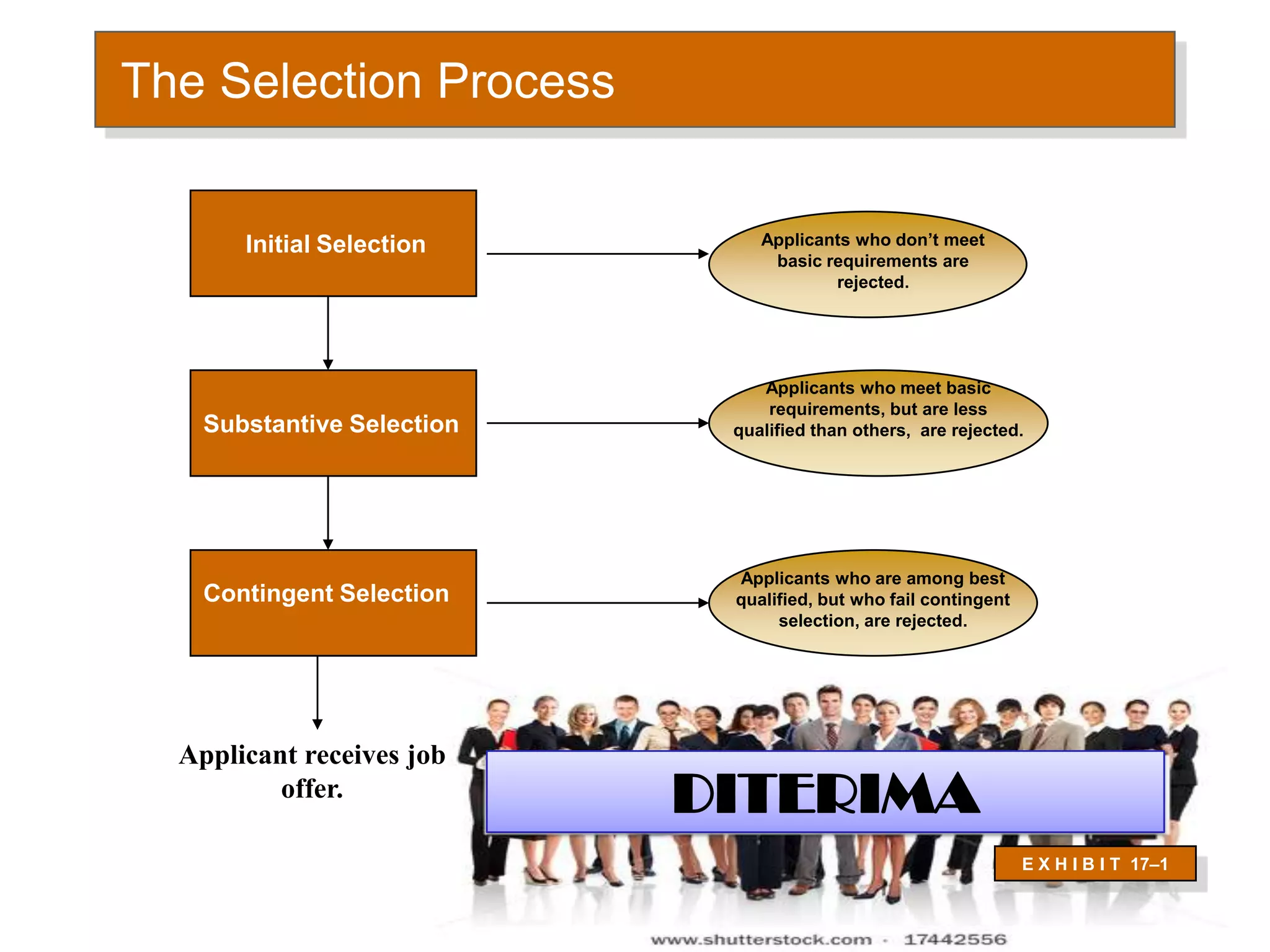
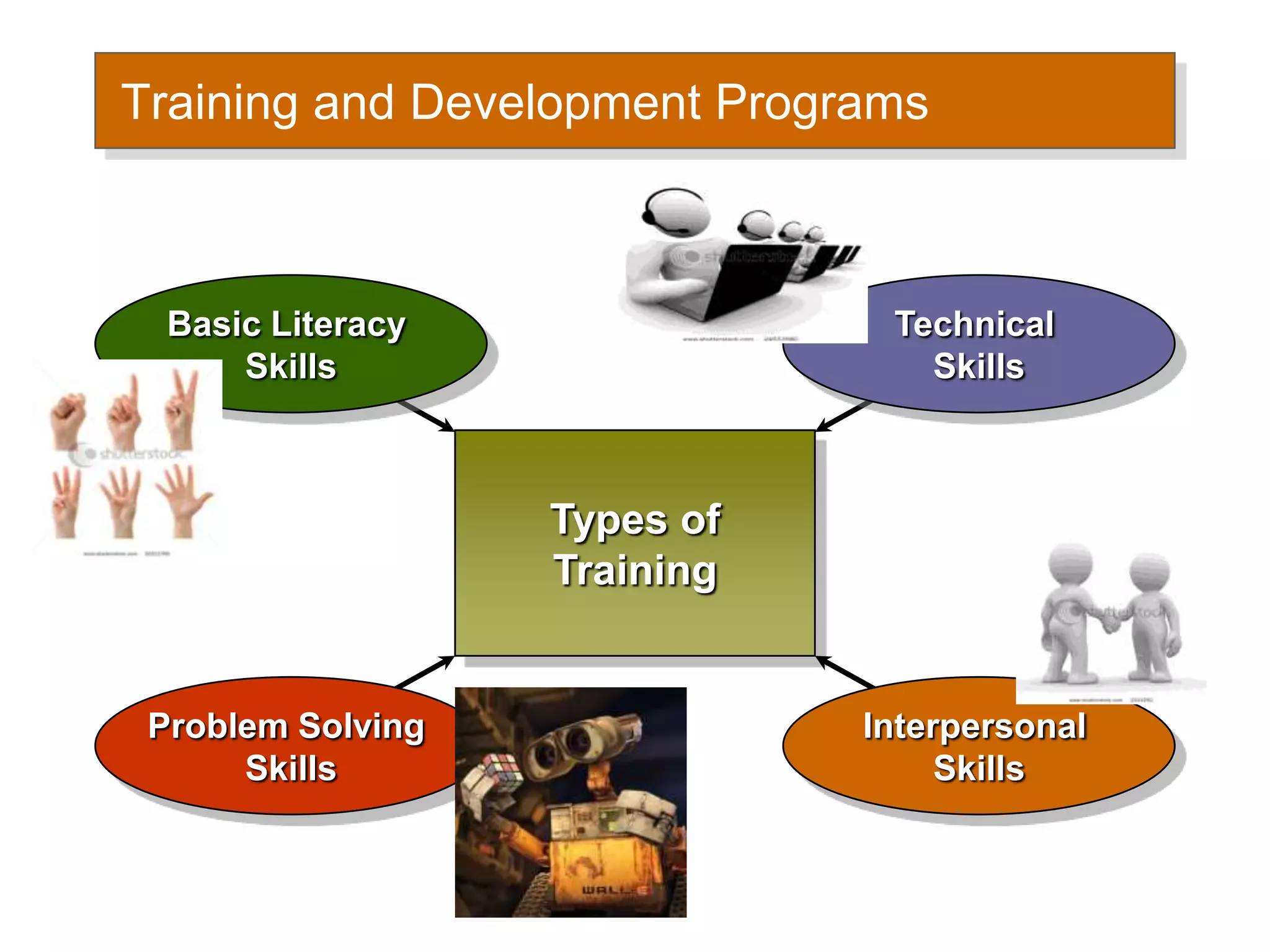
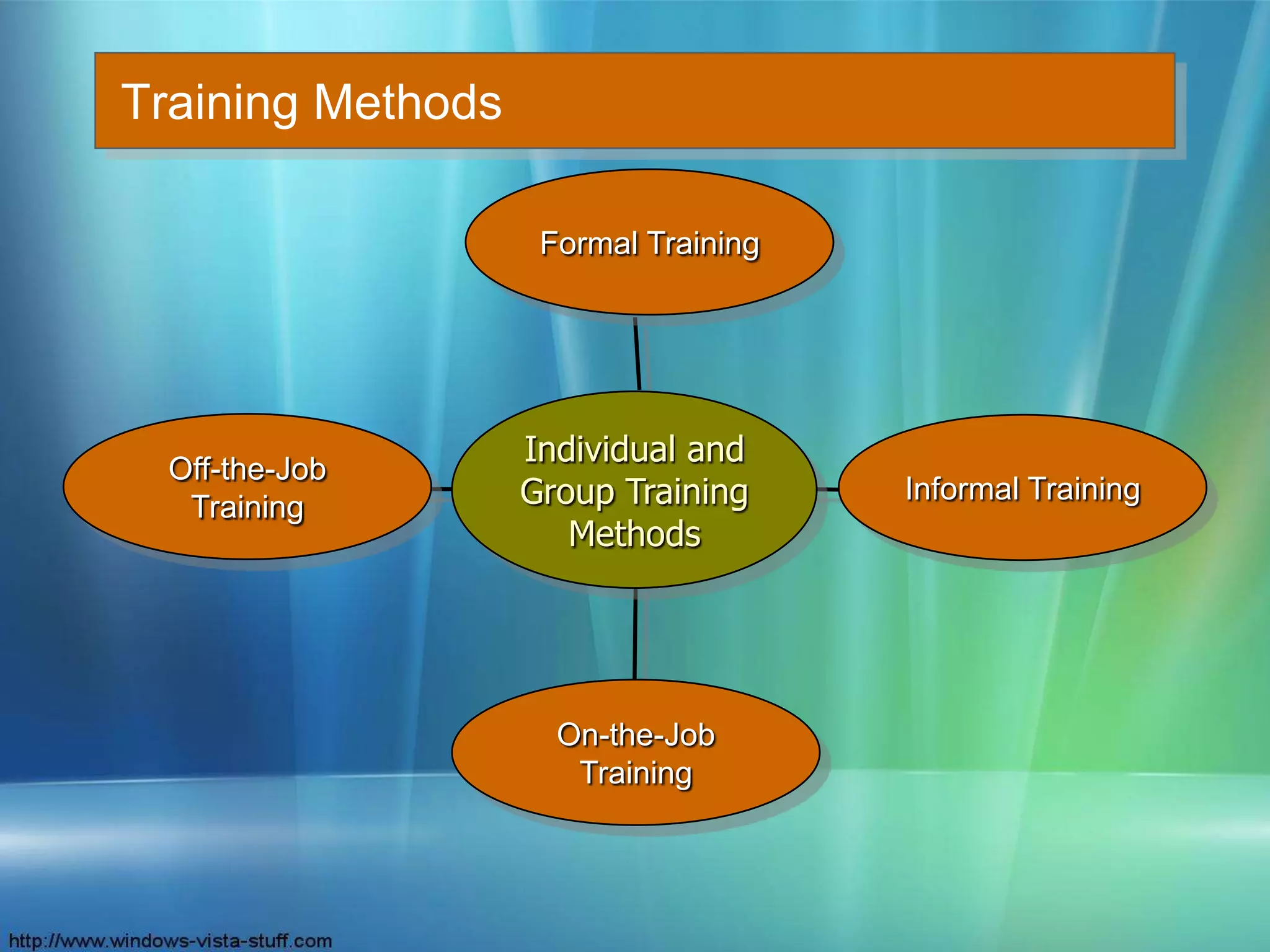
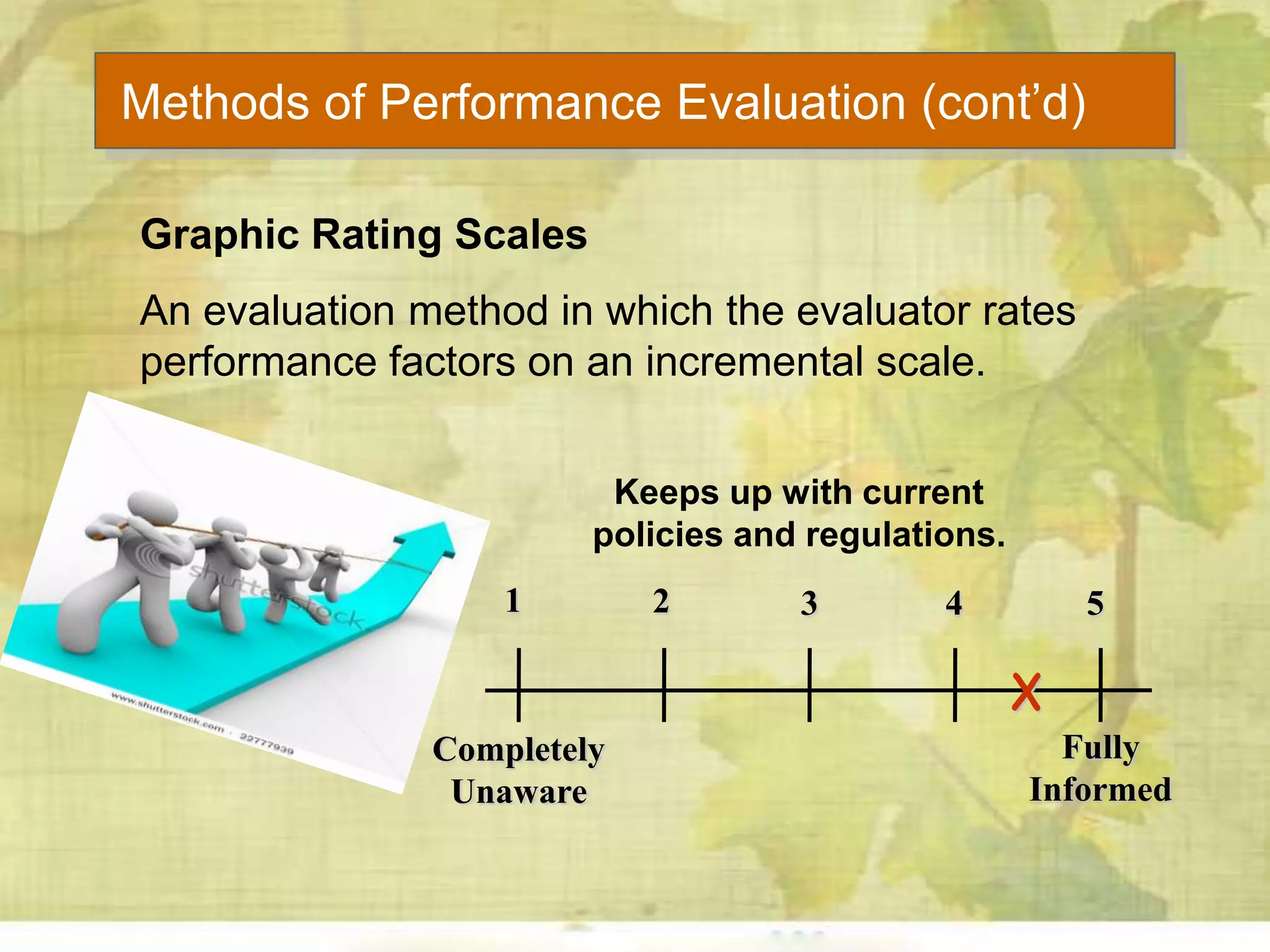
