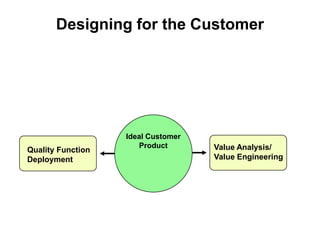
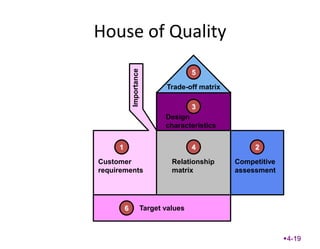
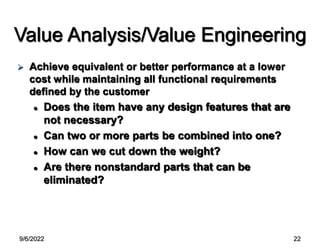
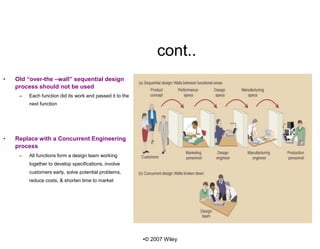
This chapter discusses the design of operations systems including product and service design, process selection, capacity planning, facility location and layout, and job design. It covers defining customer requirements, translating them into engineering characteristics, and using tools like quality function deployment. The chapter also discusses designing products and services that meet customer needs through methods like value analysis, concurrent engineering, and service blueprinting. The goal is to design products, services and processes simply and cost-effectively to reduce time to market and meet customer requirements.