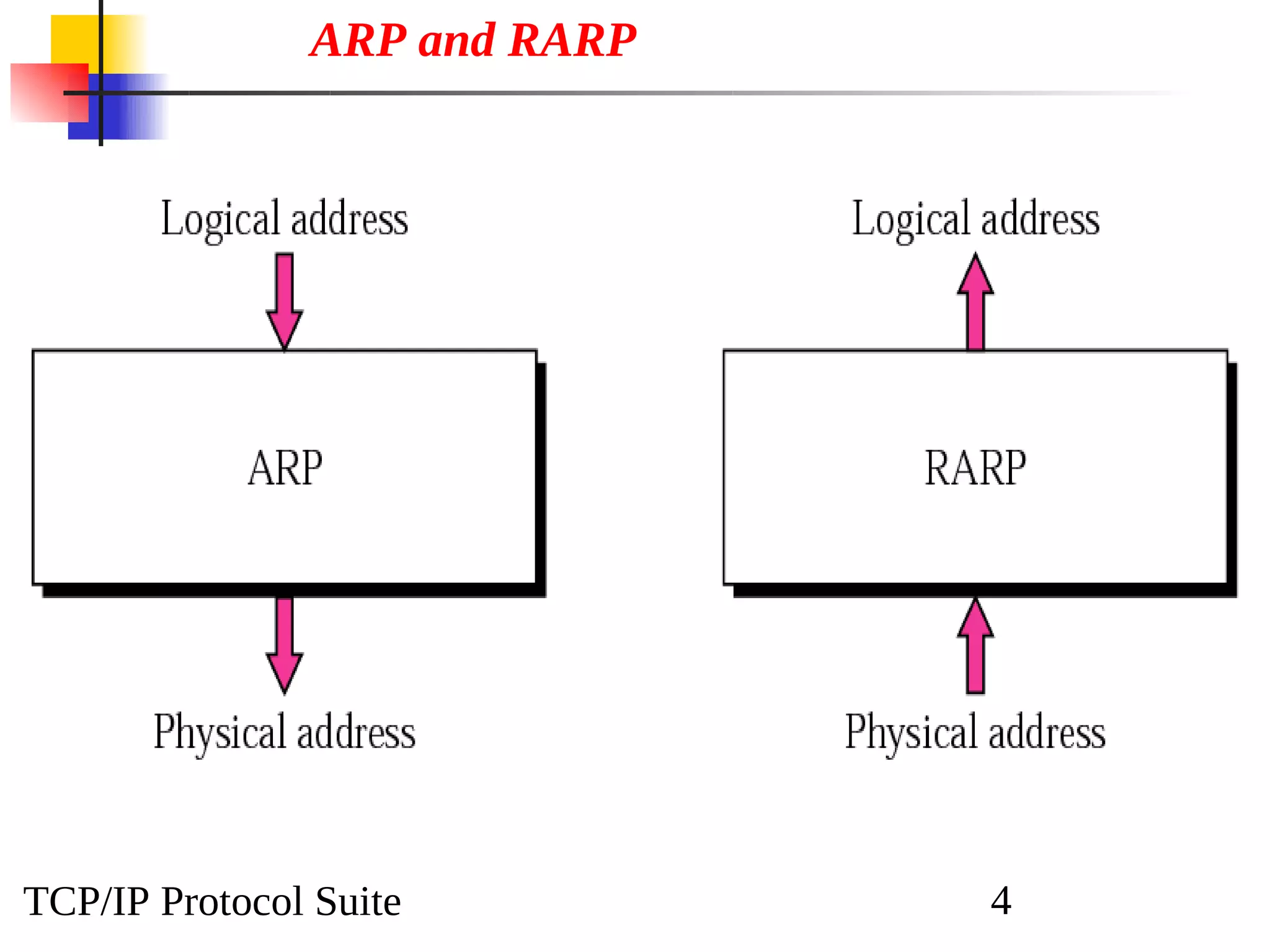
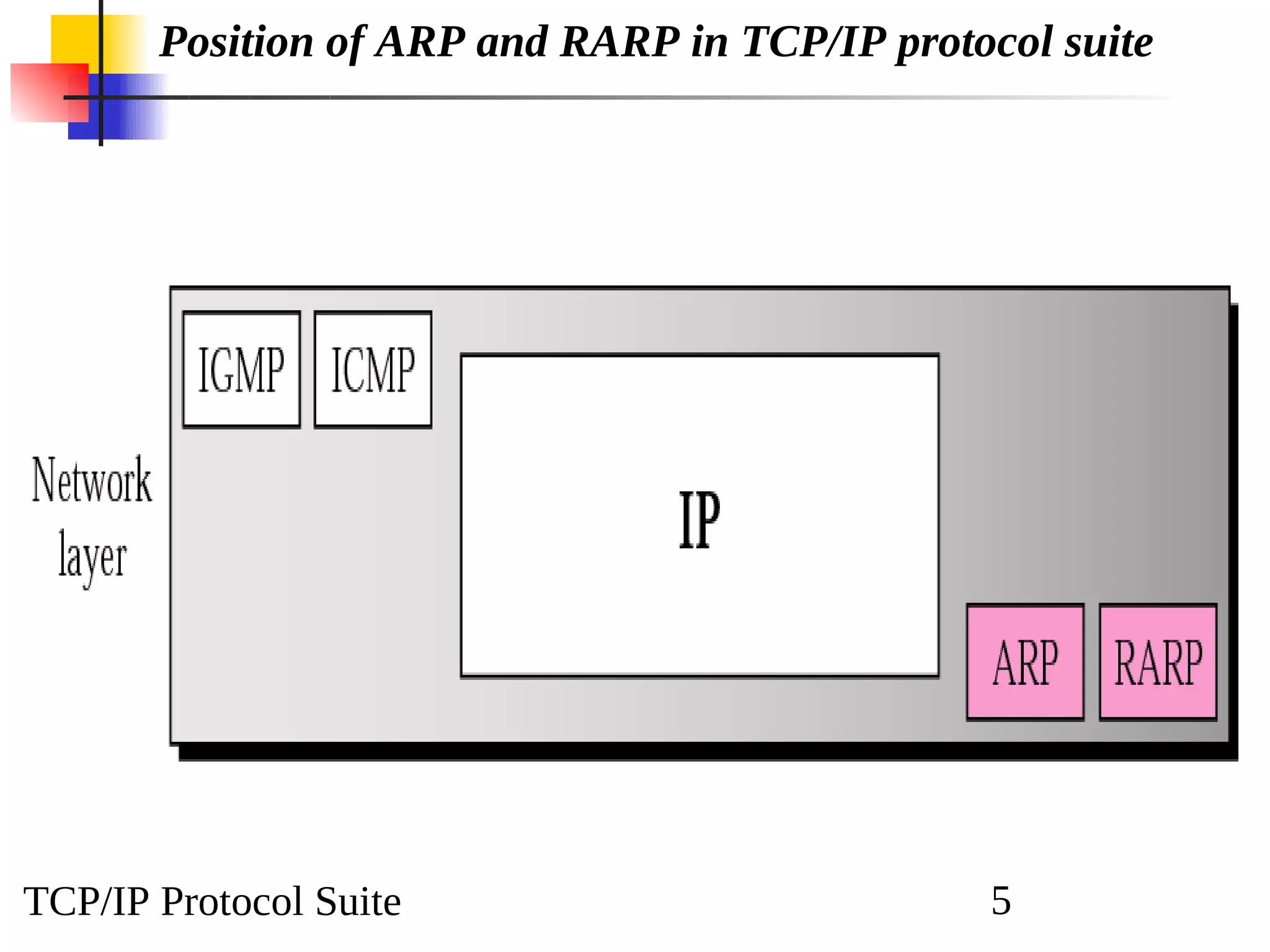
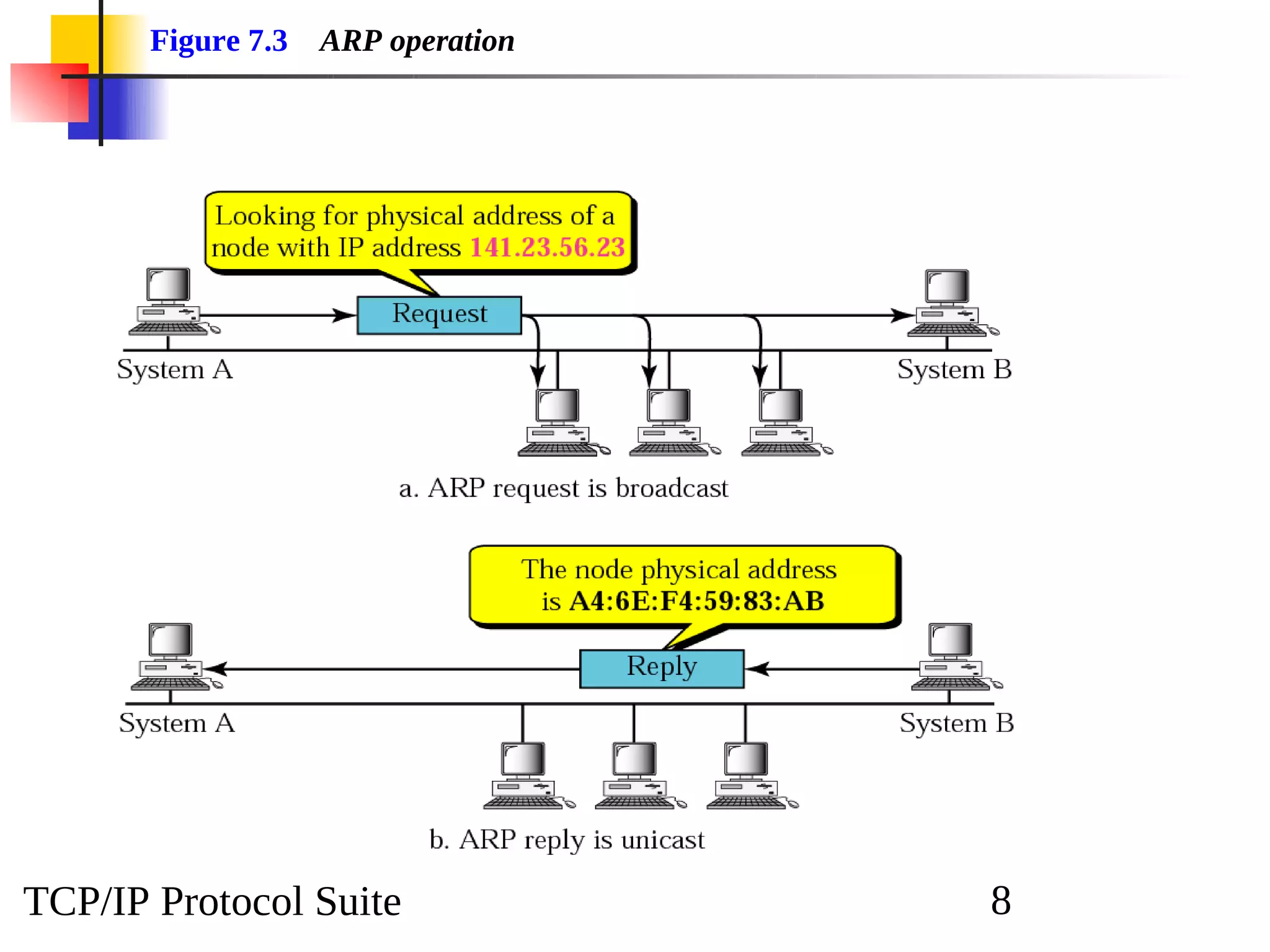
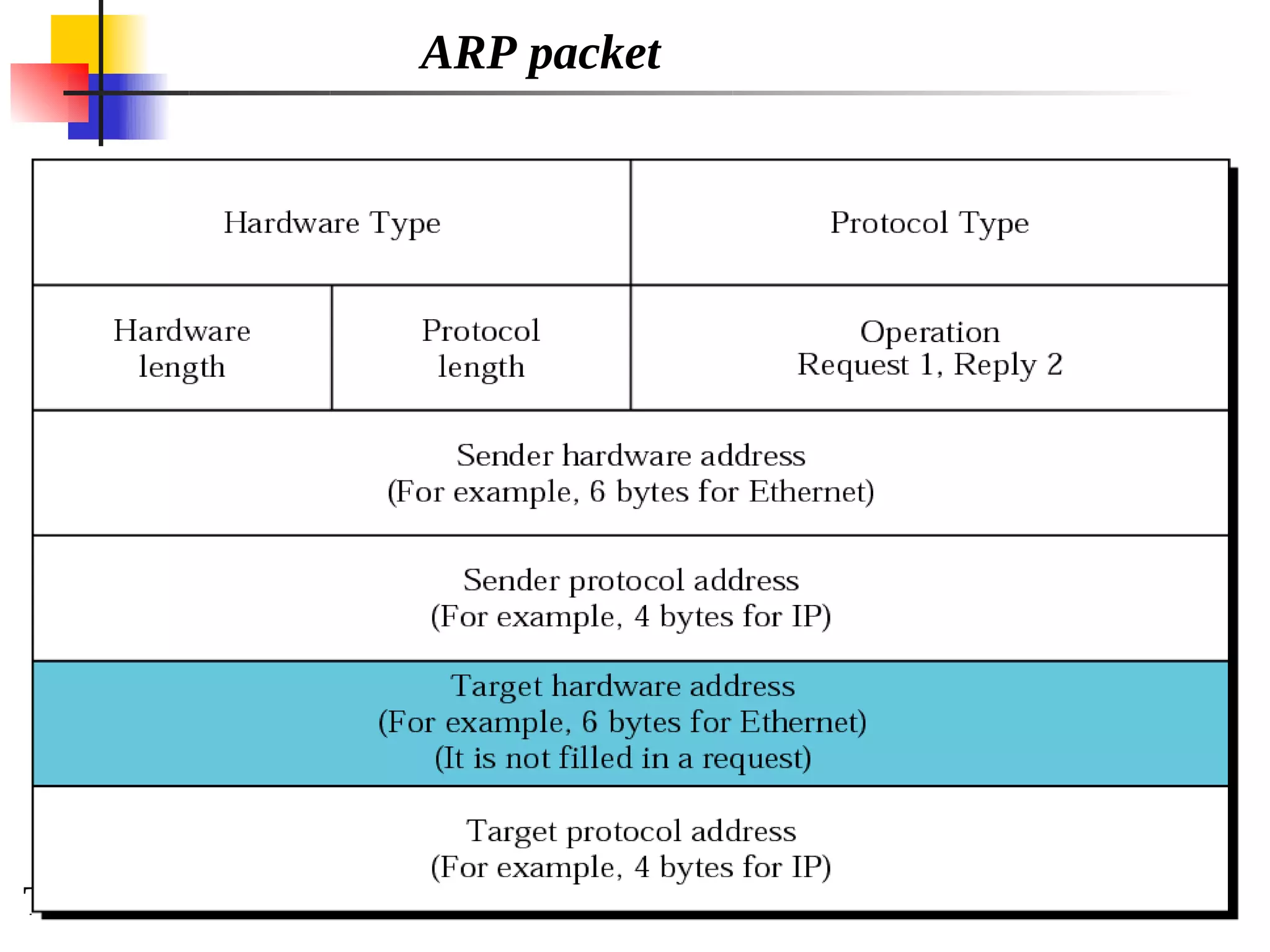
