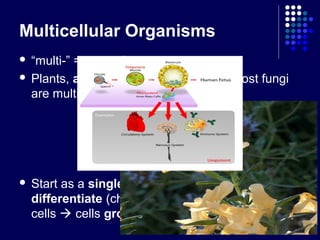
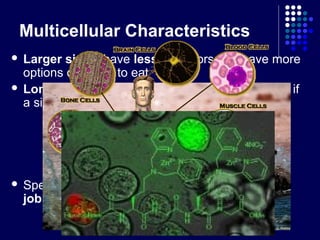
This document discusses the levels of organization in multicellular organisms. It explains that as multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate and form four levels: cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cells form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs form organ systems, each with specialized functions. The levels allow organisms like humans to have different cell types, tissues, organs, and organ systems working together.