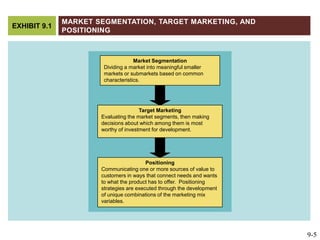
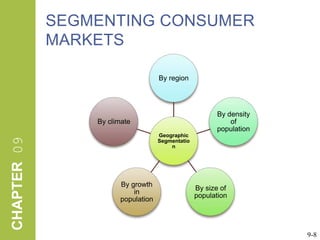
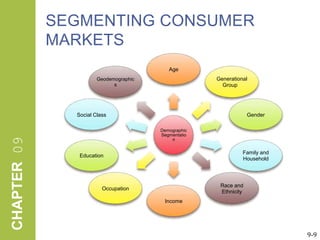
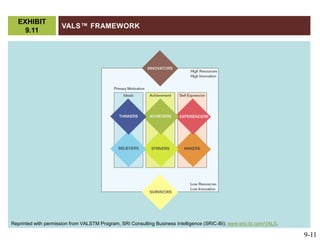
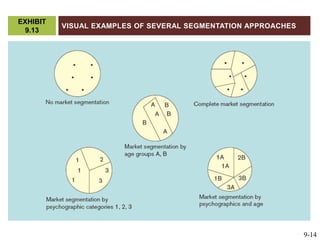
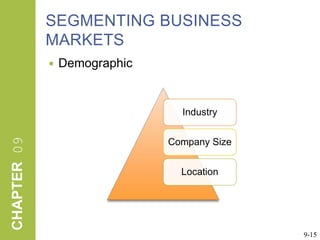
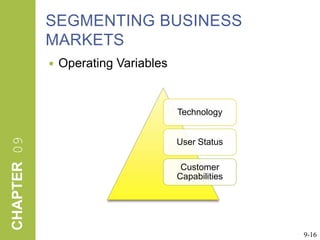
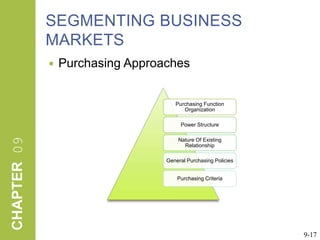
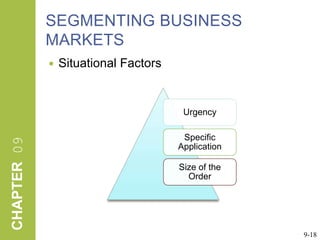
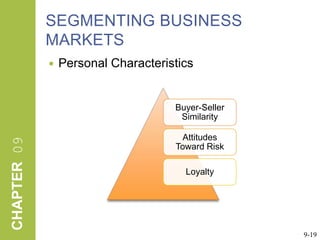
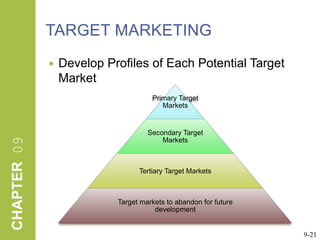
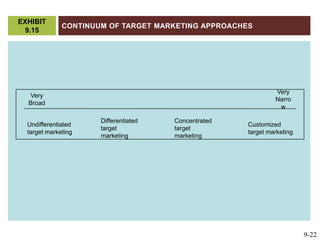
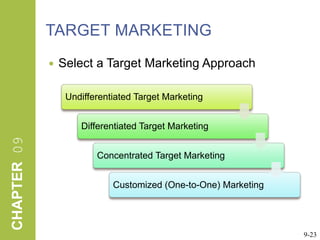
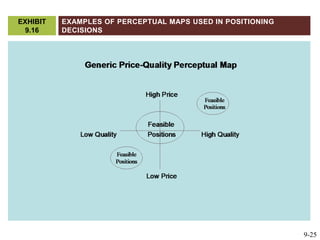
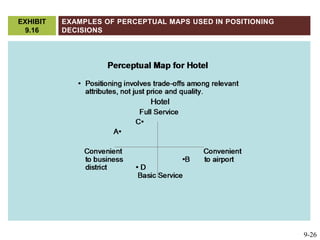
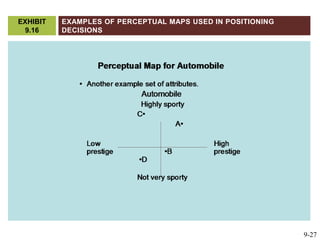
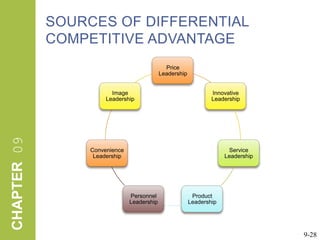
This document discusses market segmentation, target marketing, and positioning. It defines these concepts and explains how firms use segmentation to divide markets into meaningful subgroups based on common characteristics. Target marketing involves evaluating segments and deciding which to focus on developing. Positioning communicates a product's value to customers by connecting its attributes to consumer needs. The document provides examples of segmentation approaches like demographic, psychographic, and behavioral segmentation for both consumer and business markets. It also outlines the target marketing continuum and discusses developing segment profiles and selecting target markets. Perceptual maps are presented as a positioning tool, and sources of differentiation and potential positioning errors are reviewed.