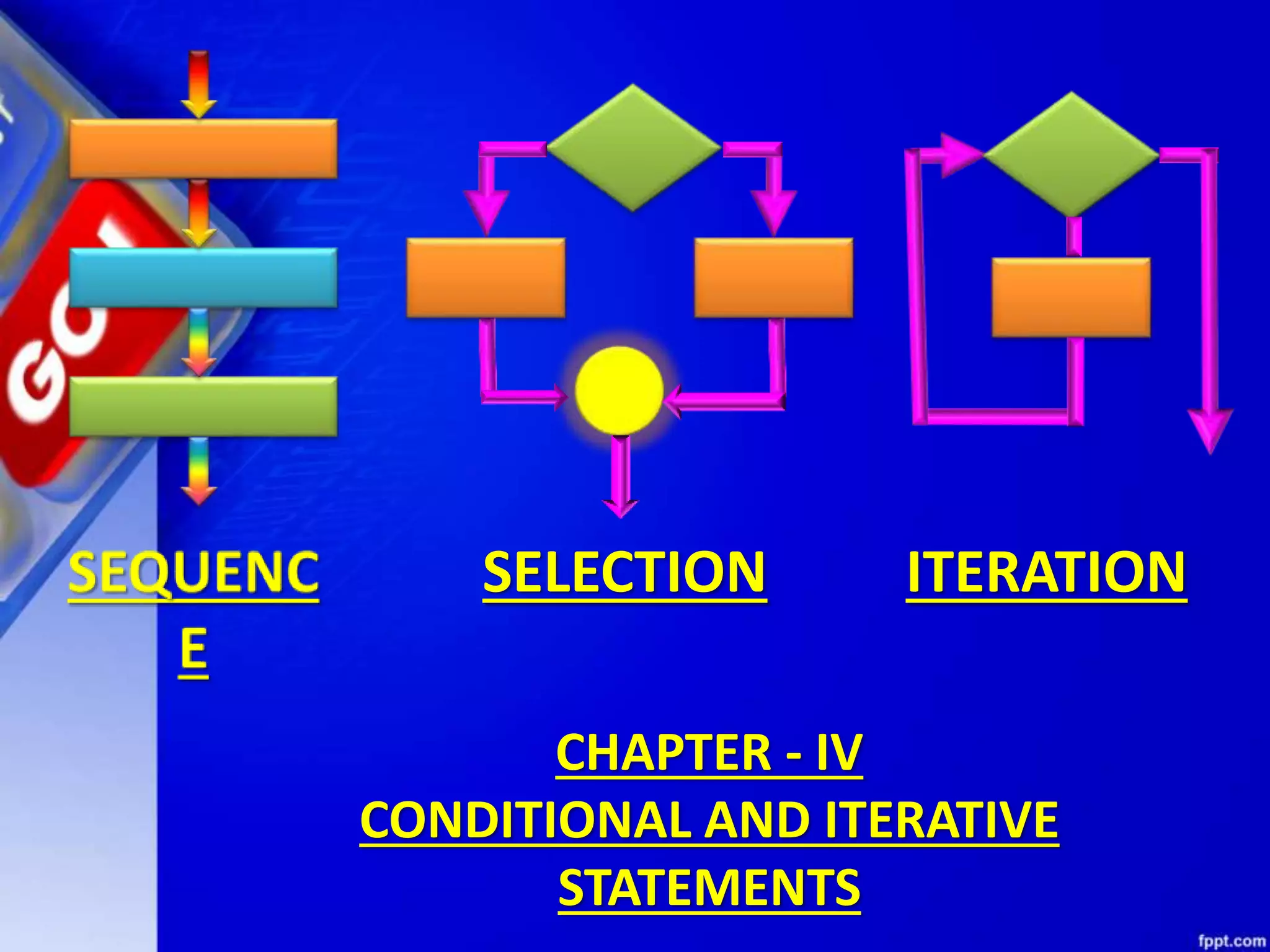
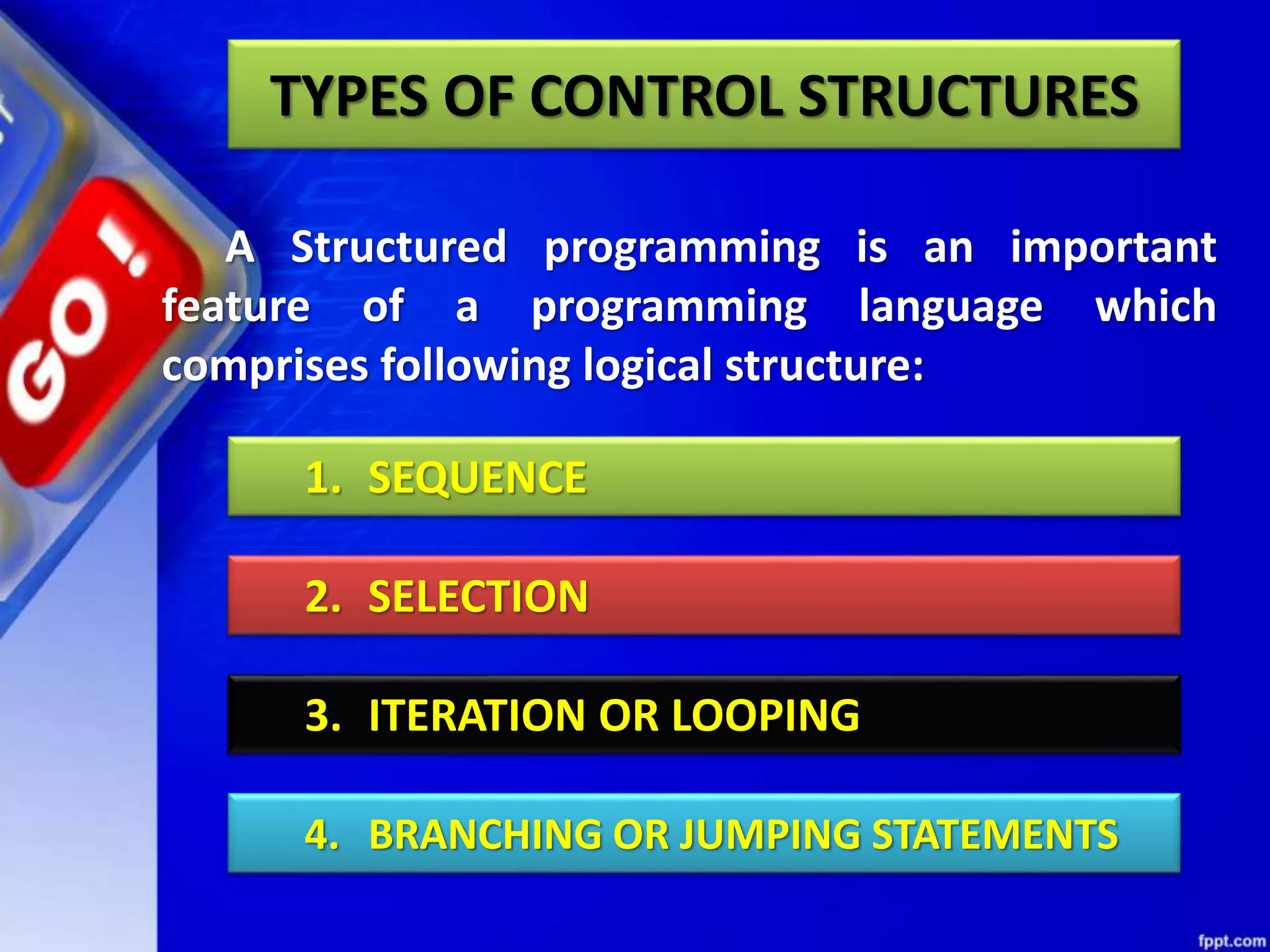
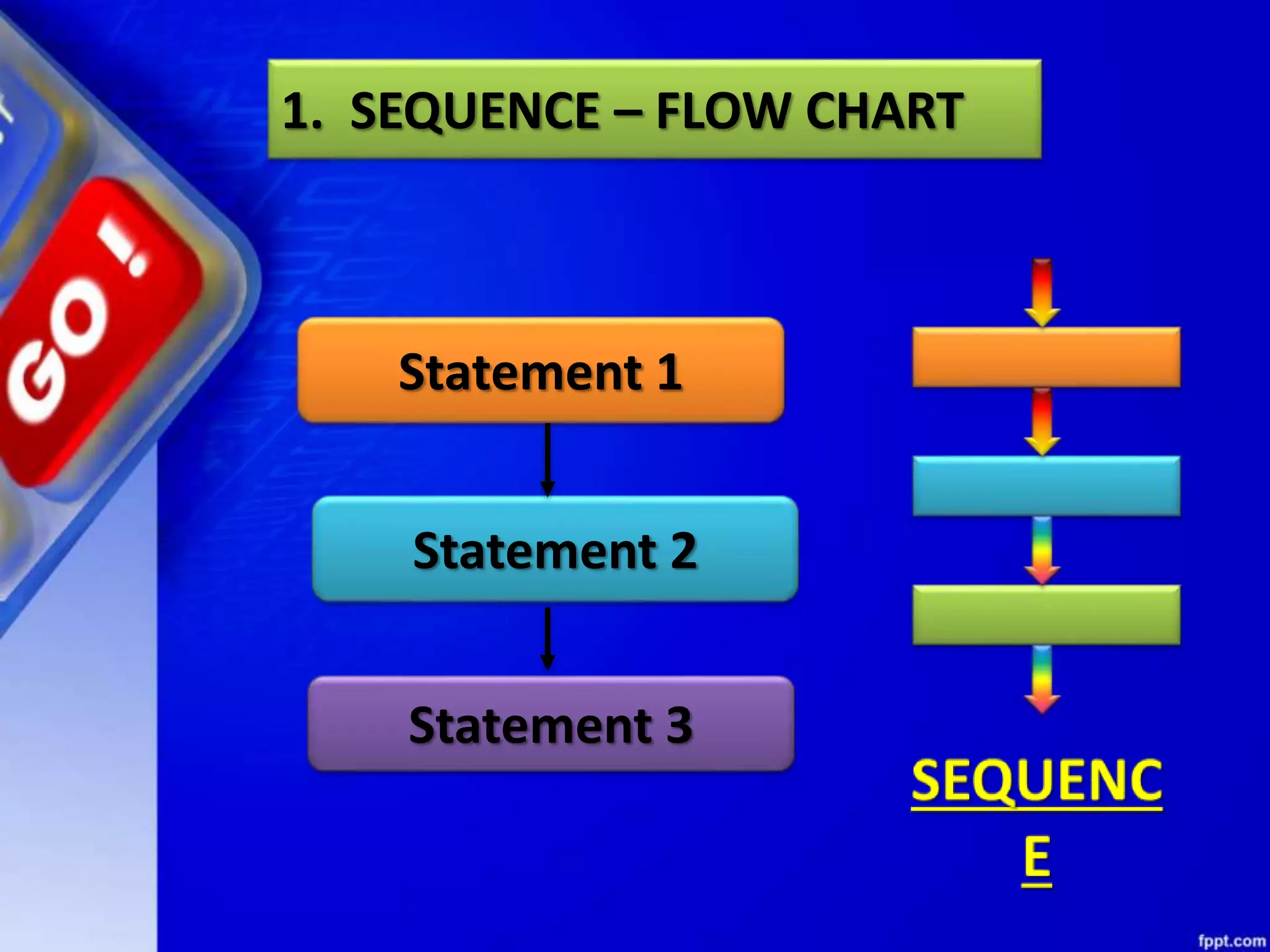
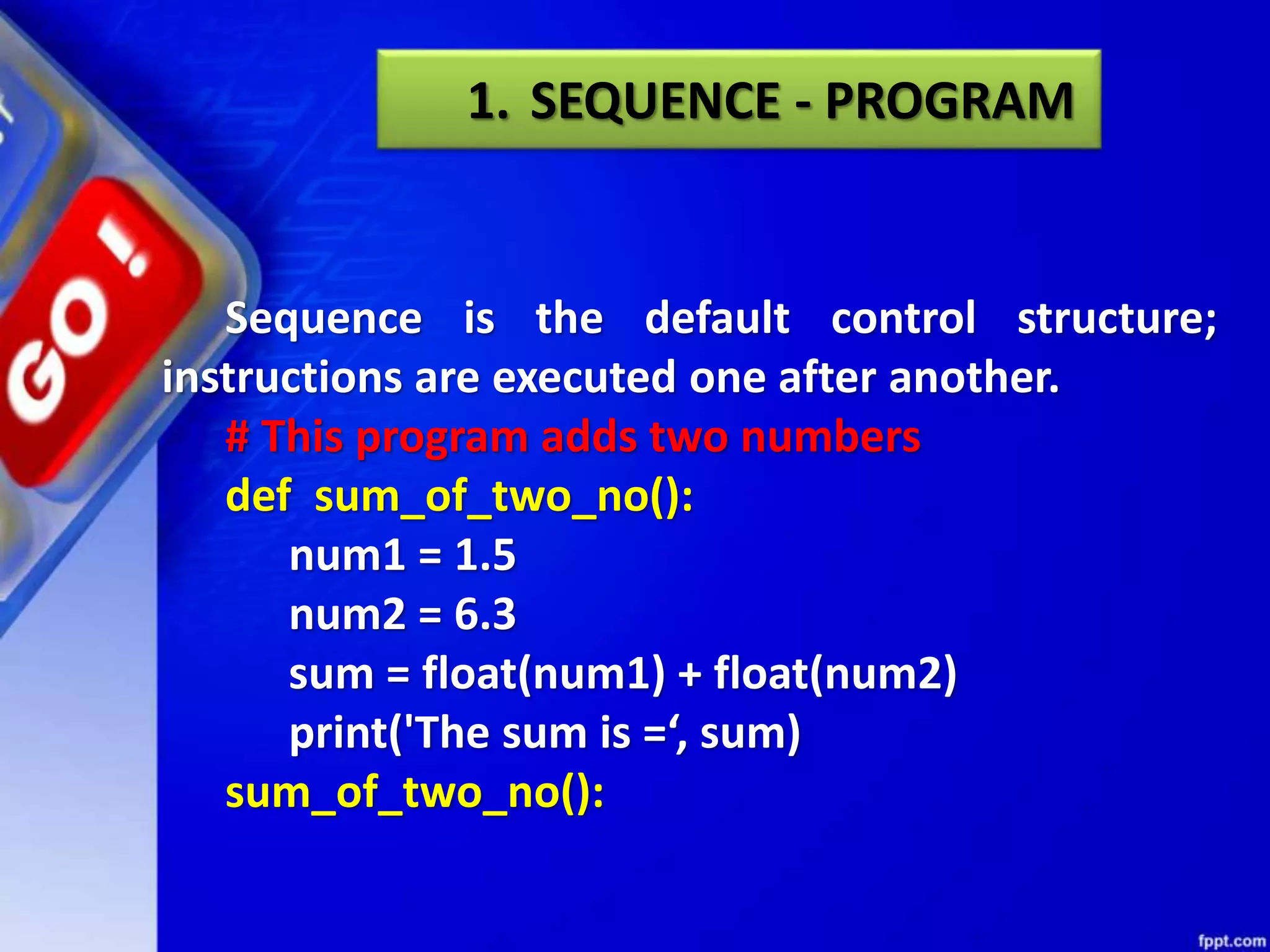
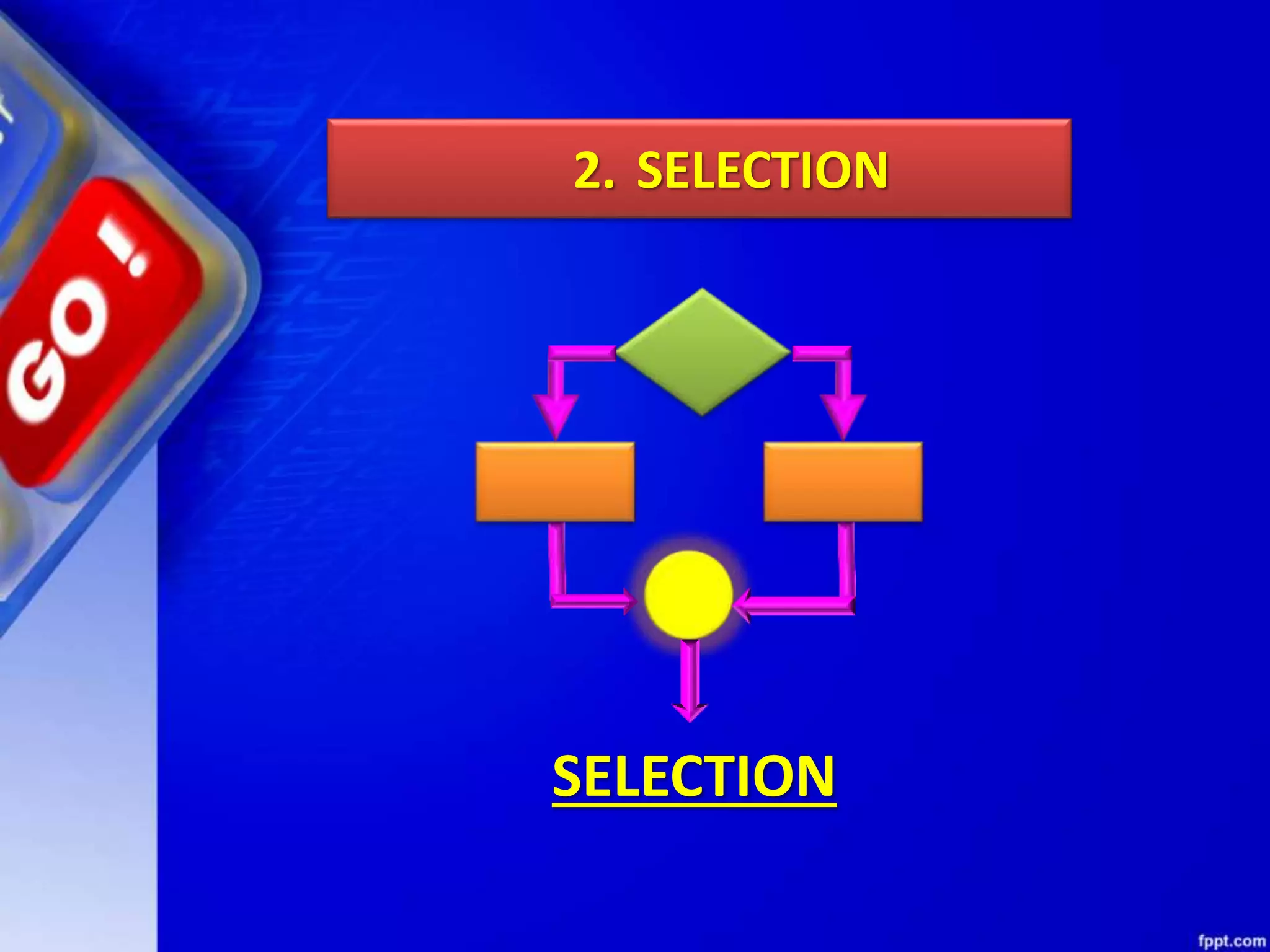
