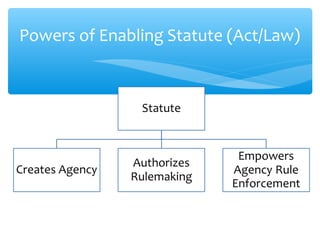
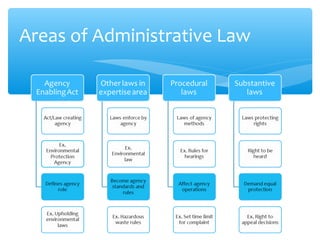
Administrative law governs administrative agencies and defines their powers and legal limits. Agencies are created by legislatures to administer laws in areas requiring expertise like environmental protection. Administrative authority comes from enabling acts that define an agency's role and delegate powers from legislatures. There are different types of administrative laws including substantive laws protecting rights and procedural laws defining legal processes. Agencies have powers granted by their enabling statutes like setting standards, making rules and regulations, and deciding cases. Agencies can be regulatory, social welfare, independent, or executive depending on their functions and organization.