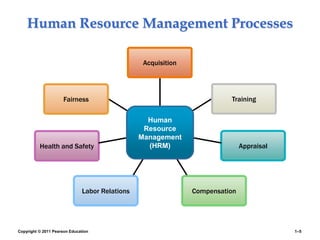
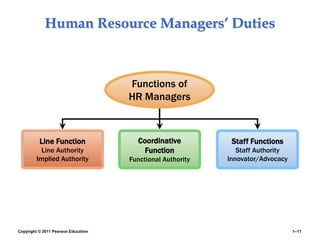
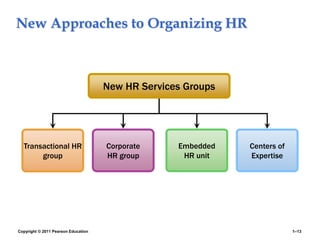
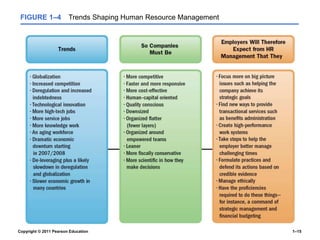
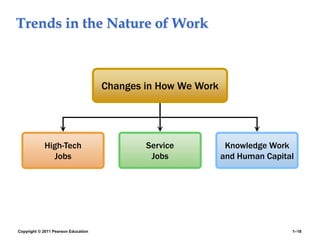
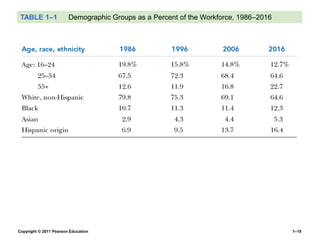
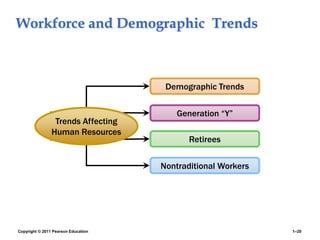
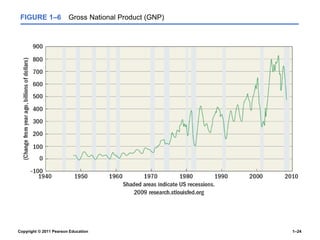
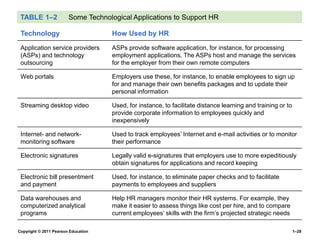
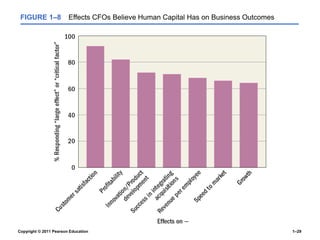
The document provides an overview of human resource management (HRM), detailing its processes such as recruitment, training, appraisal, and compensation of employees. It addresses current trends affecting HRM, including globalization, workforce demographics, and technological advancements, alongside the challenges HR managers face. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of evidence-based HR practices and ethical considerations in managing human resources effectively.