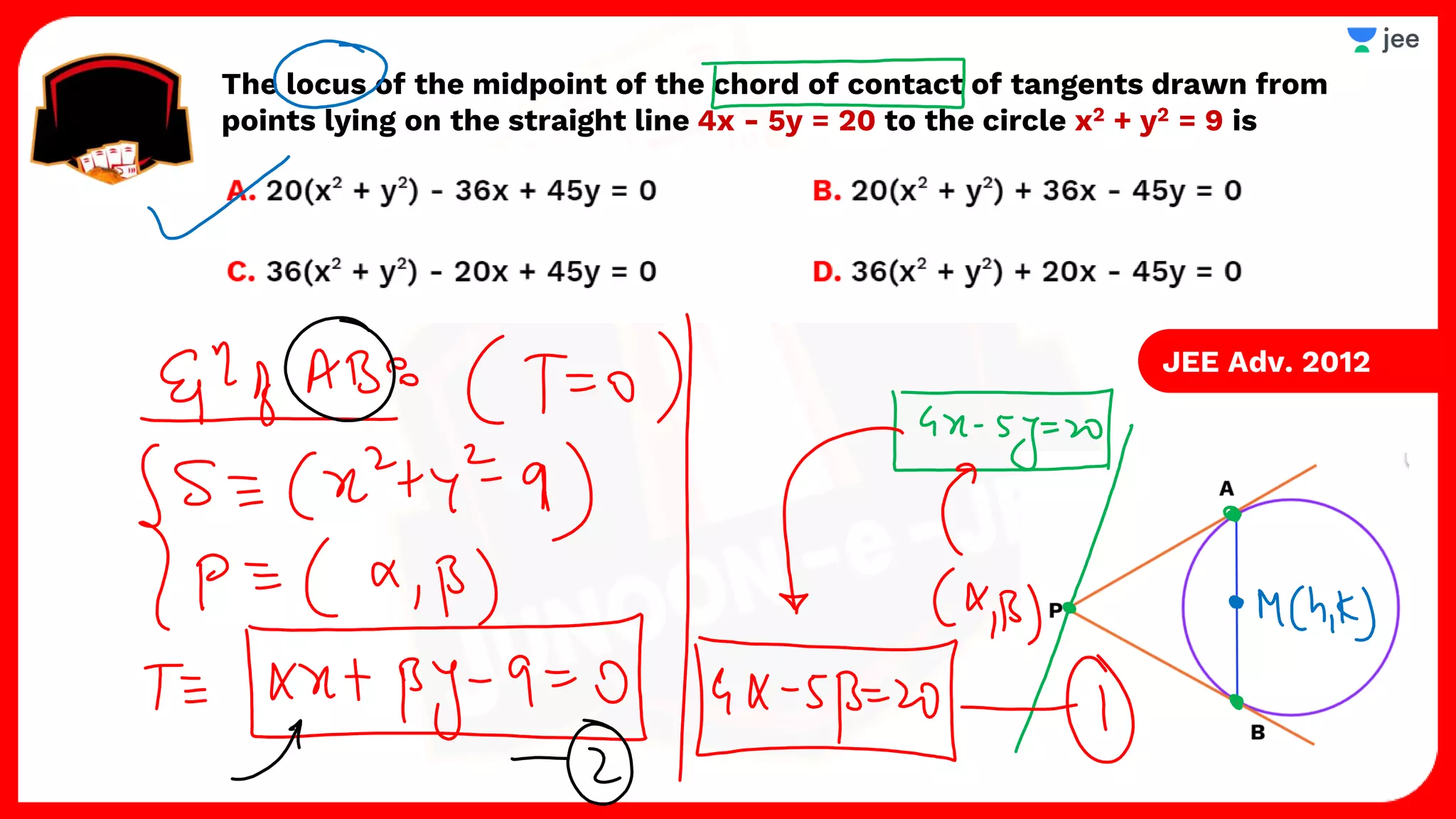
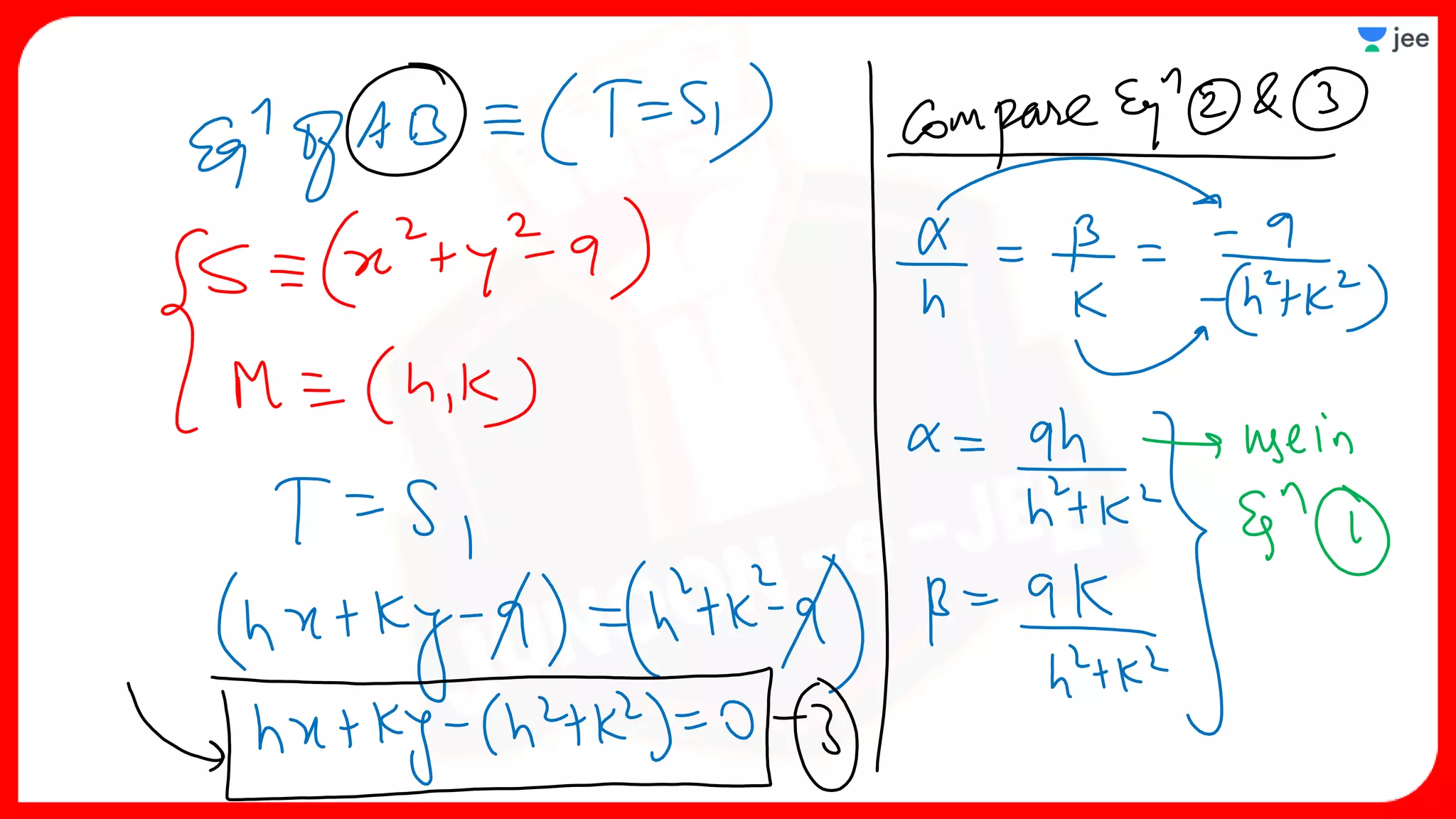
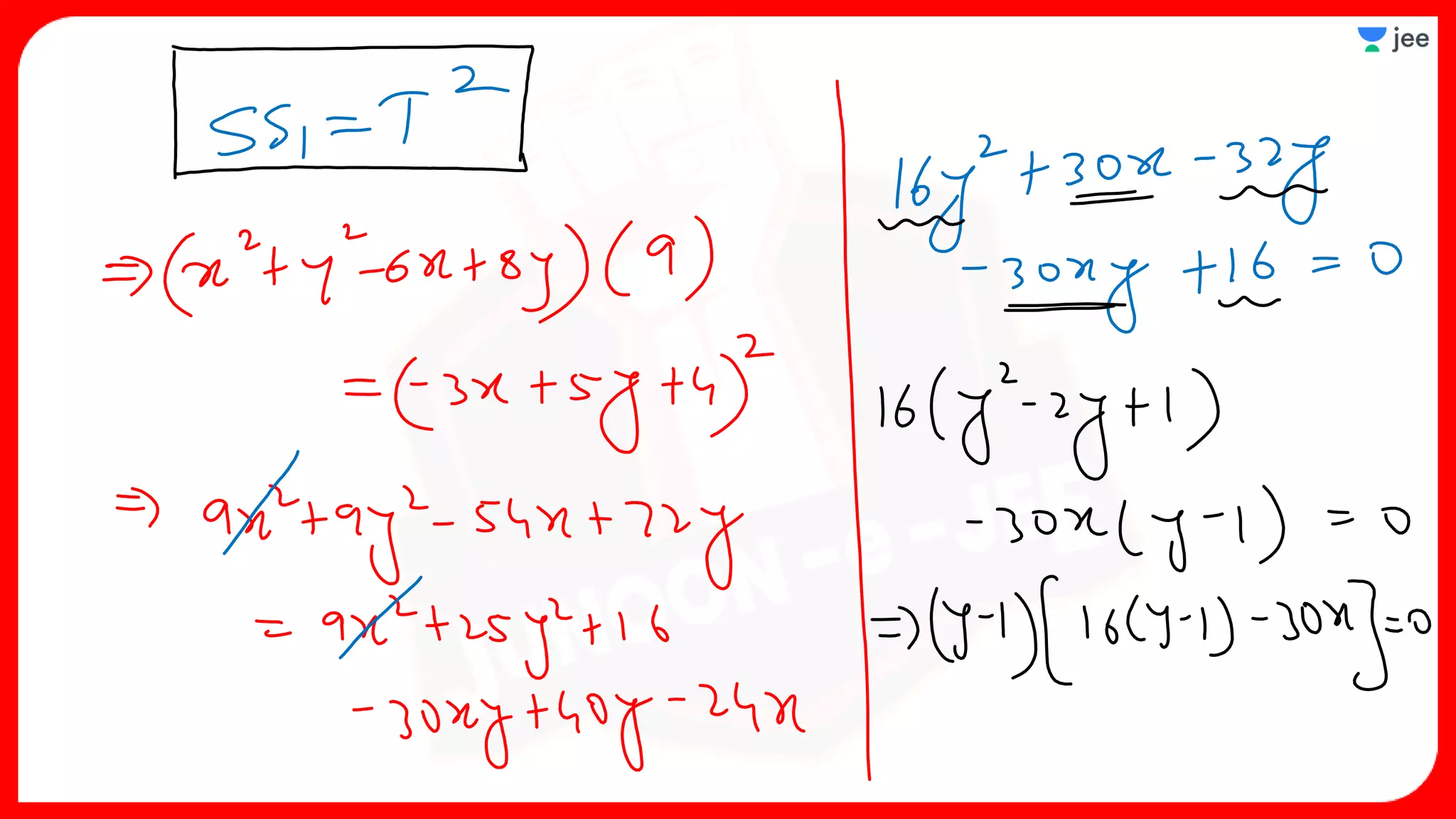
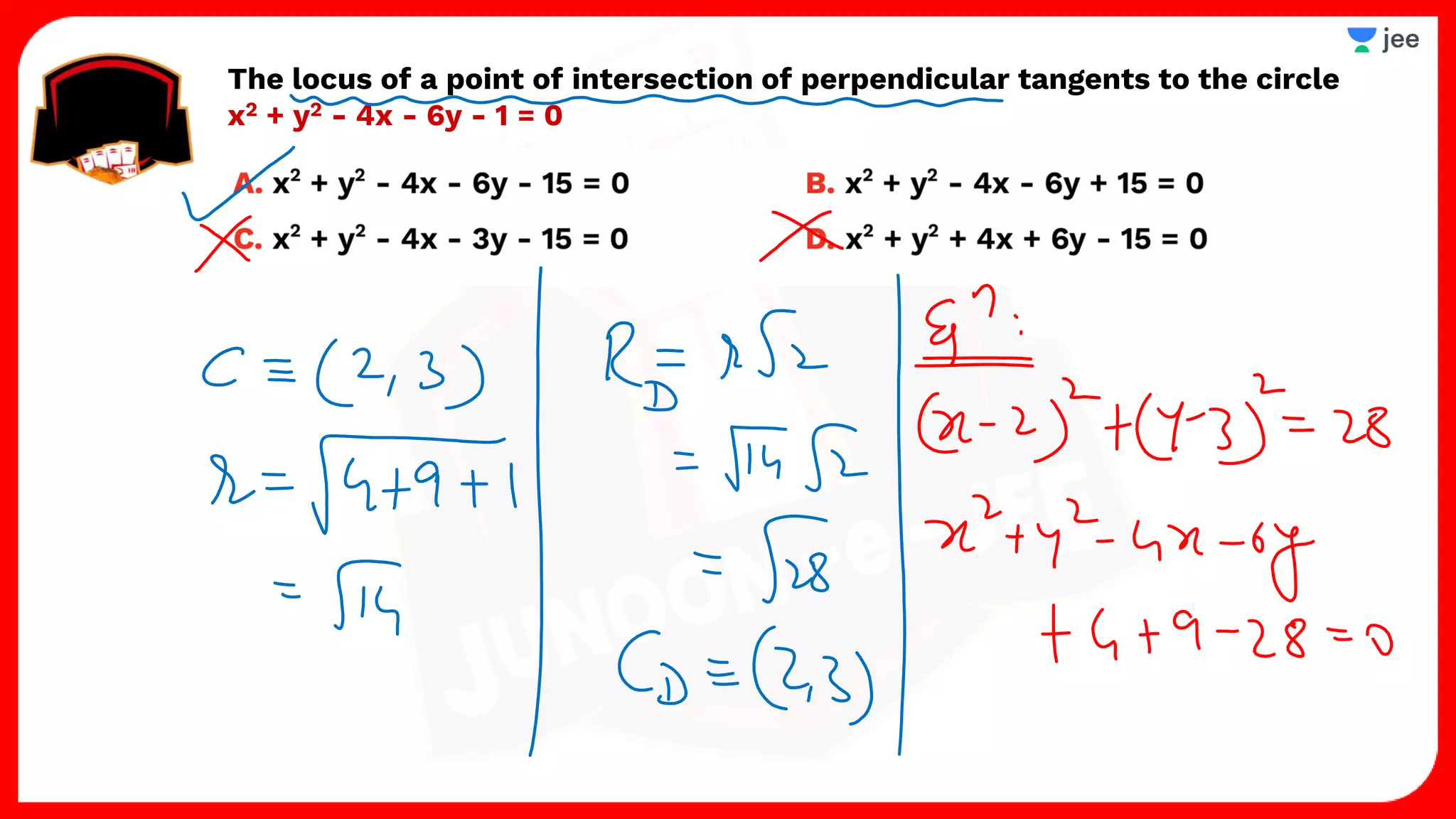
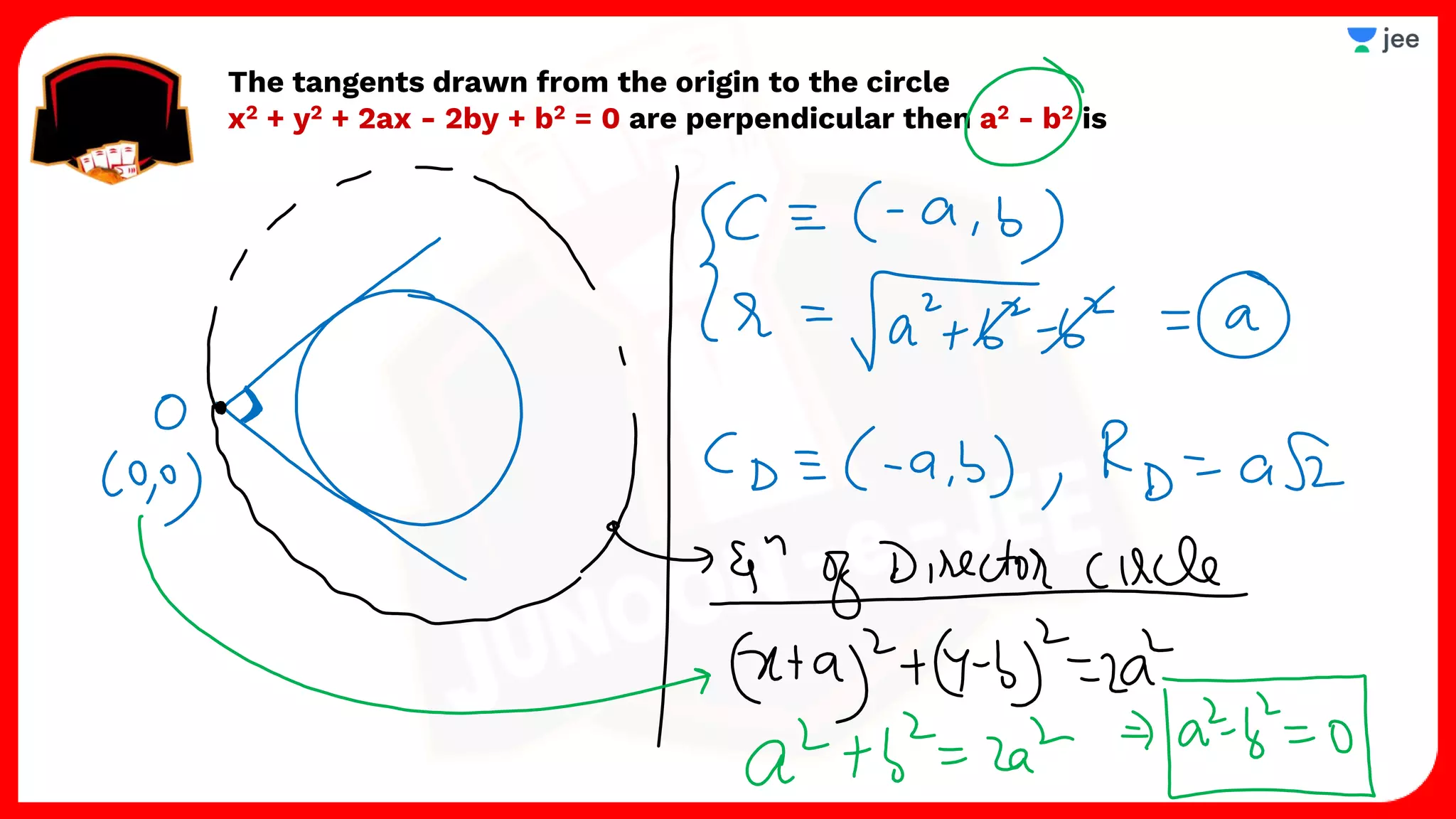
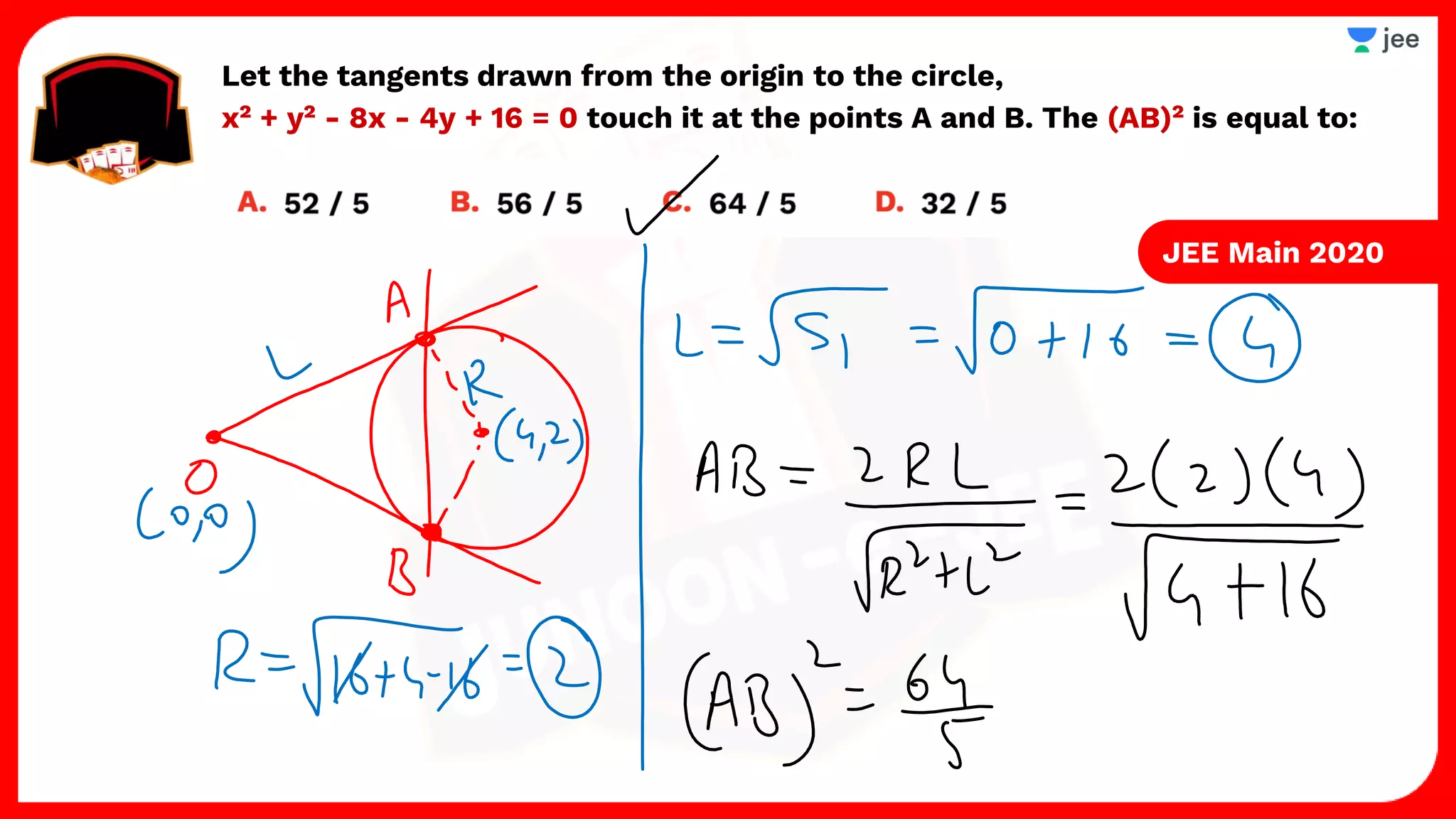
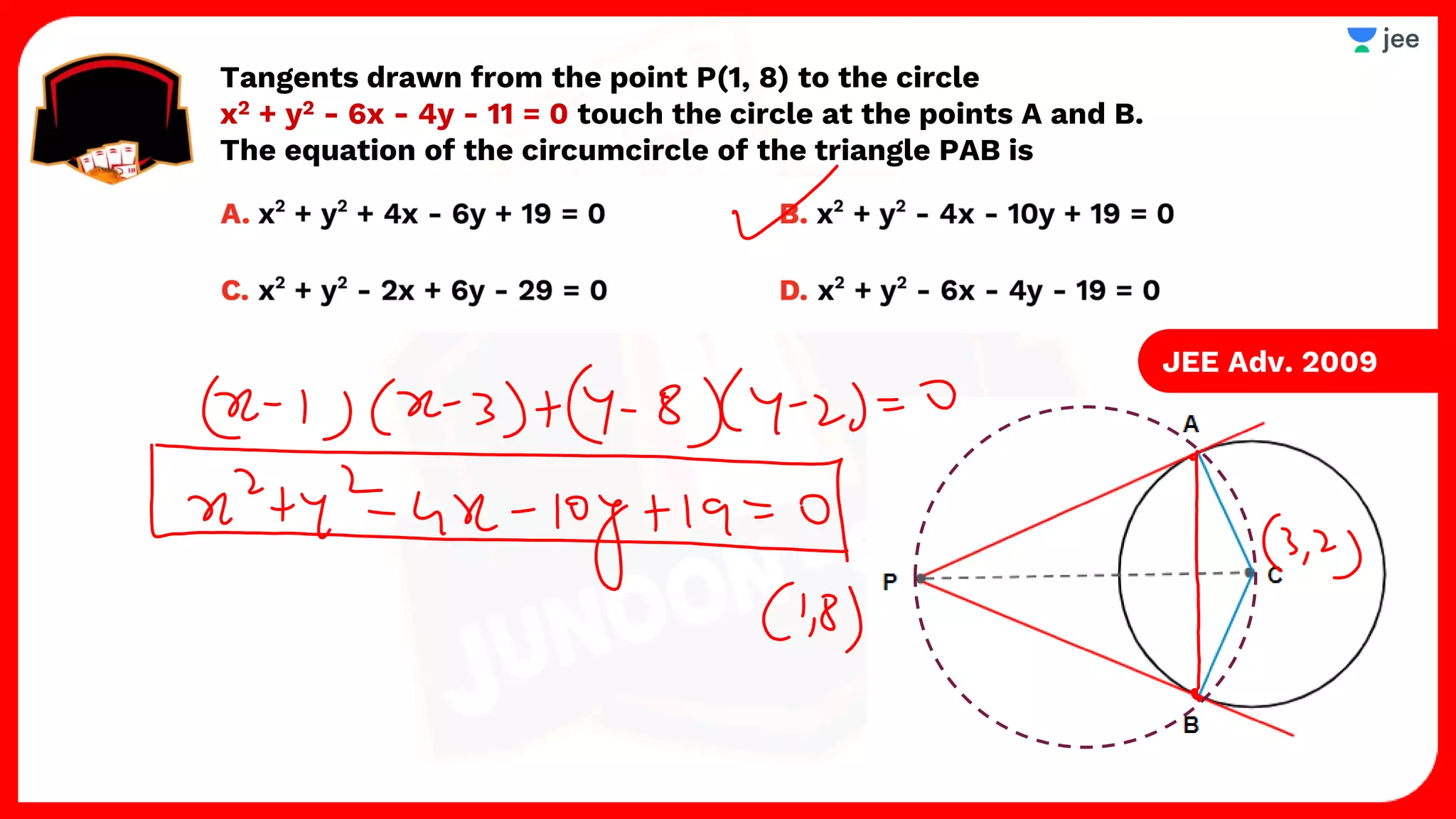