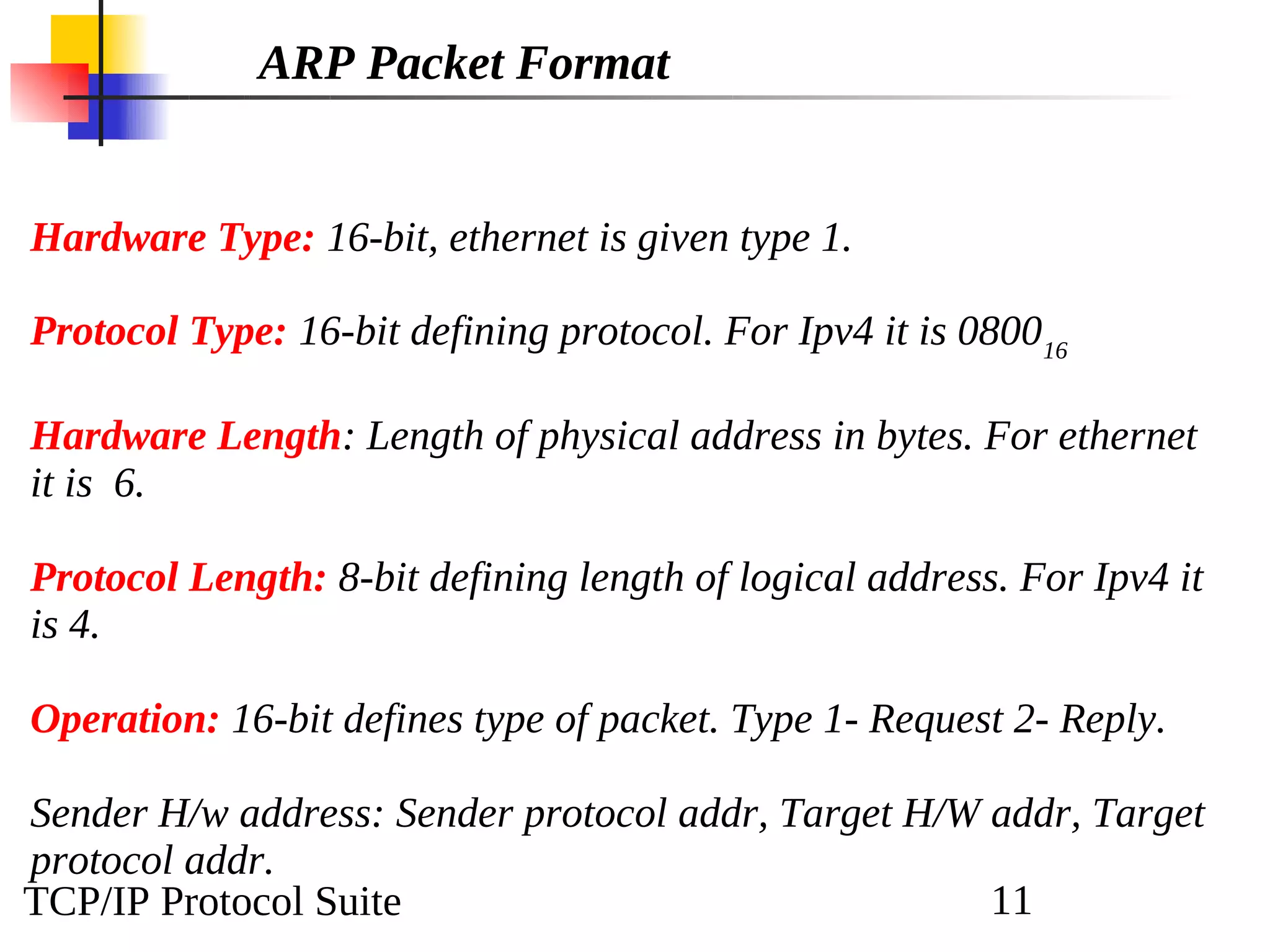
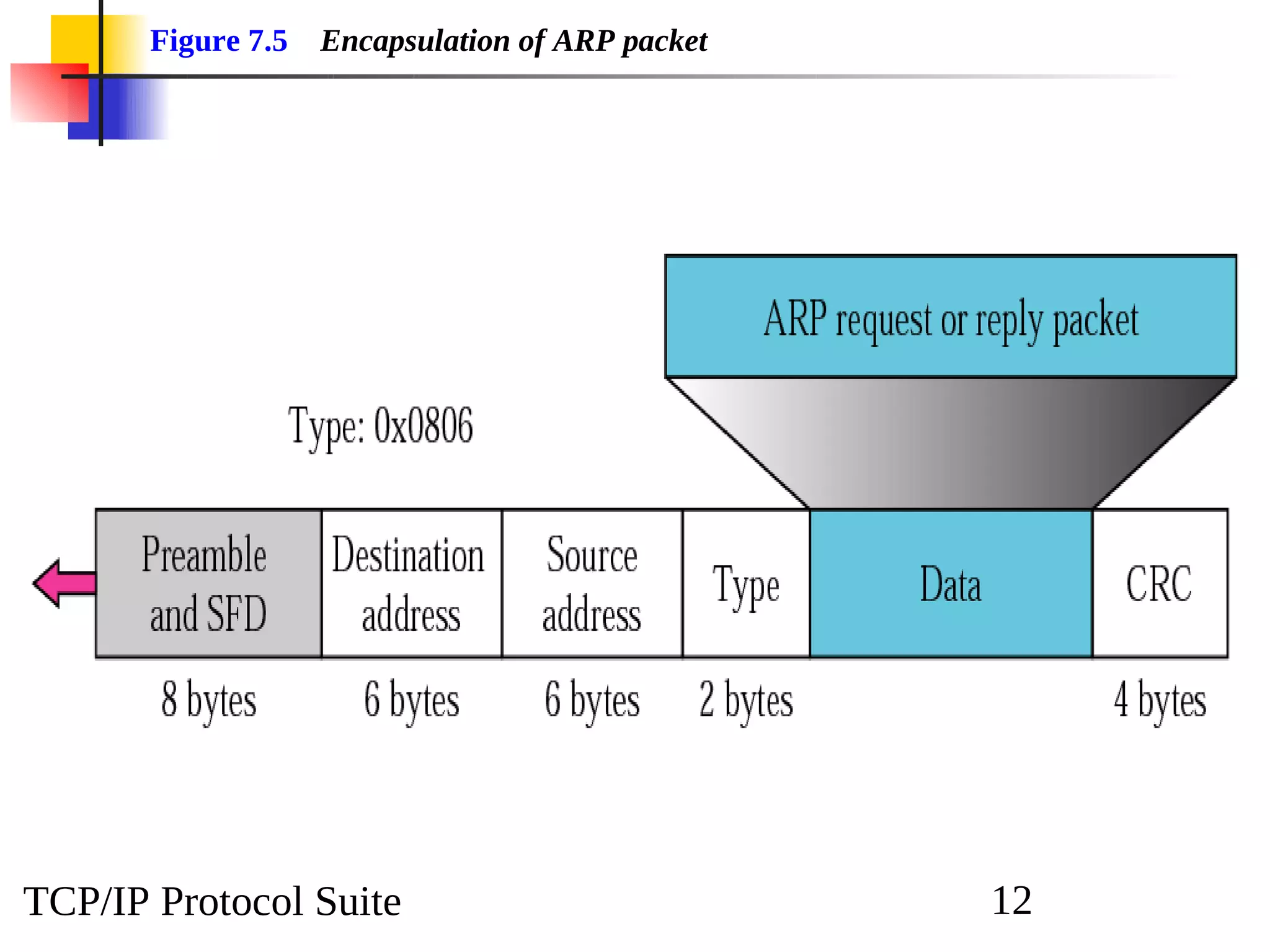
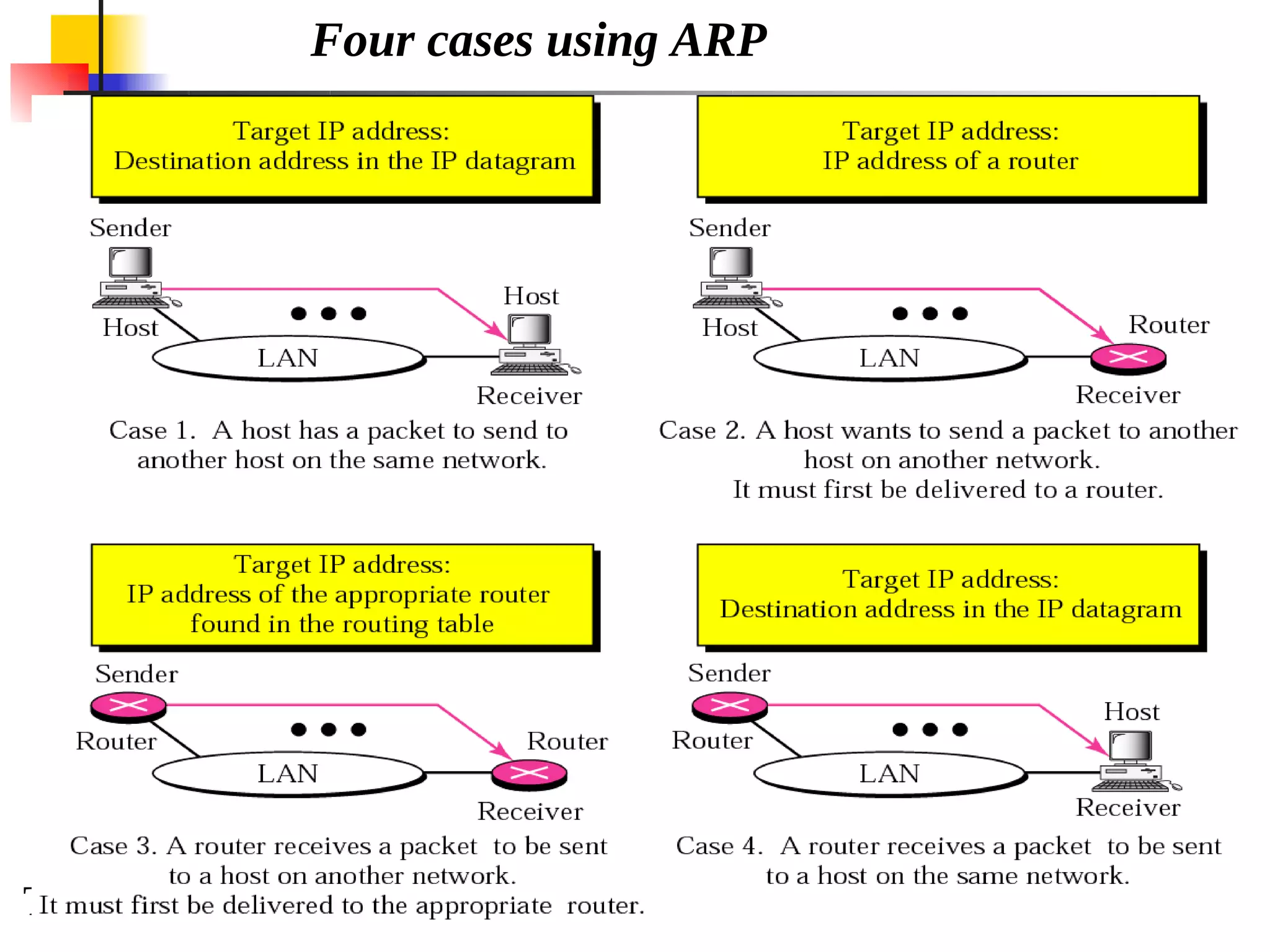
