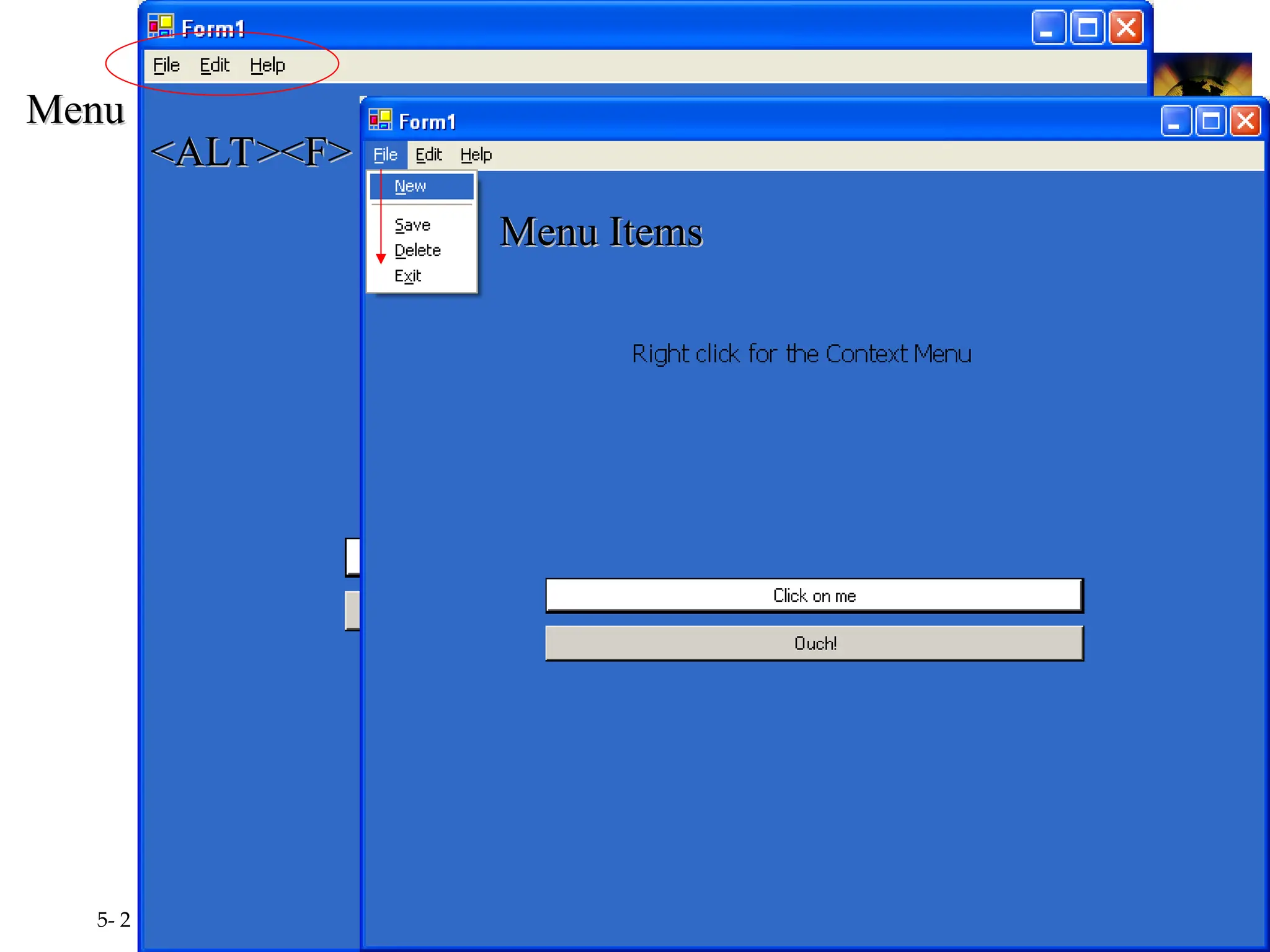
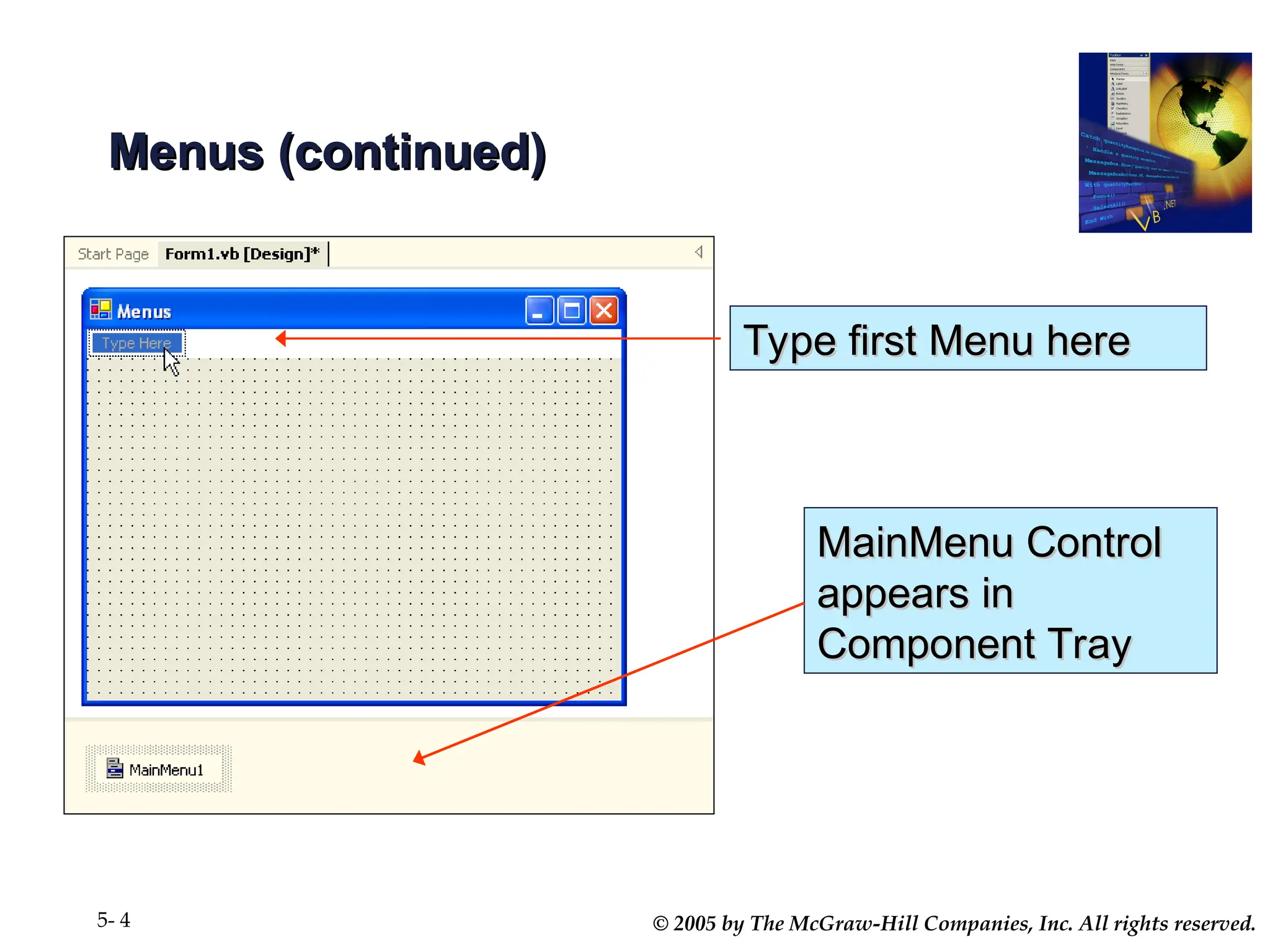
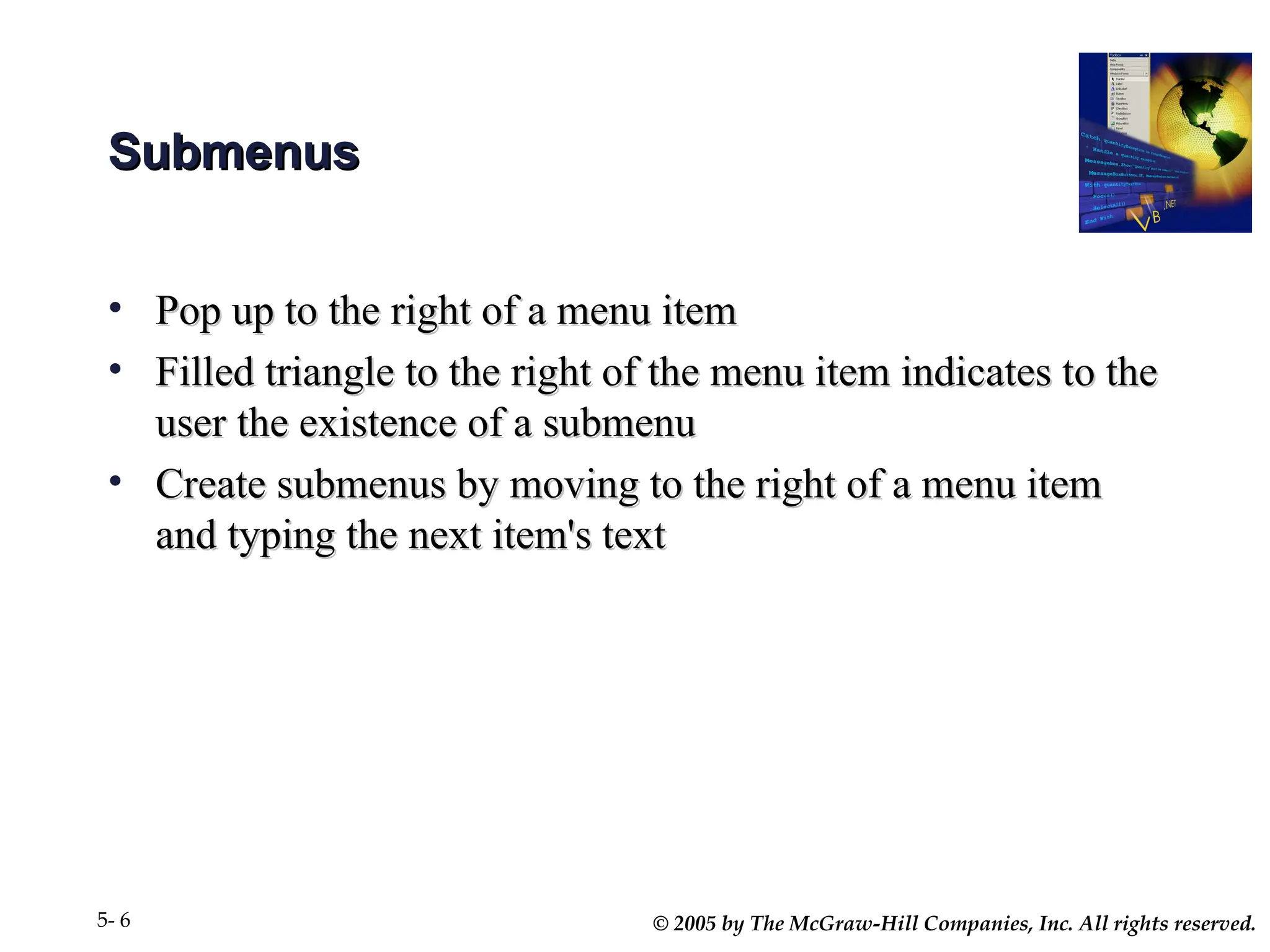