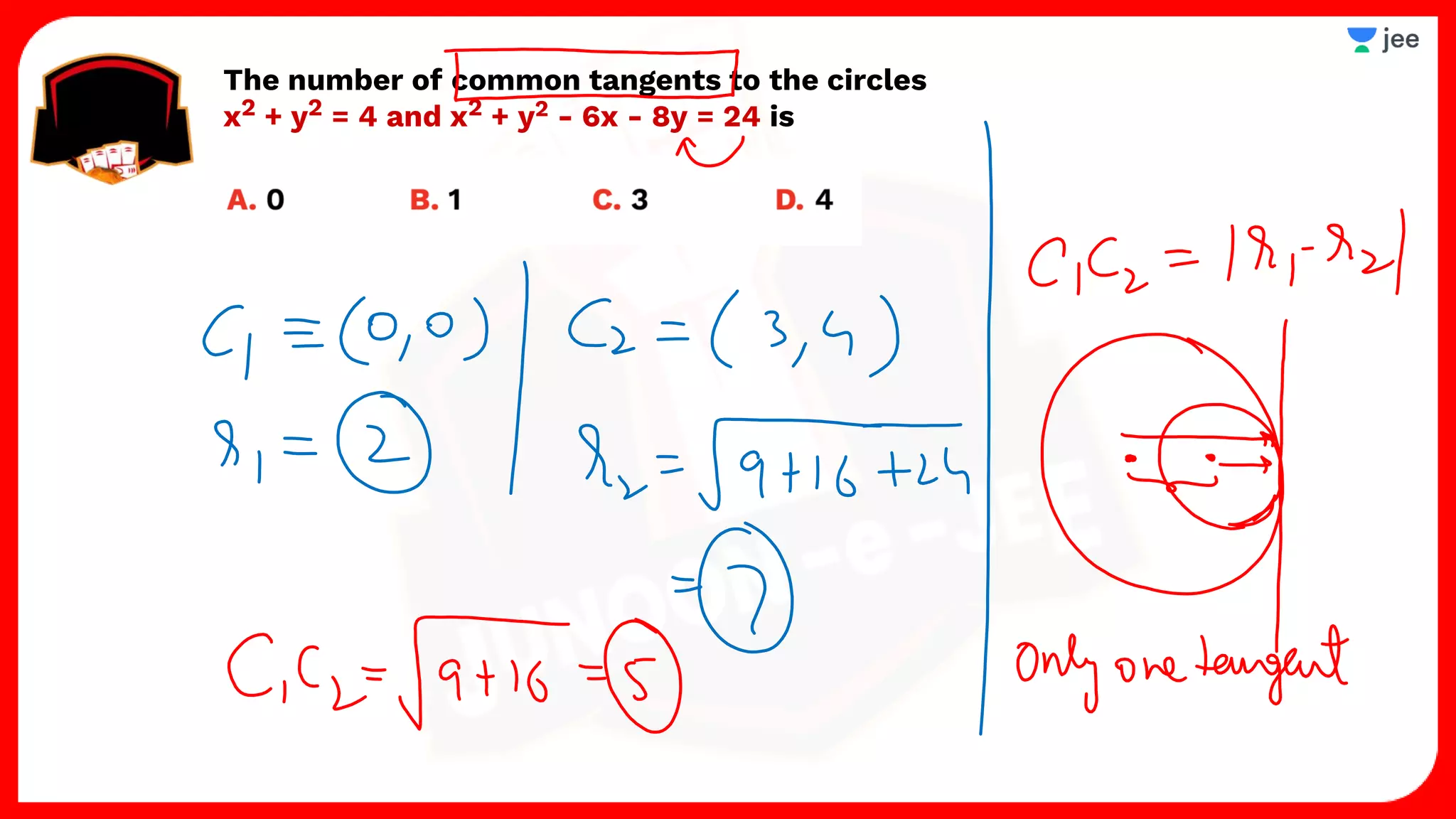
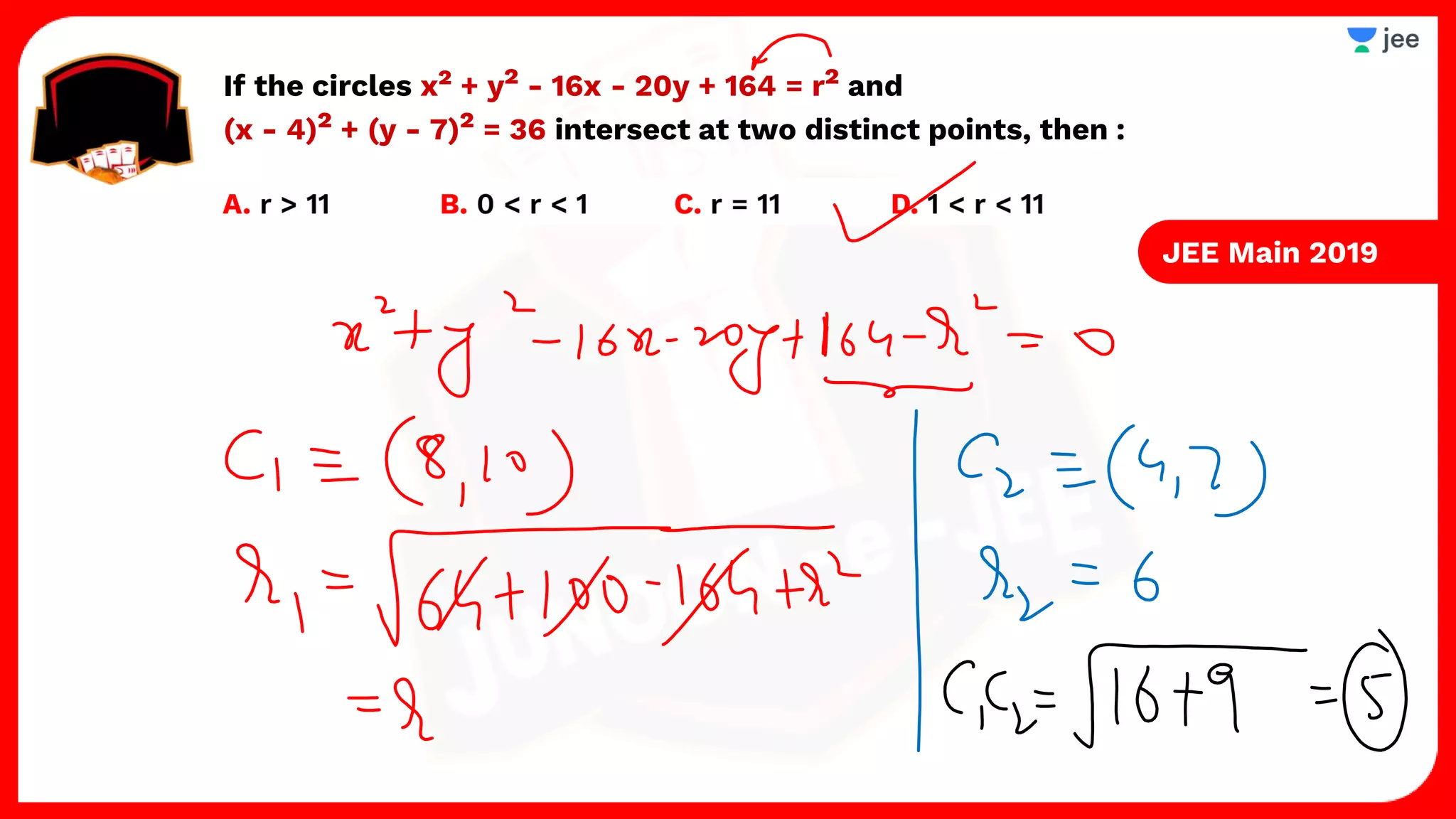
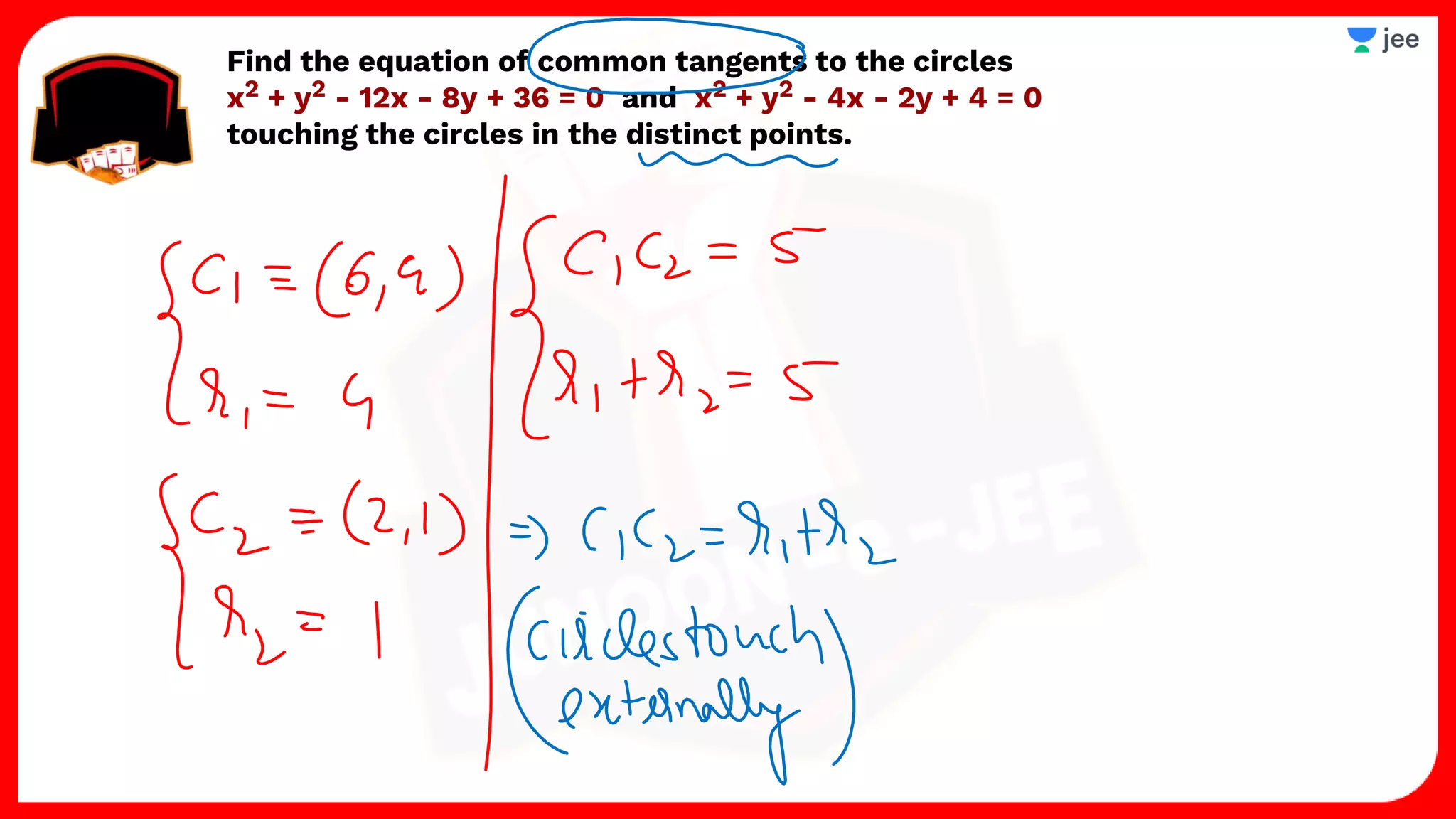
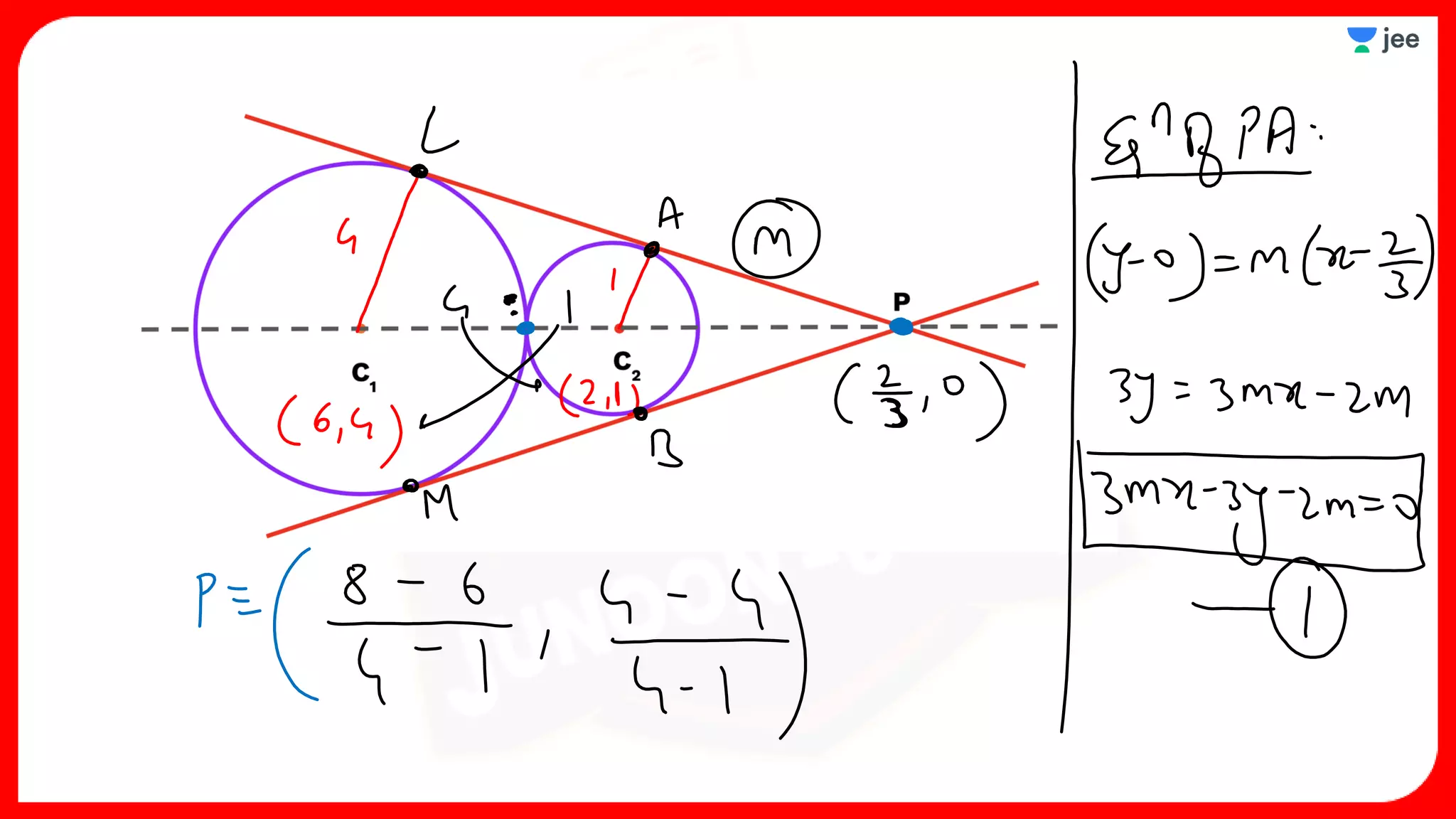
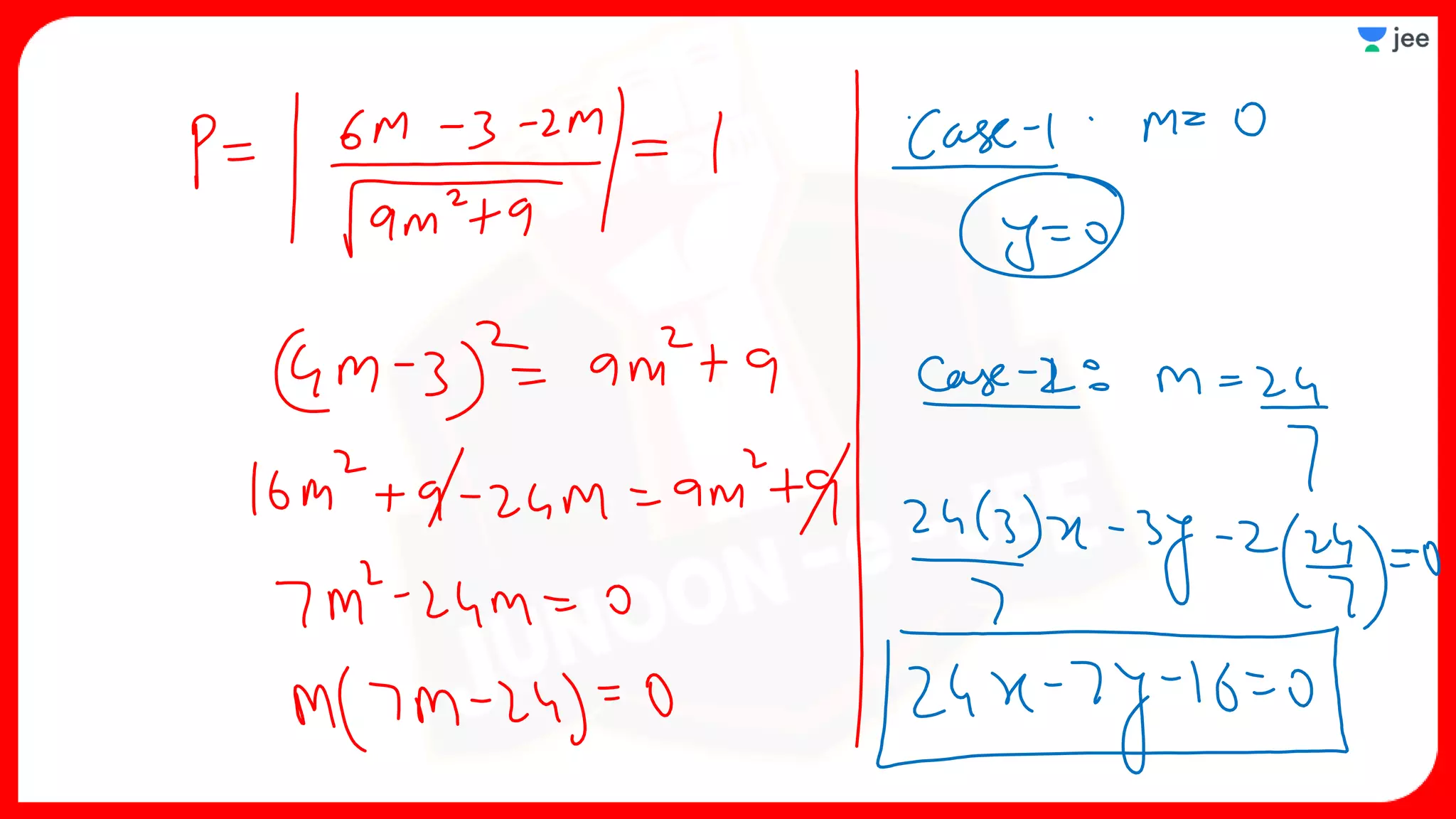
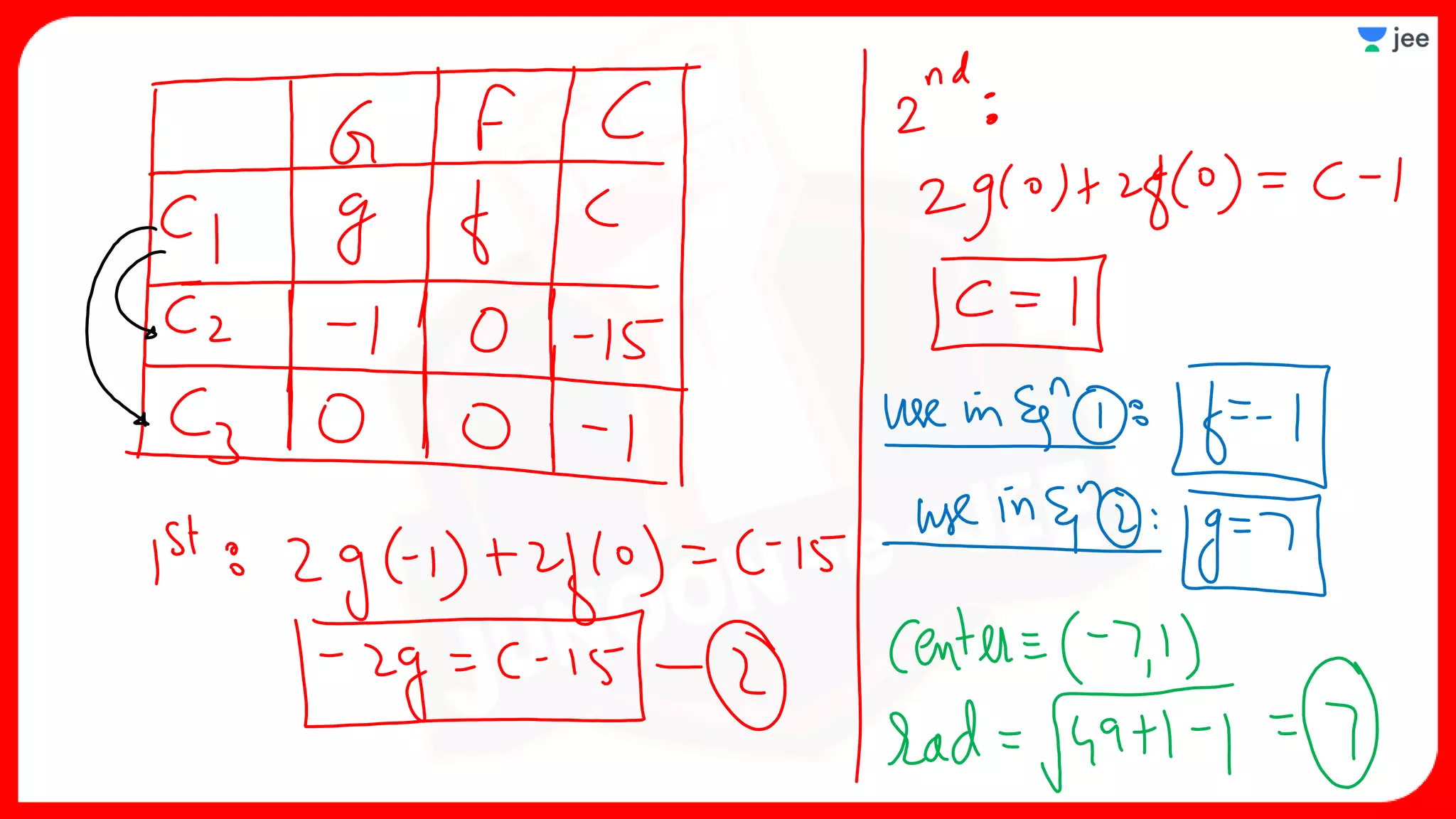
