The document discusses the basics of cloud computing including:
- Defining cloud computing as using remote servers accessed over the internet rather than local data storage.
- The key benefits as low costs, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere.
- The essential characteristics including on-demand access, elastic resources, and pay-per-use models.
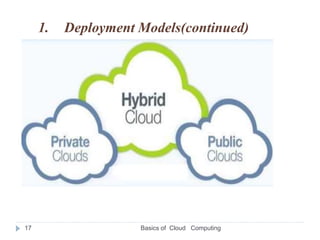
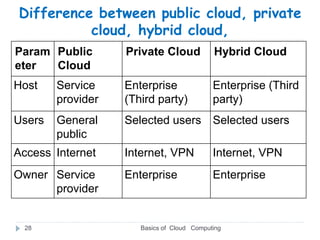
- The main cloud models are public, private, and hybrid clouds which differ in ownership and accessibility.
- Cloud services include Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service.