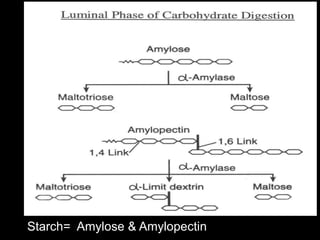
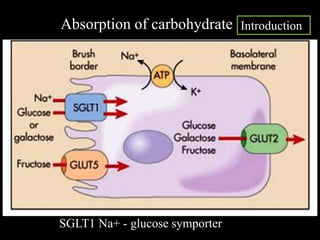
1. Carbohydrates are digested into monosaccharides like glucose in the small intestine through the actions of digestive enzymes.
2. Monosaccharides are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to tissues where they undergo further metabolism. Glucose is the primary fuel for tissues like the brain.
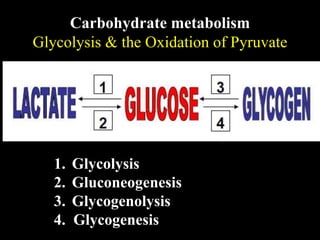
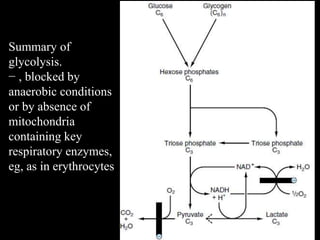
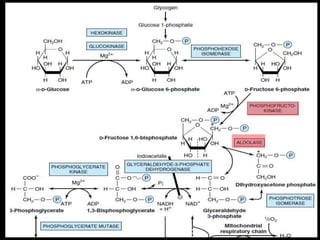
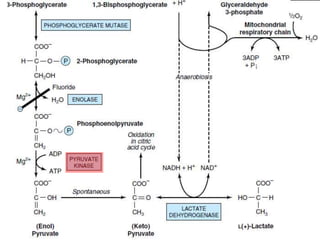
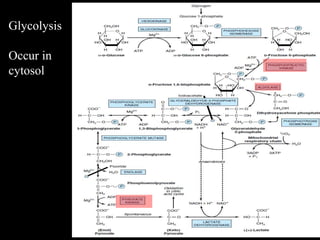
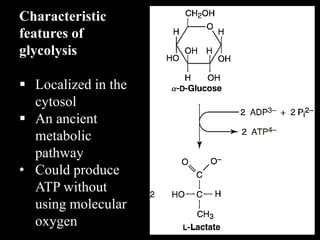
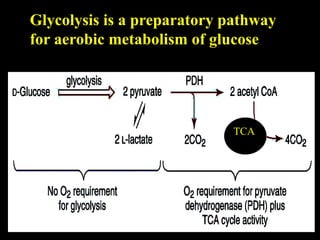
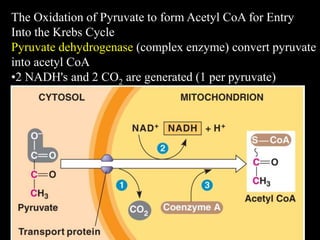
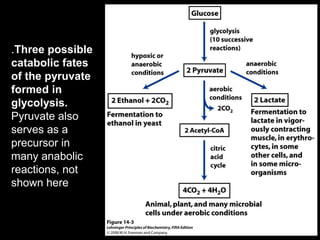
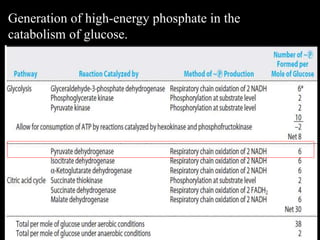
3. Glycolysis is the first step of glucose metabolism, occurring in the cytosol of cells. It breaks down glucose into pyruvate while generating a small amount of ATP.




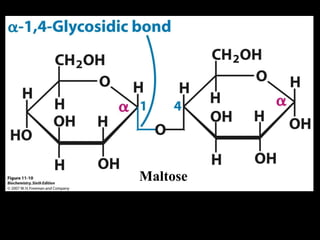
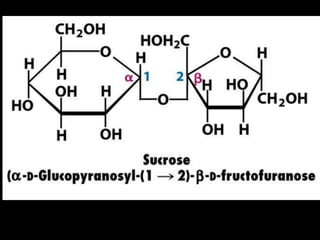
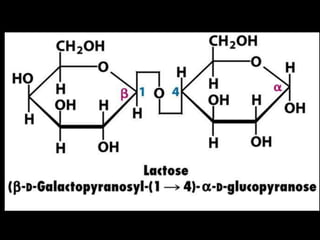
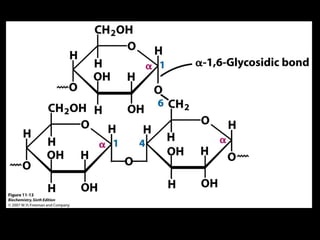




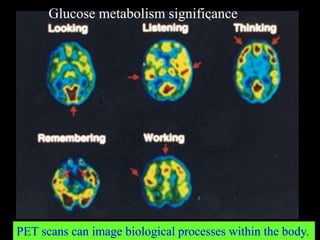

![Glucose metabolism significance
Diabetes
• related to blood glucose concentration
• altered ability to regulate glucose metabolism
• normally: when [glucose] high, insulin is released
• T1DM lack the ability to secrete insulin
•T2DM insulin resistance and decrease to secrete
insulin
Cancer
• glucose uptake/glycolysis ~ 10x faster
in cancer cells
• some glycolytic enzymes are
overproduced
Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cholec1-230102192536-11c07ef1/85/CHO-lec1-ppt-20-320.jpg)