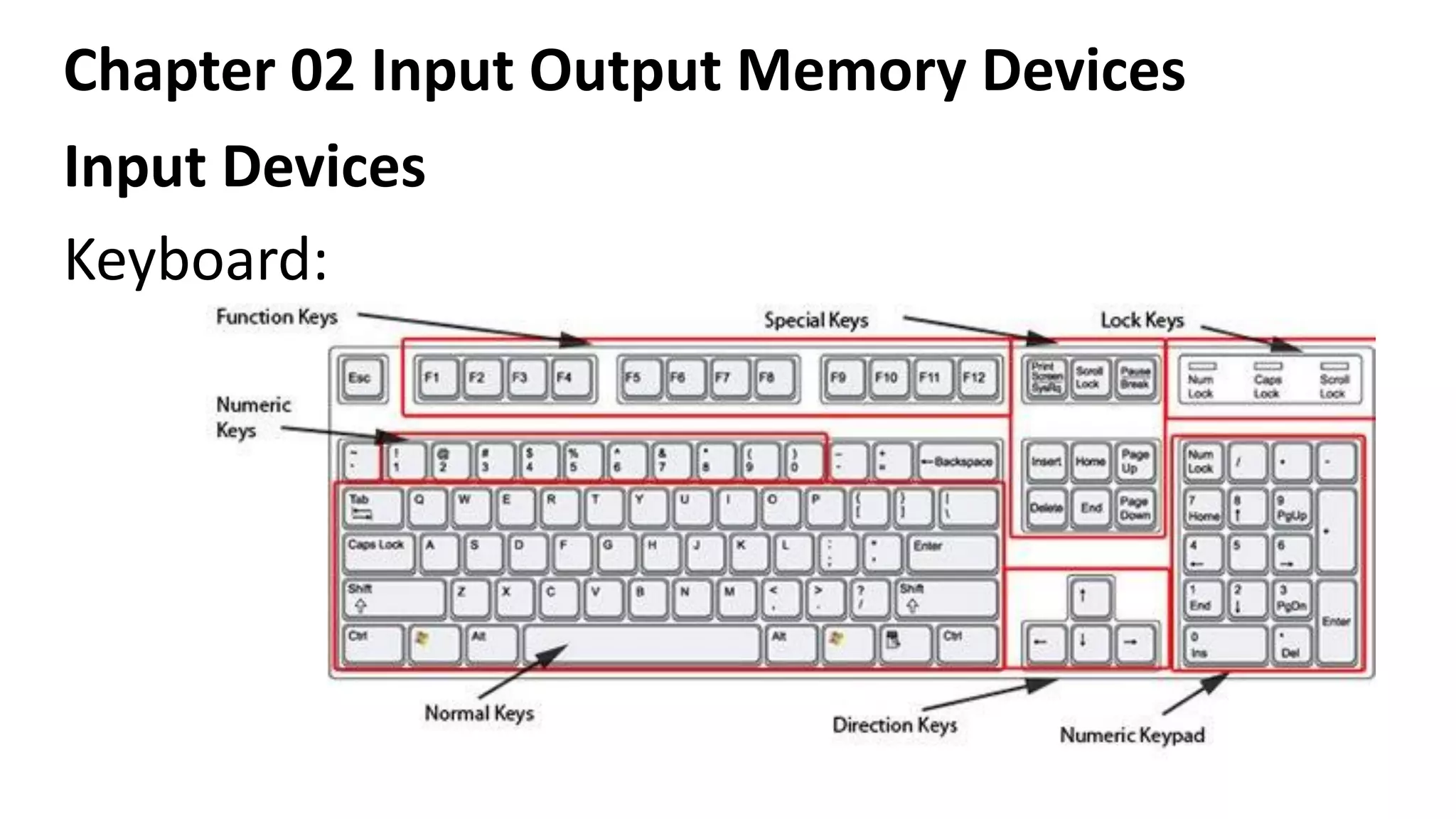
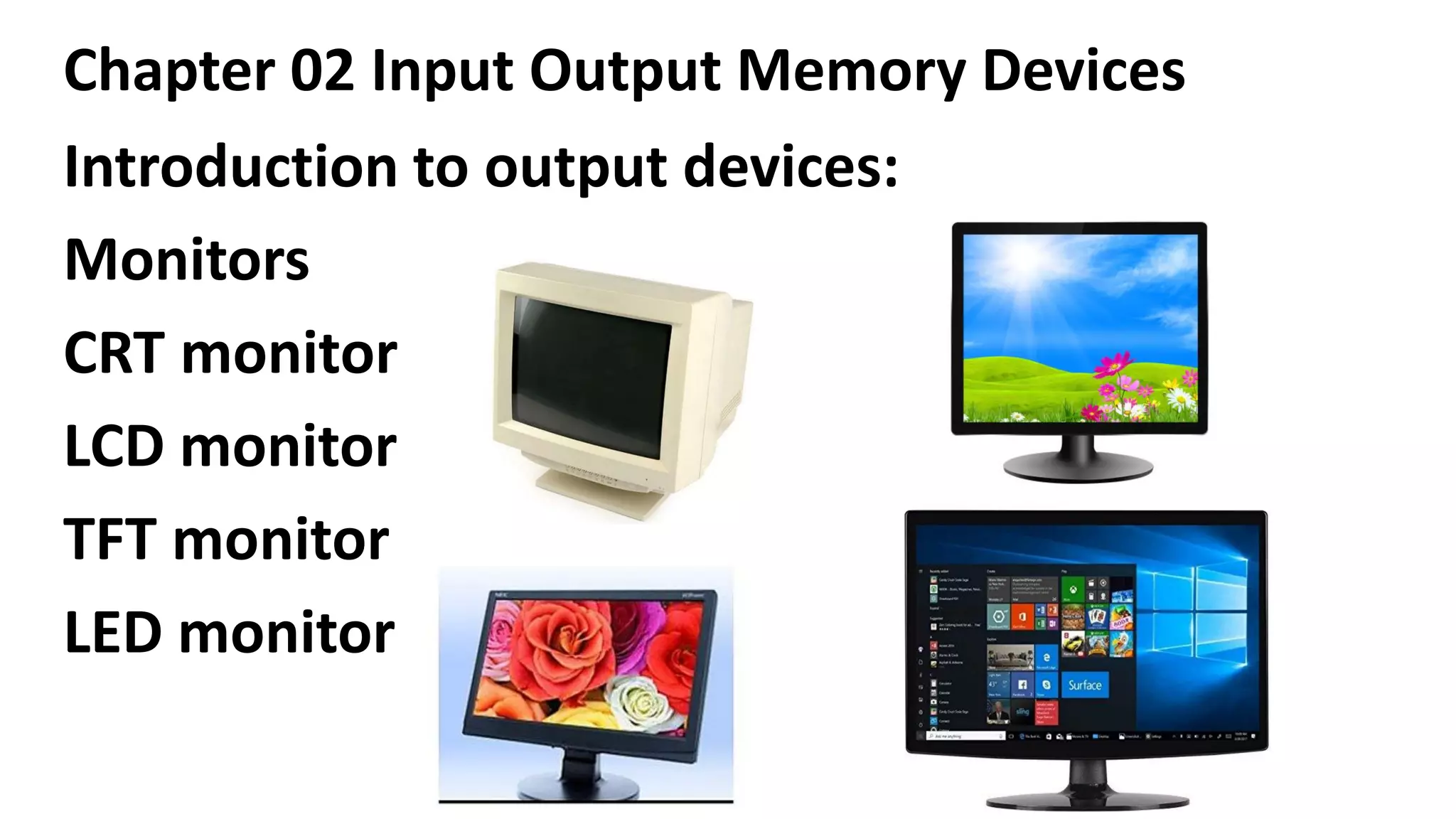
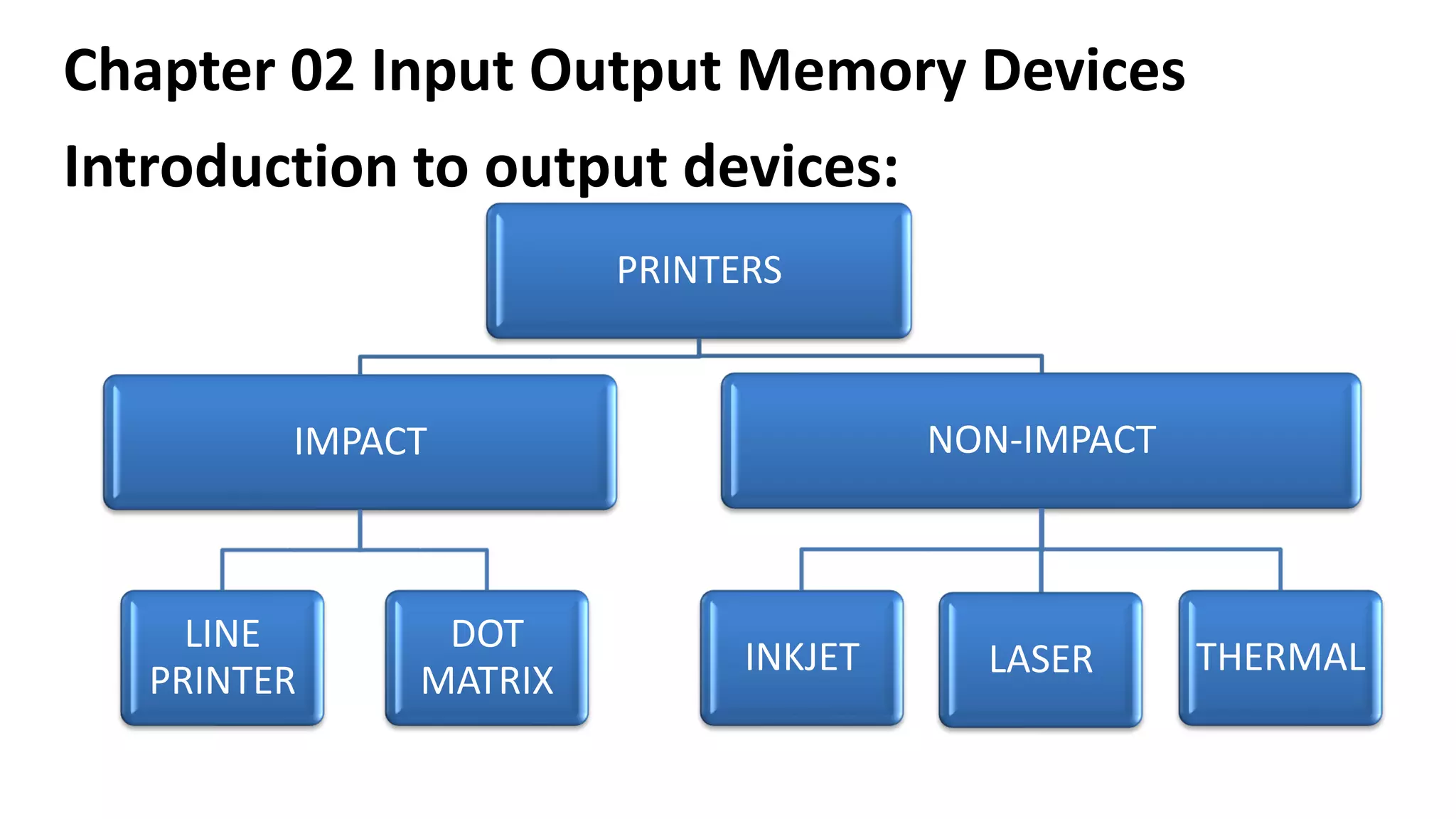