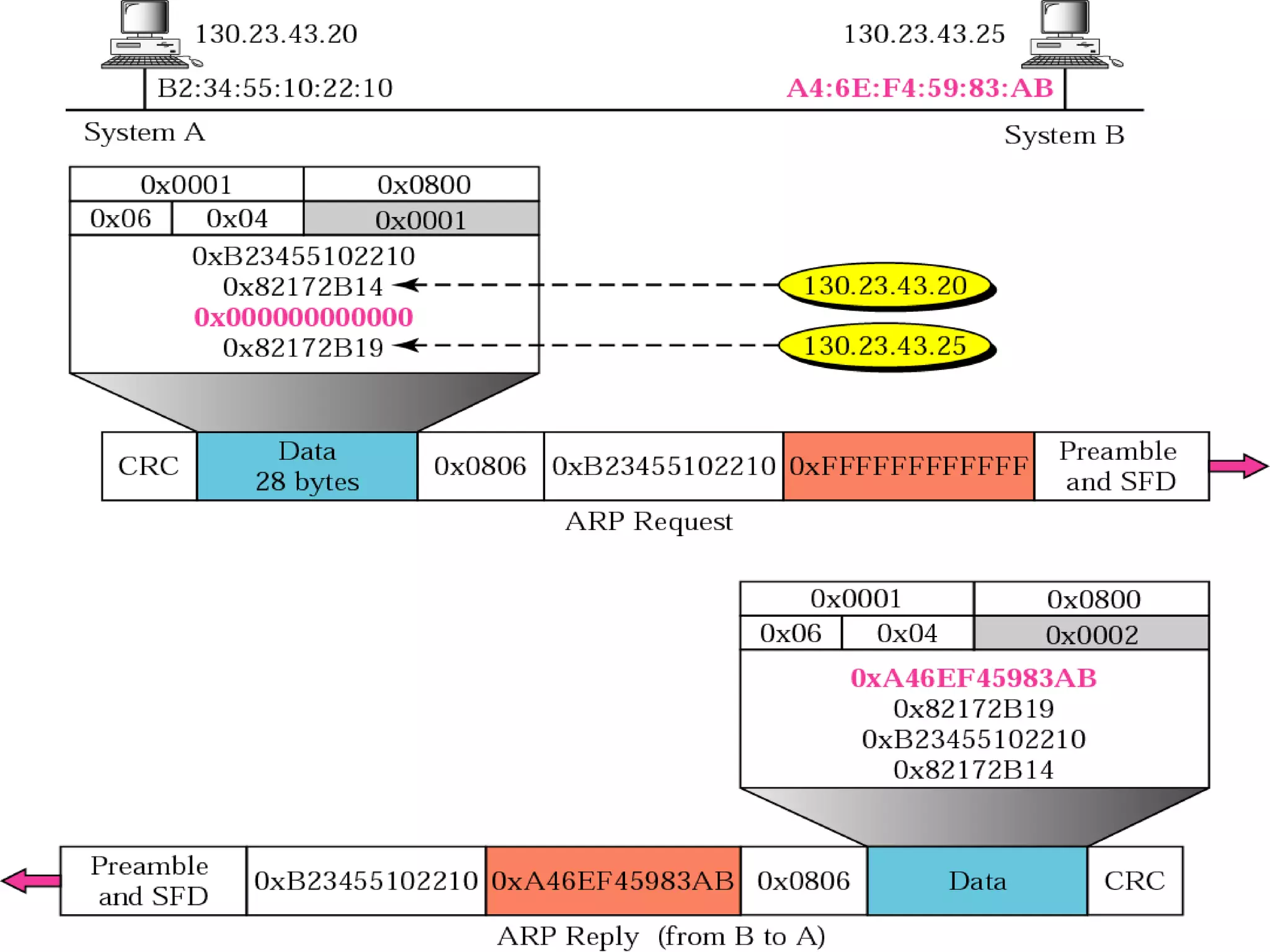
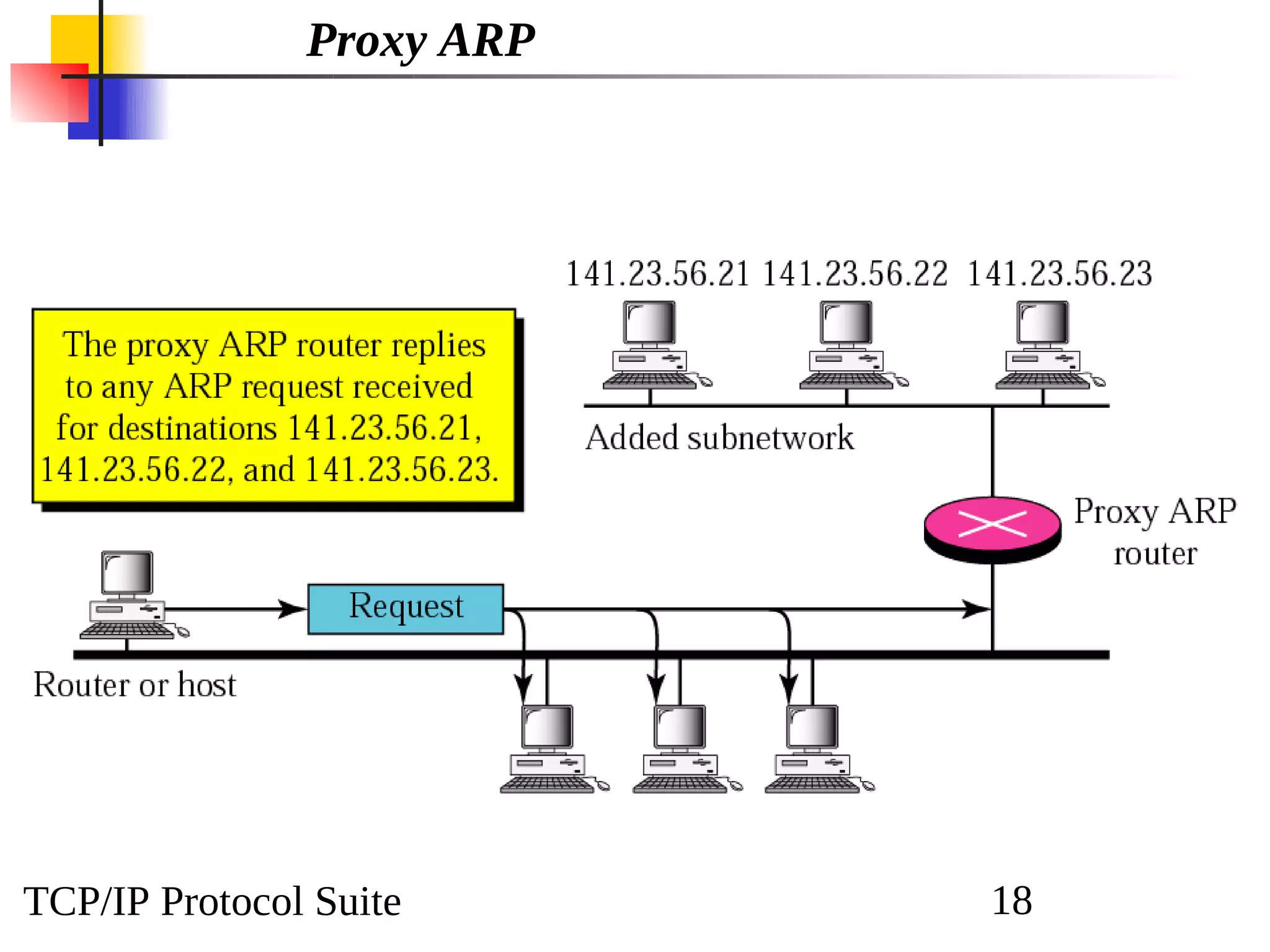
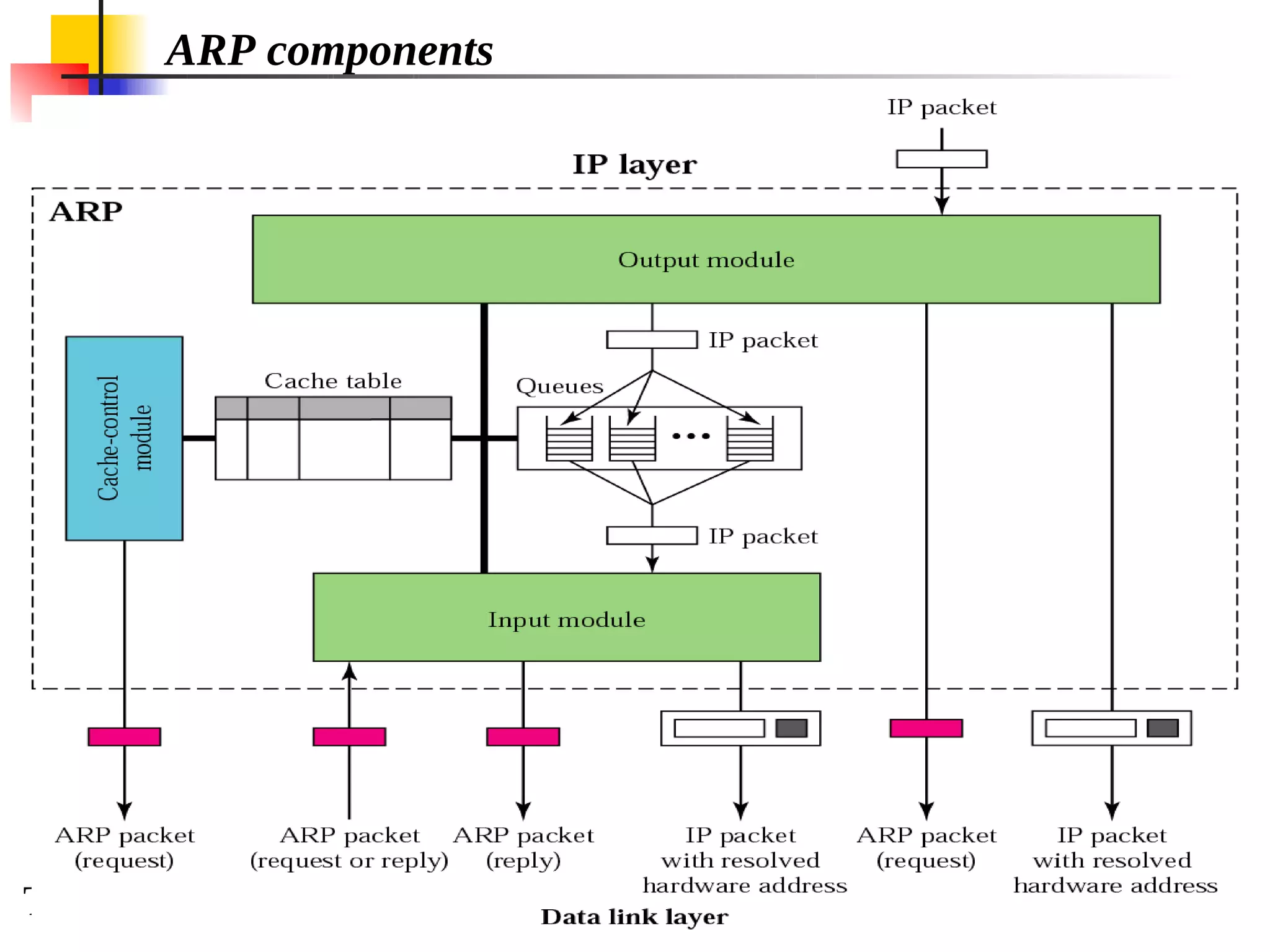
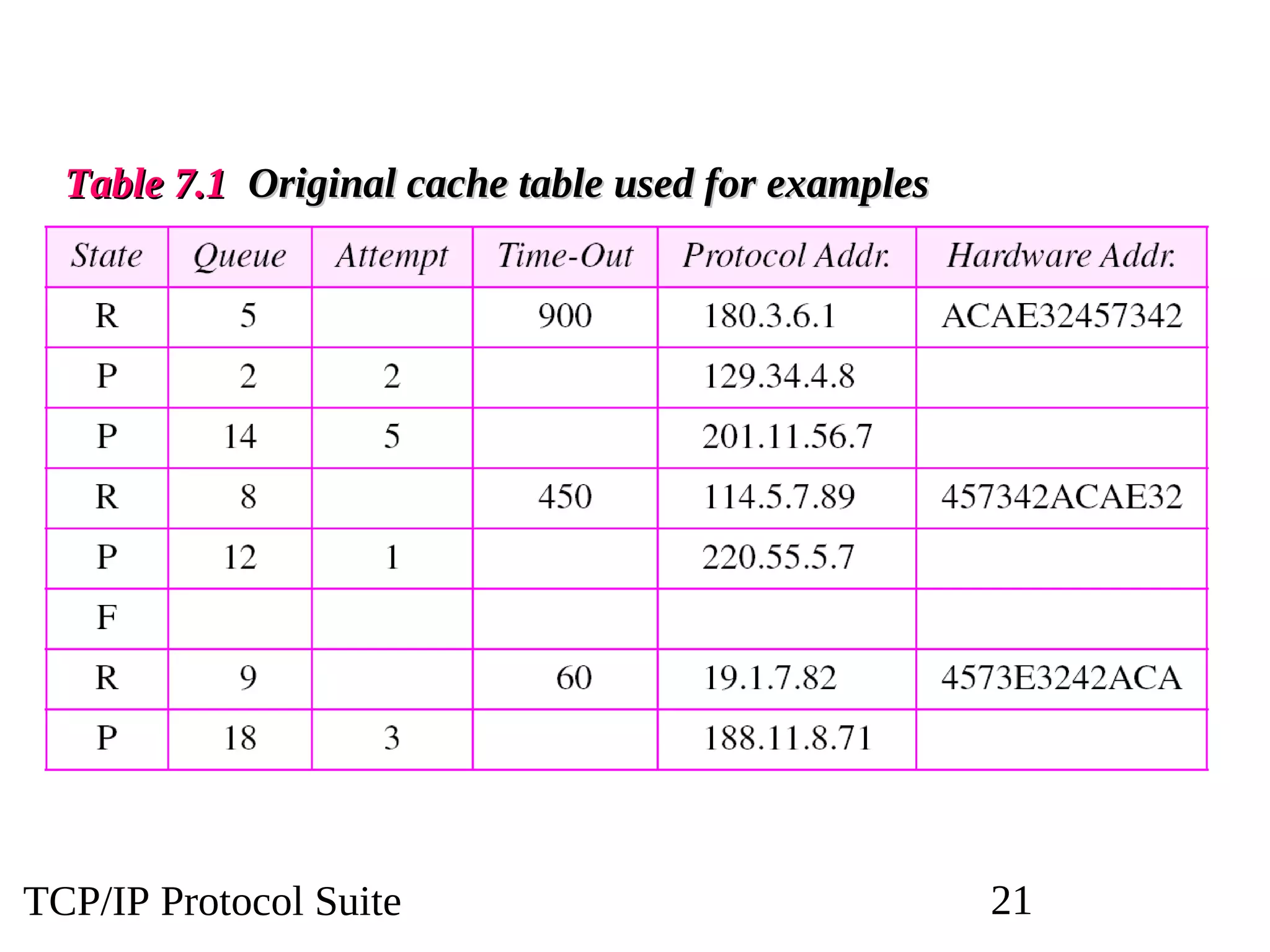
