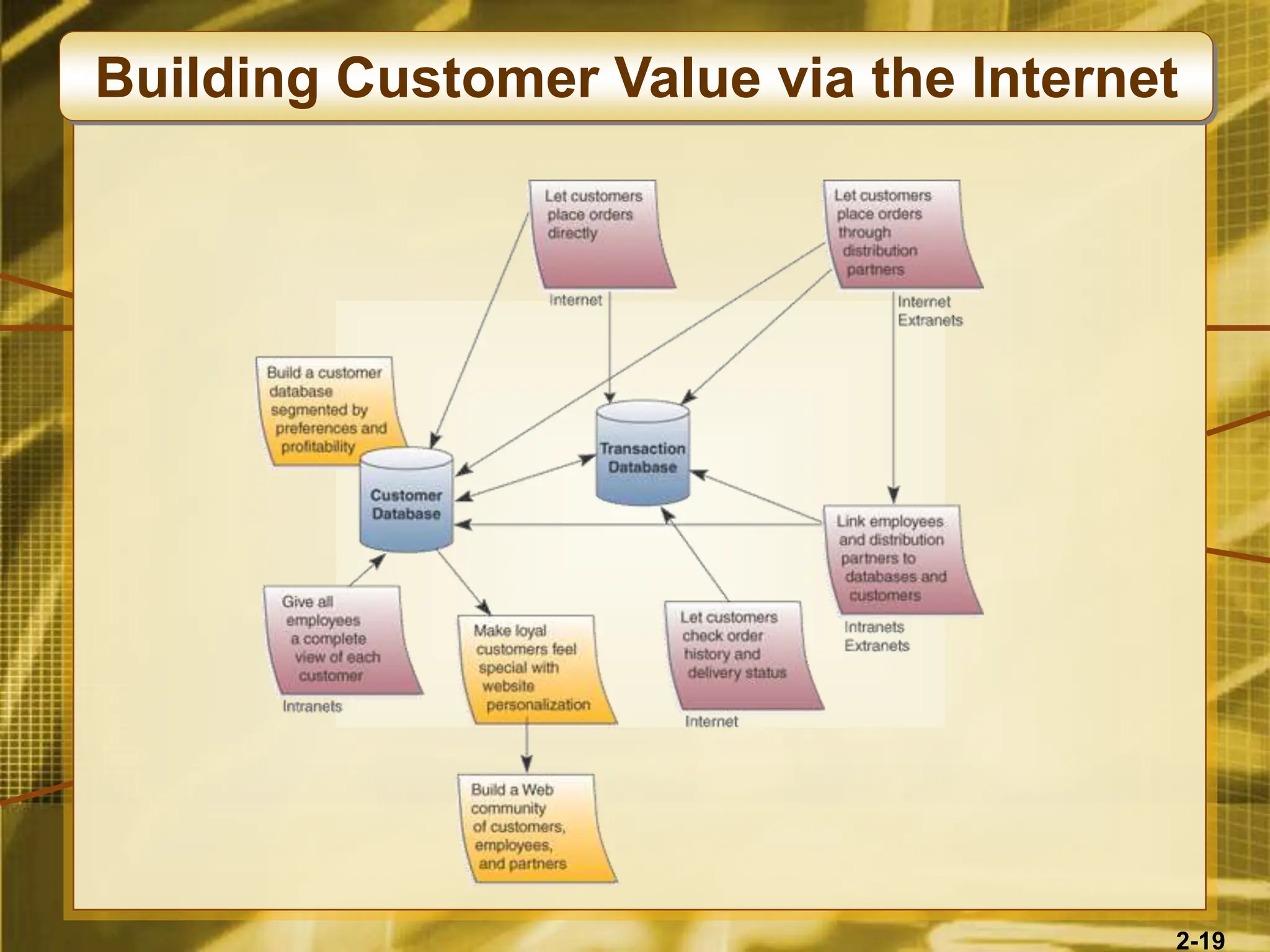
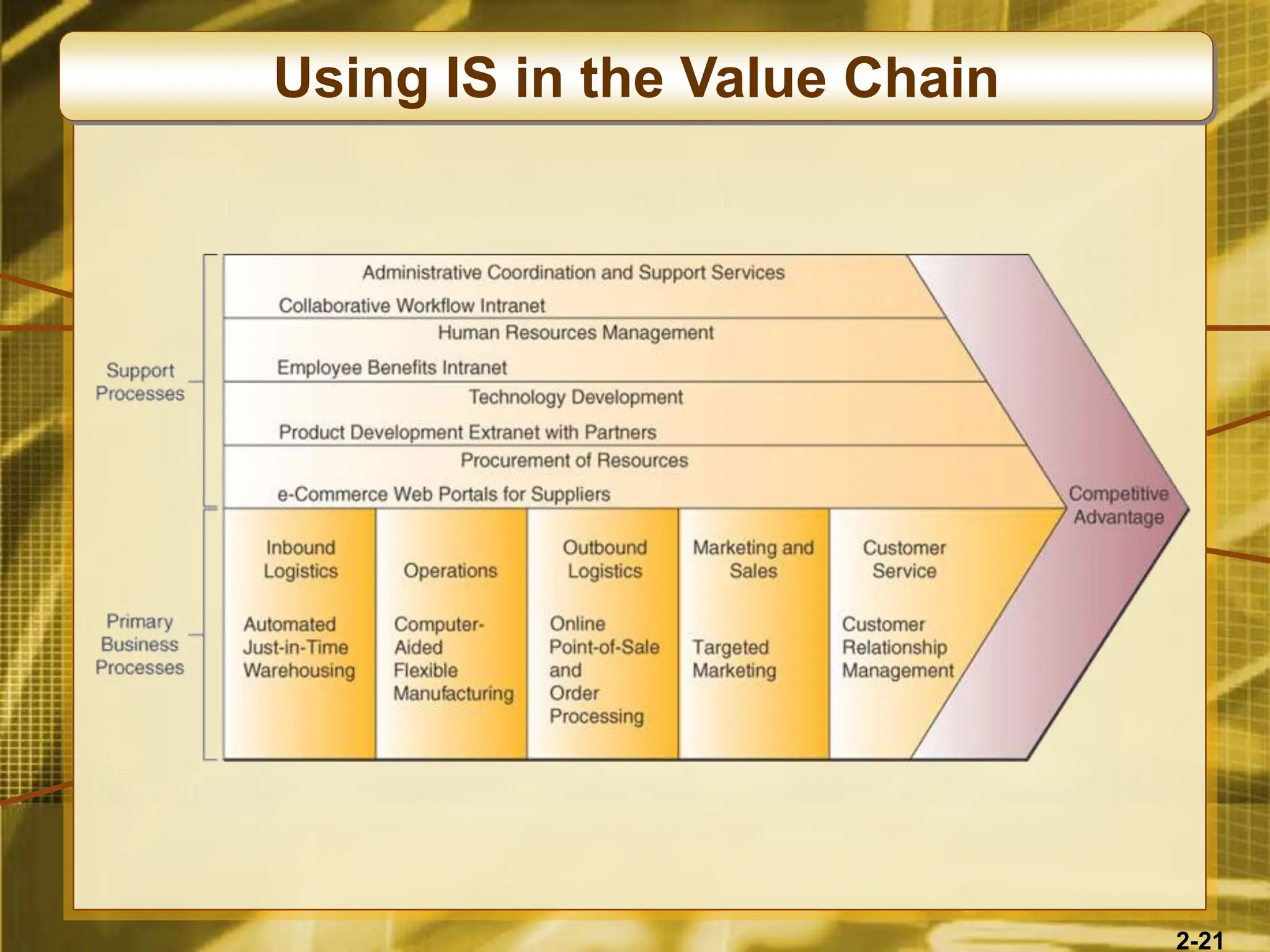
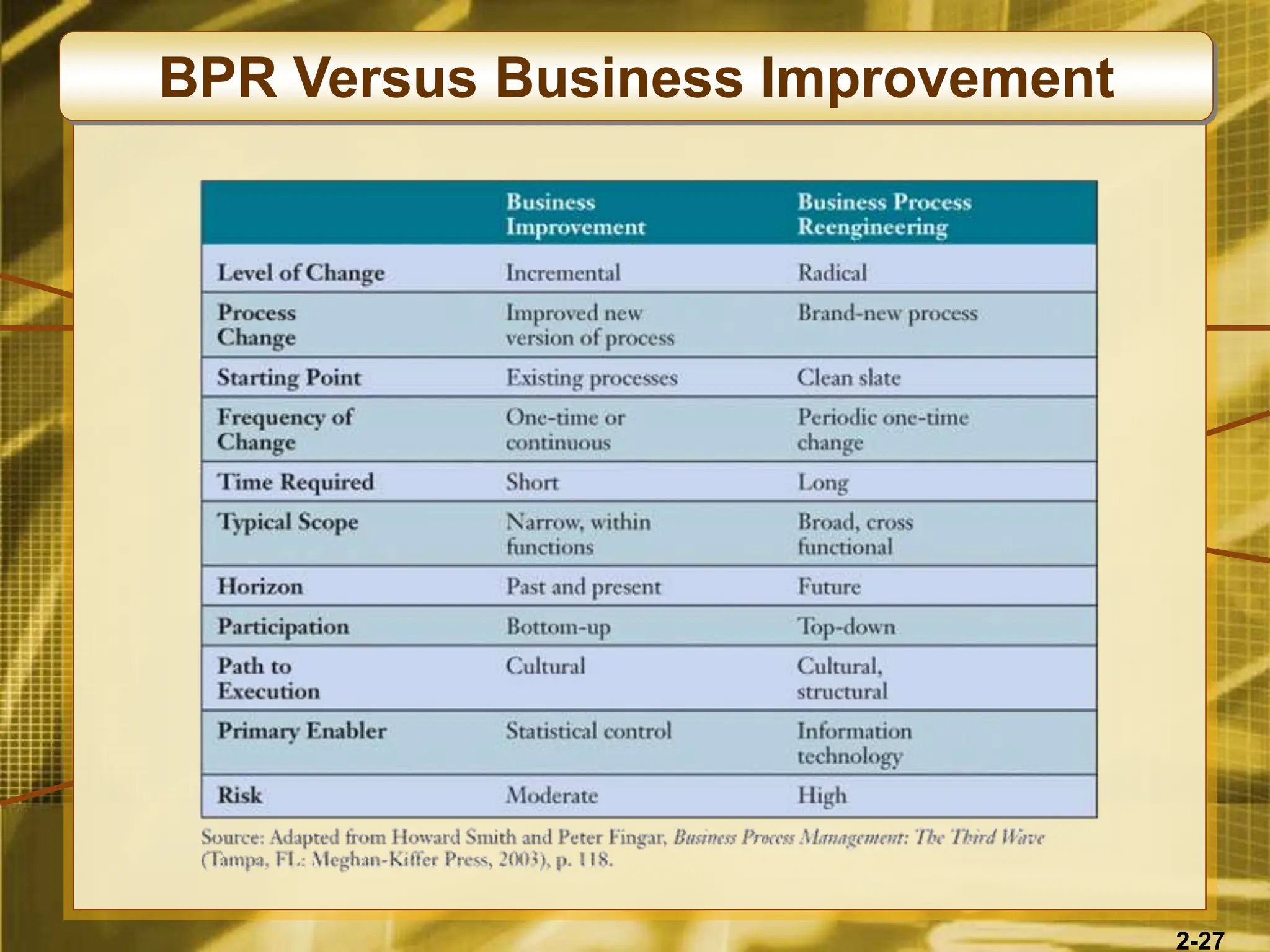
