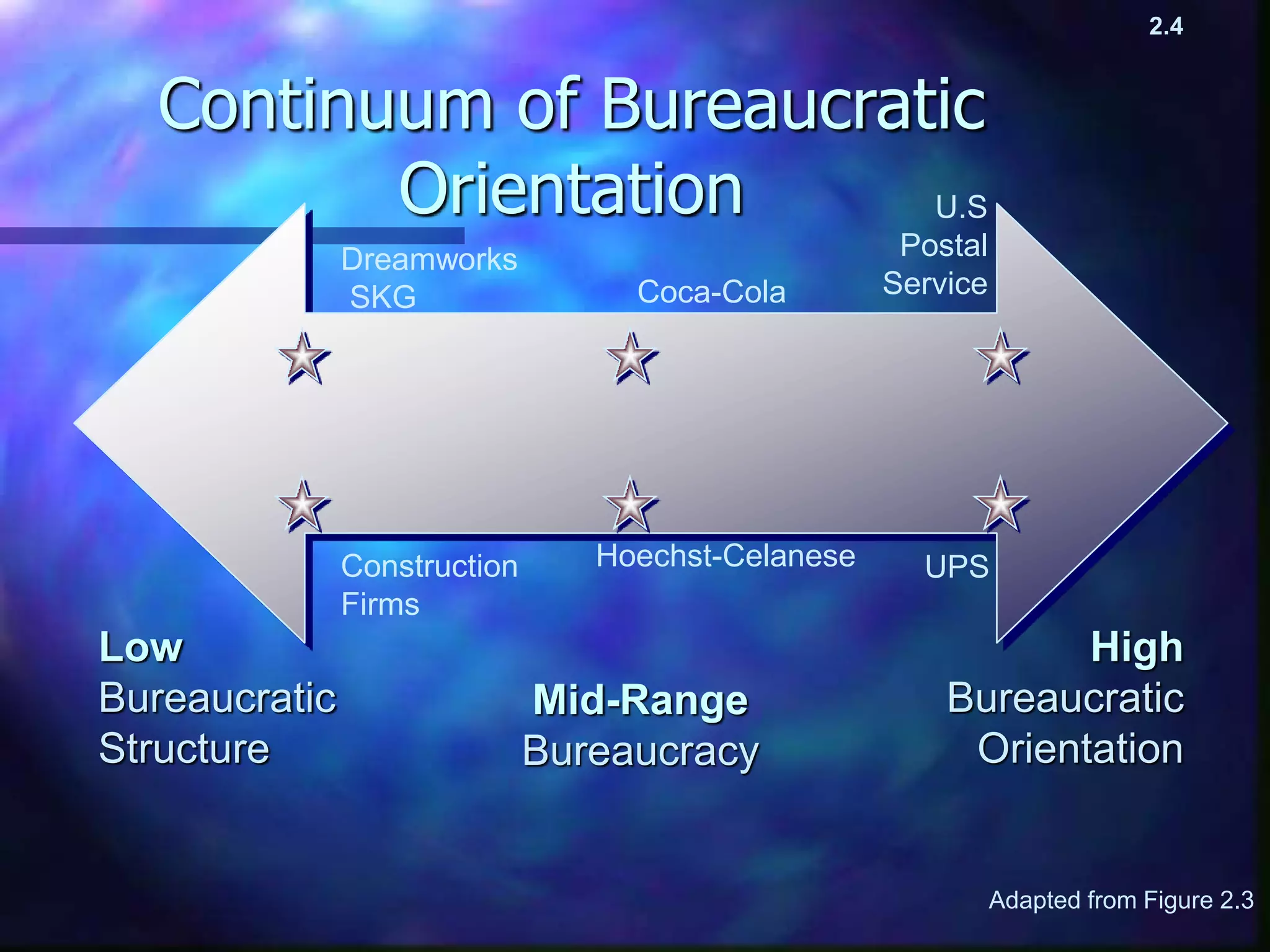
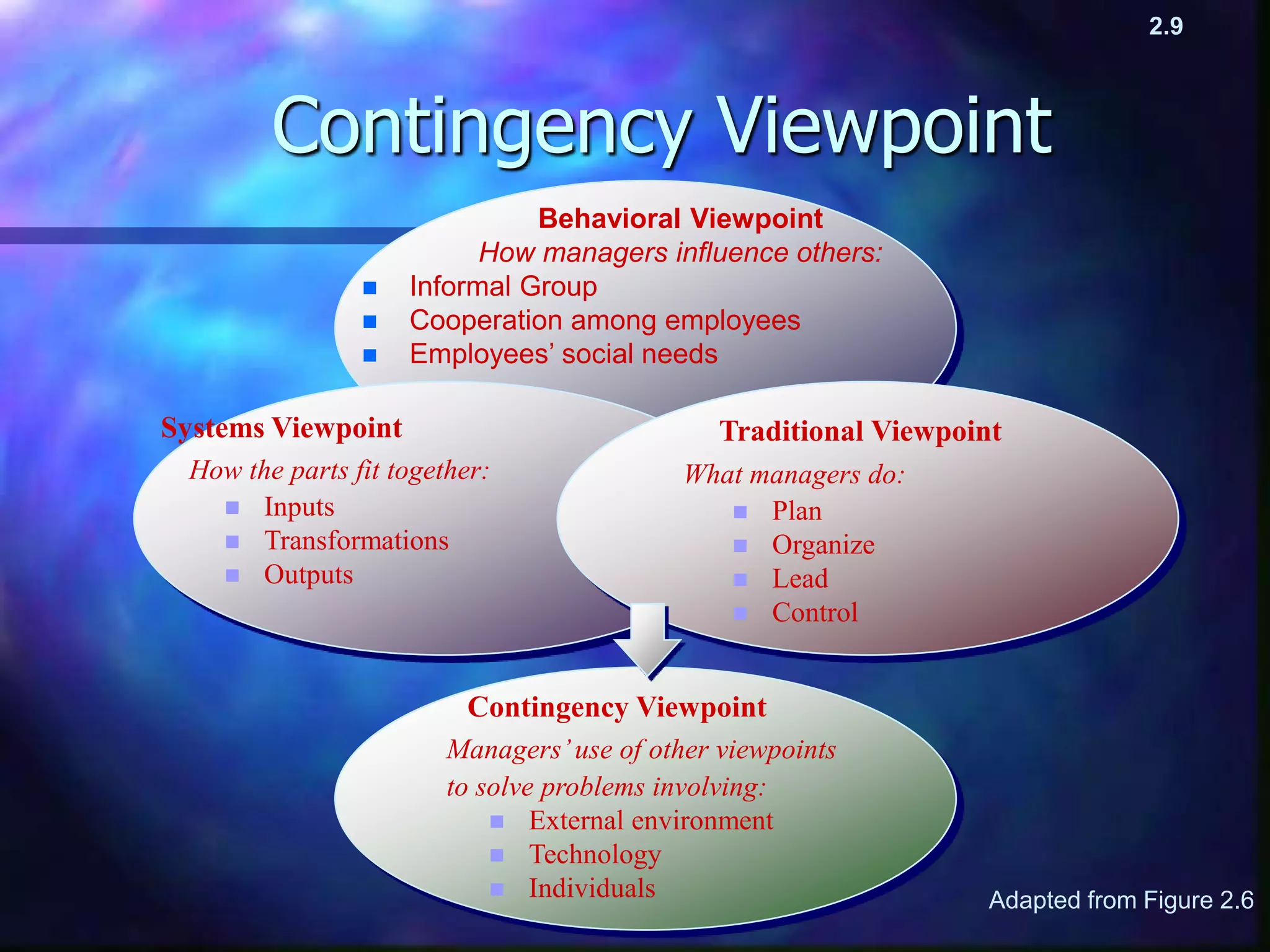
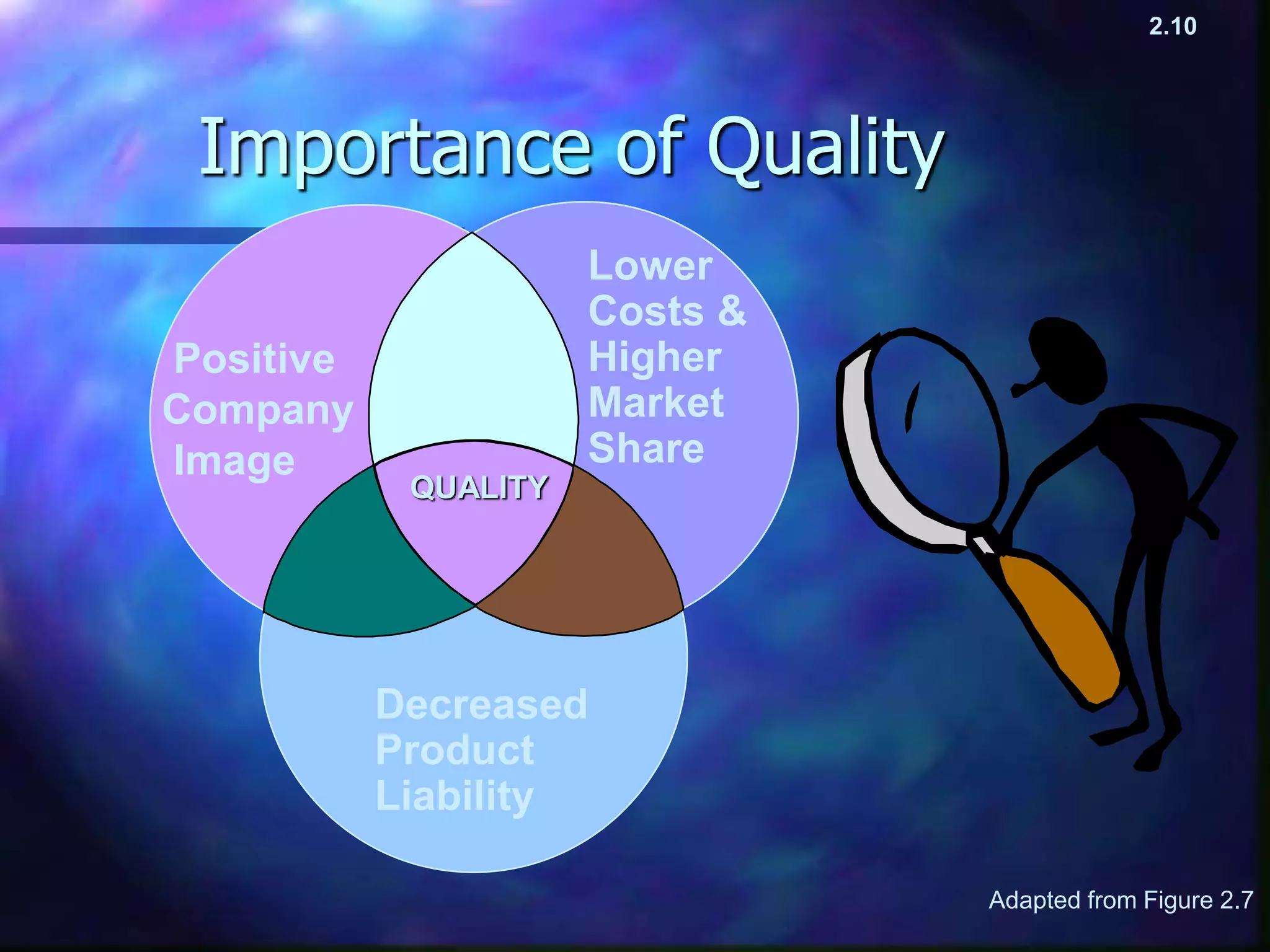
Management thought has developed over time through different viewpoints, beginning with the classical viewpoint in the late 1800s as organizations grew larger during the Industrial Revolution. Later viewpoints include behavioral in the 1930s focusing on individuals, systems in the 1950s viewing organizations as systems, contingency in the 1960s stressing that there is no single best way and the approach depends on factors like the environment, and quality in the 1980s championed by Deming focusing on quality to reduce costs and drive performance. Each viewpoint built on those before but had a different focus, and current approaches may incorporate aspects of multiple viewpoints.