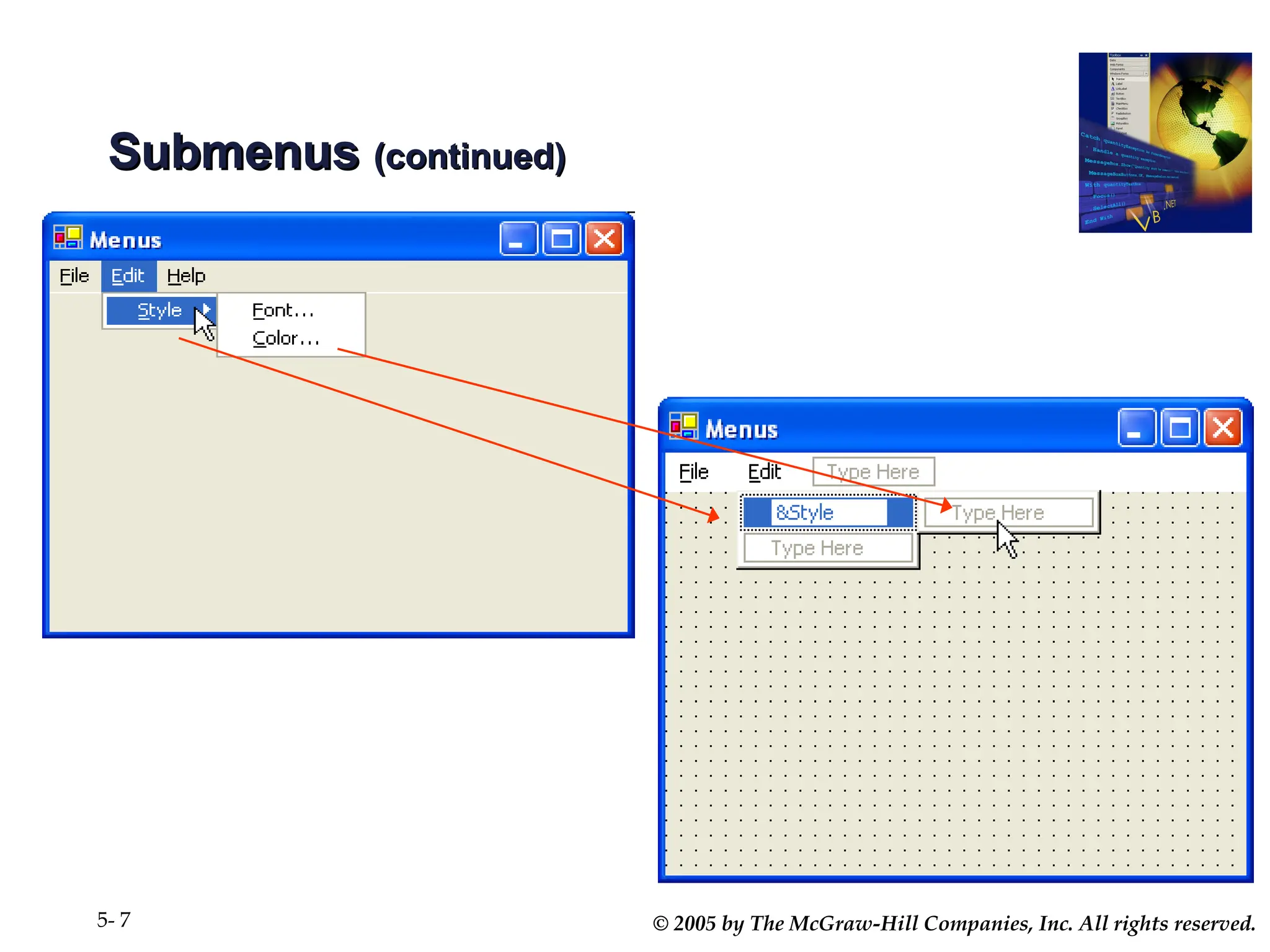
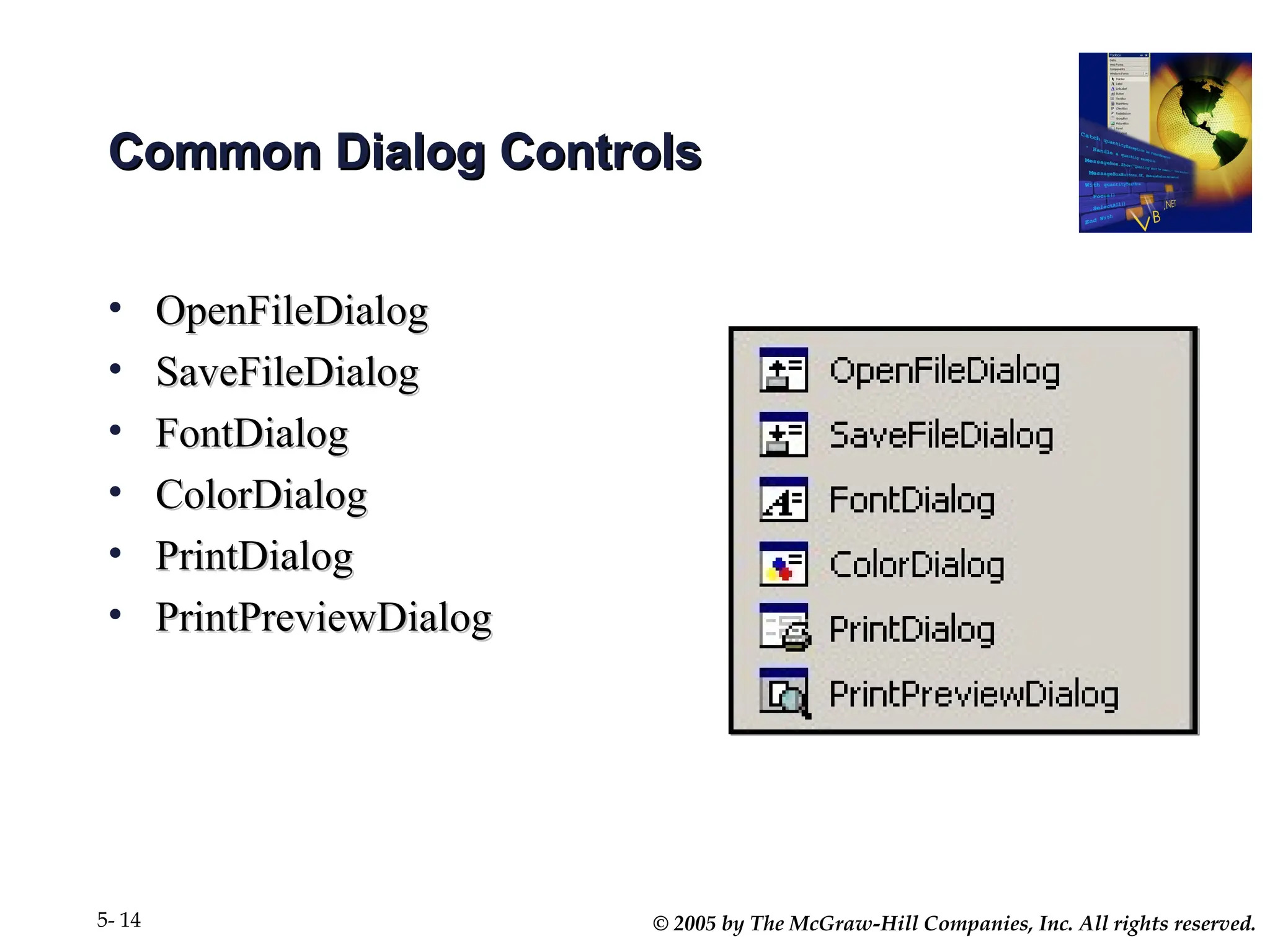
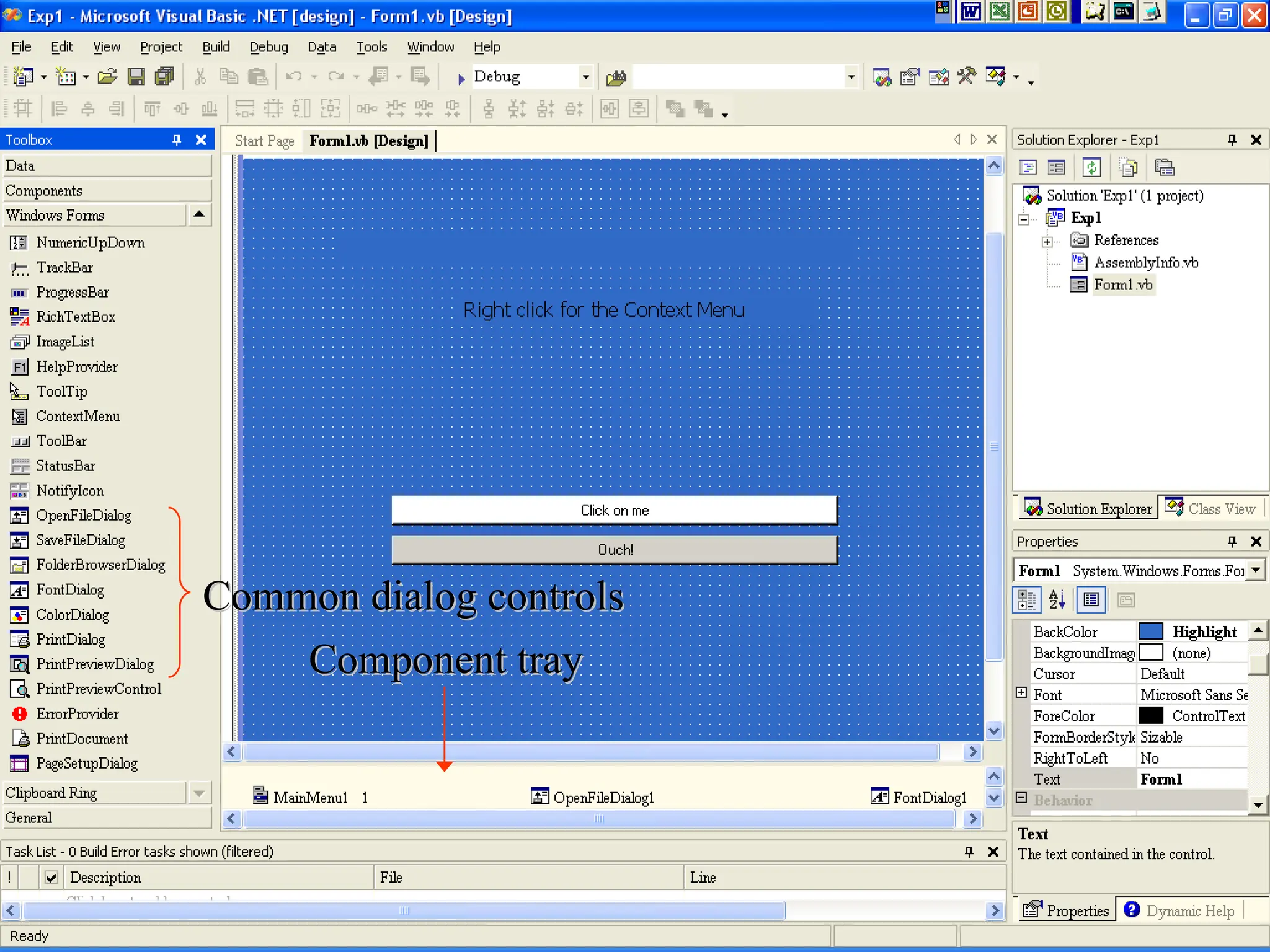
