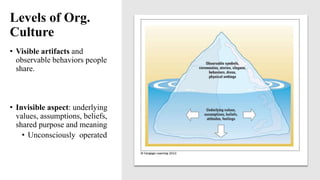
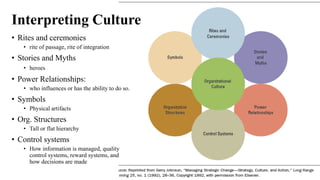
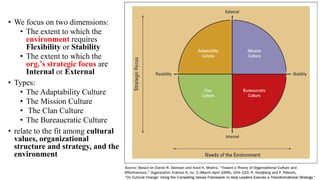
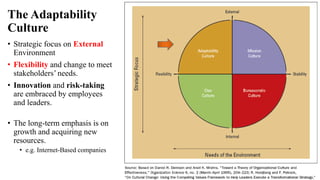
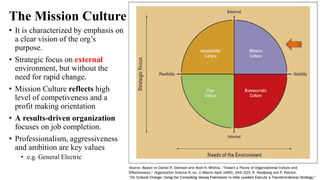
This document discusses organizational culture and its importance. It begins by defining organizational culture as an organization's shared values, norms, beliefs and understandings that are taught to new members. There are visible and invisible aspects of culture. Culture serves two functions - internal integration and external adaptation. There are four main types of organizational culture: adaptability culture, mission culture, clan culture and bureaucratic culture. These types relate to an organization's strategic focus and flexibility. The document emphasizes that organizational culture should be consistent with and support an organization's strategy and external environment. Managers should understand and shape their culture accordingly.