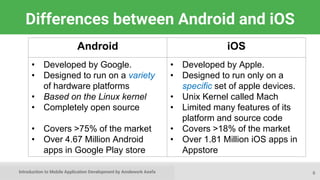
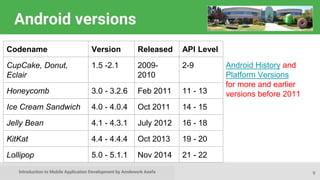
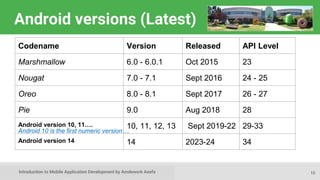
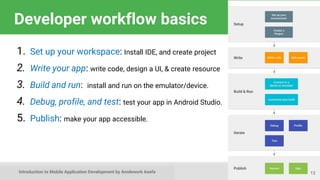
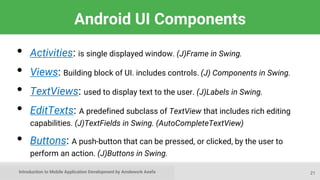
This document provides an introduction to mobile application development, focusing on Android and iOS platforms. It covers mobile app development tools, the differences between the two systems, challenges faced during development, and the basics of Android app structure and lifecycle. Additionally, it offers insights into UI components and suggests resources for further learning in the field.