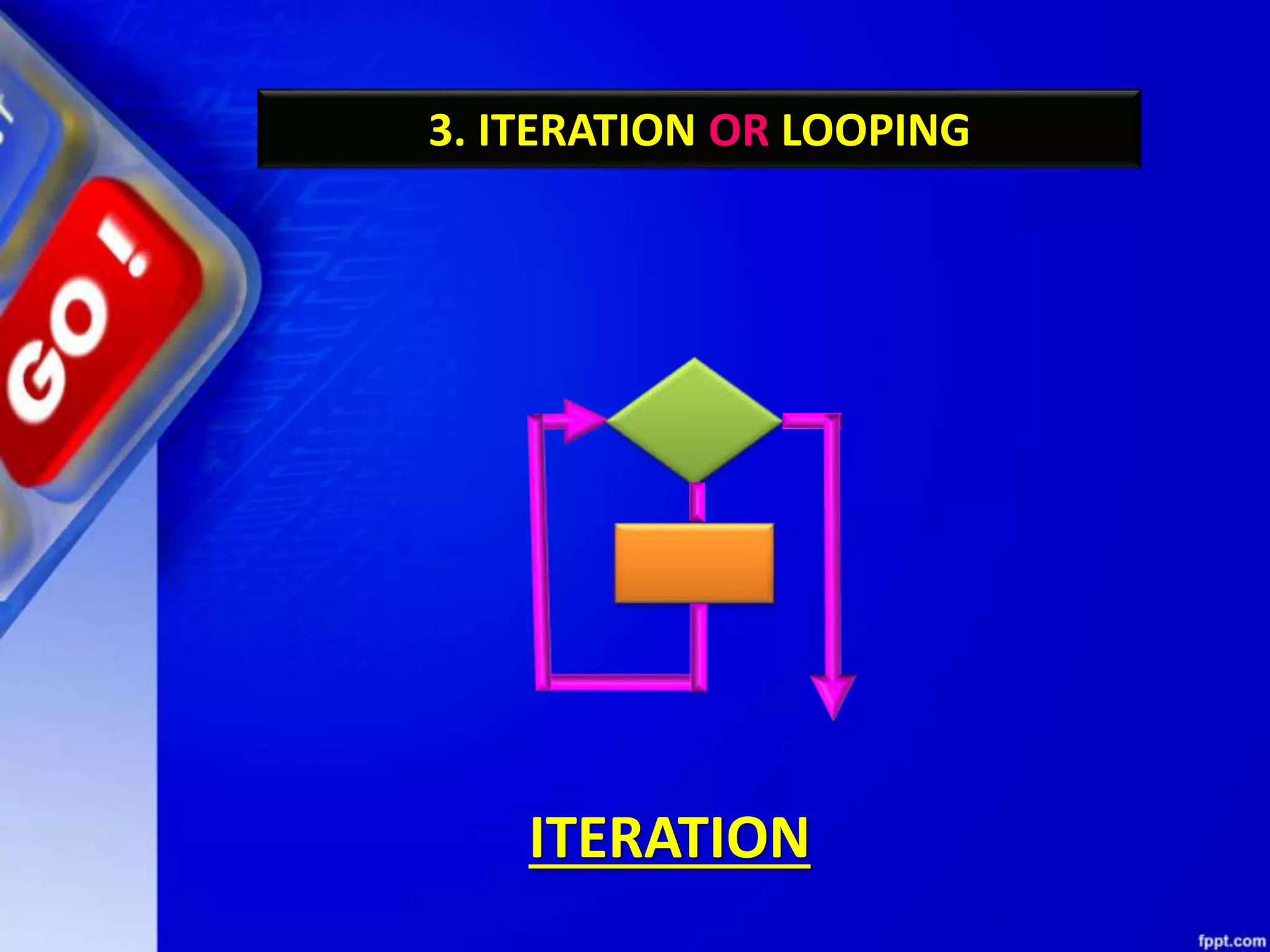
This document provides an overview of conditional and iterative statements in Python. It begins by defining selection and iteration