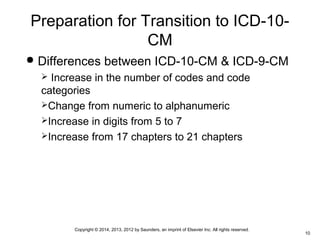
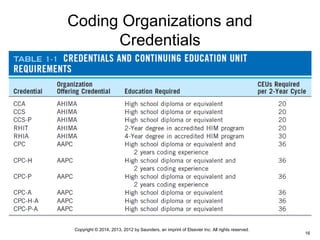
This document discusses the rationale for and history of medical coding. It covers the basics of coding including definitions of nomenclature and classification systems. The historical timeline of coding is reviewed, beginning in 1893 with Bertillon's system, and progressing to the current ICD-9 system used in the United States. Preparation for the upcoming transition to ICD-10 in 2014 is also addressed, including differences between the two systems and training needs for coders. The roles of various coding organizations are defined as well as common credentials for medical coders. Ethical standards, compliance, and confidentiality considerations are also summarized.