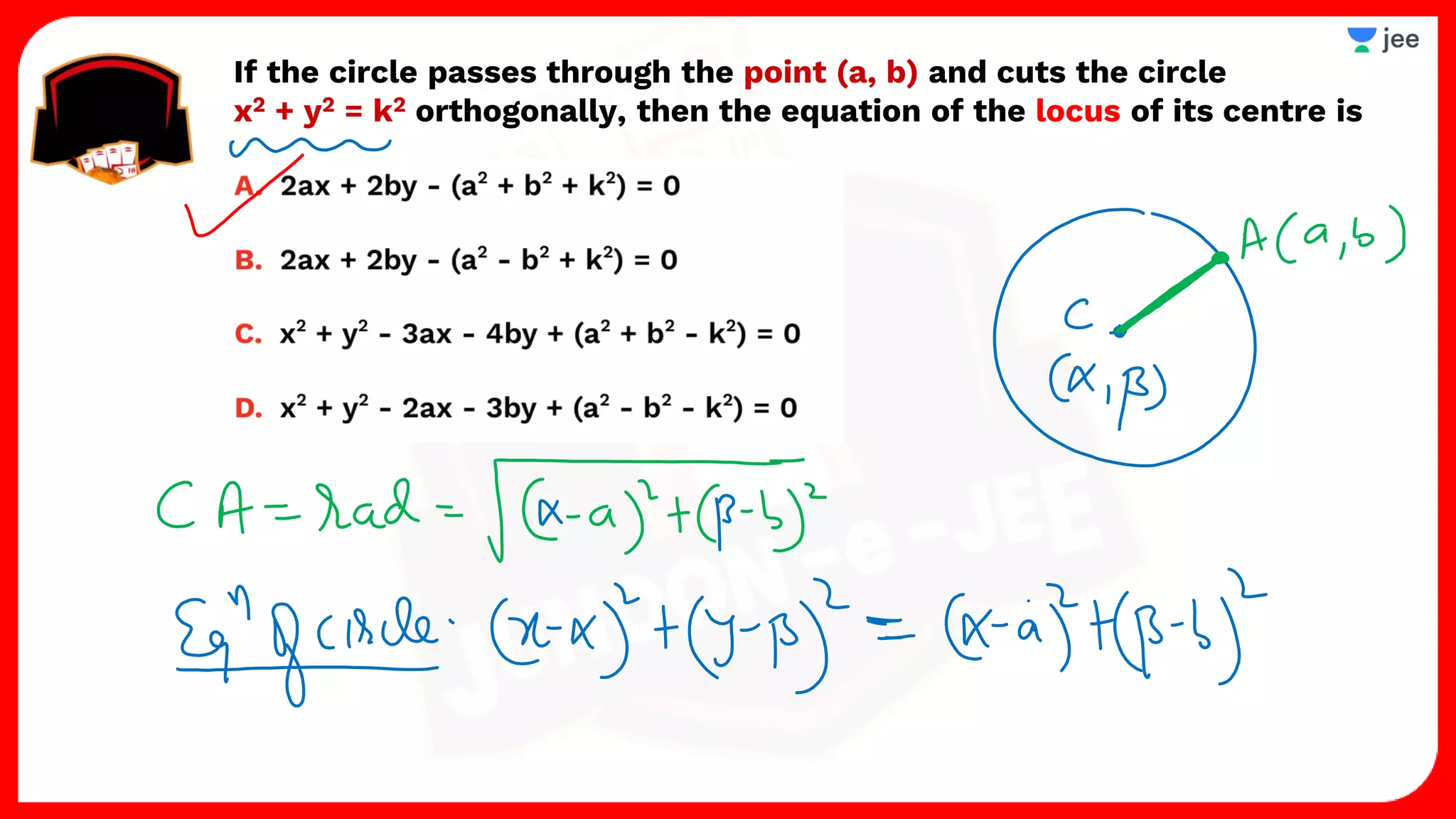
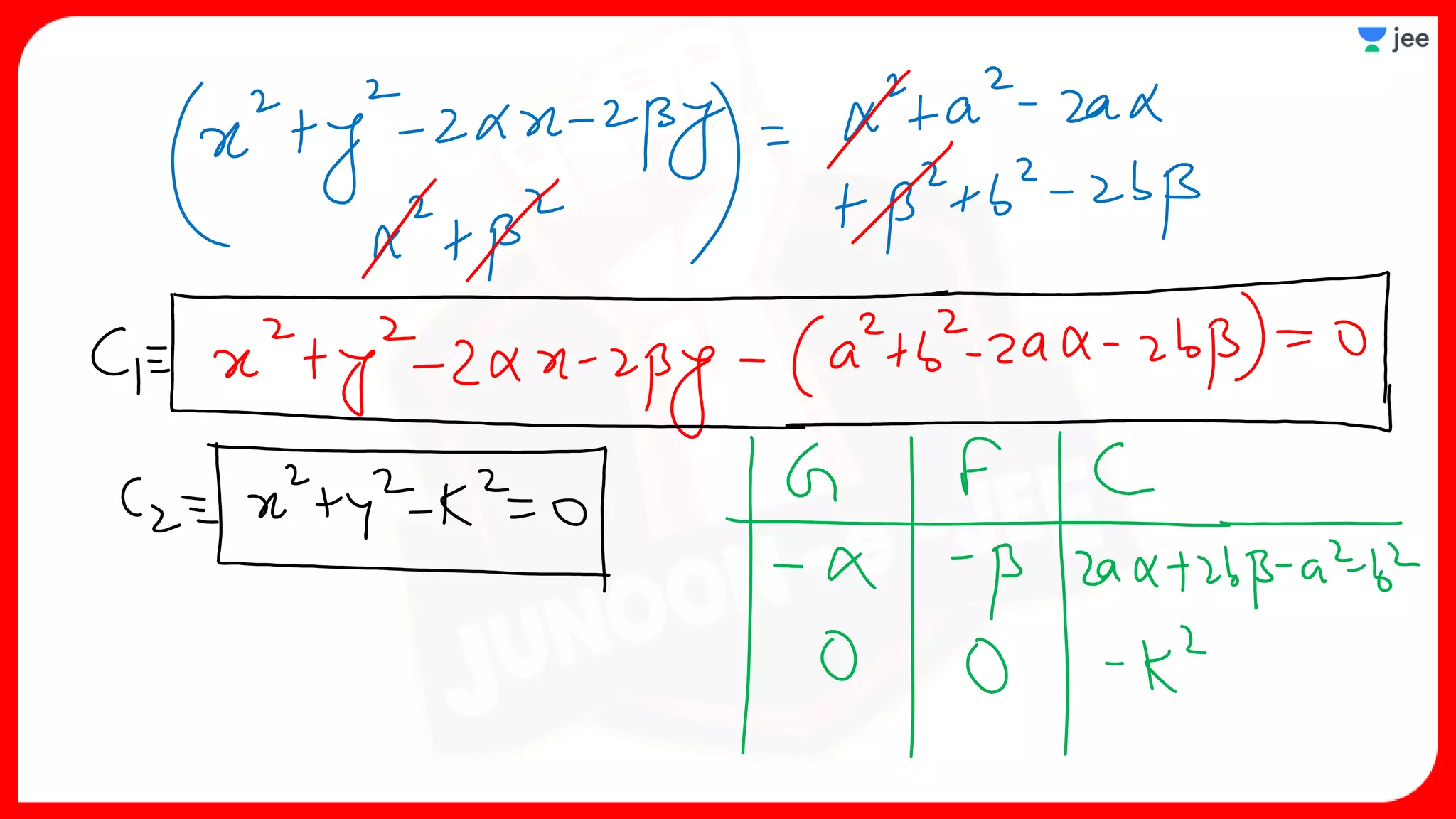
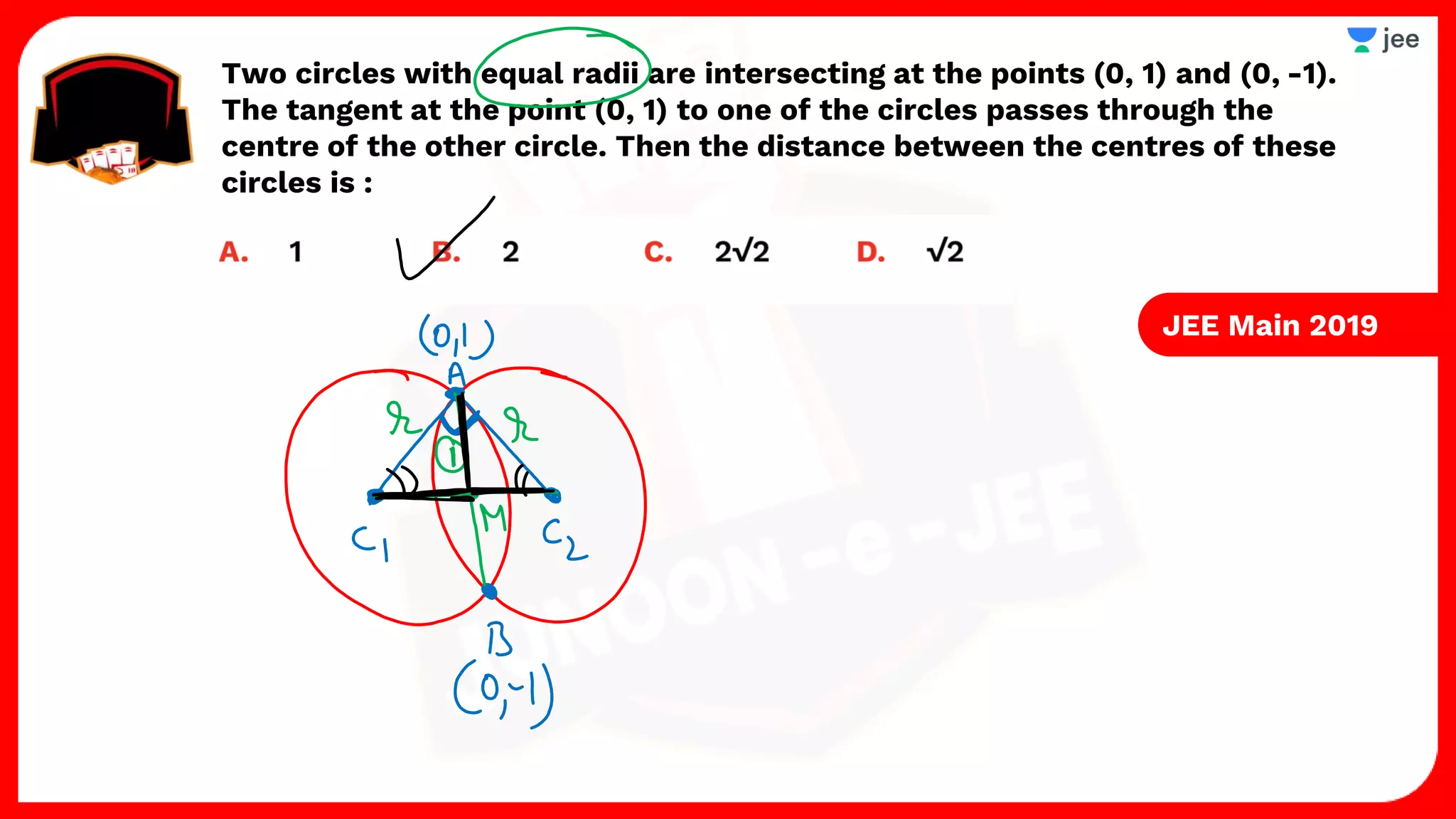
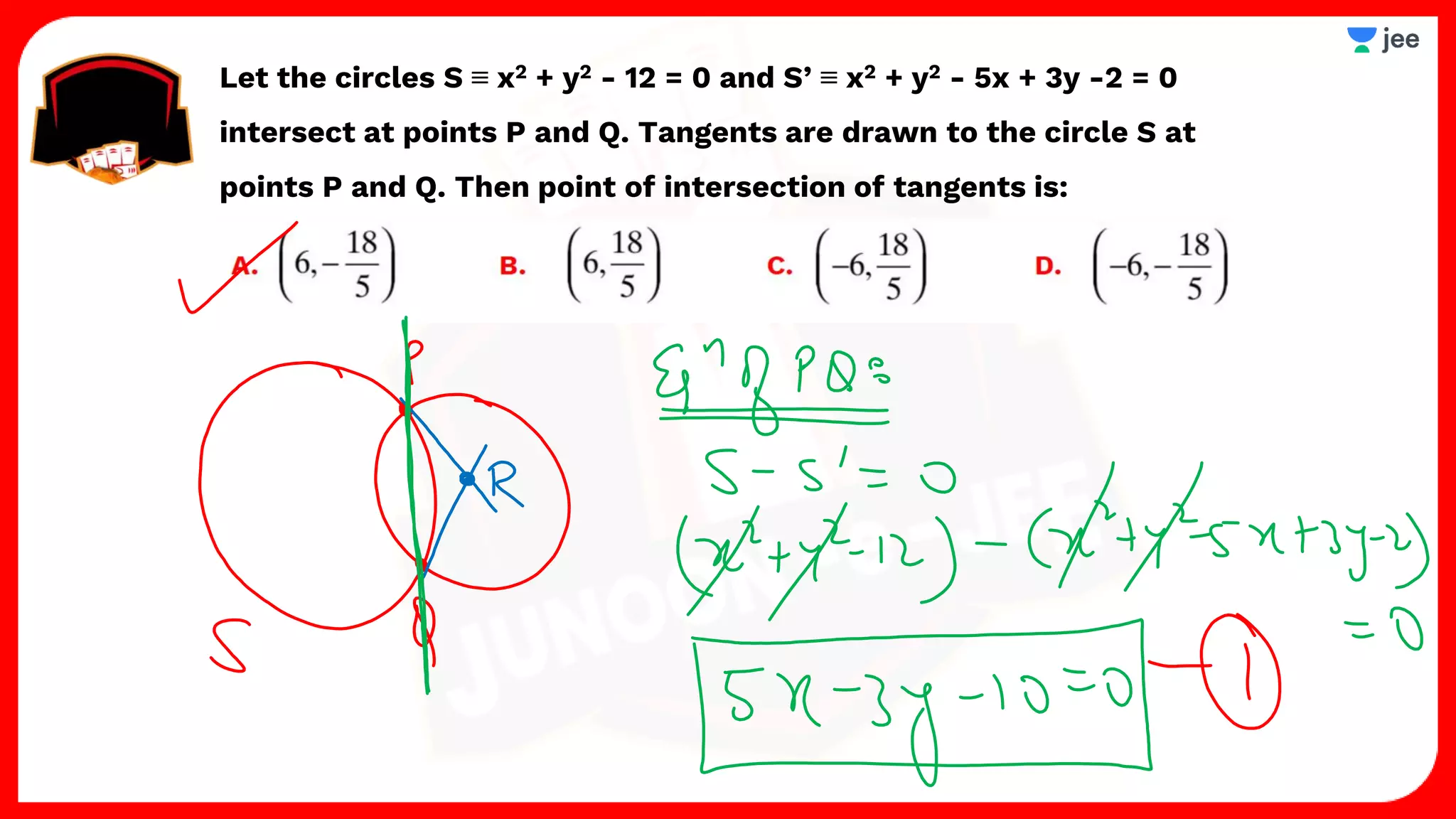
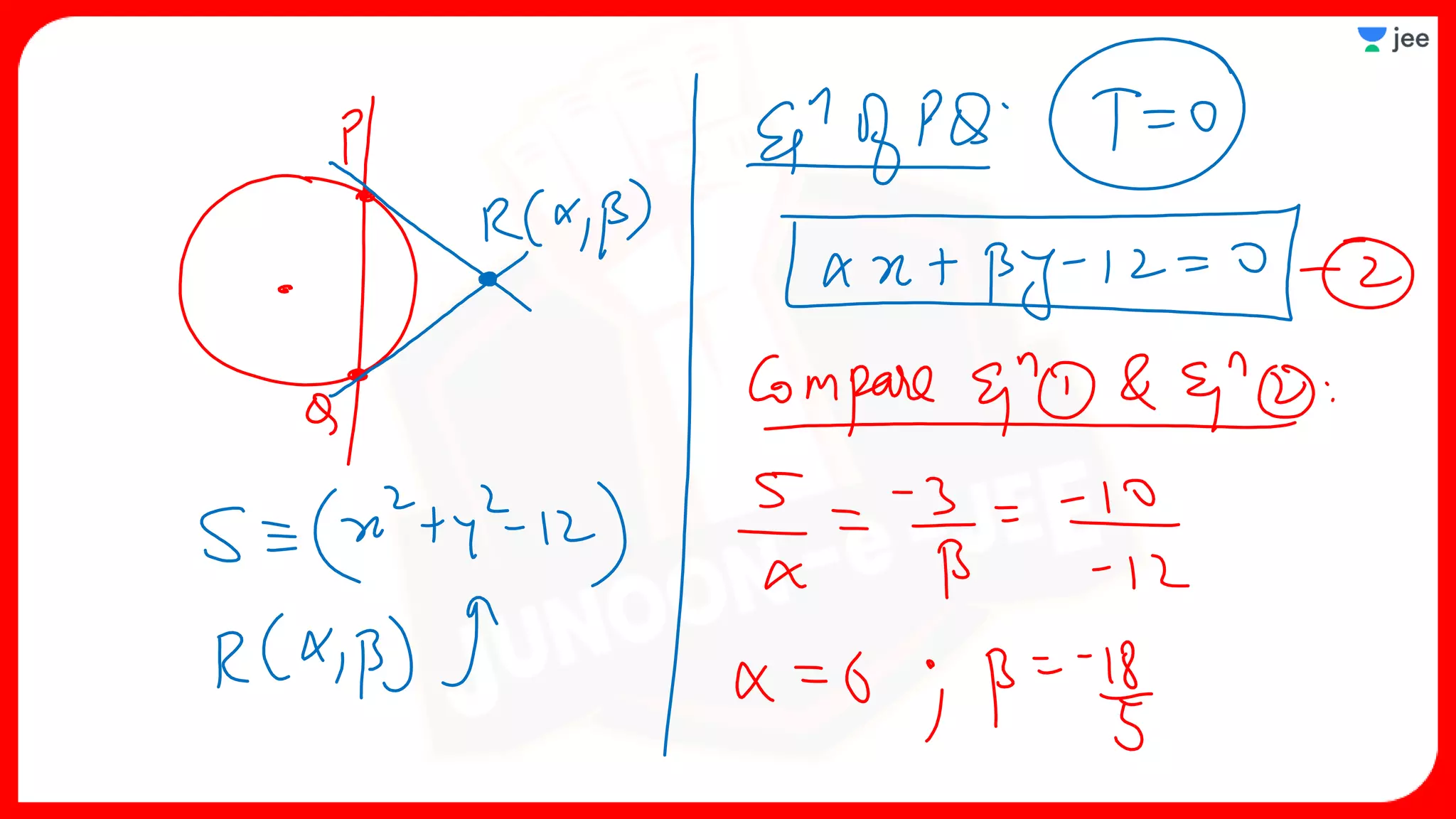
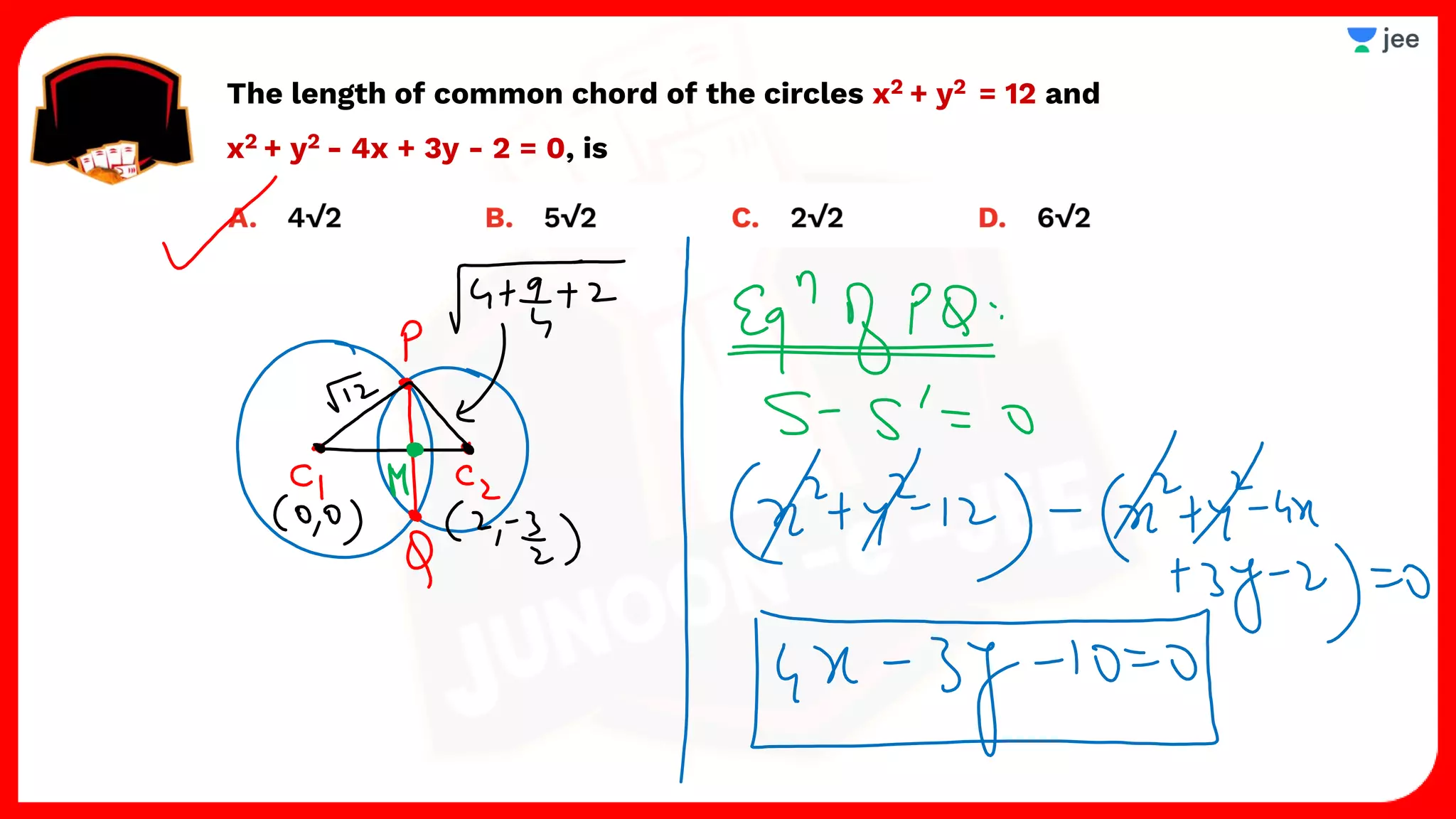
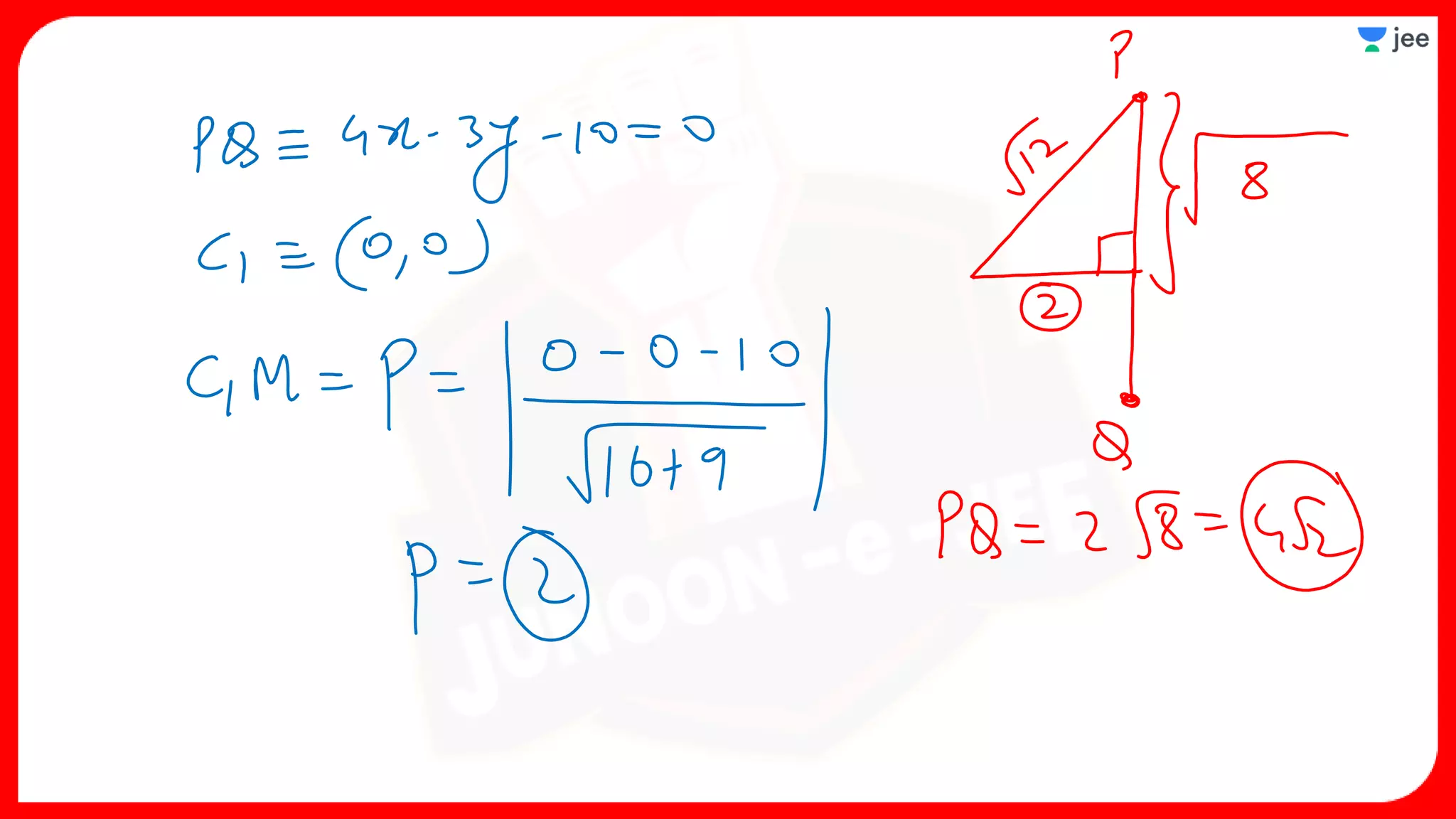