as two types of control structures that allow programs to control the flow of execution.
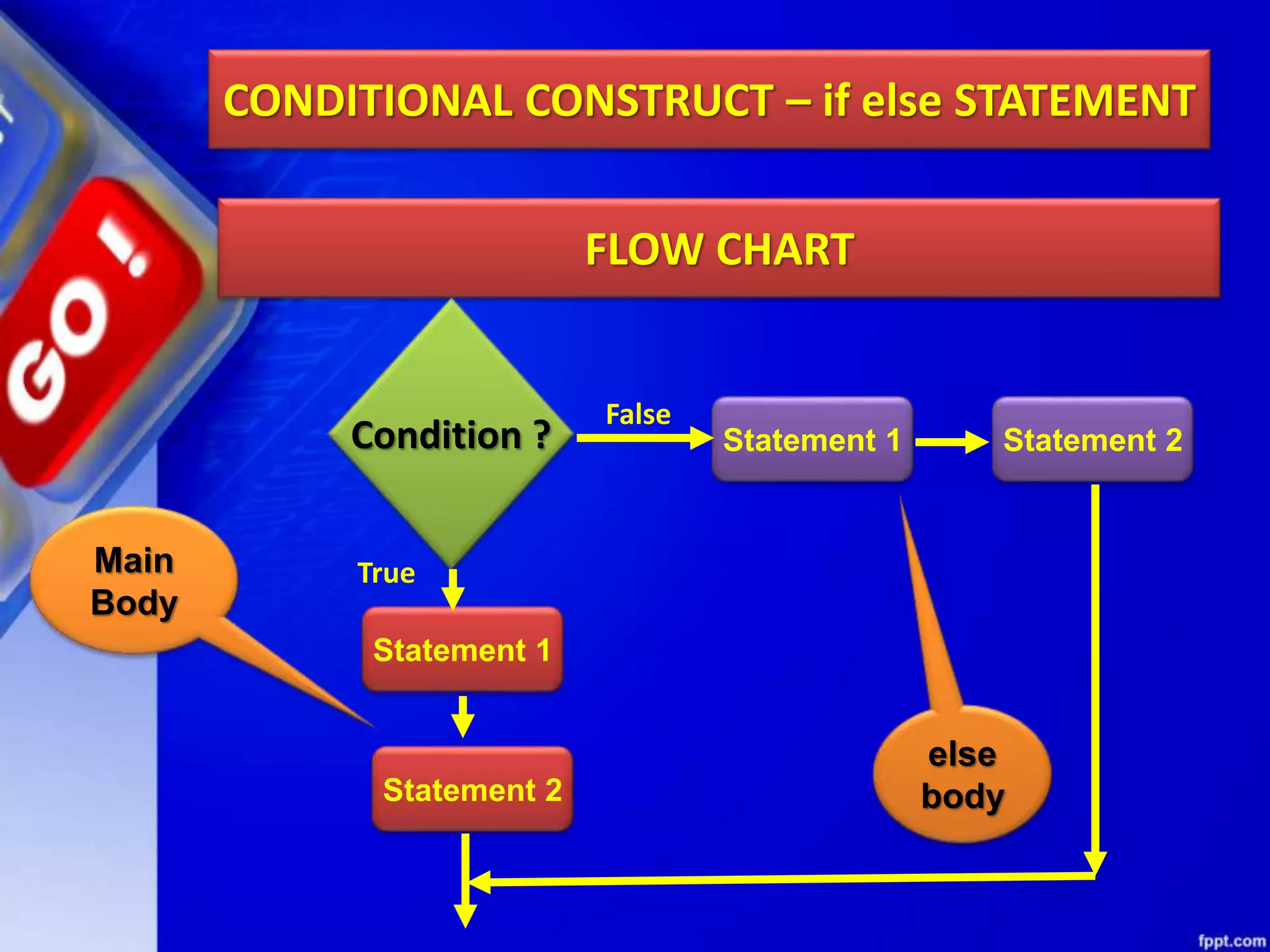
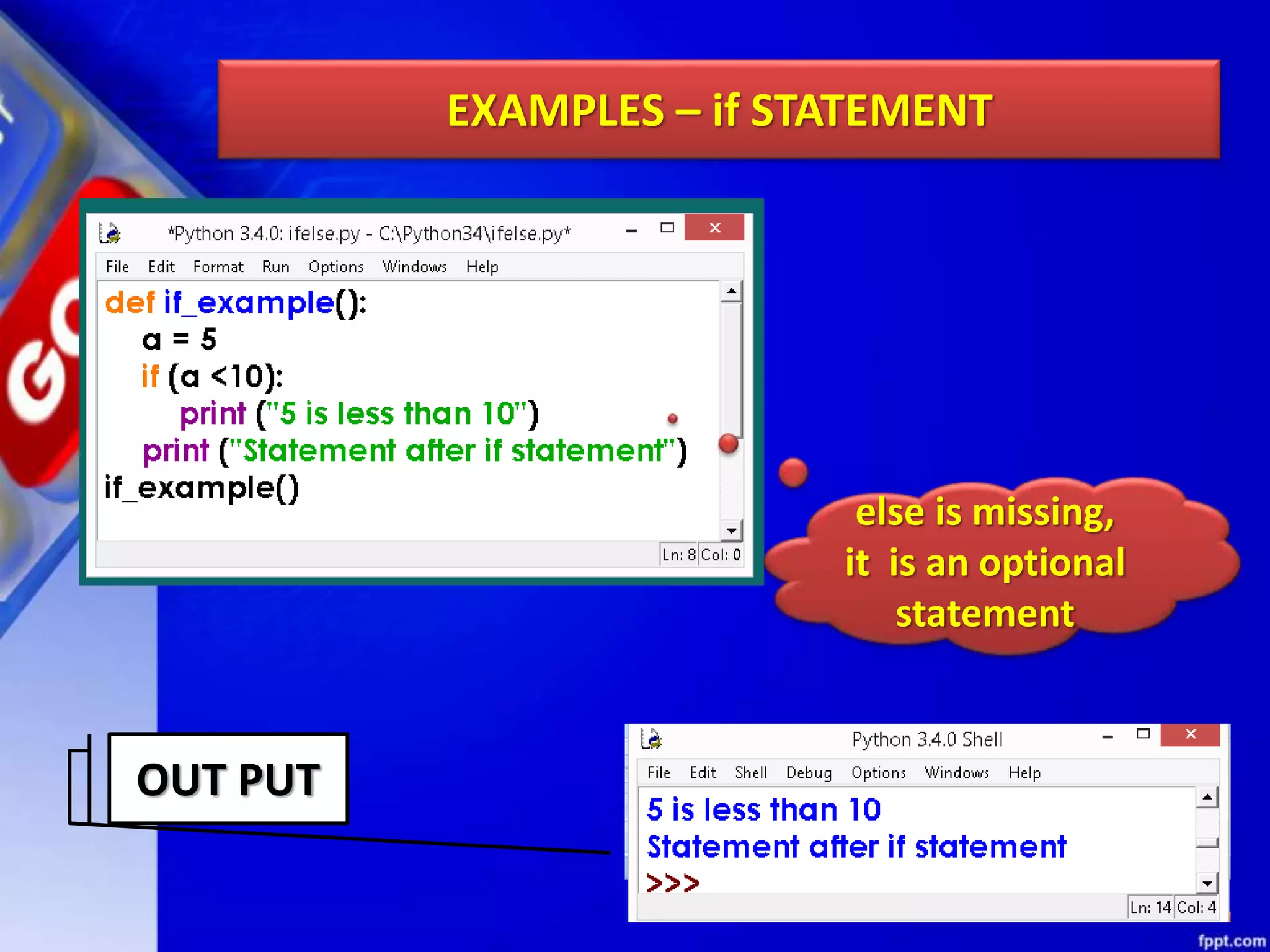
