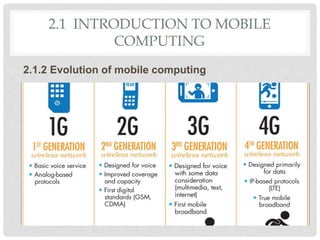
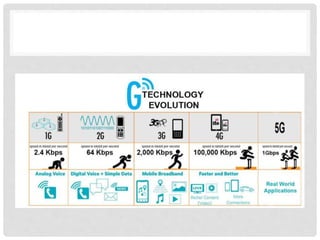
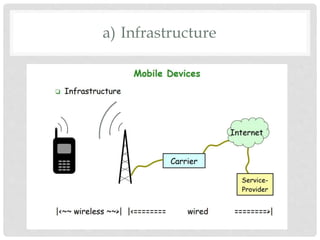
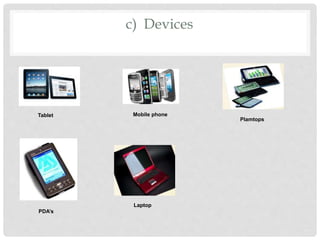
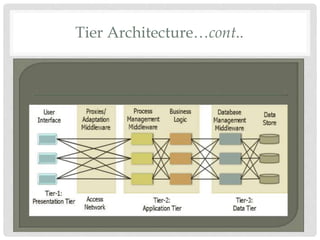
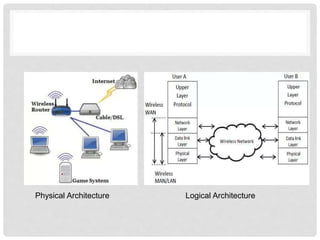
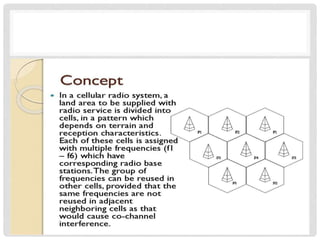
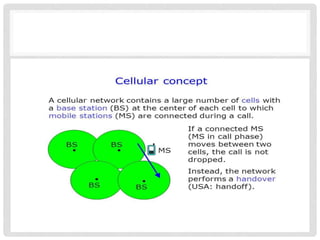
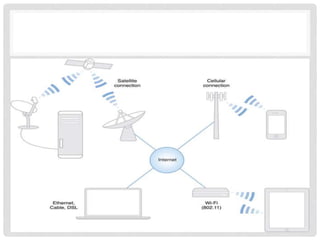
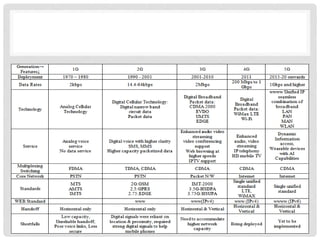
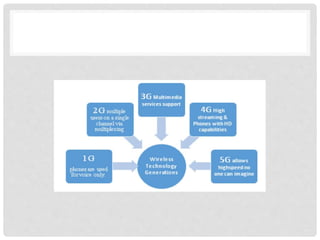
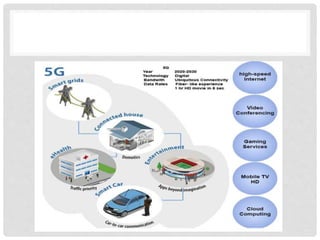
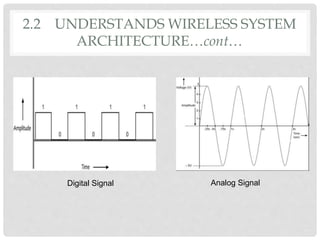
The document provides an overview of mobile computing technologies, covering aspects like mobile communication, hardware, software, and applications. It discusses the three-tier architecture for mobile computing and the logical and physical architectures of wireless networks. Additionally, it details various mobile computing devices, cellular network concepts, and the evolution of mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android.