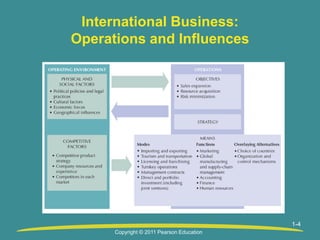
This document provides an overview of international business. It discusses how international business involves commercial transactions between two or more countries. Studying international business is important because most companies are international or compete with international companies, and the best business practices may differ by country. The rapid growth of international business is fueled by factors like increased technology, liberalized trade, expanded global competition, and changing political situations. Companies engage in international business to expand sales into new markets, acquire resources, and diversify risks. Modes of operation include exports/imports and foreign direct investment. Physical, social, and competitive factors must be considered when operating business internationally.