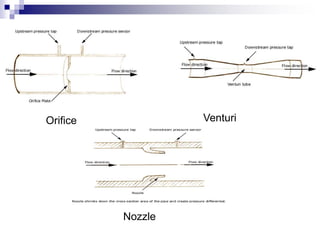
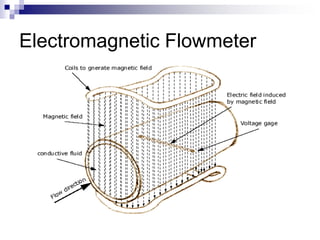
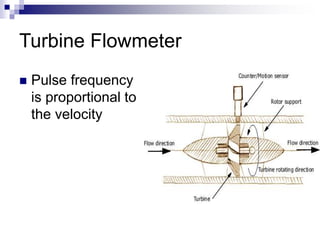
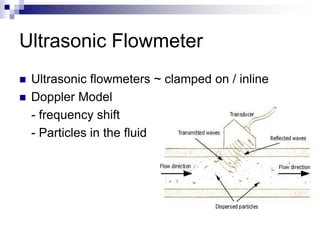
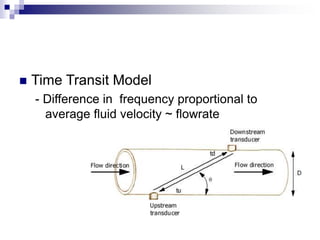
This chapter focuses on flow measurement, defining its significance and operations of various devices. It covers several types of flowmeters including differential pressure meters, electromagnetic, vortex, turbine, and ultrasonic flowmeters, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. The essential role of flow in processes involving the movement of materials and energy is also discussed.