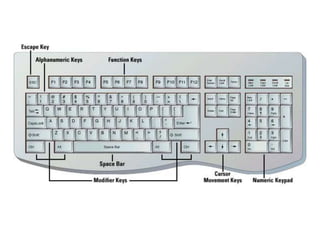
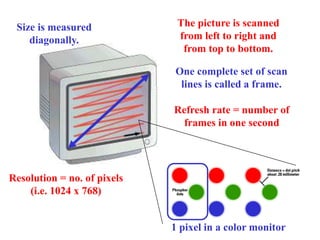
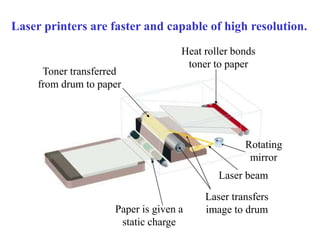
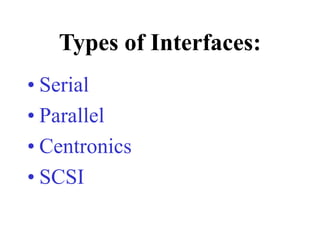
This chapter discusses computer input and output devices. It describes common input devices like keyboards, mice, and touch screens. It explains how monitors use pixels and refresh rates to display images. Mouse components and maintenance techniques are covered. The chapter also details inkjet, laser, and dot-matrix printers; factors that affect printer choice; and serial, parallel, and SCSI interfaces that allow devices to connect to computers. Learning objectives review key input/output devices, monitor display processes, mice, printer types and characteristics, and interface types.