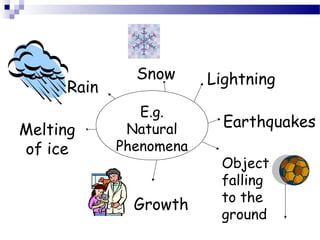
This document discusses the definition and importance of science. It defines science as the systematic study of nature through observation and experimentation. The main branches of science are then outlined such as physics, chemistry, biology, and others. The importance of science in areas like agriculture, medicine, transportation, and industry is highlighted through examples. Careers in science like doctors, engineers, and microbiologists are also mentioned. The document concludes that scientific knowledge benefits mankind through new discoveries, technologies, and job opportunities.