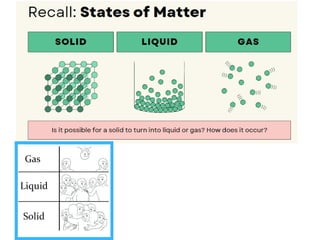
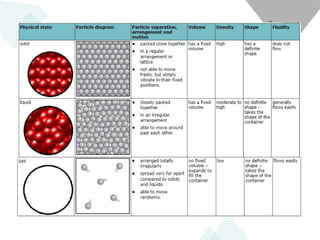
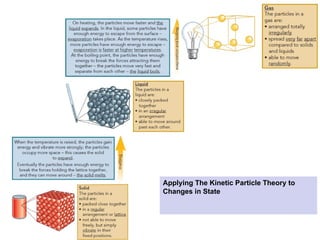
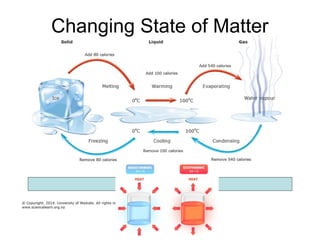
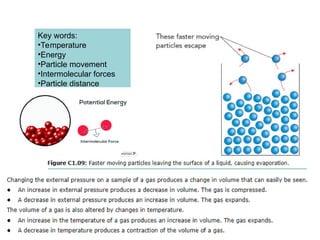
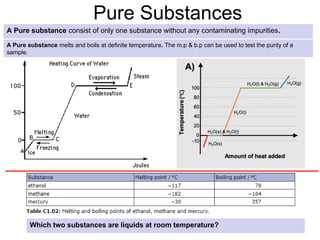
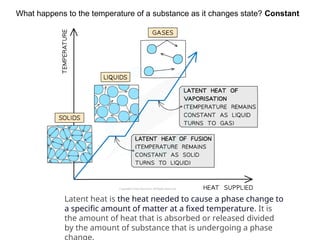
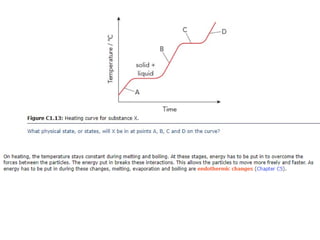
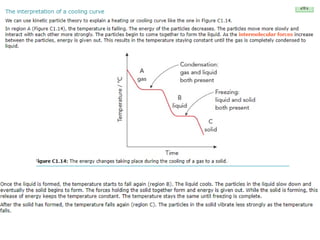
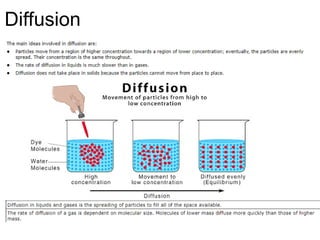
The document outlines learning objectives for understanding the properties and states of matter, including solids, liquids, and gases, as well as changes of state such as melting and boiling. It introduces kinetic particle theory to explain the behavior of matter under varying temperature and pressure conditions, and discusses the concept of pure substances and diffusion. Additionally, the document provides links to simulations and videos for further exploration of these topics.