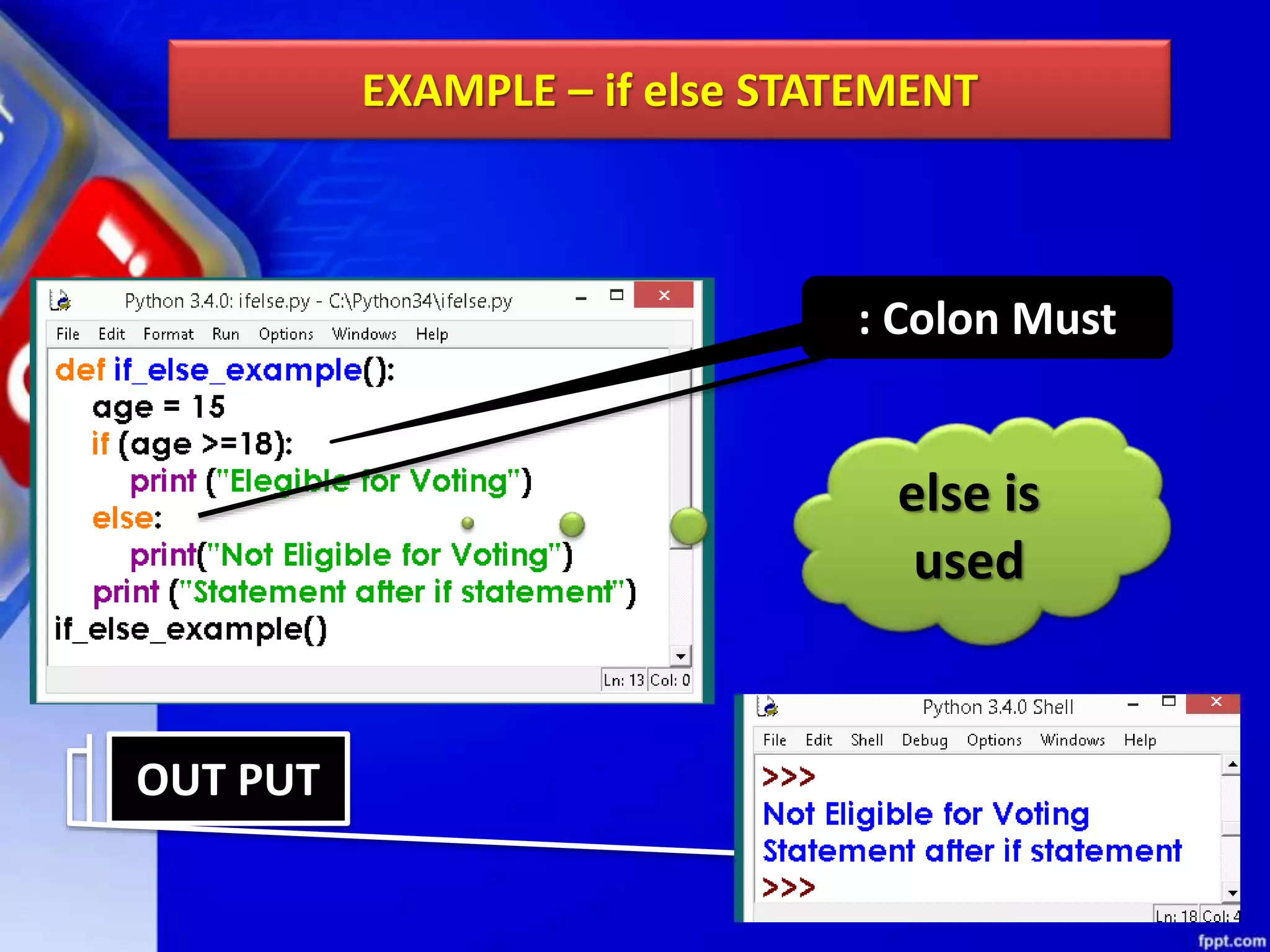
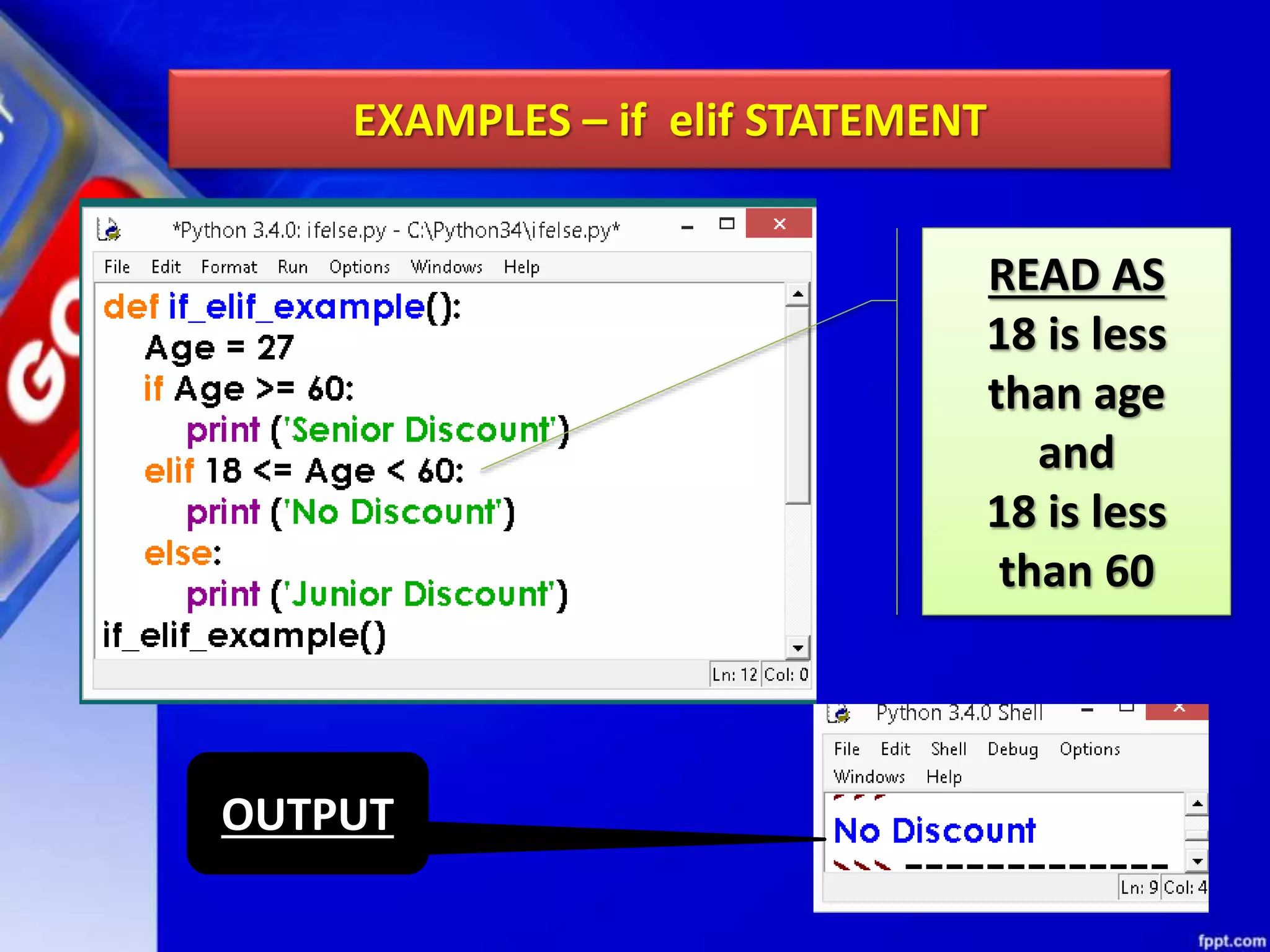
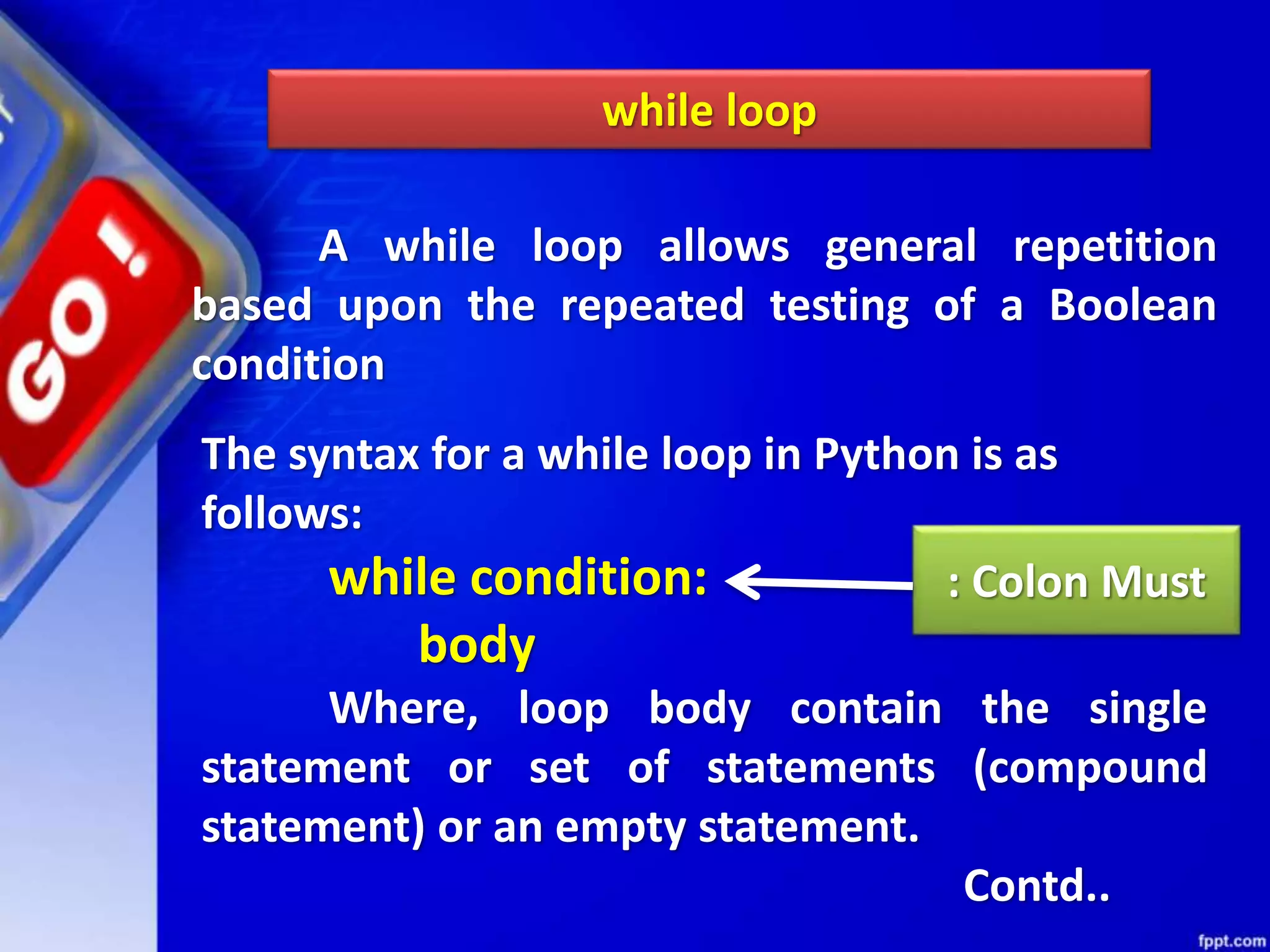
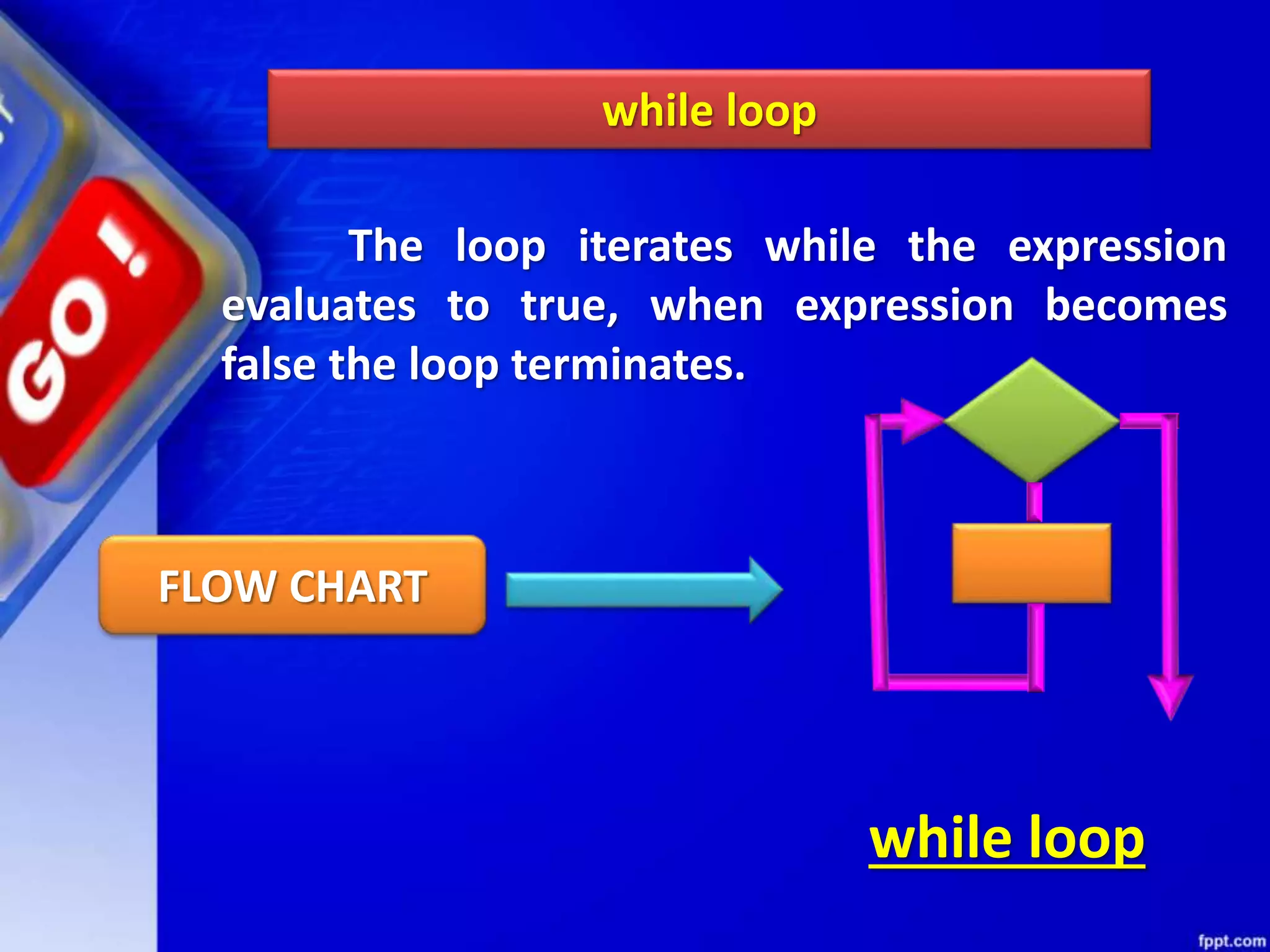
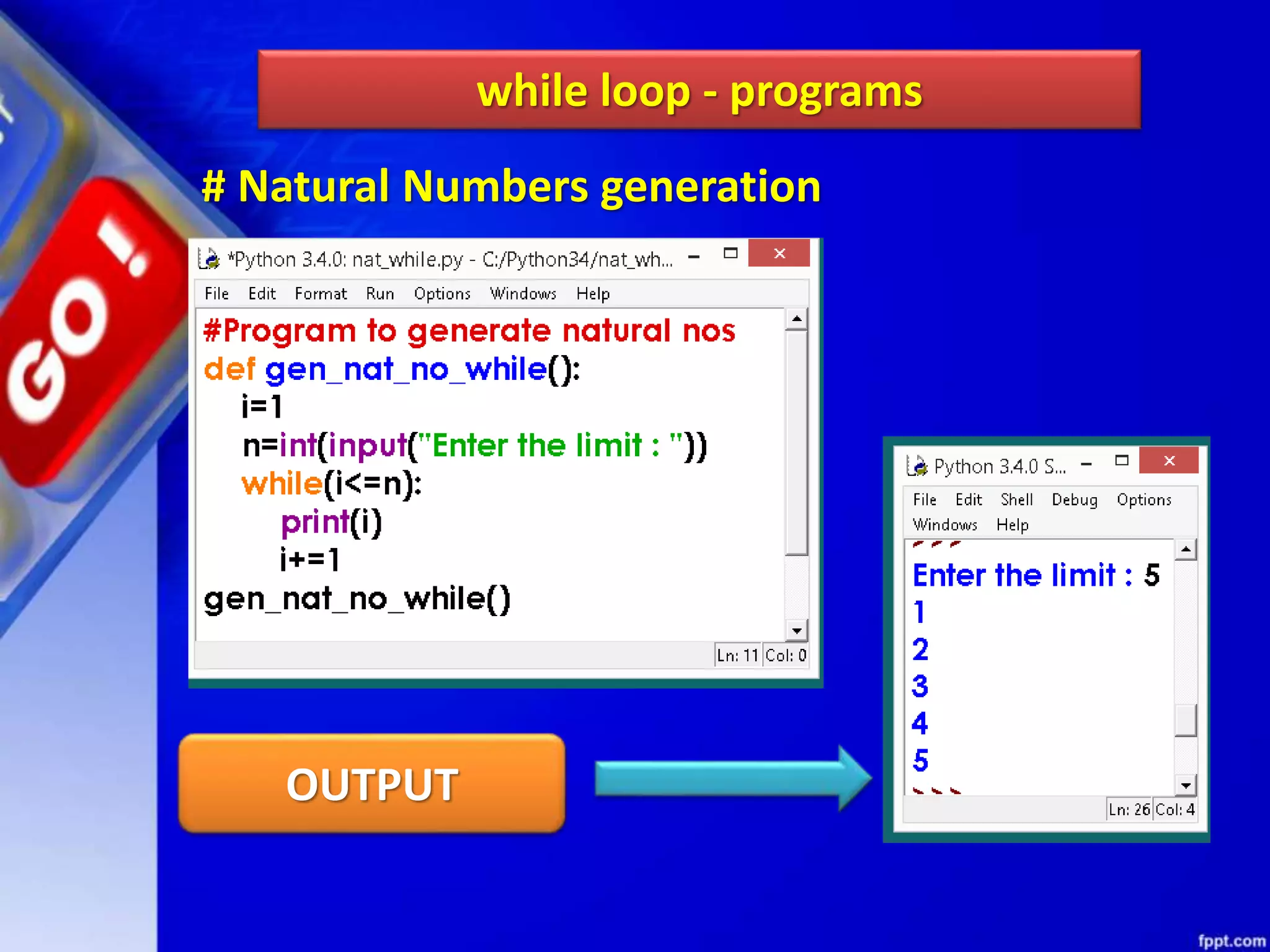
