1. This document defines commercial discount as the interest retained by a bank when discounting a commercial paper like a bill of exchange before its maturity date.
2. It provides the formula to calculate commercial discount and shows examples of discount calculations for bills of different values and maturity dates.
3. In addition to the actual discount, discounting a bill involves other fees like commissions which together are called the "agio". The document illustrates how to calculate agio for a sample bill.
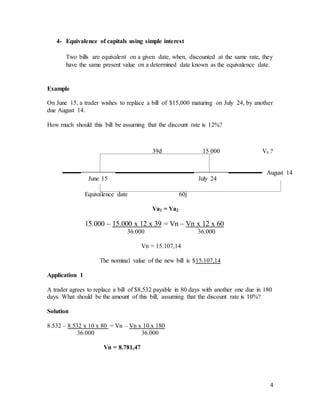
4. It explains the concept of equivalence of capitals using simple interest - that two bills are equivalent if their discounted present values are equal on a given date. Examples show how to determine the value of a replacement bill for equivalence