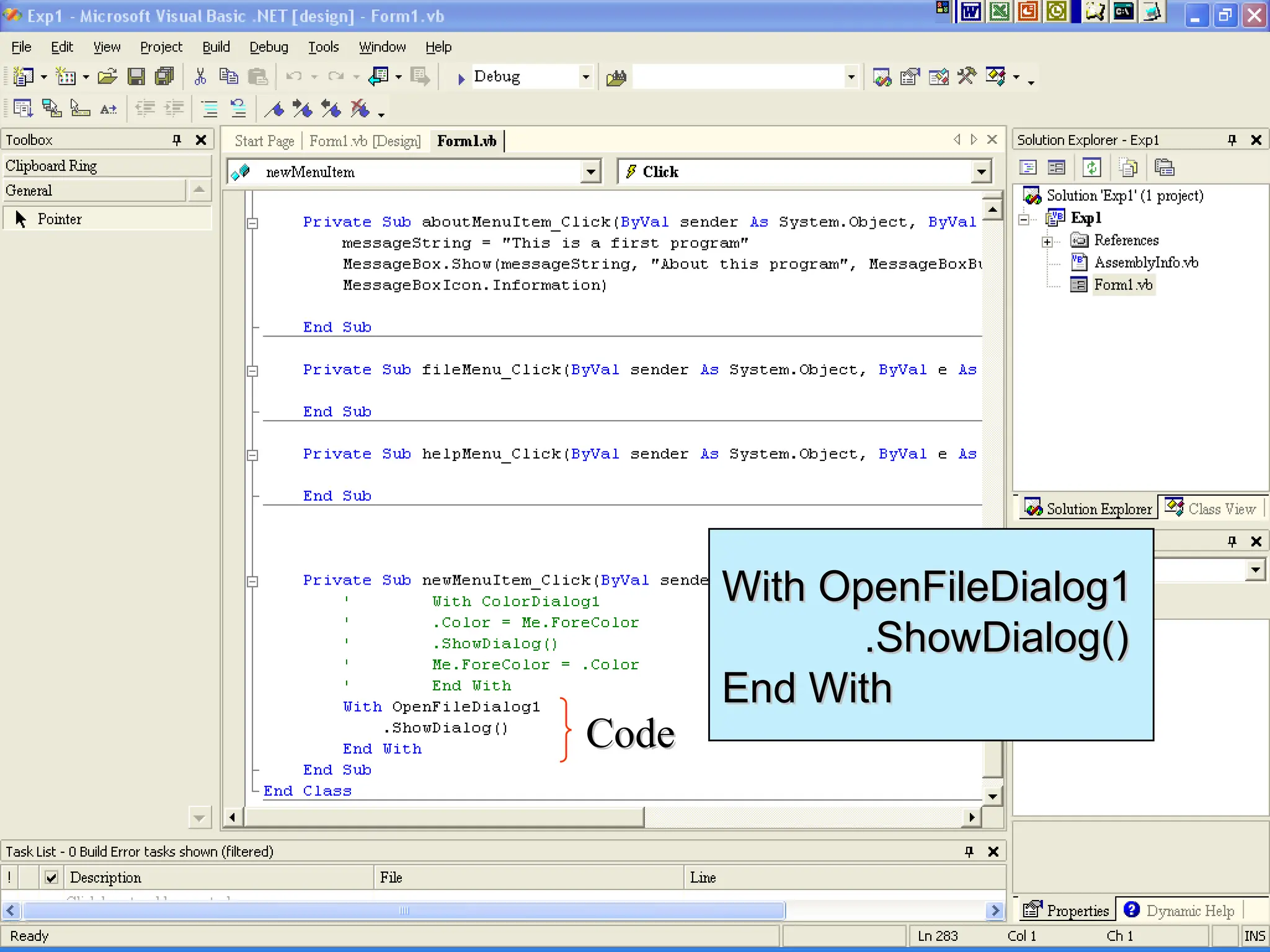
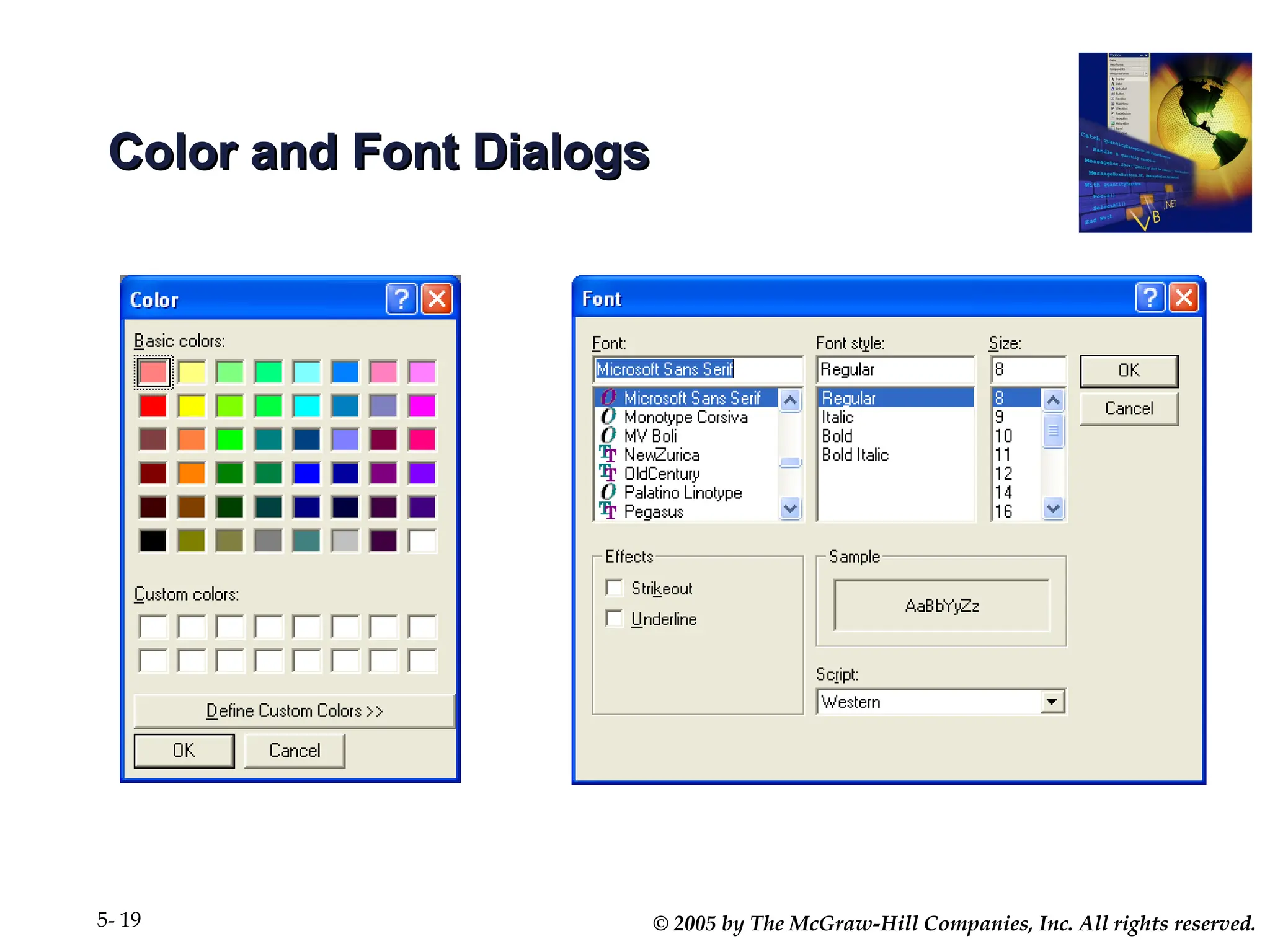
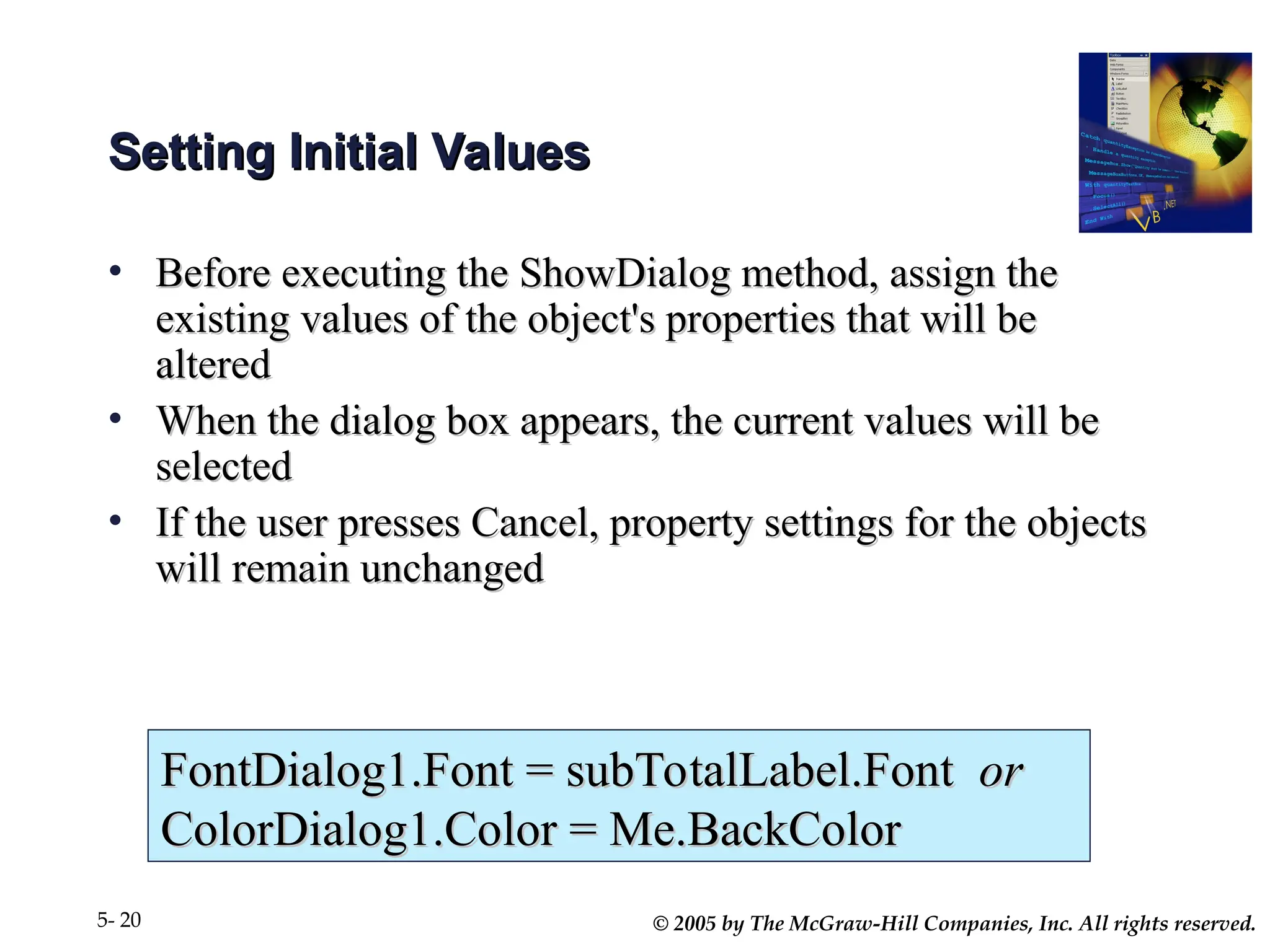