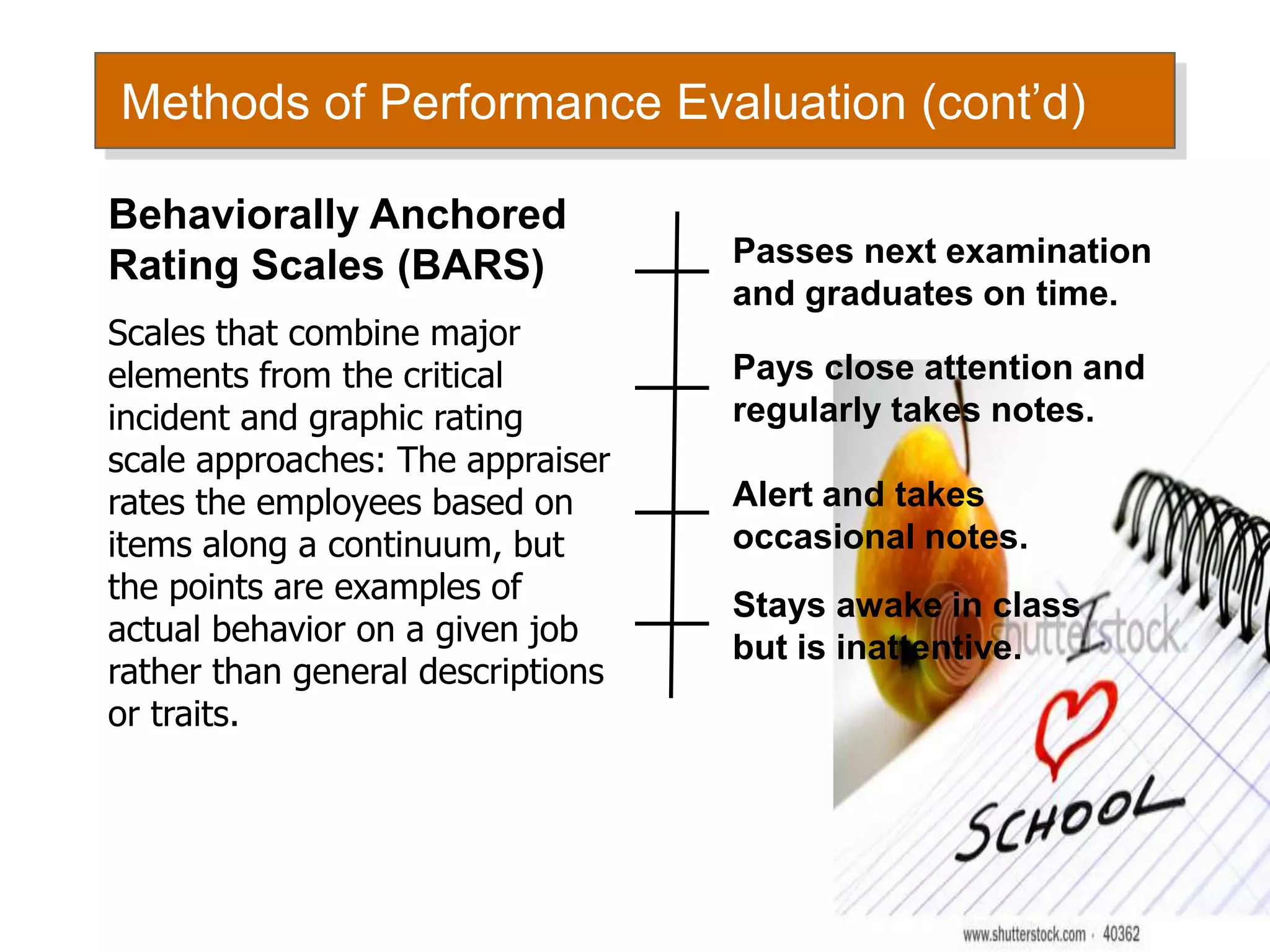
This document discusses human resource policies and practices, including selection processes, training methods, performance evaluation, and managing work-life conflicts. It describes the initial, substantive, and contingent stages of selection where applicants are rejected or receive job offers. Various selection devices and training types are identified. Performance evaluation purposes and methods like rating scales and rankings are outlined. Suggestions for improving evaluations are provided. Finally, the document discusses work-life conflicts and initiatives organizations use to address them, such as flexible schedules and on-site services.