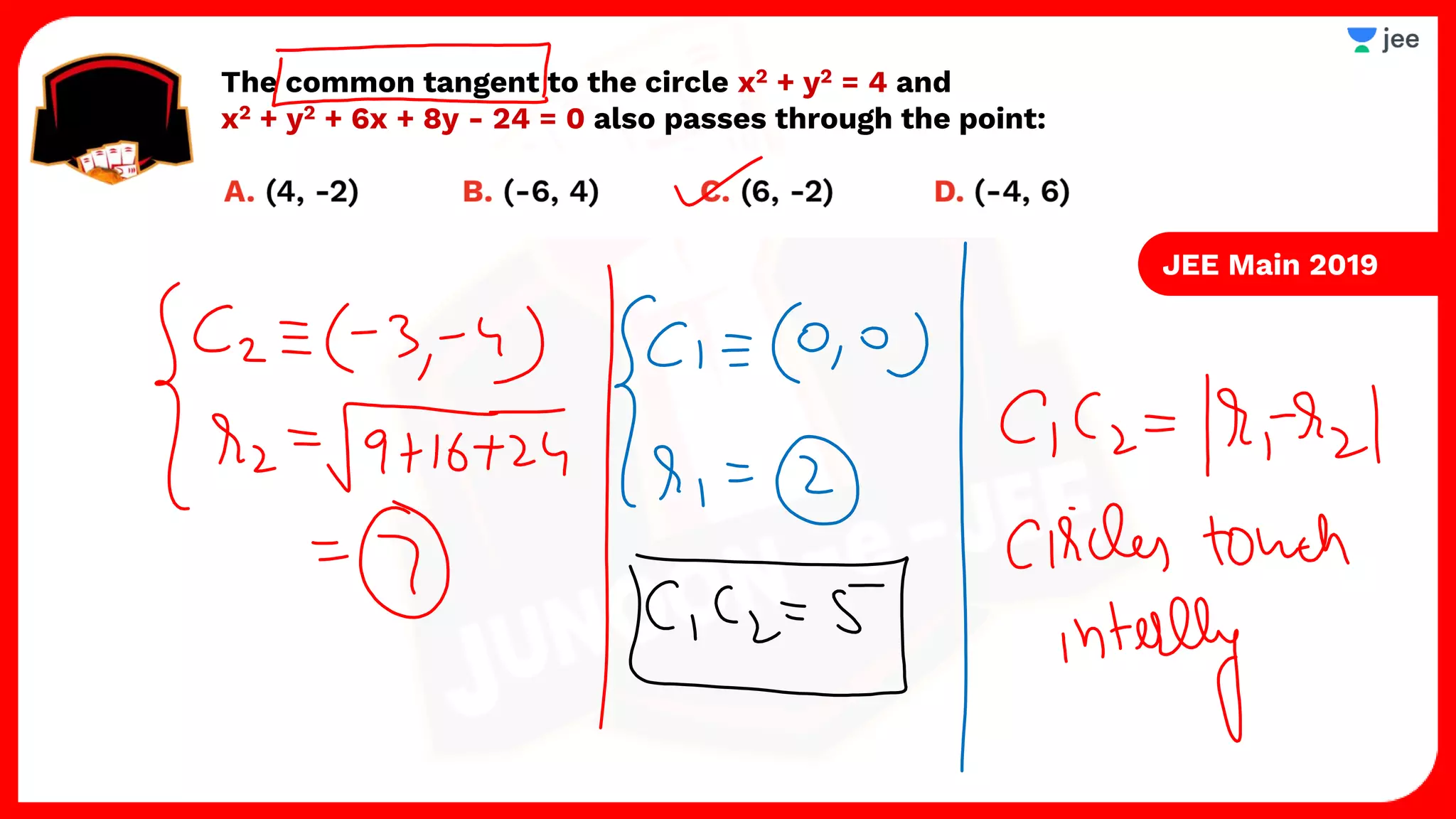
3. The document provides sample problems from engineering entrance exams involving the application of circle concepts.

















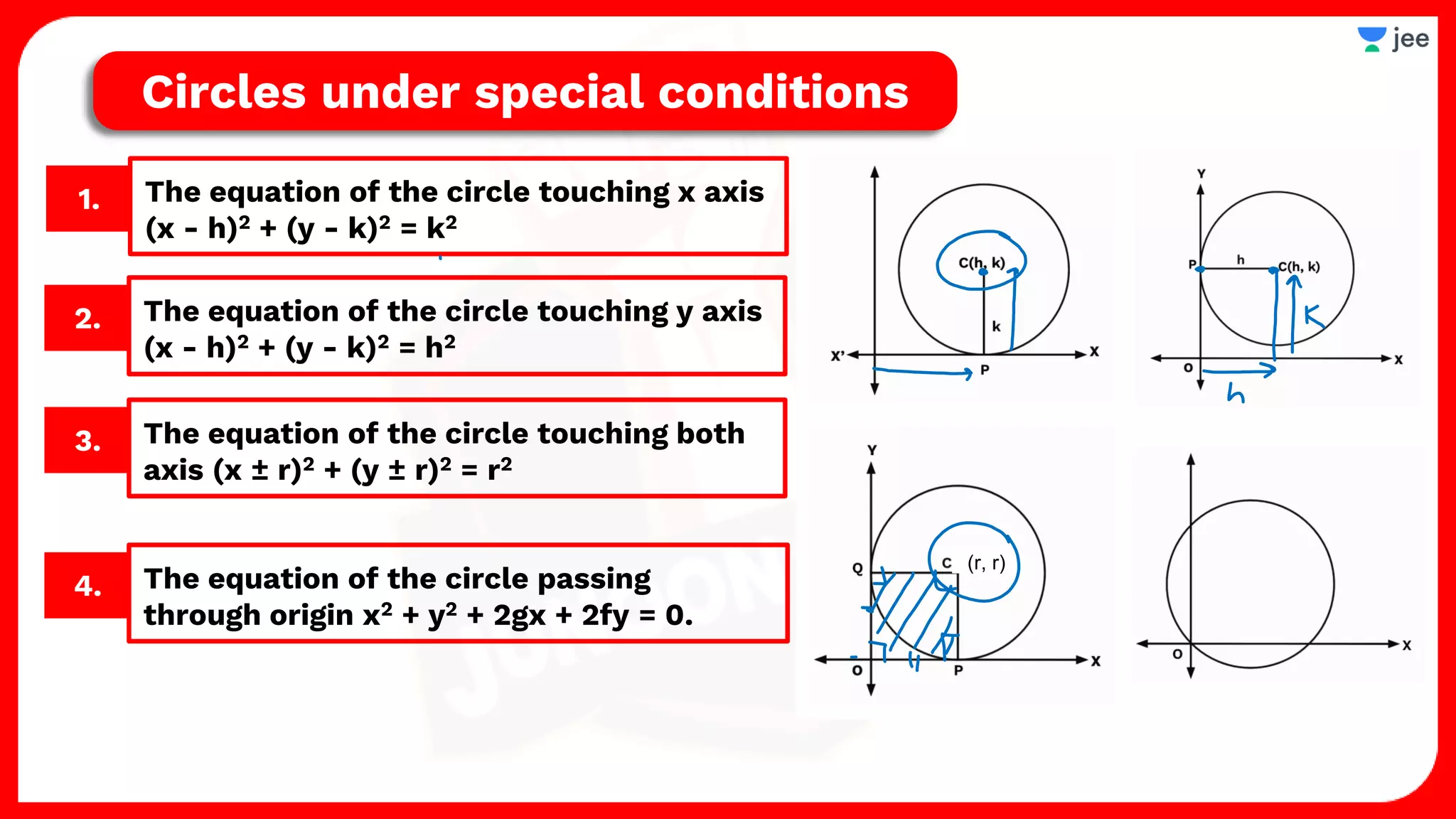
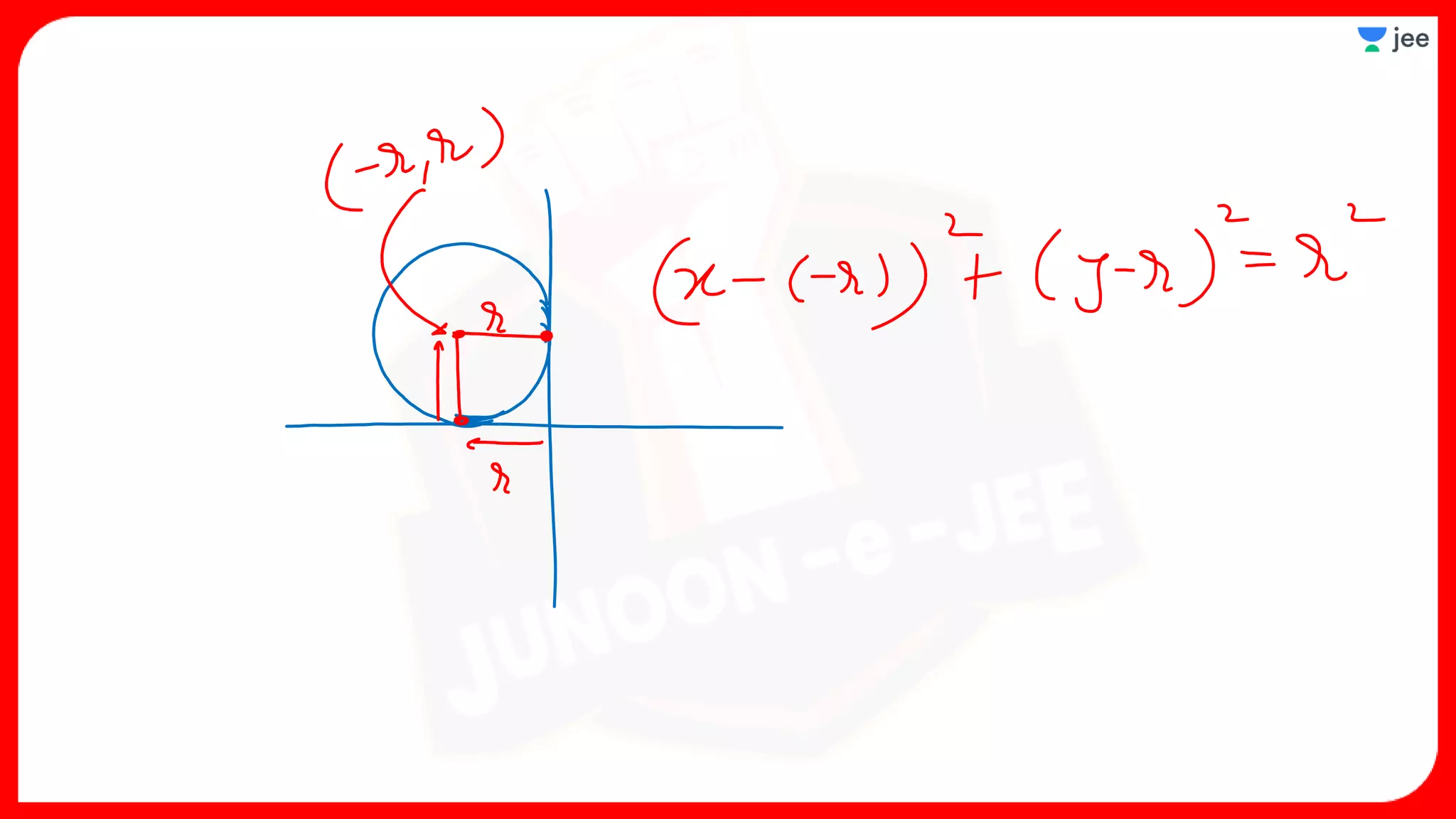