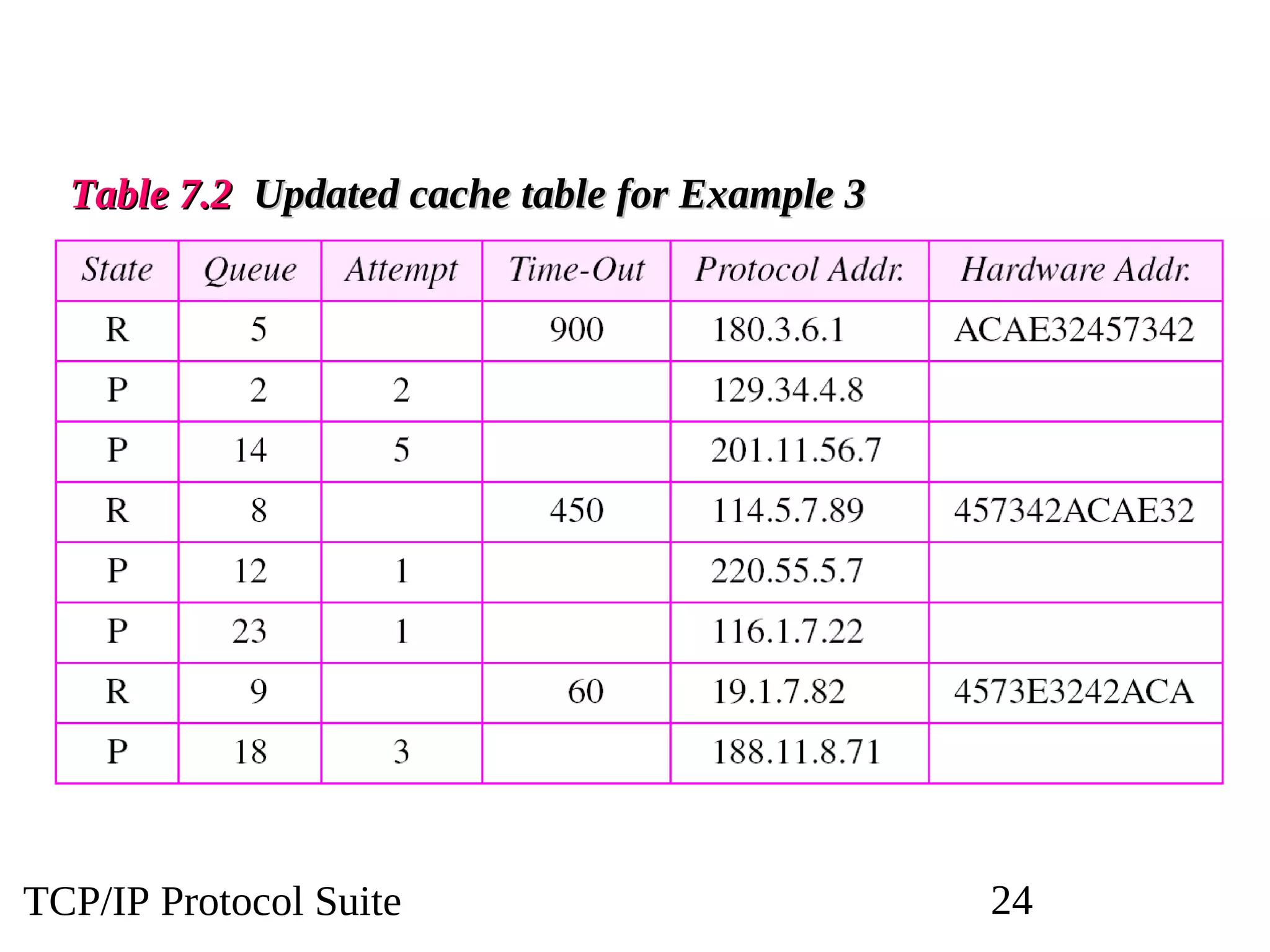
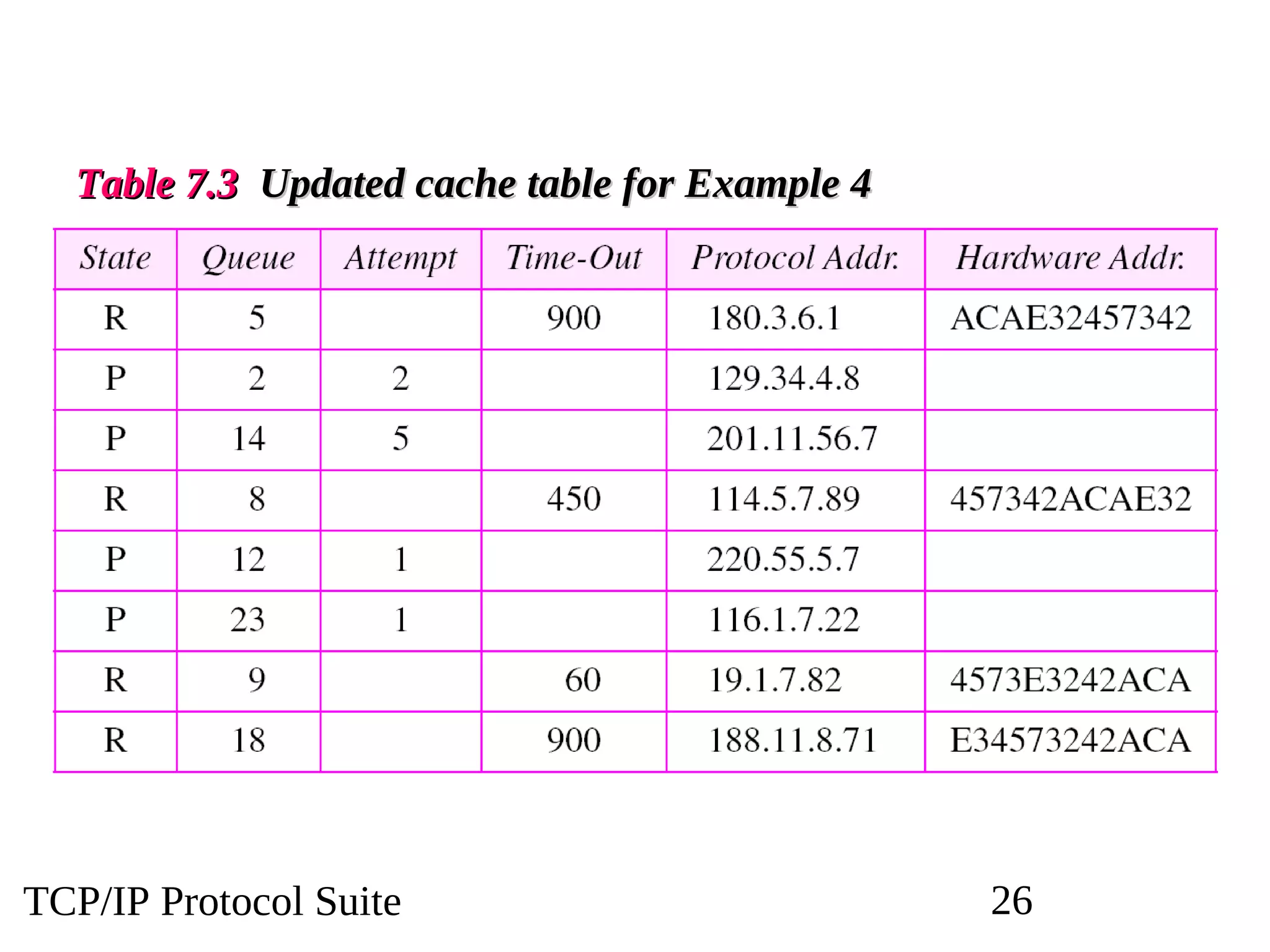
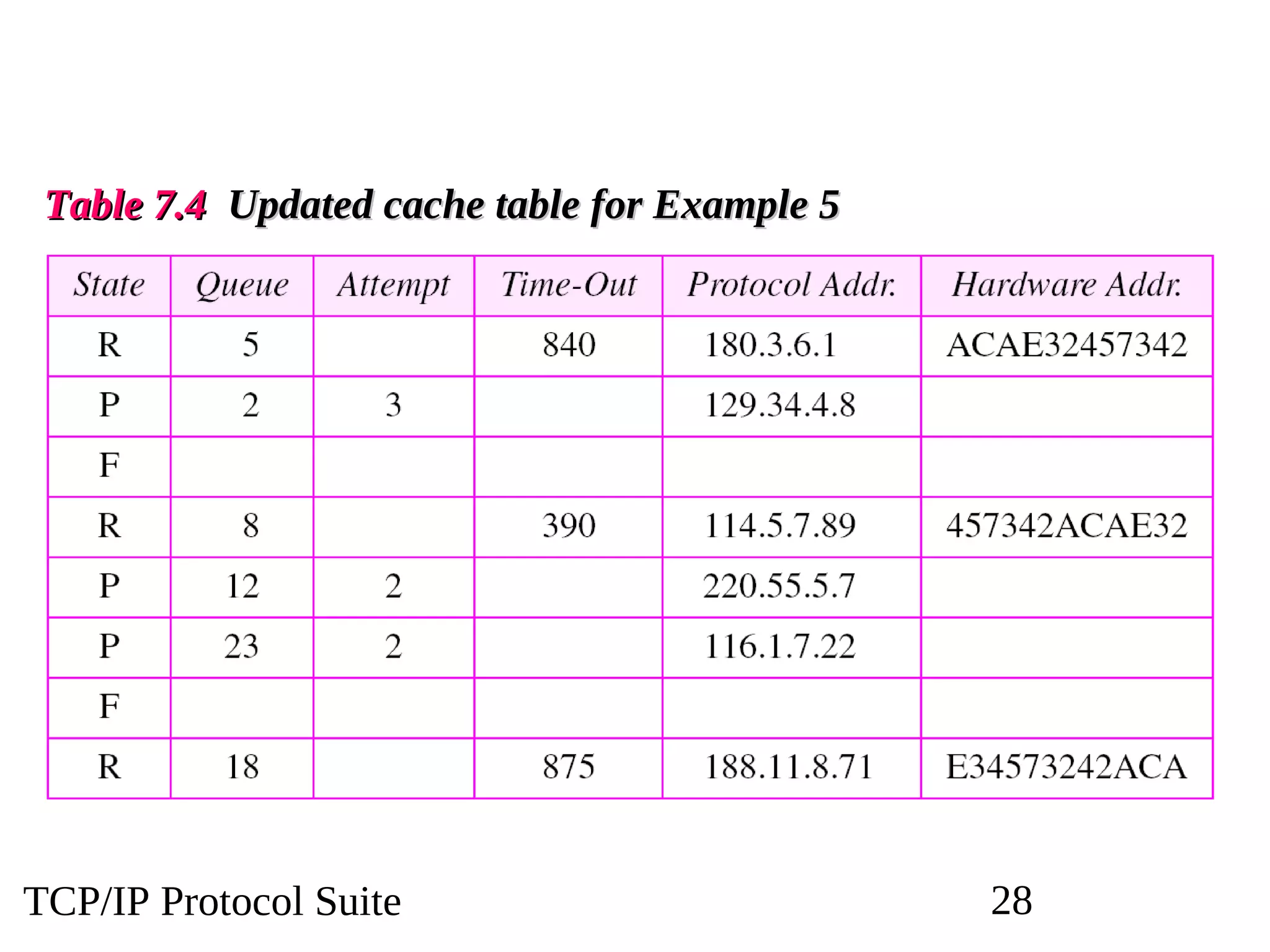
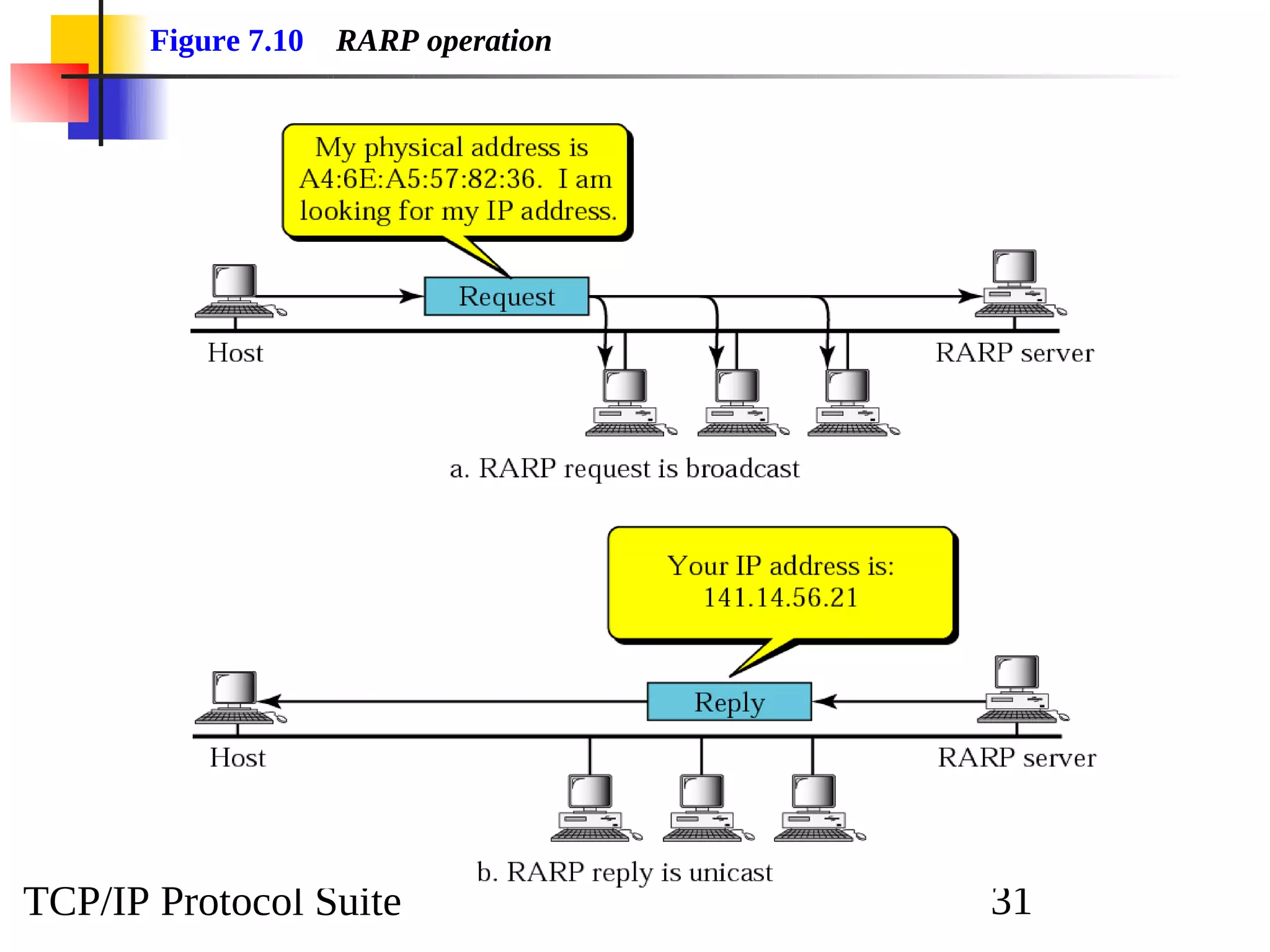