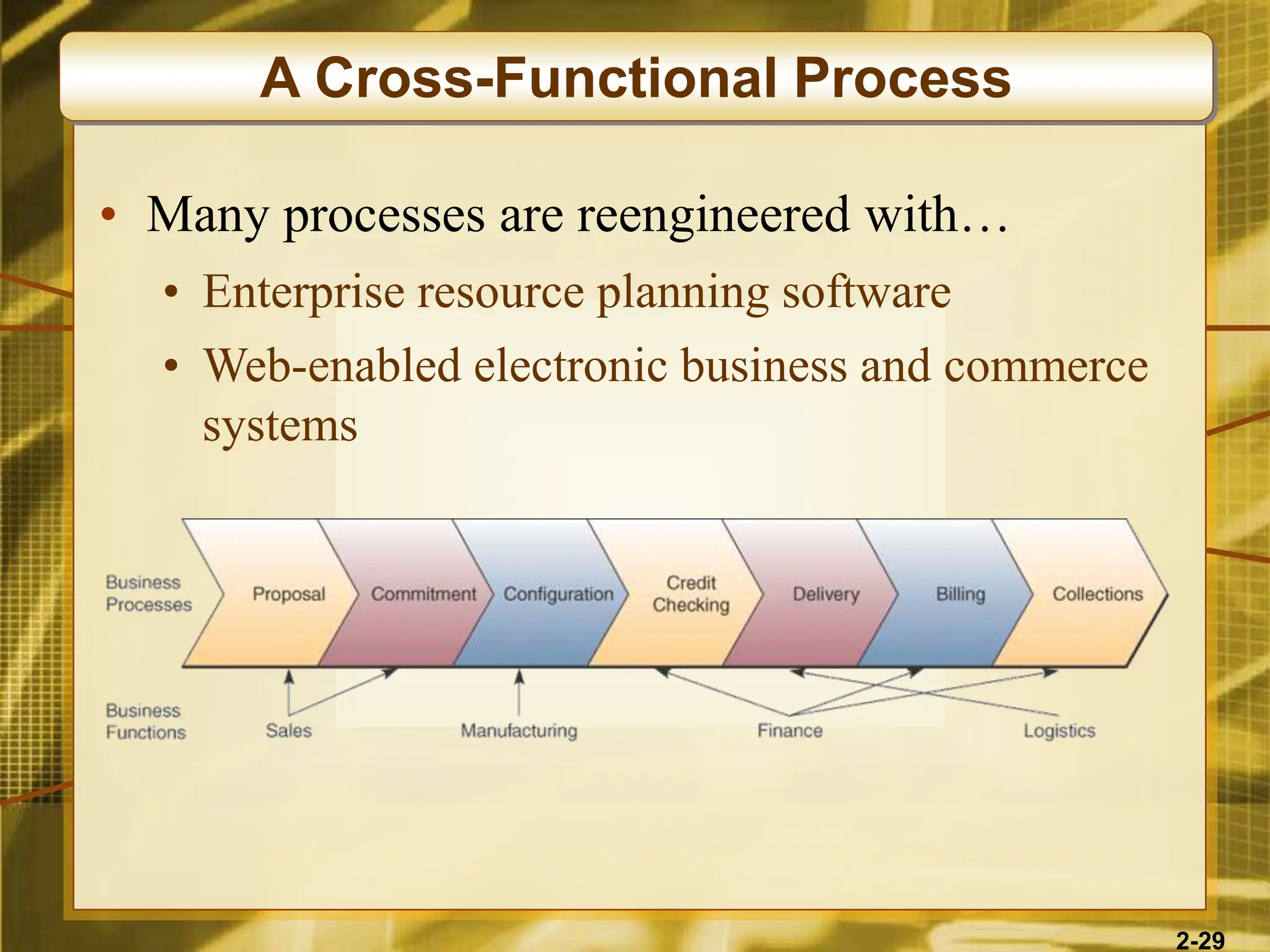
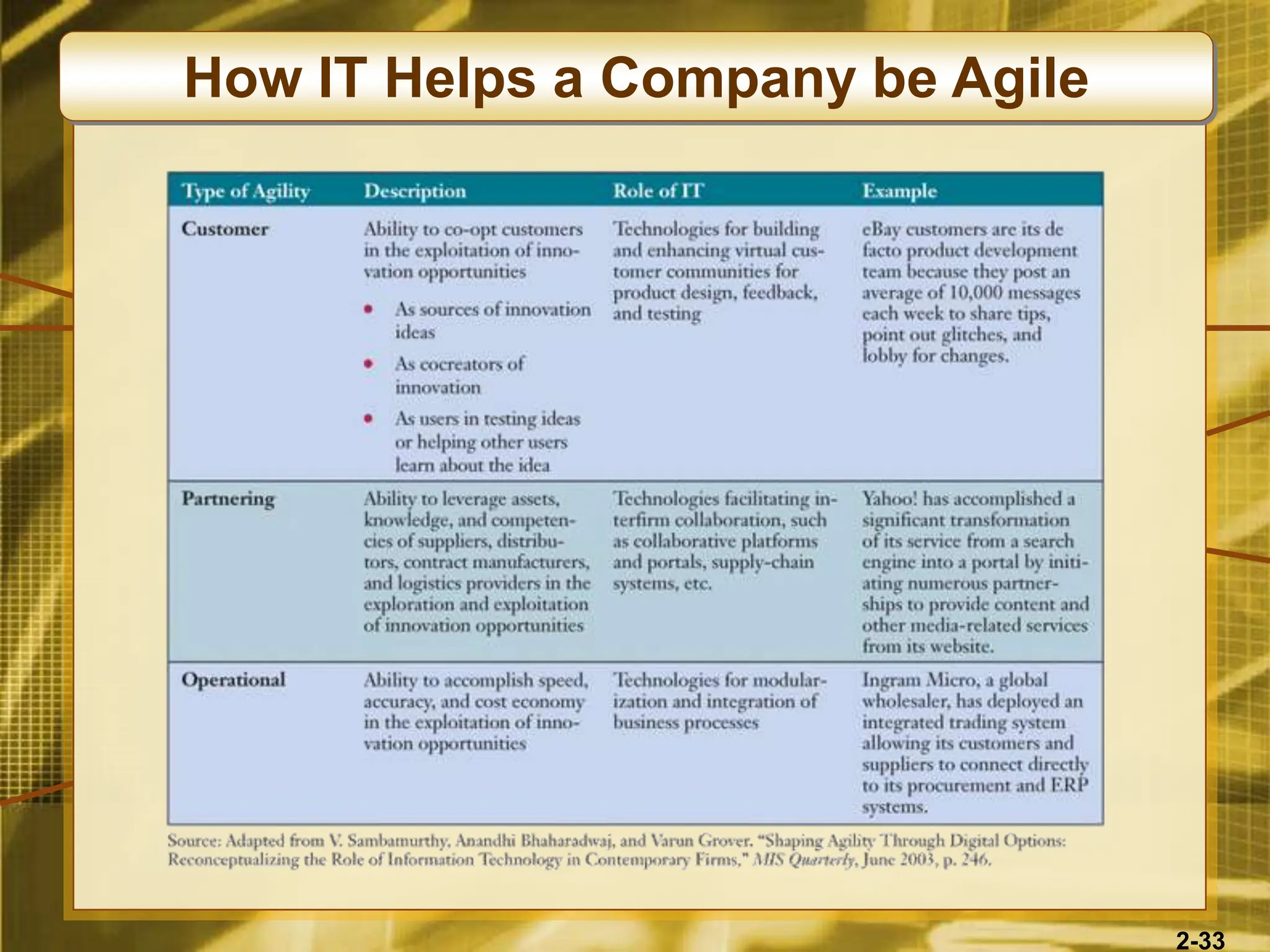
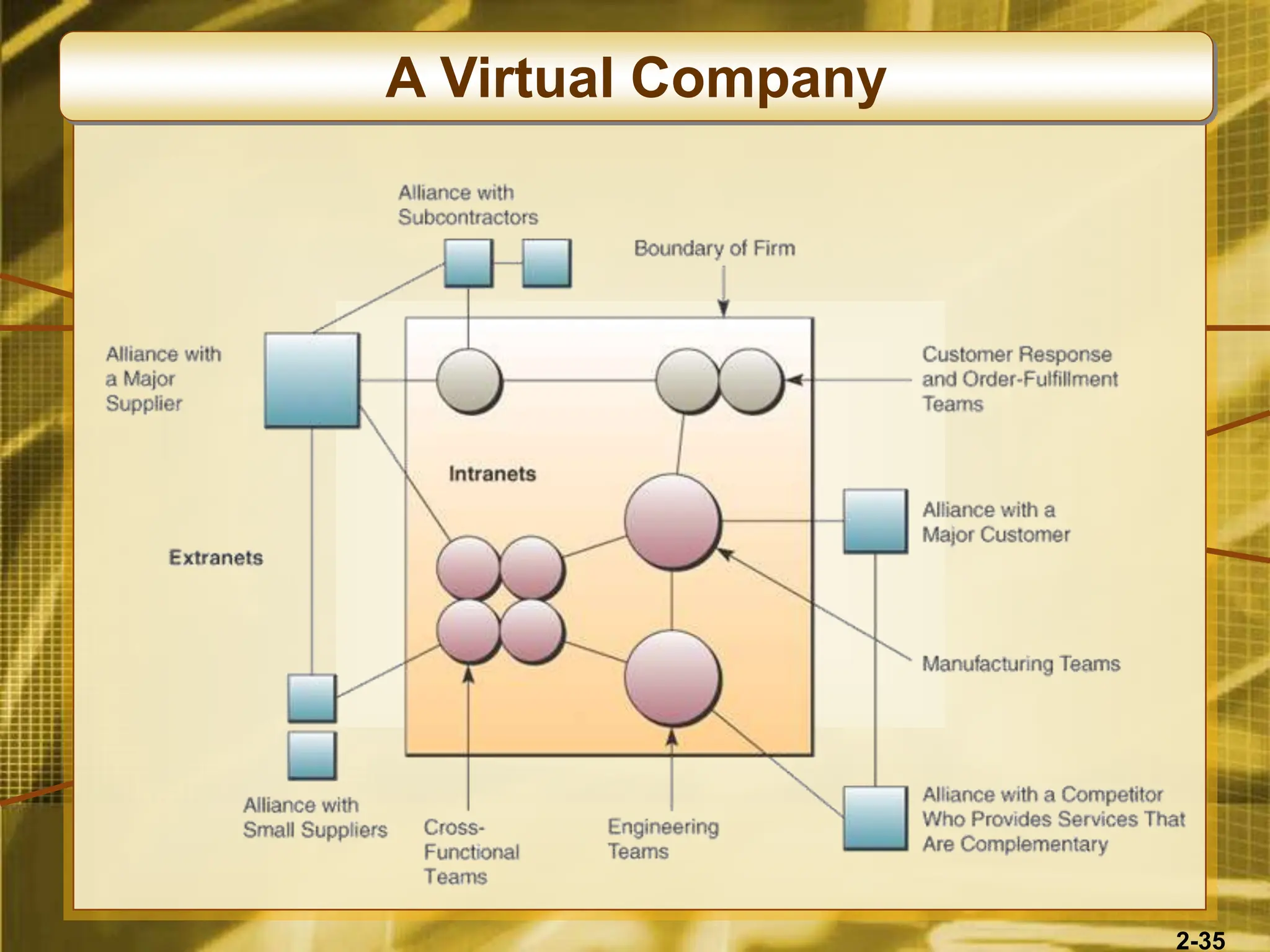
