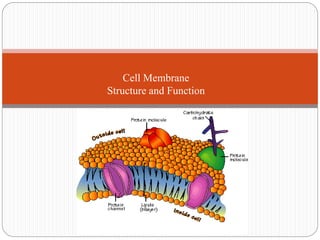
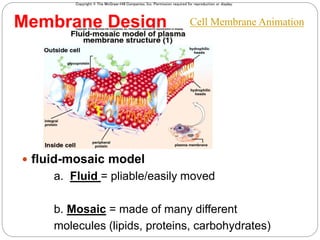
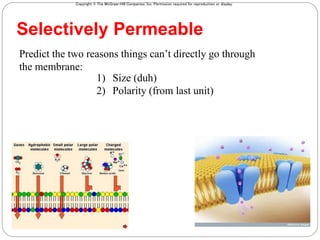
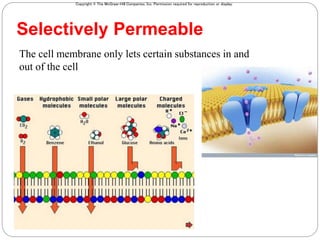
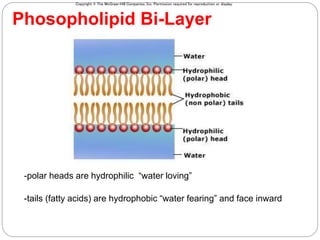
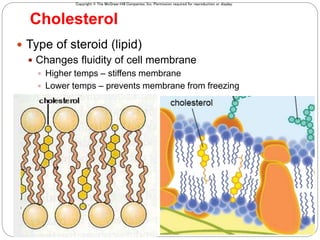
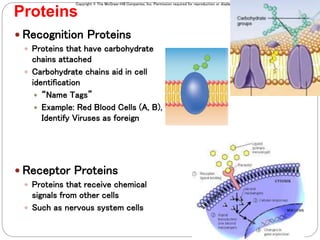
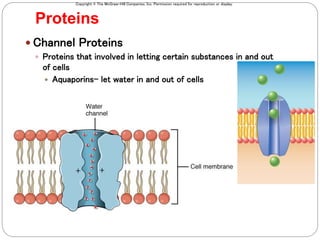
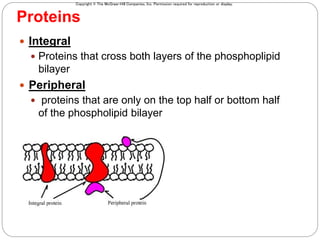
The cell membrane is composed of a fluid-mosaic structure containing phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. Phospholipids form a bilayer with hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads facing outward. Cholesterol maintains membrane fluidity at different temperatures. Membrane proteins perform important functions like recognition, signaling, and selectively transporting substances into and out of the cell based on size and polarity.