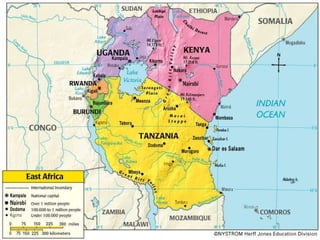
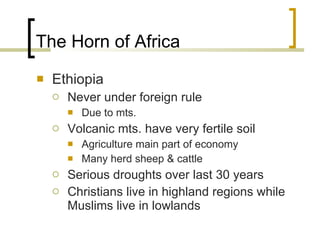
East Africa is a land of high plains and plateaus with long, deep rift valleys running through it. The Great Rift Valley stretches from the Red Sea through Ethiopia and Tanzania. East Africa has many large volcanic mountains like Mount Kilimanjaro and plains home to national parks. The region features lakes like Lake Victoria and the Nile River. Climate varies from desert in the north to tropical in the south. East Africa has a diverse population and was influenced by European colonization in the 19th century. Many countries struggle with issues like poverty, conflict, and reliance on agriculture.