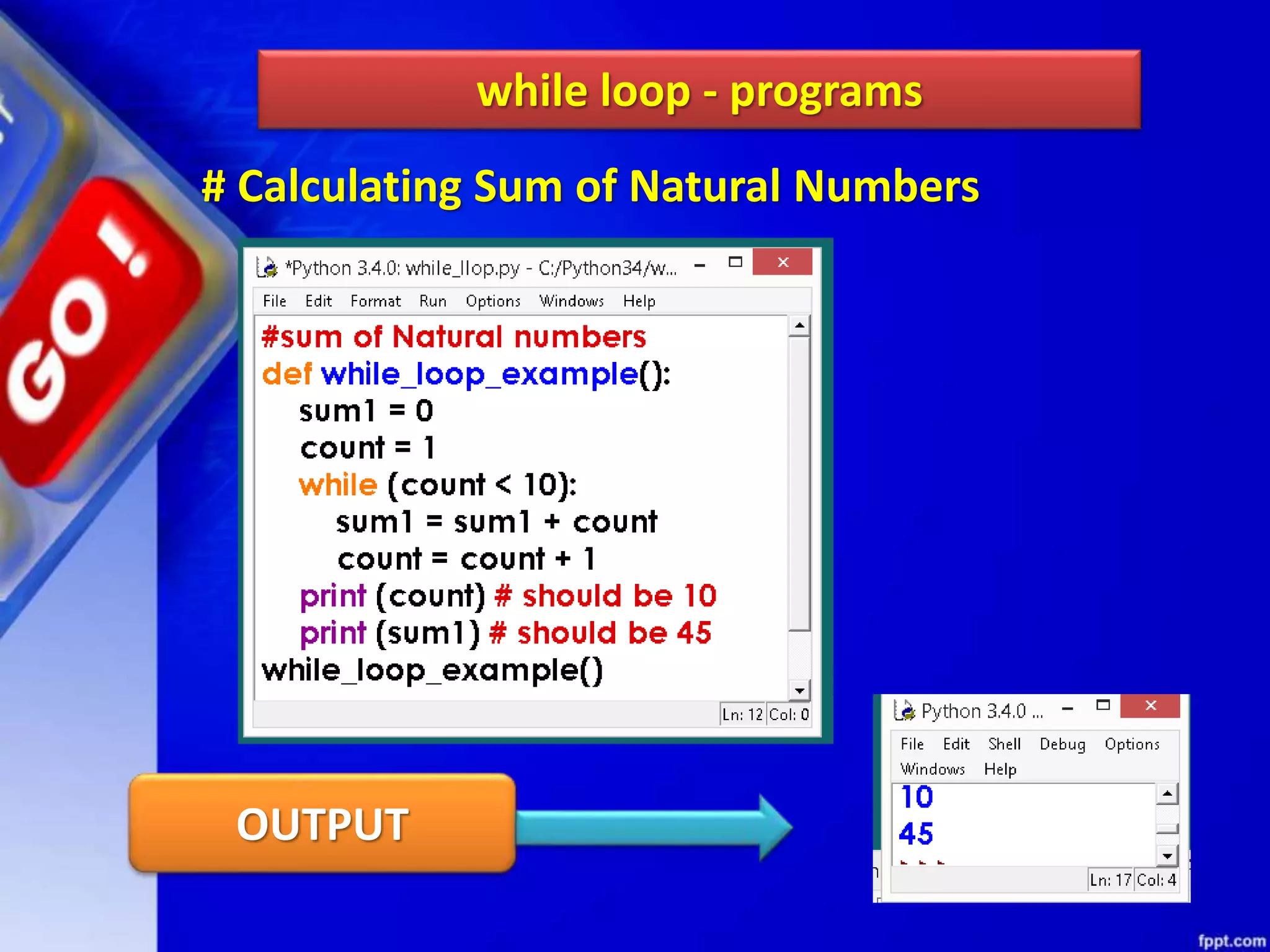
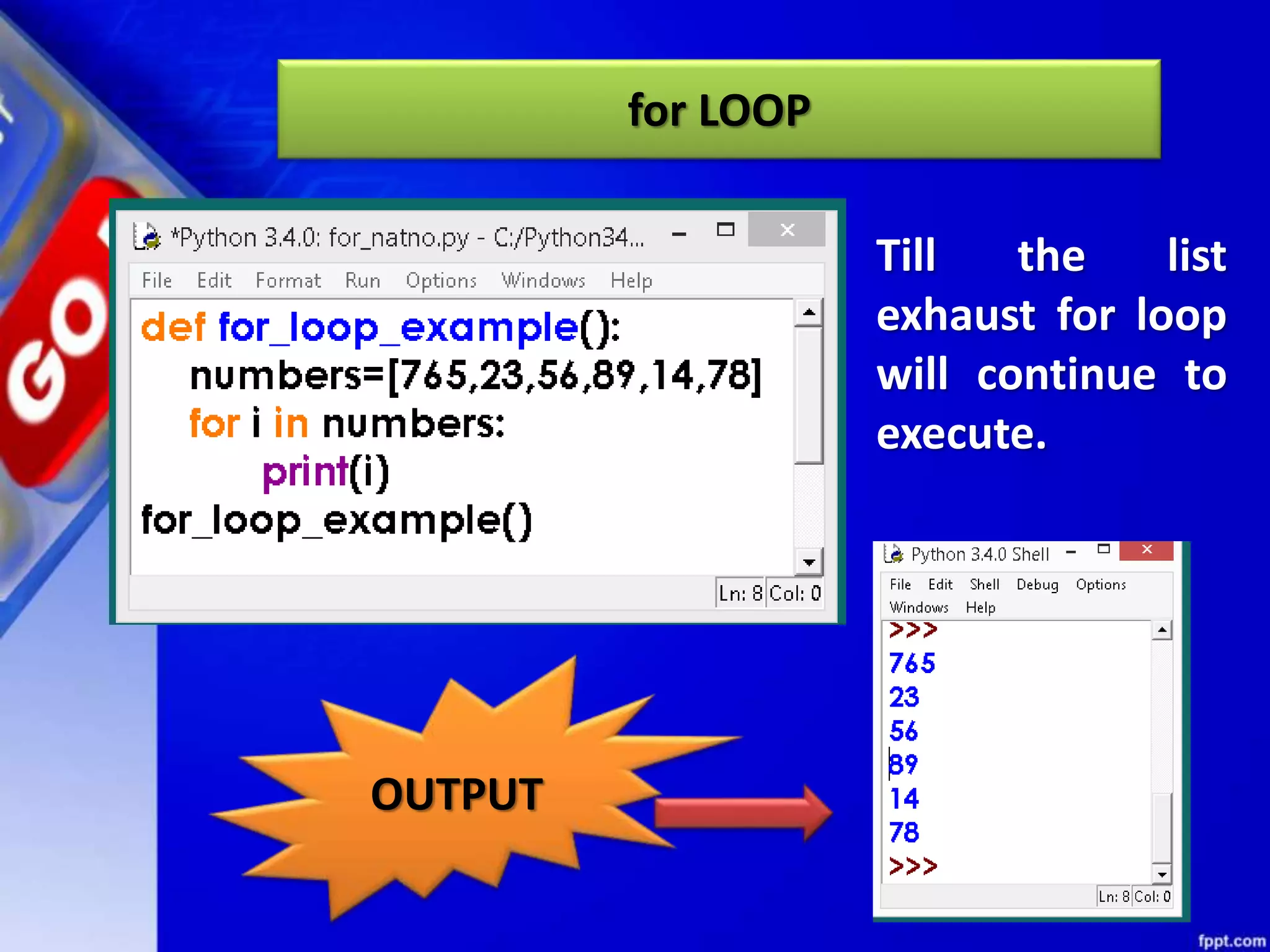
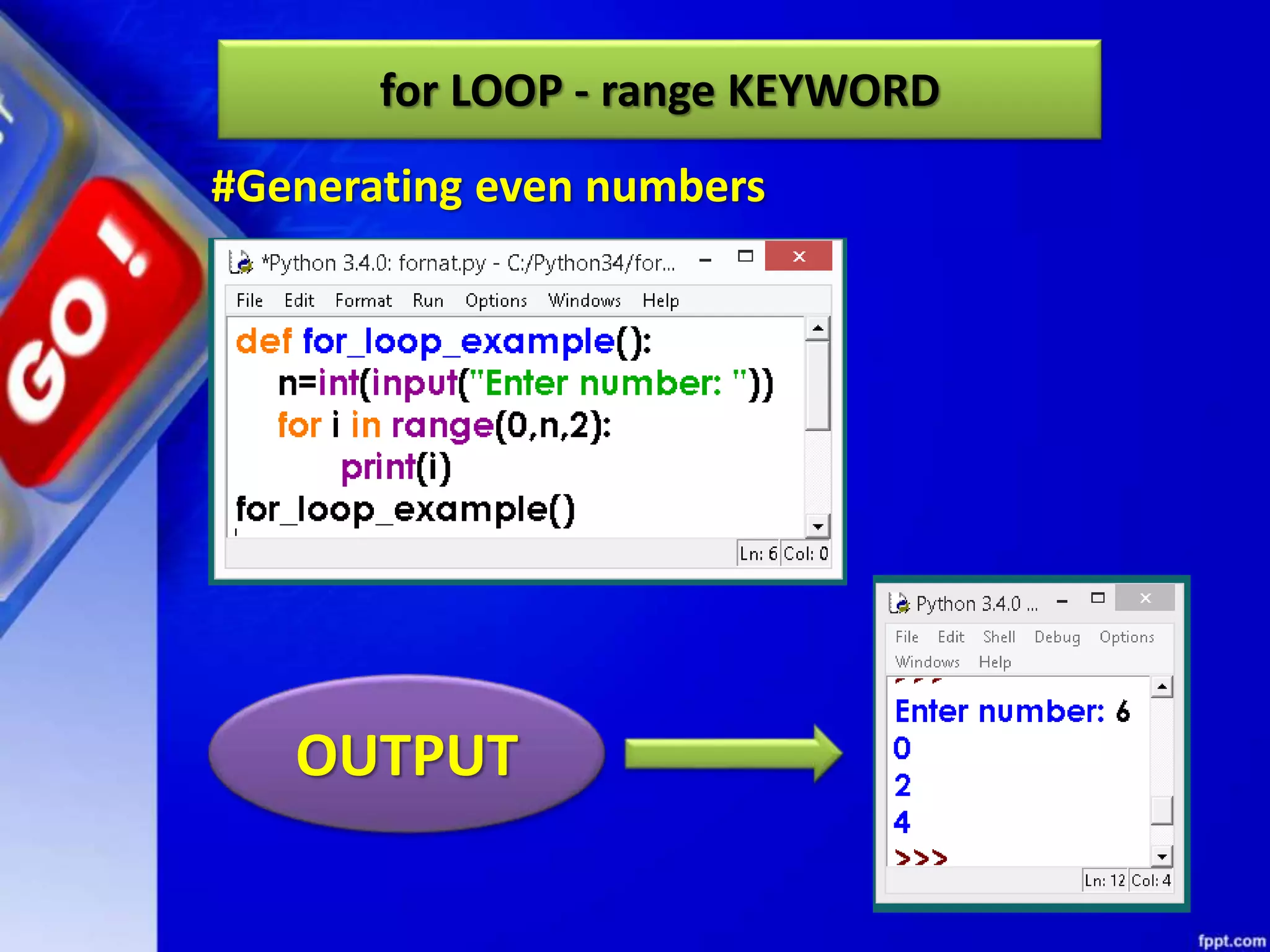
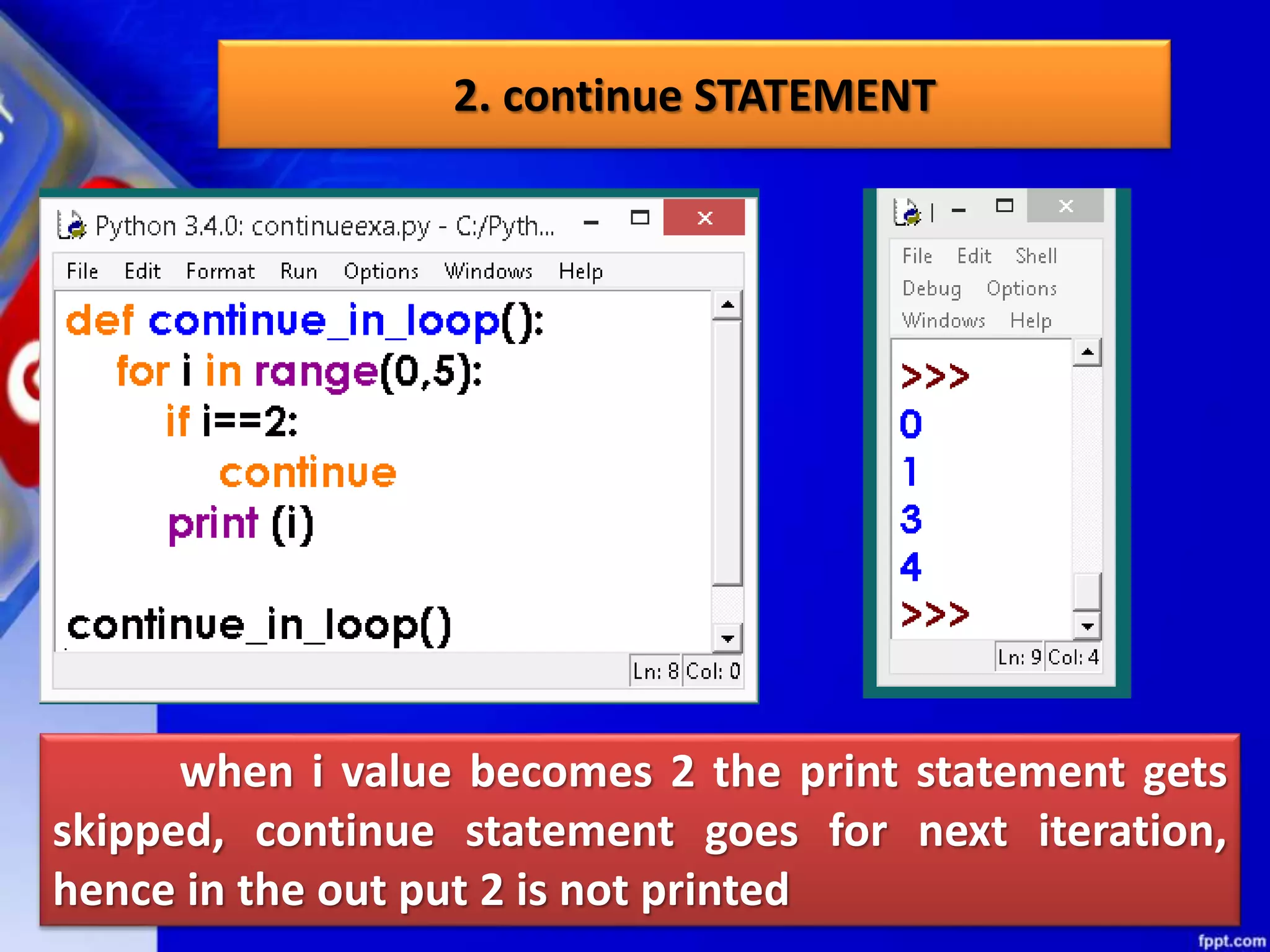
