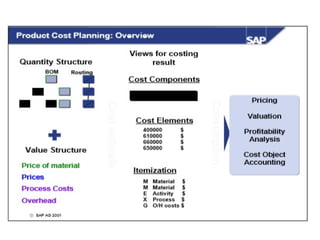
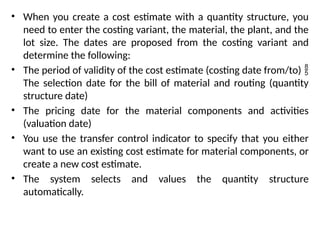
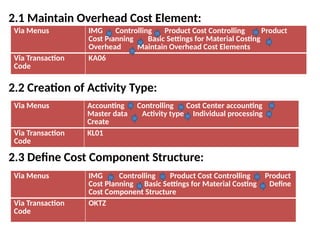
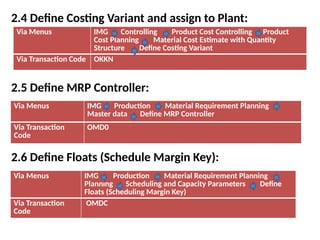
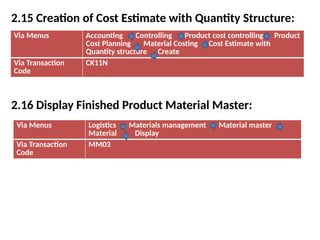
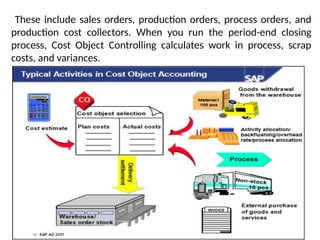
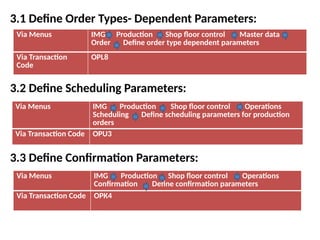
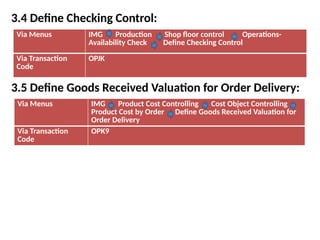
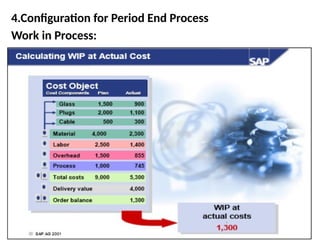
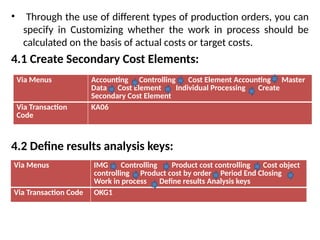
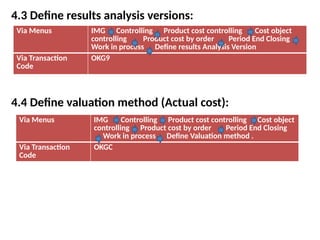
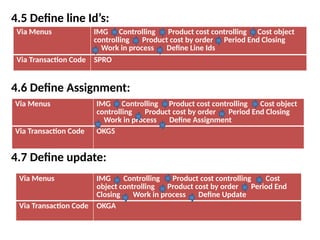
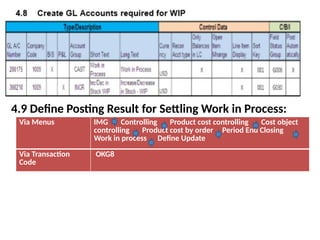
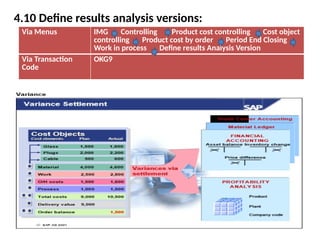
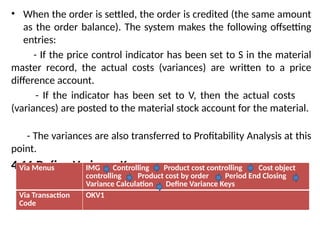
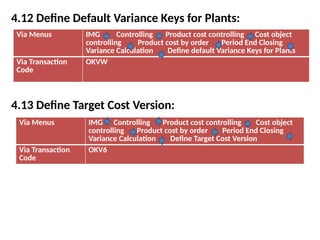
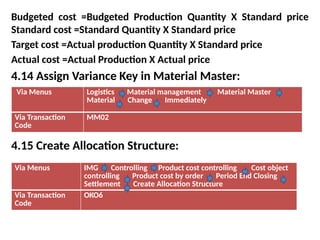
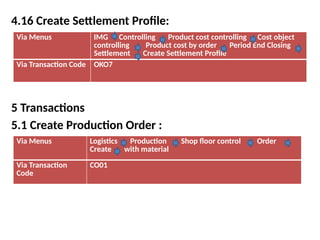
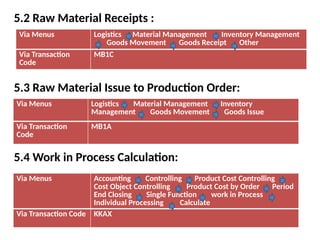
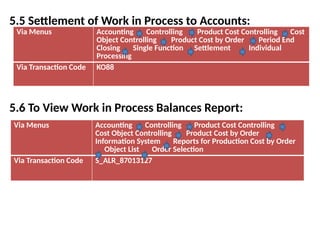
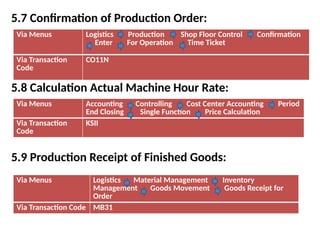
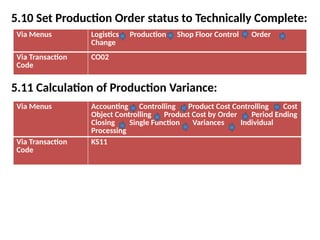
Product cost controlling is a tool within SAP that manages costs in manufacturing and service rendering, utilizing overhead cost data for accurate cost planning, monitoring, and variance analysis. This includes estimating production costs via various structures, defining costs, and managing different cost objects through defined configurations and transaction codes. The process also covers the marking and releasing of cost estimates as well as period-end closing processes for accurate financial tracking.