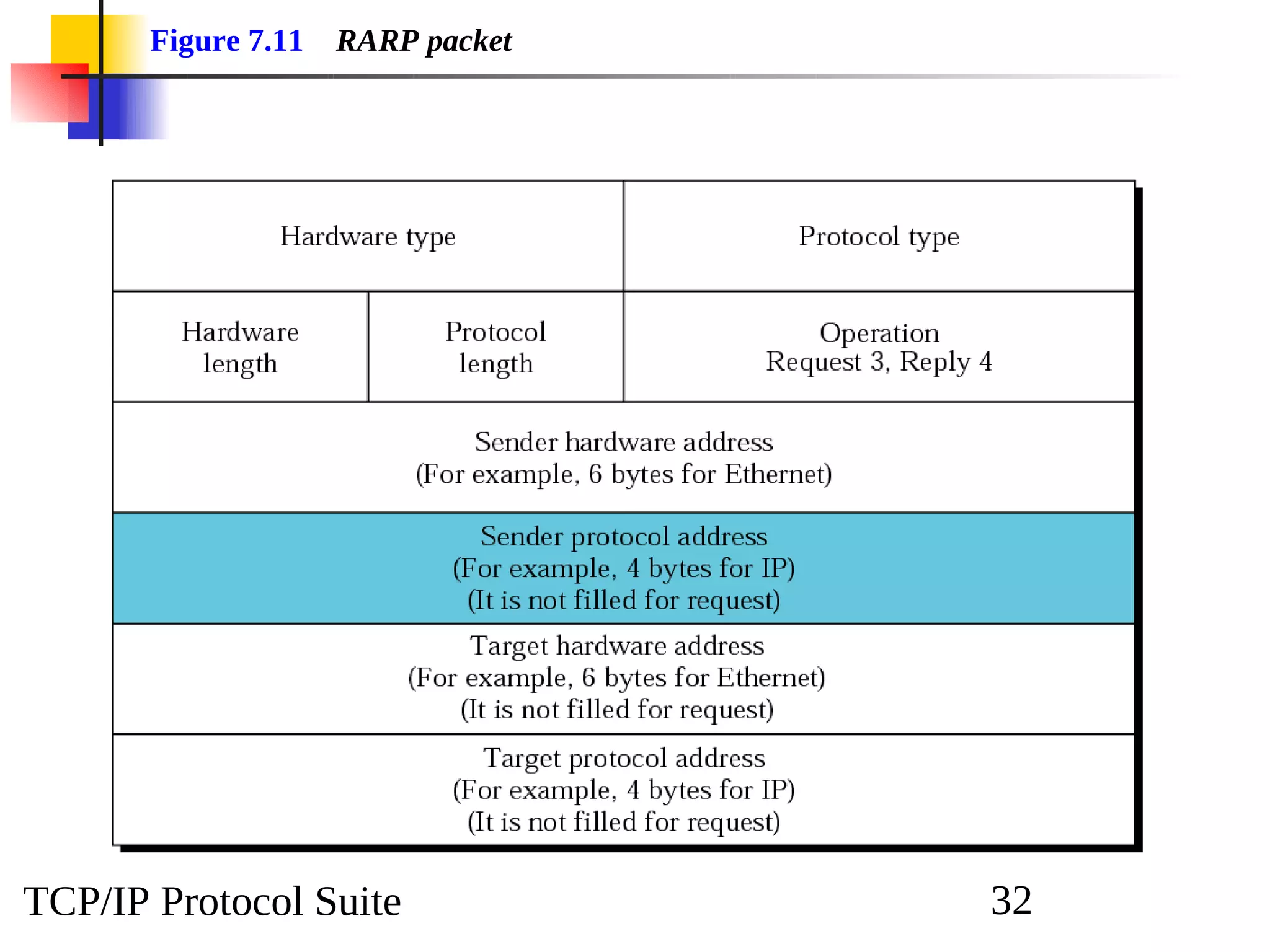
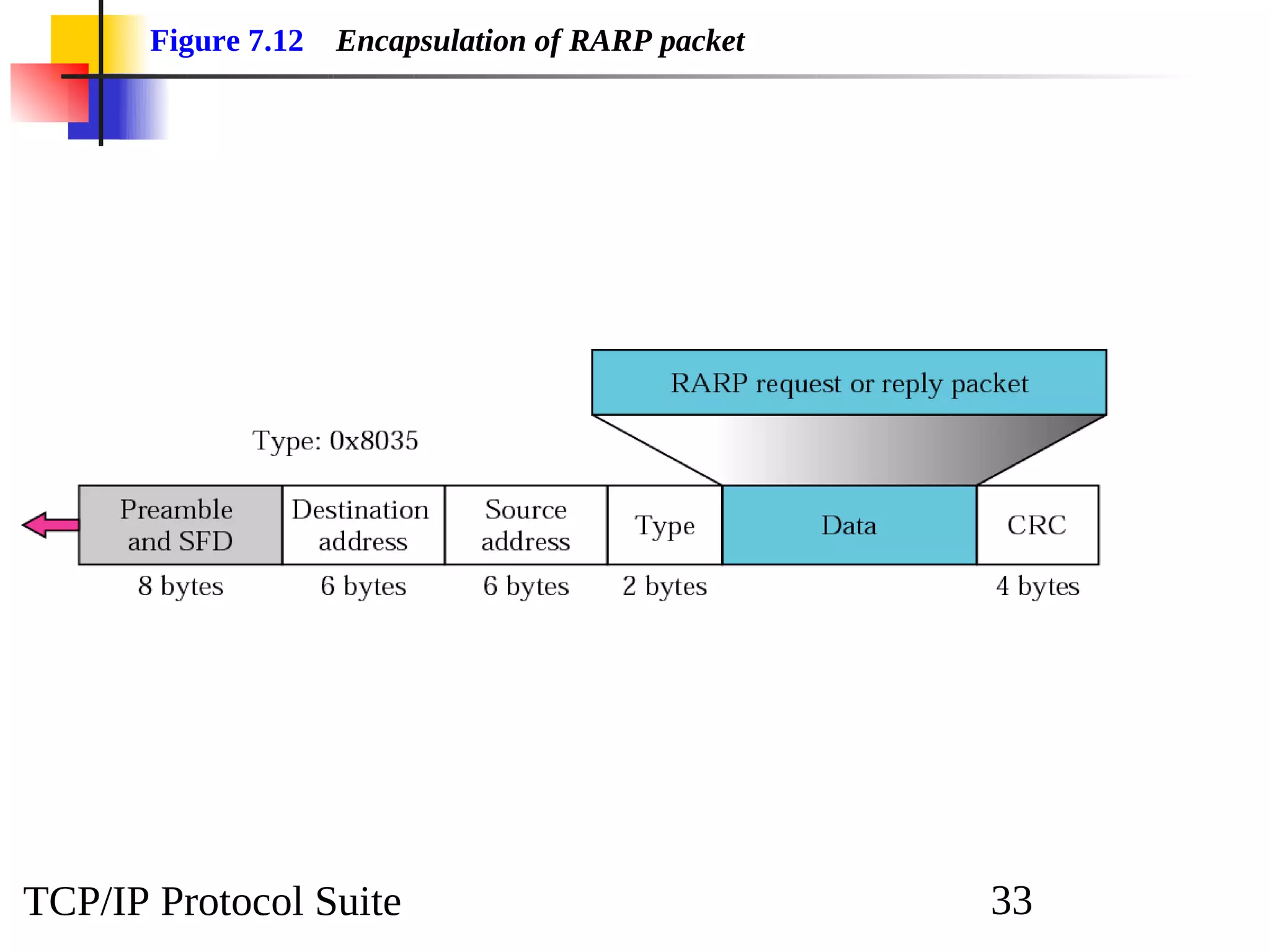
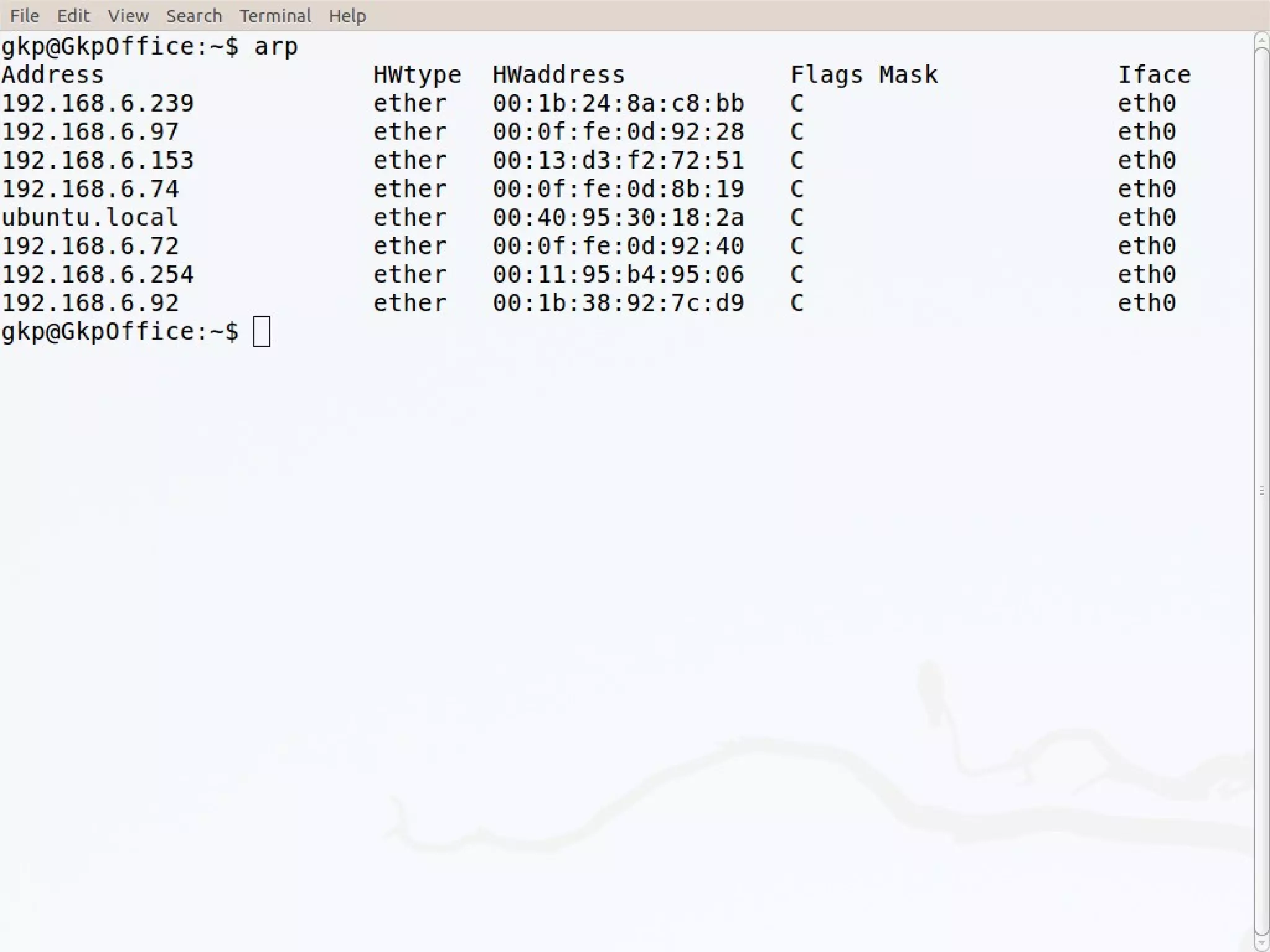
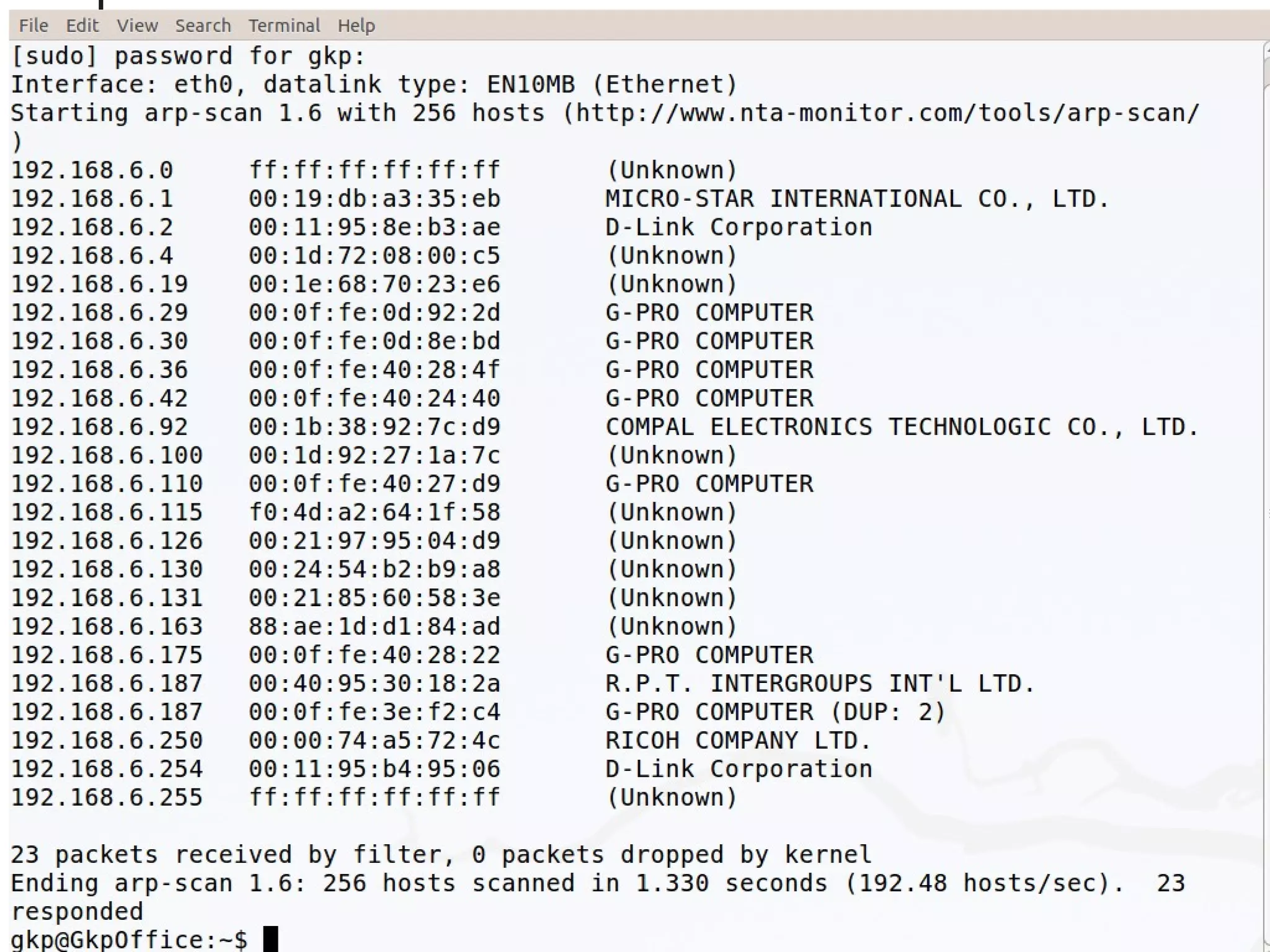
This document discusses the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP). ARP maps logical IP addresses to physical hardware addresses, allowing communication on a local area network. RARP performs the inverse mapping of physical to logical addresses. The document covers the need for and use cases of ARP and RARP, their packet formats, encapsulation, and key components like caches, queues and servers that perform the address mappings.