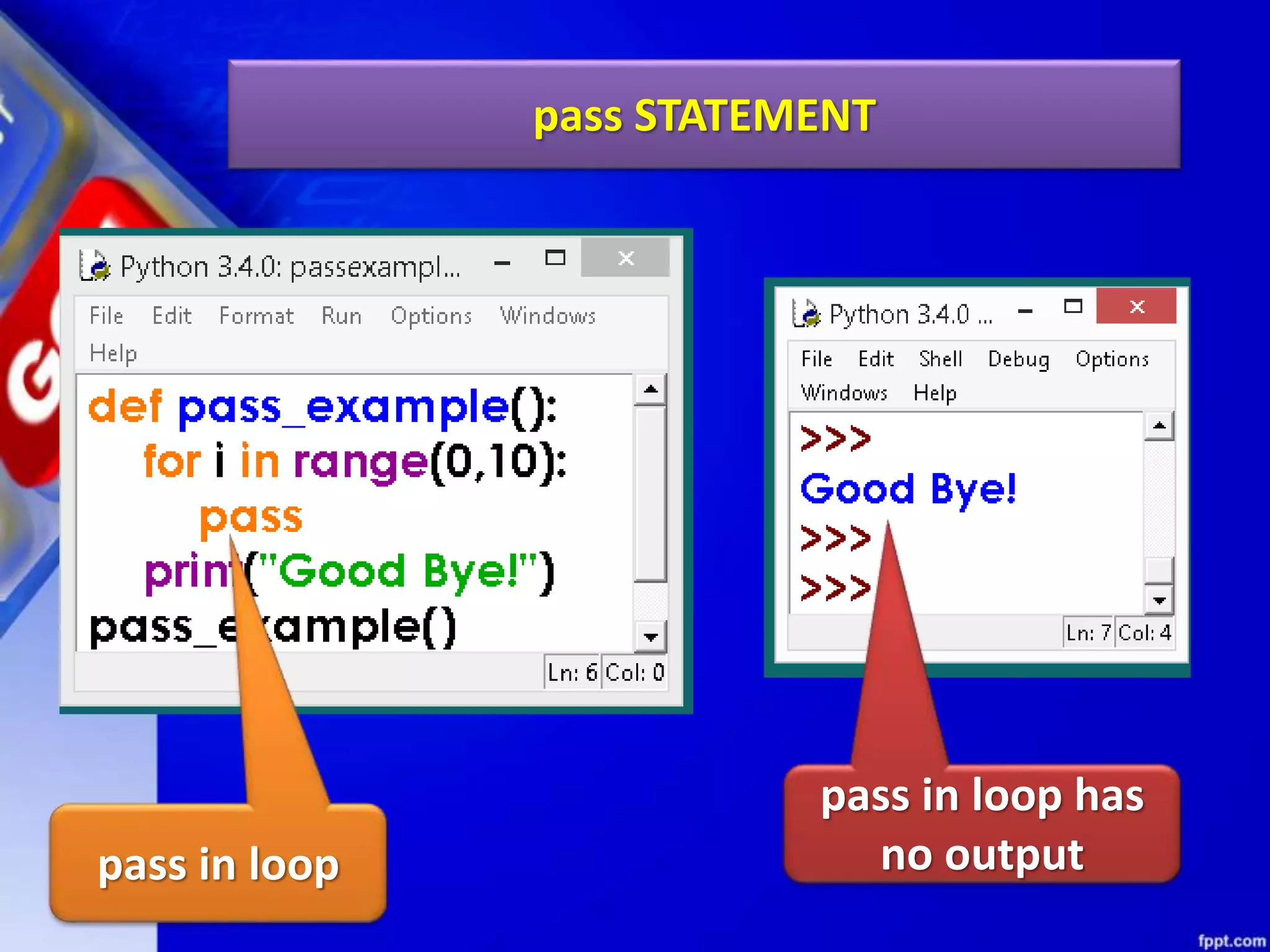
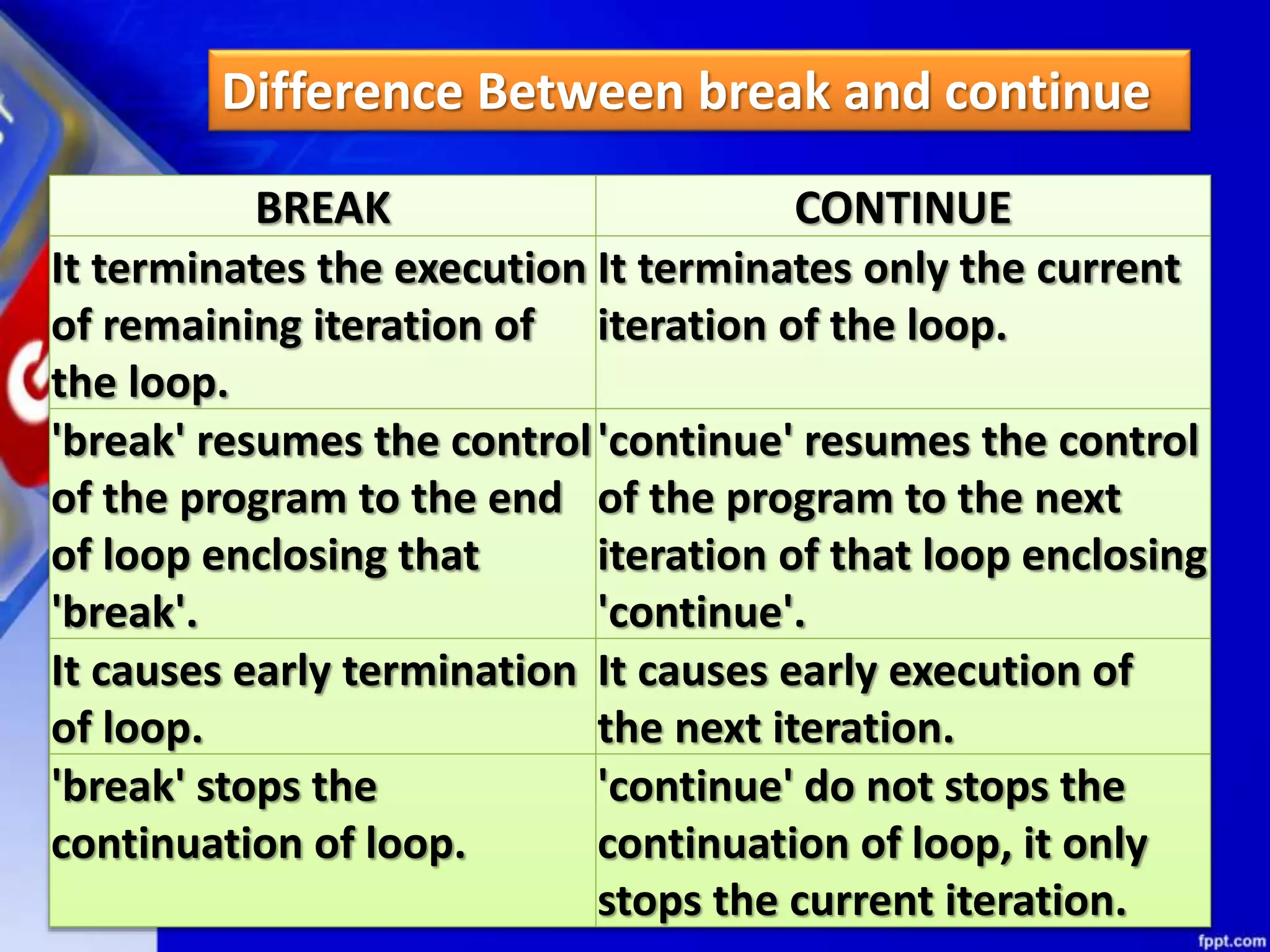
It then discusses conditional constructs like if/else statements, providing examples of how to write if/else and if/elif/else statements. It also covers loops, specifically while and for loops. The while loop repeats a block of code as long as a condition is true, and for loops iterate over a sequence. Examples are given of using range() and len() with for loops. Finally, the document lists several programming problems suited for different levels that involve conditional and iterative statements.