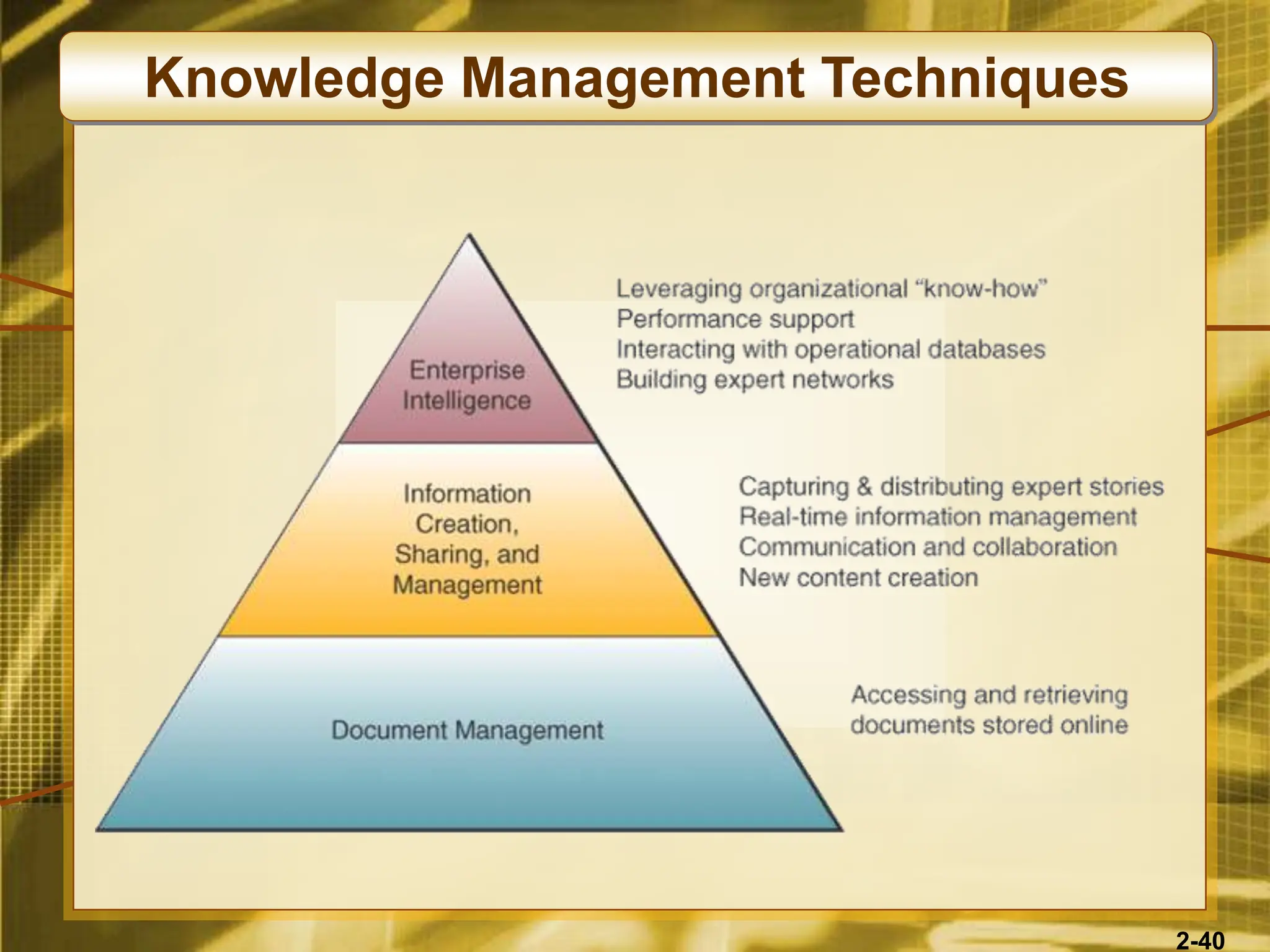
The document outlines various competitive strategies businesses can employ using information technology to gain advantages in the marketplace, including cost leadership, differentiation, and alliances. It discusses the role of technology in business strategy, particularly how it shapes competitive forces and can aid in business process reengineering. Additionally, the importance of knowledge management and the development of agile, customer-focused companies are emphasized as key elements for success.