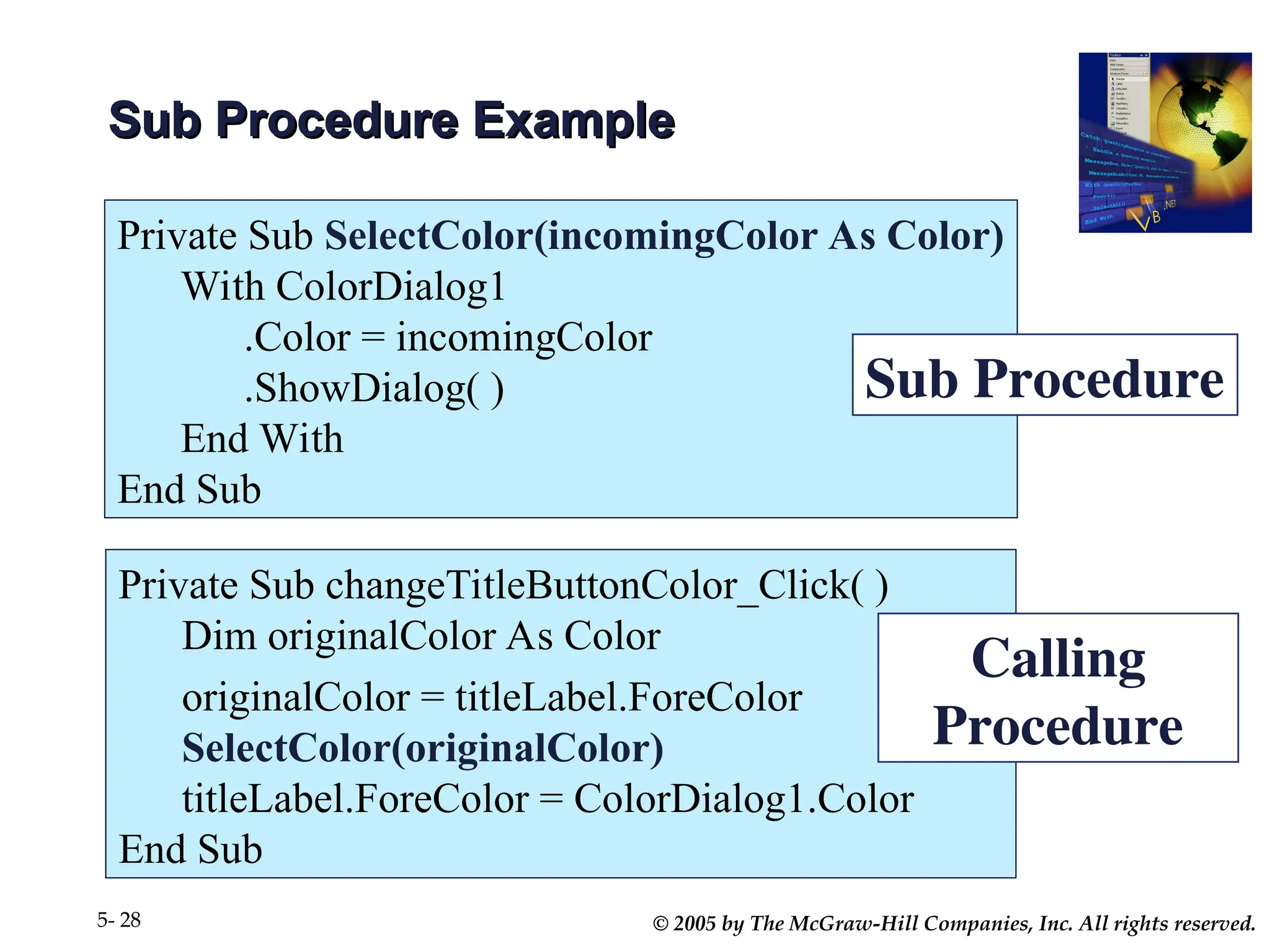
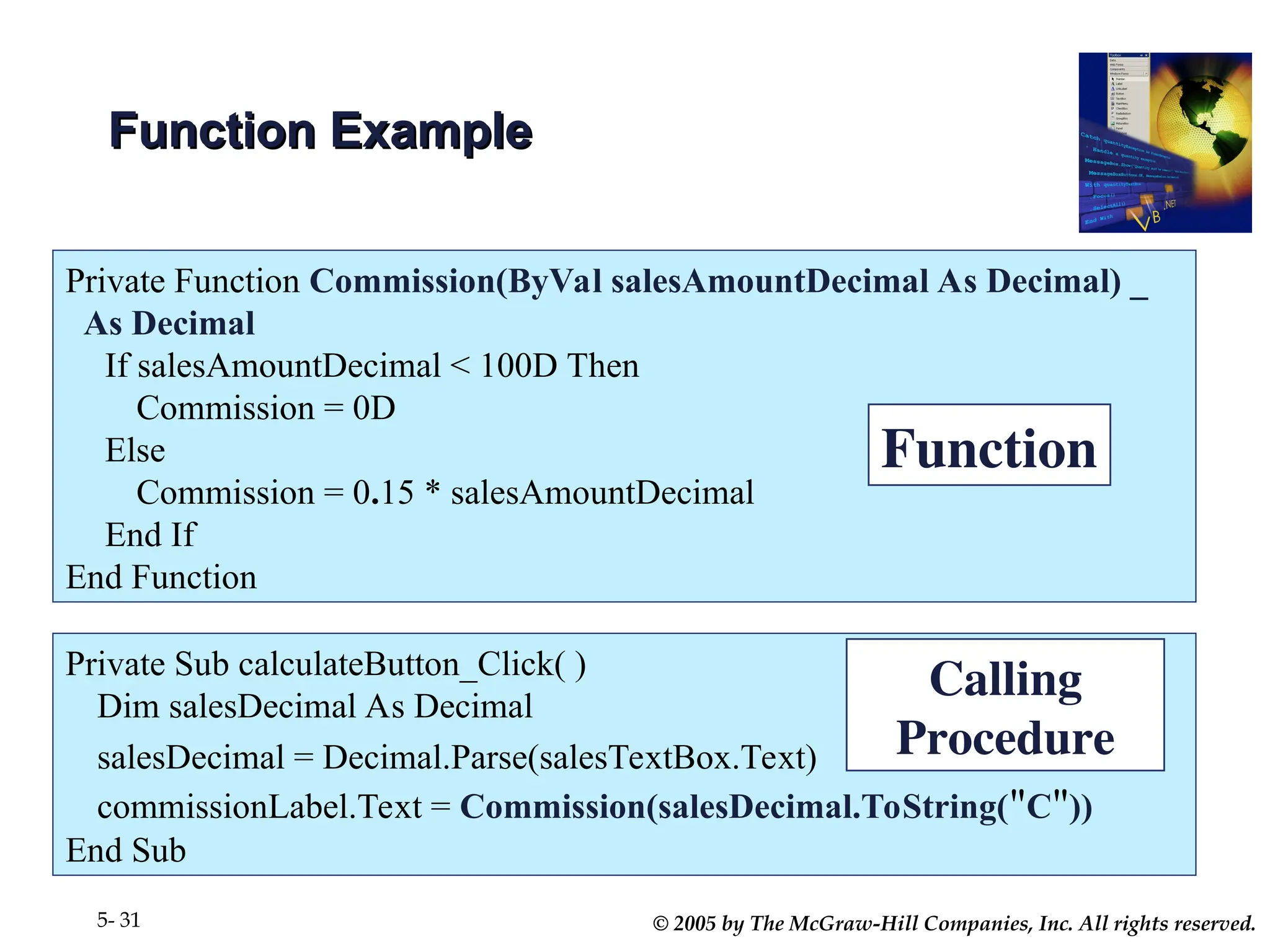
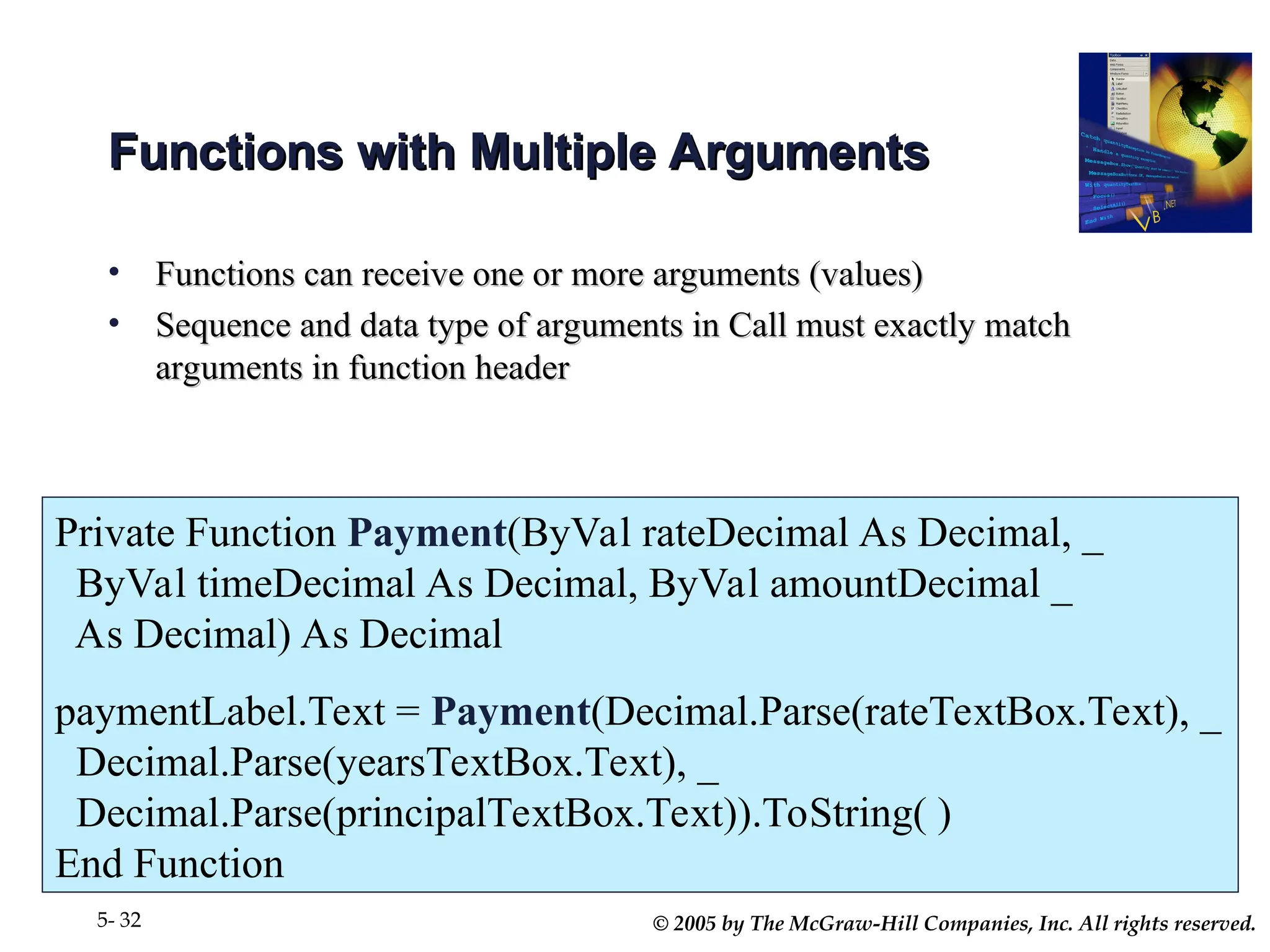
Chapter 5 covers the creation and management of menus and dialog boxes in Visual Basic .NET, detailing the steps to define menus, create submenus, and implement dialog controls for file, font, color, and print options. It emphasizes coding for menu items, modifying menu properties, establishing context menus, and writing procedures to improve code reusability. The chapter also explains the usage of function procedures and passing arguments, facilitating structured programming practices.