![Circle
[Under Special Conditions]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circles-220810070352-e6634afd/75/Circles-pdf-28-2048.jpg)




![Position of Point
[w.r.t. a Circle]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circles-220810070352-e6634afd/75/Circles-pdf-44-2048.jpg)
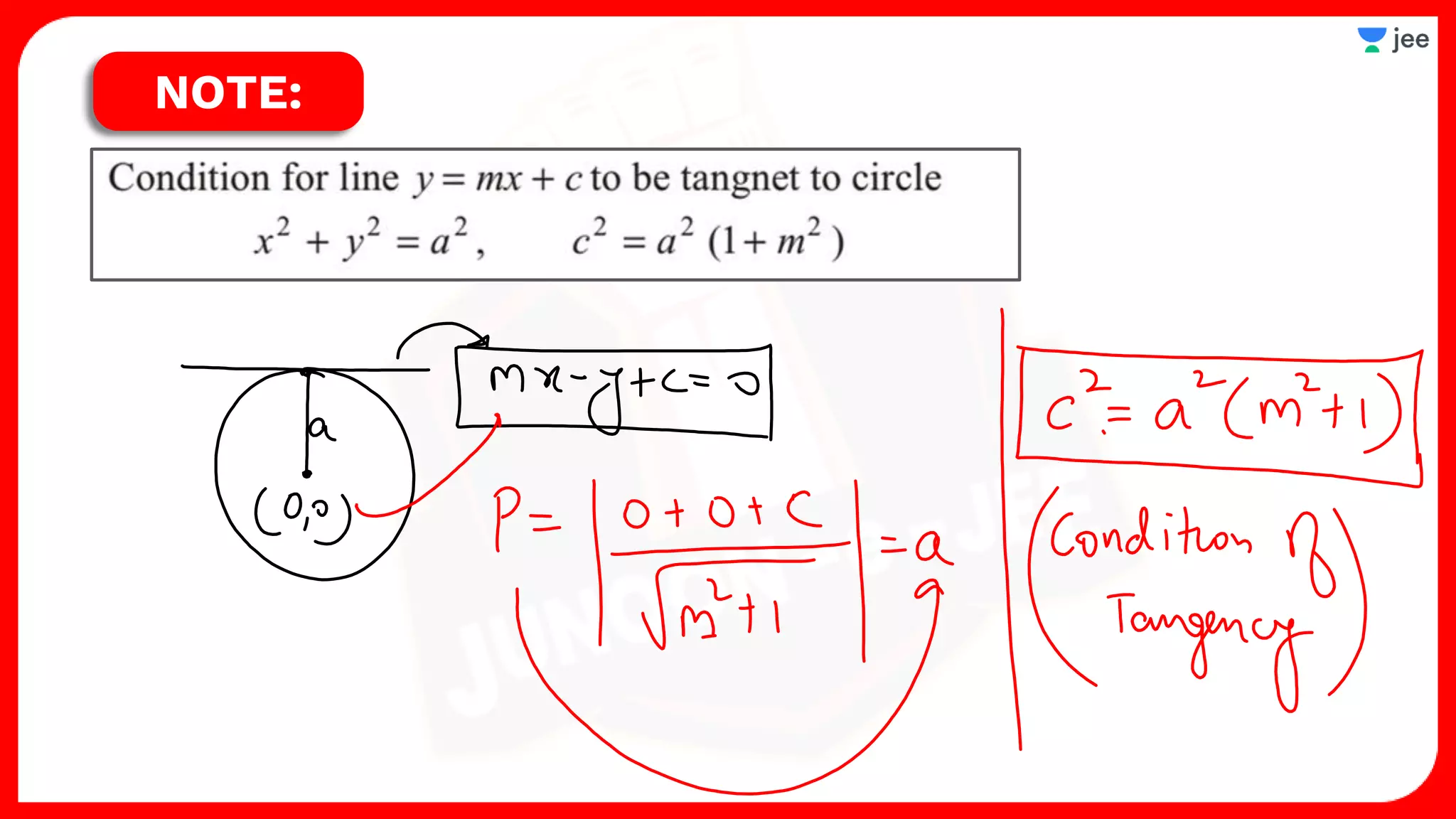
![Position of Line
[w.r.t. a Circle]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circles-220810070352-e6634afd/75/Circles-pdf-48-2048.jpg)

















