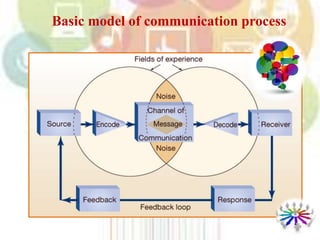
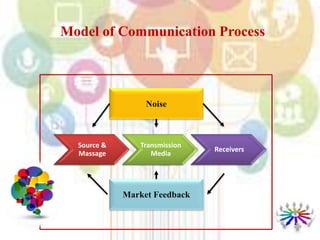
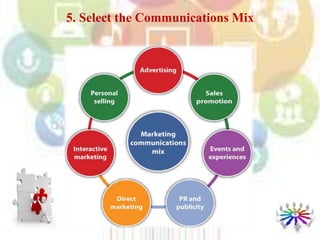
This document provides an overview of marketing communications and integrated marketing communications. It discusses key concepts like the SOSTAC model for developing an integrated marketing communications plan. The SOSTAC model involves performing a situation analysis, setting objectives, developing strategies, creating tactical plans, taking action, and applying controls to monitor and evaluate the plan. The document also outlines the basic elements and benefits of developing a formal communications plan, including identifying target audiences, setting communication objectives, developing message and media strategies, creating implementation schedules and budgets, and measuring results.