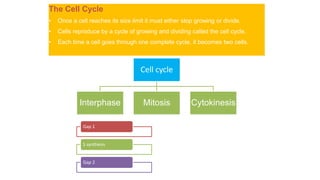
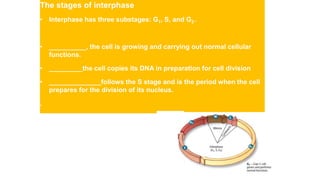
The document discusses the cell cycle, which consists of interphase and mitosis followed by cytokinesis. Interphase includes the G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. Mitosis is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the cell nucleus and chromosomes divide. Cytokinesis then separates the cytoplasmic contents into two daughter cells completing the cell cycle. The cycle allows cells to grow and divide to form more cells.