This document provides information on ceramics, including:
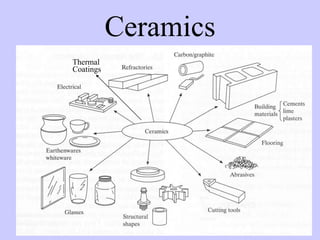
- Ceramics can be amorphous or crystalline, with ionic atomic bonds. Common uses include pottery, bricks, glass, and thermal barrier coatings.
- Crystalline ceramics have good mechanical properties like strength but low ductility. Common structures include NaCl, MgO, and SiC.
- Important ceramics include silica, carbon forms like diamond and graphite, and fullerenes like C60 which can be superconducting.
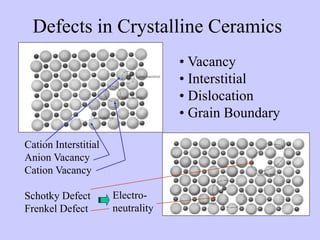
- Defects, mechanical testing methods, and the relationship between properties and porosity are discussed for crystalline ceramics. Glassy ceramics deform viscously





![Try it!
a
a
Cl-
Na+
For this NaCl structure, the
crystal lattice parameter is
a= 2 ( r Na+ + r Cl -),
where r is ionic radius.
Compute the theoretical density of Rock Salt based on its crystal structure.
)
2.16g/cm
(actual
g/cm
14
2
)ions/mol
(6.023x10
)]cm
0.181x10
0
2[(0.102x1
g/mol
35.45)
(22.99
ions
4
N
a
)
A
A
(
4
V
M
3
3
23
3
7
7
A
3
Cl
Na
.
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceramics1-230106173102-7940de00/85/ceramics1-ppt-7-320.jpg)