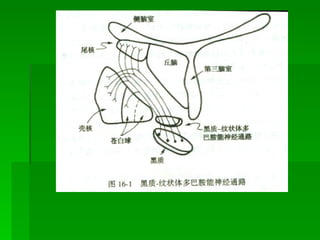
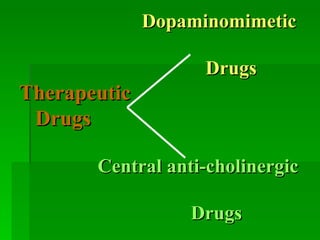
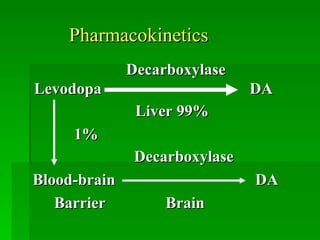
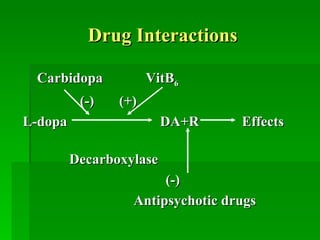
The document discusses drug therapies for Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. It first covers dopaminergic drugs like levodopa that are used to treat Parkinson's disease. It then discusses central anticholinergic drugs that can help treat tremors and rigidity caused by Parkinson's. Finally, it outlines therapies for Alzheimer's disease, including cholinesterase inhibitors to potentiate cholinergic function and drugs that may improve neuronal growth factors or microcirculation in the brain.

![药 理 学 PHARMACOLOGY 张岫美 山东大学医学院 药理学研究所 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1054721/85/chapter-16-2-320.jpg)