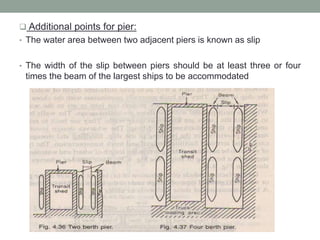
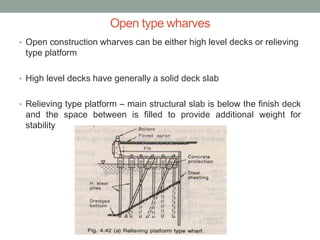
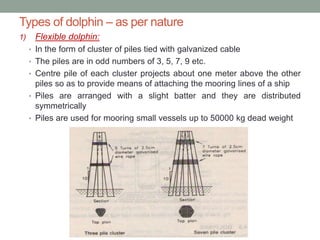
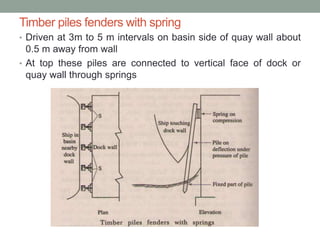
Piers and wharves are key harbor facilities for ships. Piers are platforms built perpendicular to shore for ships to berth. They can be open or solid construction. Wharves are platforms parallel to shore where ships load/unload cargo. Wharves are generally built continuous with shore. Dolphins are clusters of piles used for ship mooring and transferring cargo between ships. Fenders on jetty faces cushion ship impacts and protect ships and structures. Harbor design considers ship sizes and cargo handling for efficient port operations.