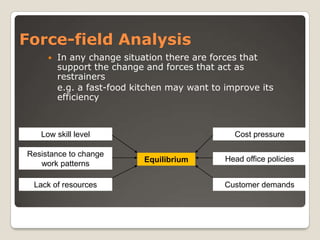
This document discusses change management and the forces that drive organizational change. It outlines several models of the change process, including Lewin's three-stage model of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. Resistance to change is also examined, as are methods for managing resistance like participation, education, and negotiation. The document also differentiates between developmental, transitional, and transformational types of change within an organization.