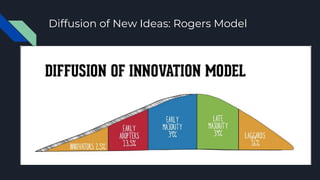
This document provides an overview of computer-mediated communication (CMC) and social media theories. It discusses how CMC allows for new forms of identity and interaction online. Early CMC occurred through bulletin board systems and email, while the World Wide Web expanded opportunities in the 1990s. Social networking sites now facilitate maintaining connections and engaging in online communities. New ideas and trends diffuse through social media, following models of technology adoption. Users are motivated by social and entertainment needs. Social media both extends existing power structures and empowers new voices. While enhancing connections, overreliance on online socializing can impact well-being. Memes and online culture shape understandings in new ways.