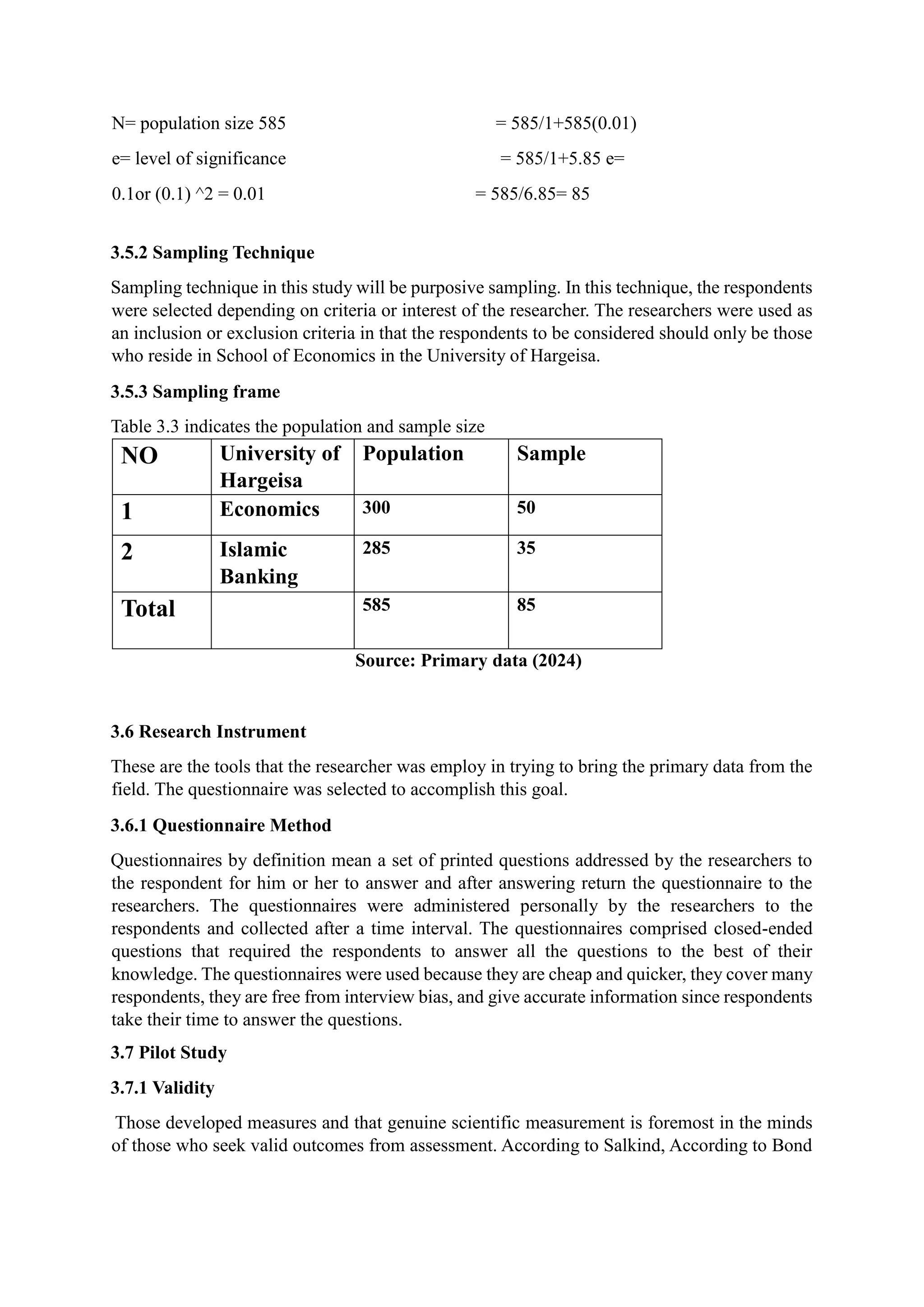
This chapter outlines the research methodology for a study at the University of Hargeisa, focusing on Islamic commercial banks among undergraduate students. It details the descriptive correlational research design, target population of 585 respondents, and the sample of 85 using purposive sampling. Data was collected through a self-administered questionnaire, with analysis conducted using quantitative methods and SPSS software.