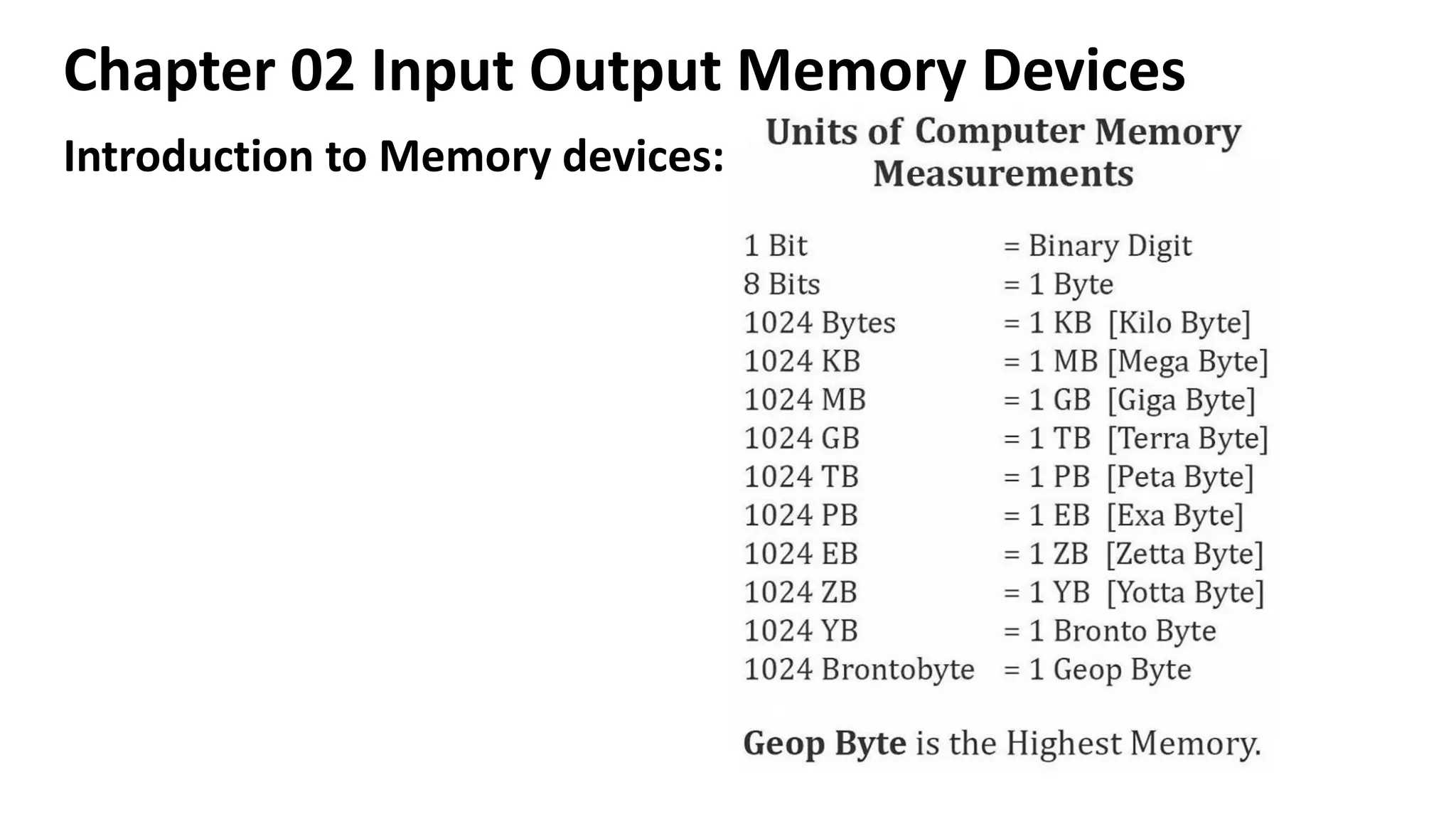
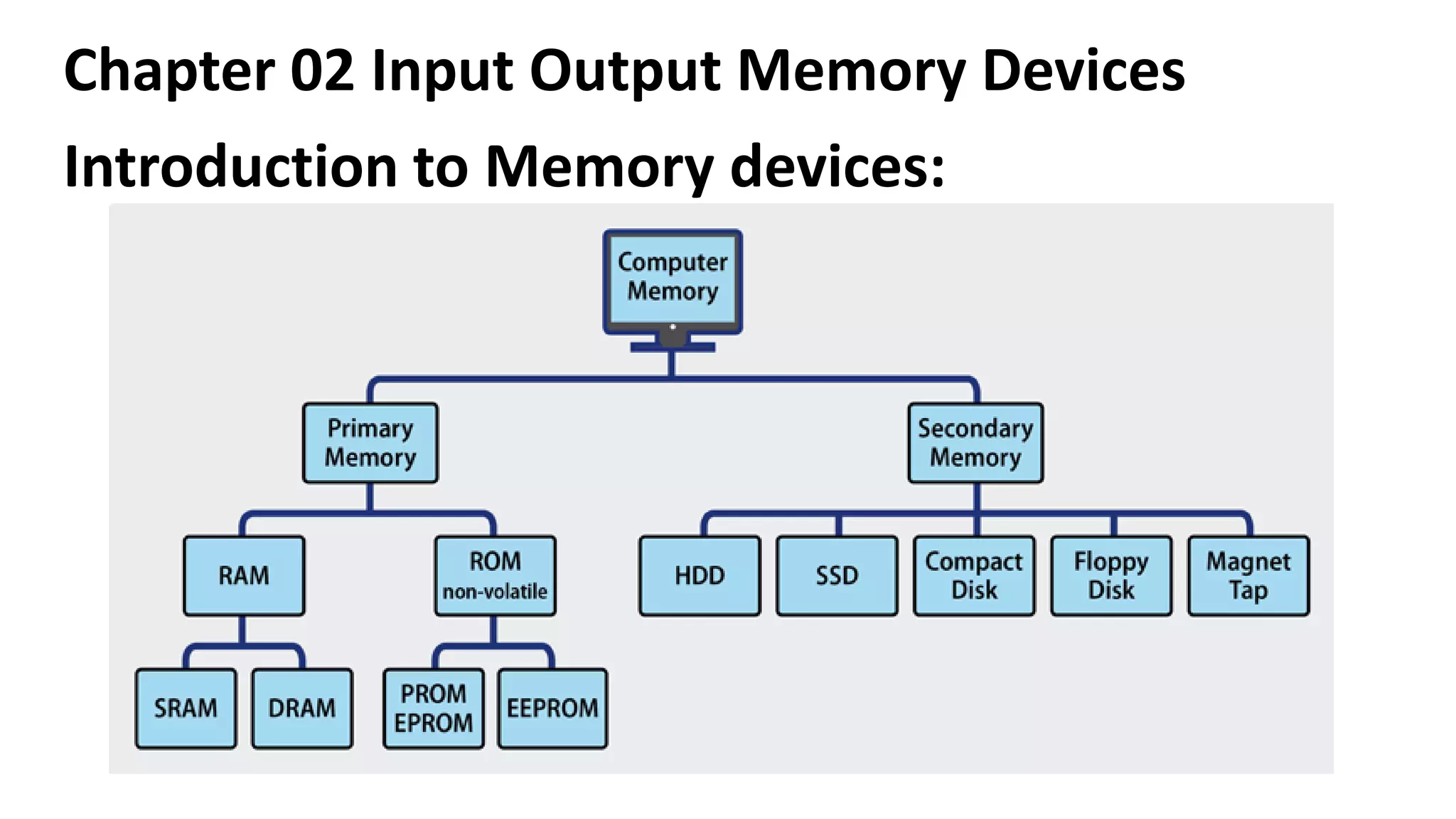