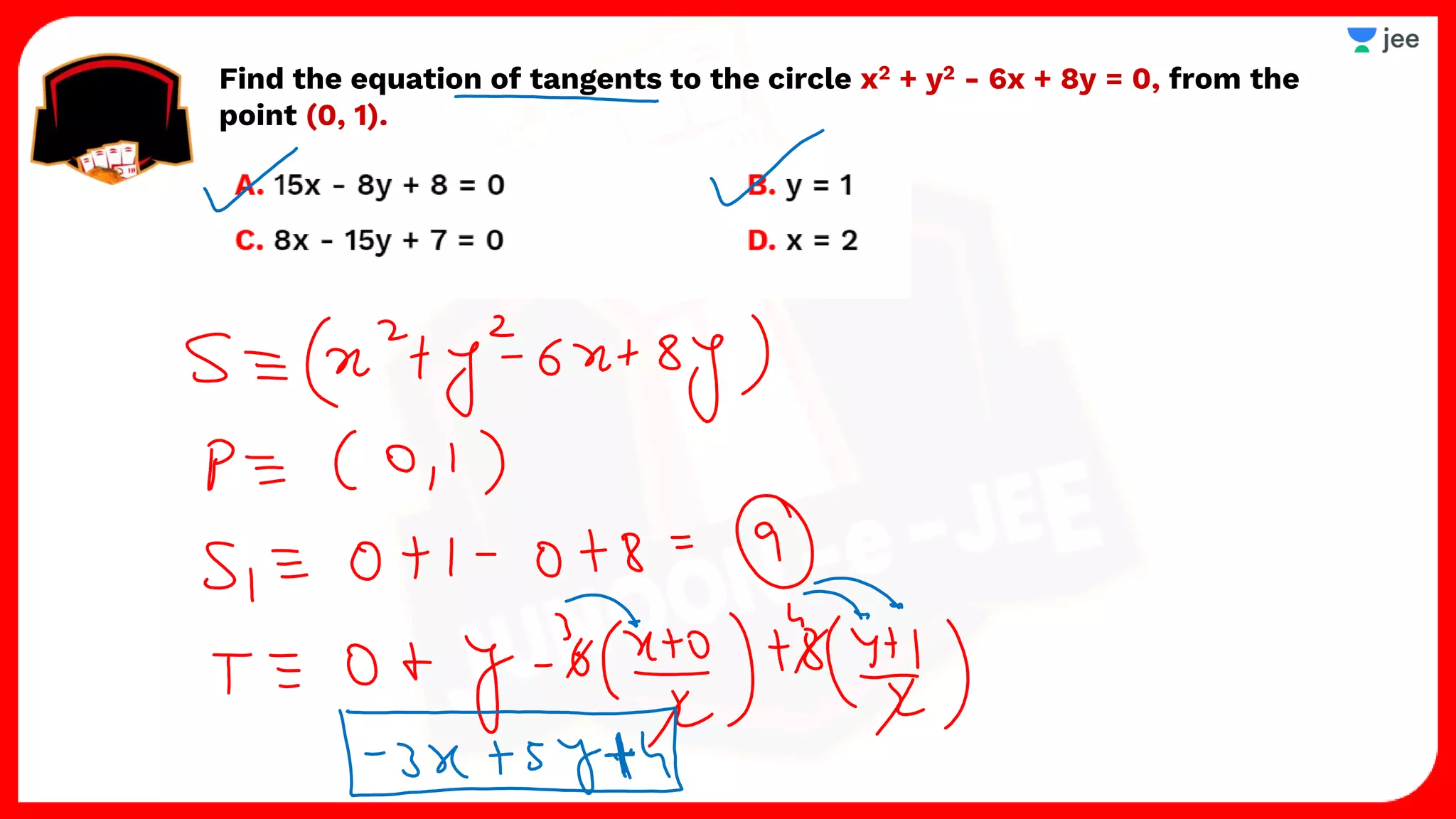






















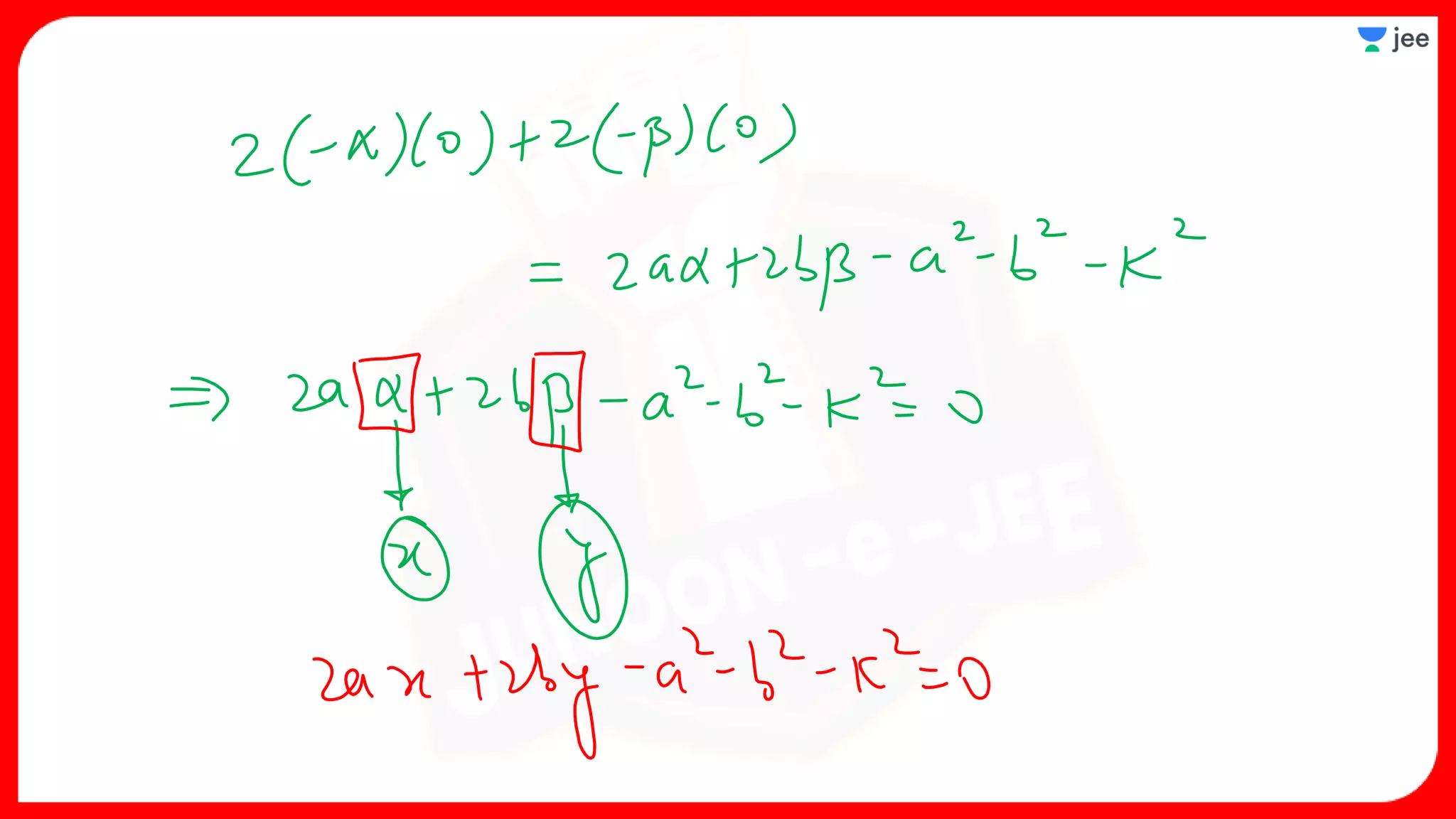







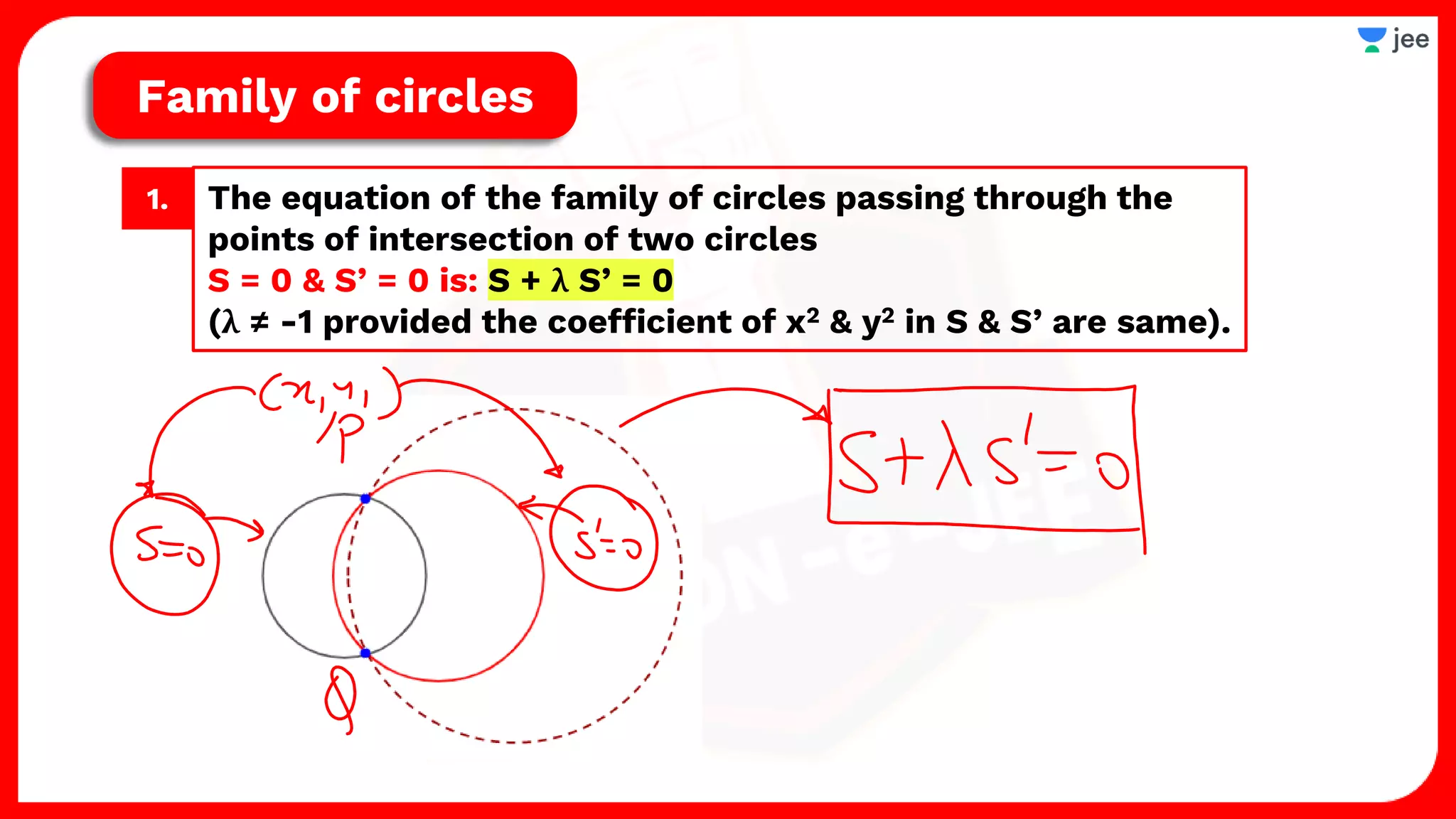
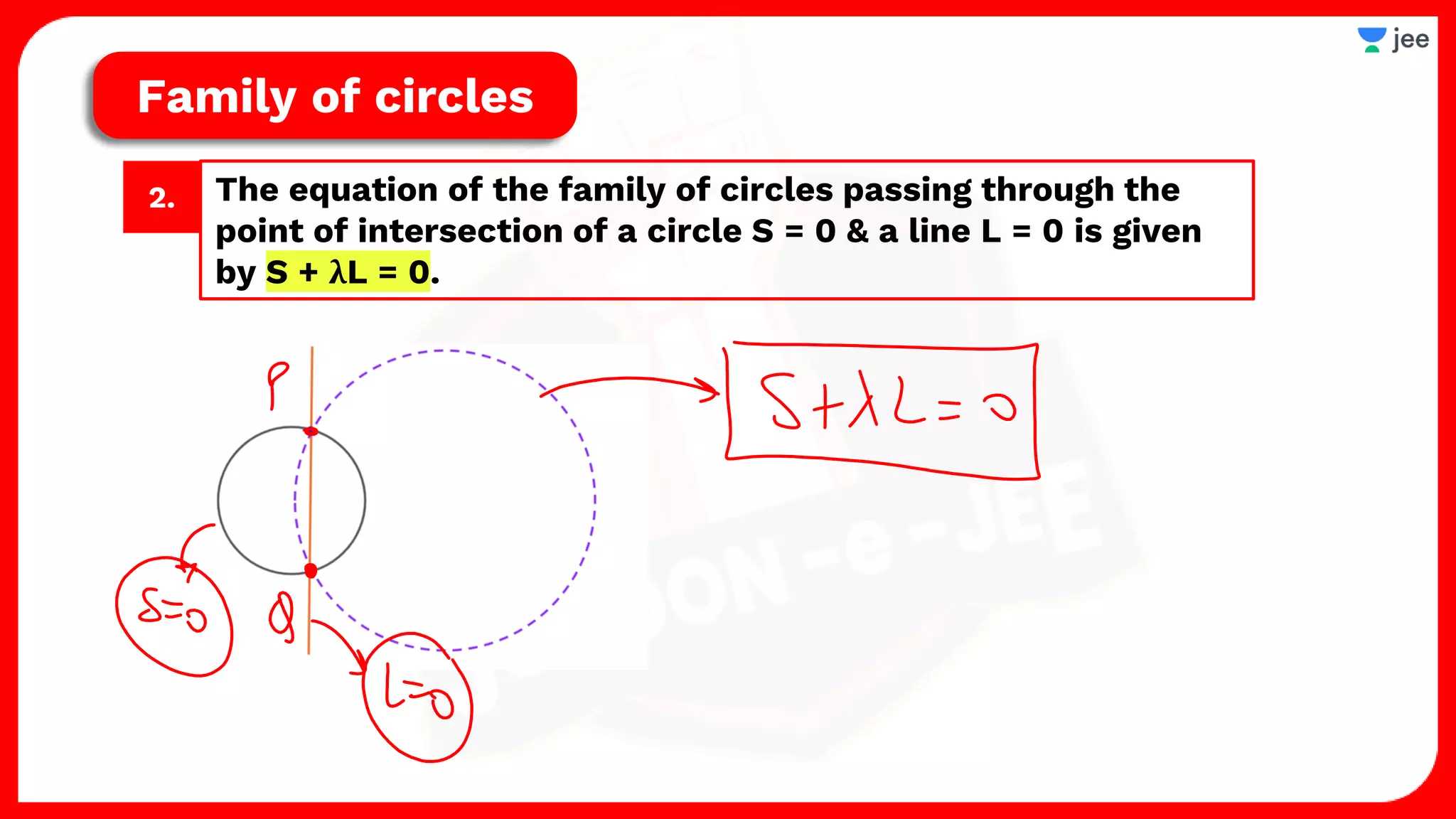
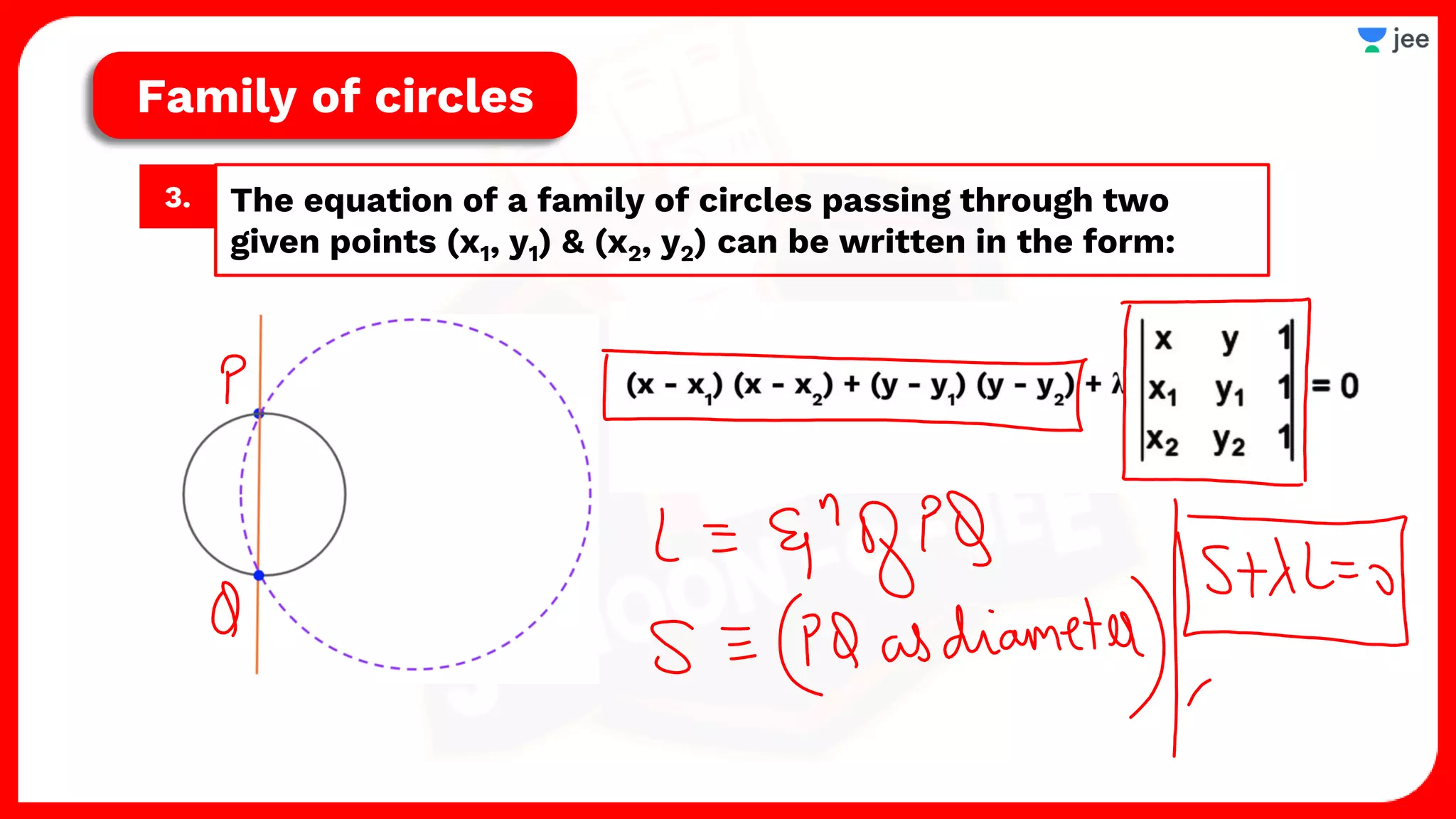
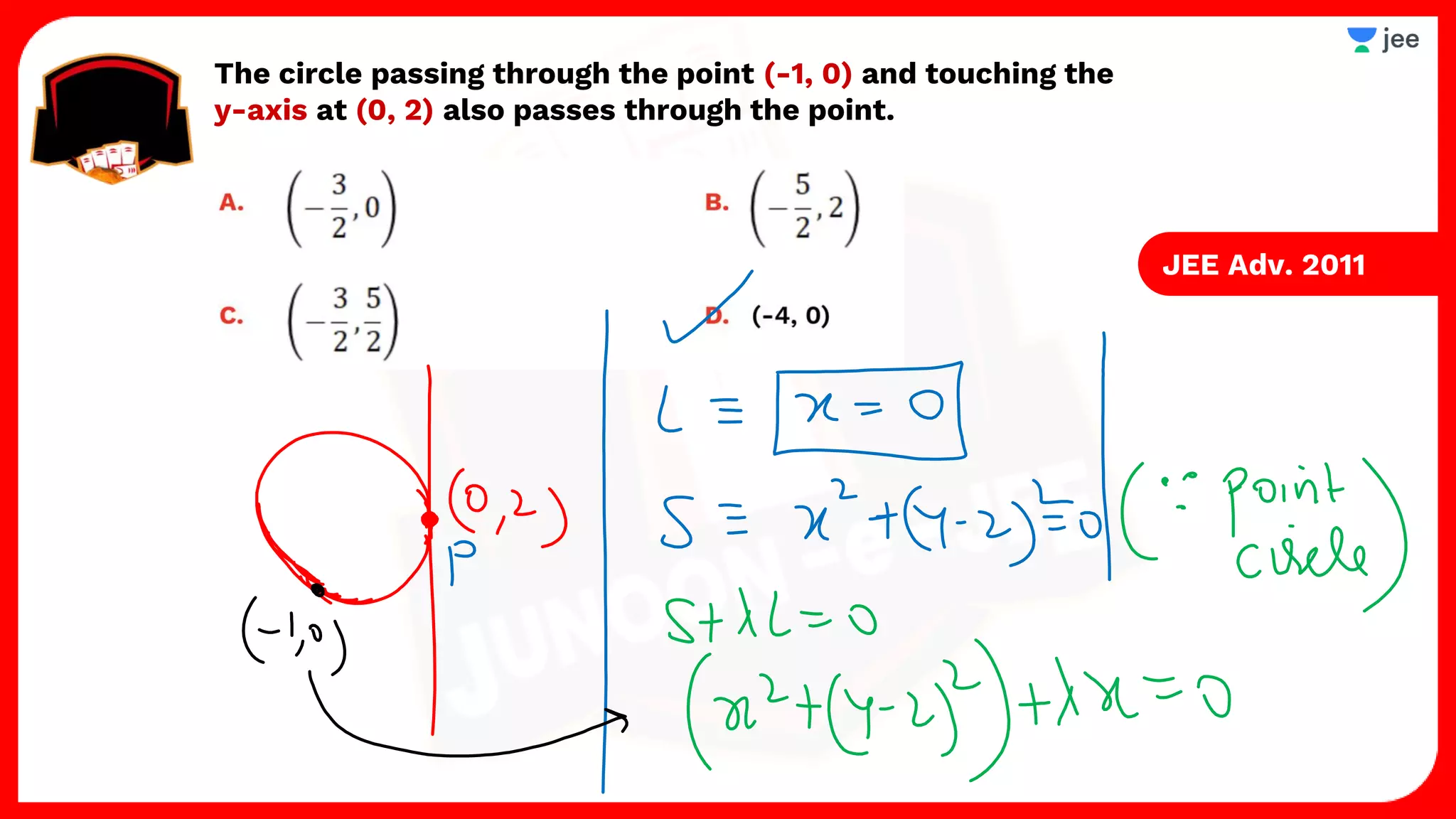
![The equation of a family of circles touching a fixed line
y - y1 = m(x - x1) at the fixed point (x1, y1) is
(x - x1)2 + (y - y1)2 + λ [(y - y1)- m(x - x1)] = 0,
4.
Family of circles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circles-220810070352-e6634afd/75/Circles-pdf-177-2048.jpg)