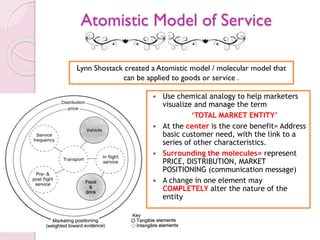
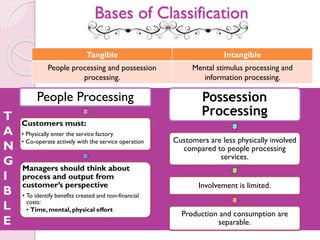
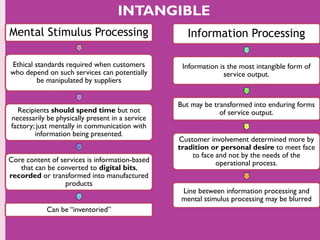
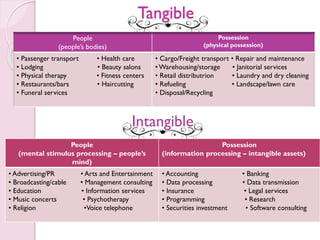
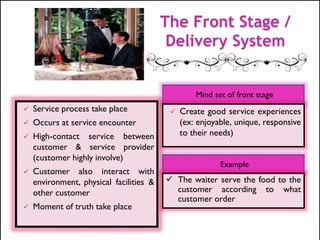
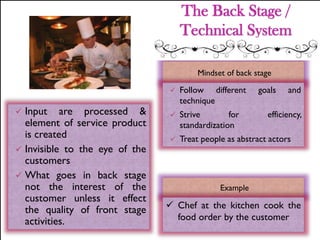
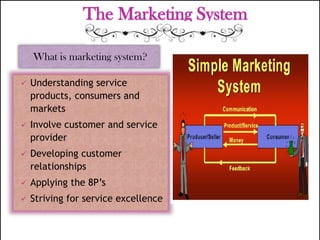
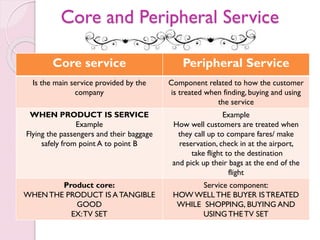
The document discusses the atomistic model of service, created by Lynn Shostack, which helps marketers manage the 'total market entity' by visualizing core benefits and surrounding characteristics. It outlines different service classifications based on customer involvement and the distinctions between tangible and intangible services, emphasizing the importance of understanding consumer needs in service delivery. Additionally, it explores the roles of front-stage and back-stage systems in service encounters and the significance of customer experience in various market segments.