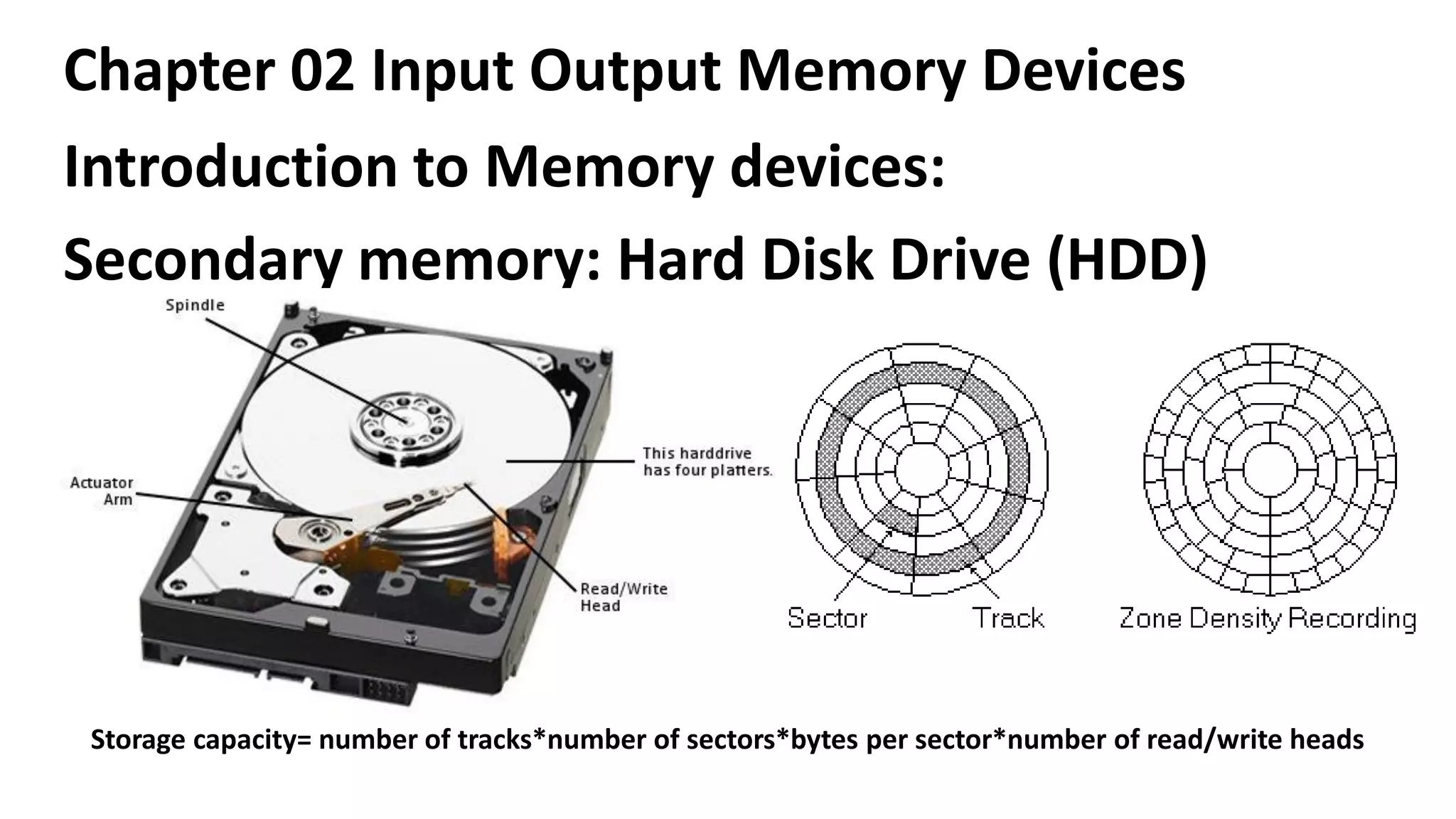
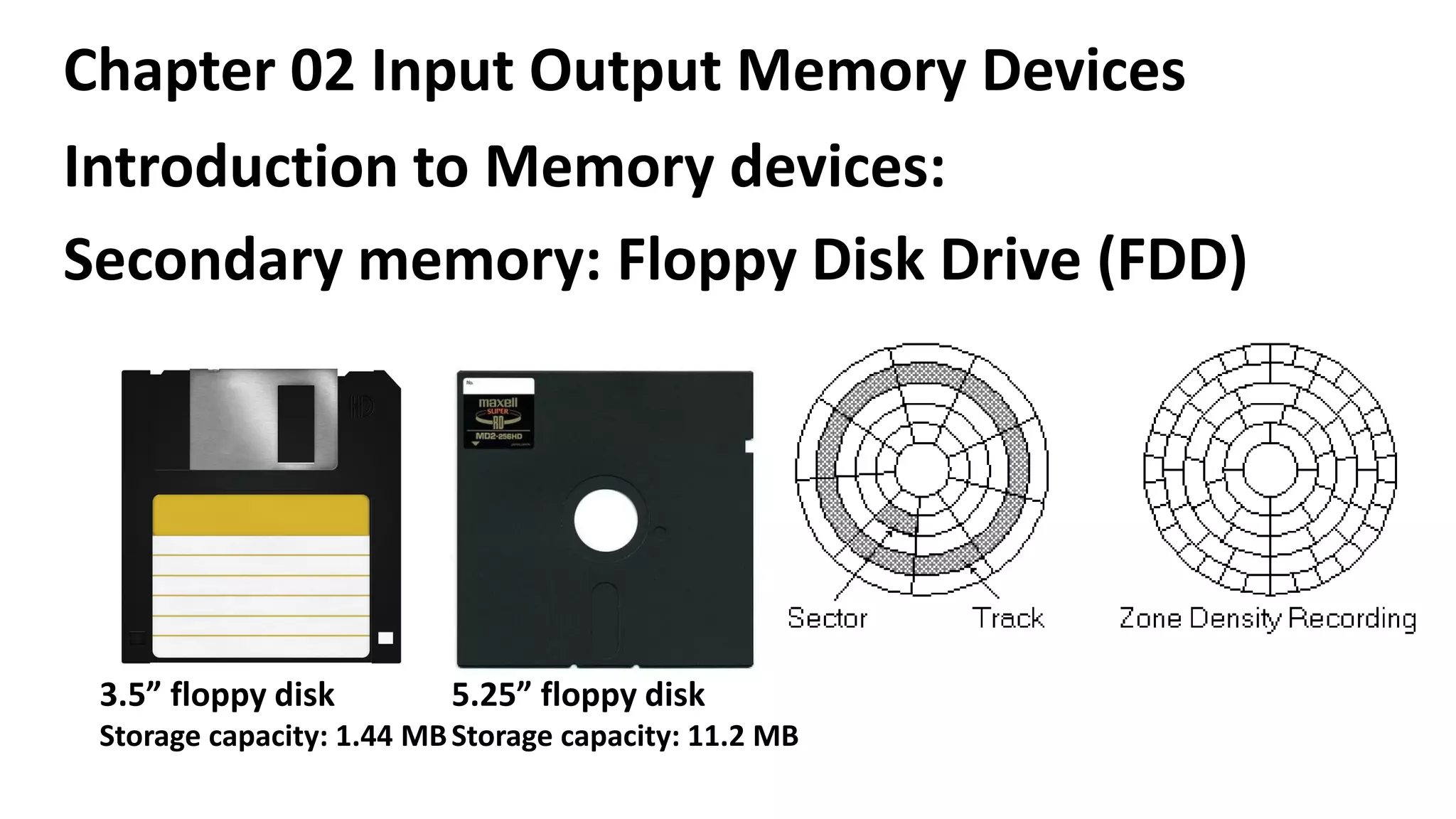
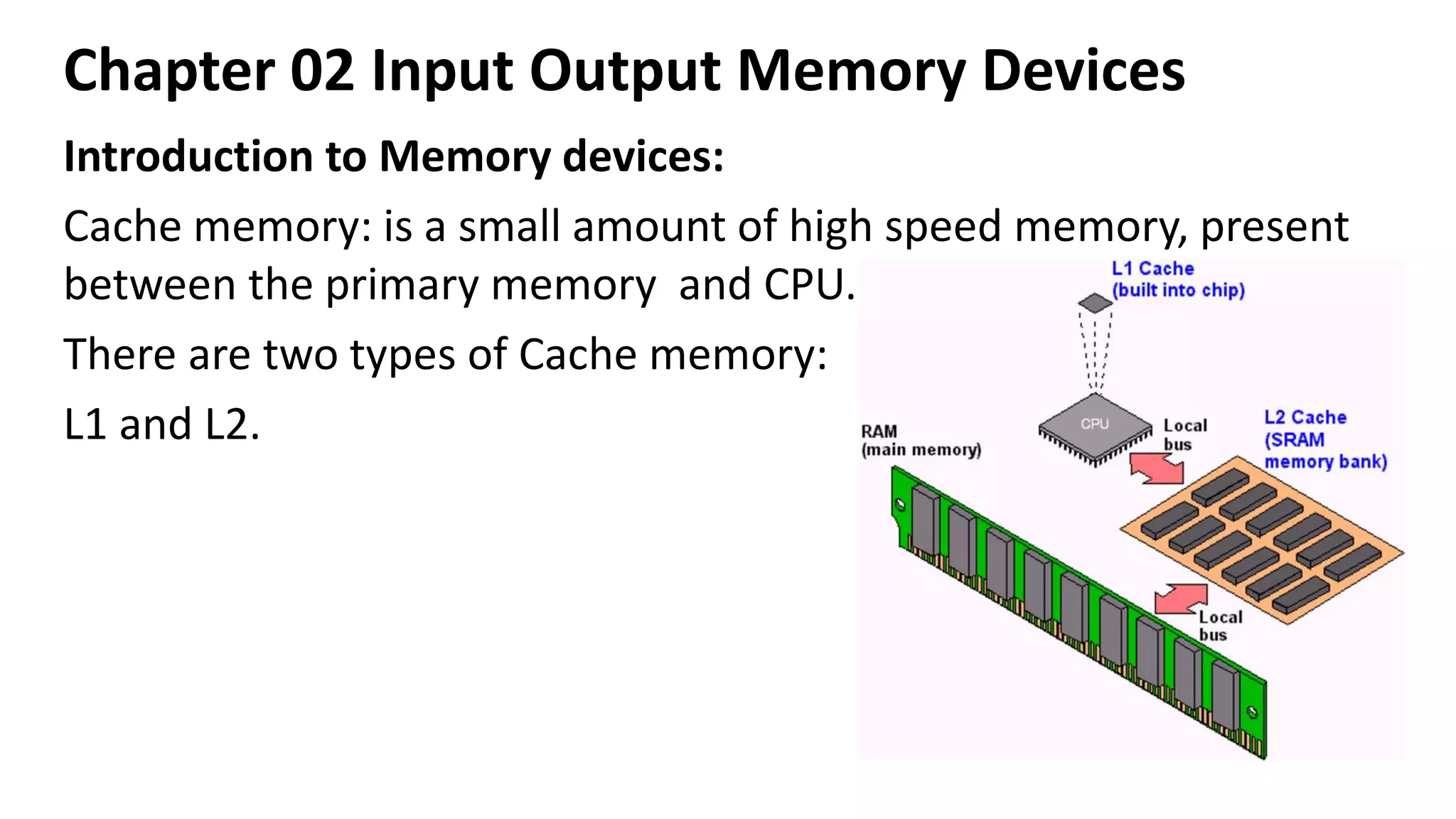
This document discusses various input, output, and memory devices. It describes different types of keyboards, mice, joysticks, and optical mark recognition devices as examples of input devices. As output devices it examines monitors, printers including impact, non-impact, inkjet, laser, and thermal printers, as well as plotters and speakers. It also discusses hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and portable storage devices as examples of secondary memory and how cache memory works.