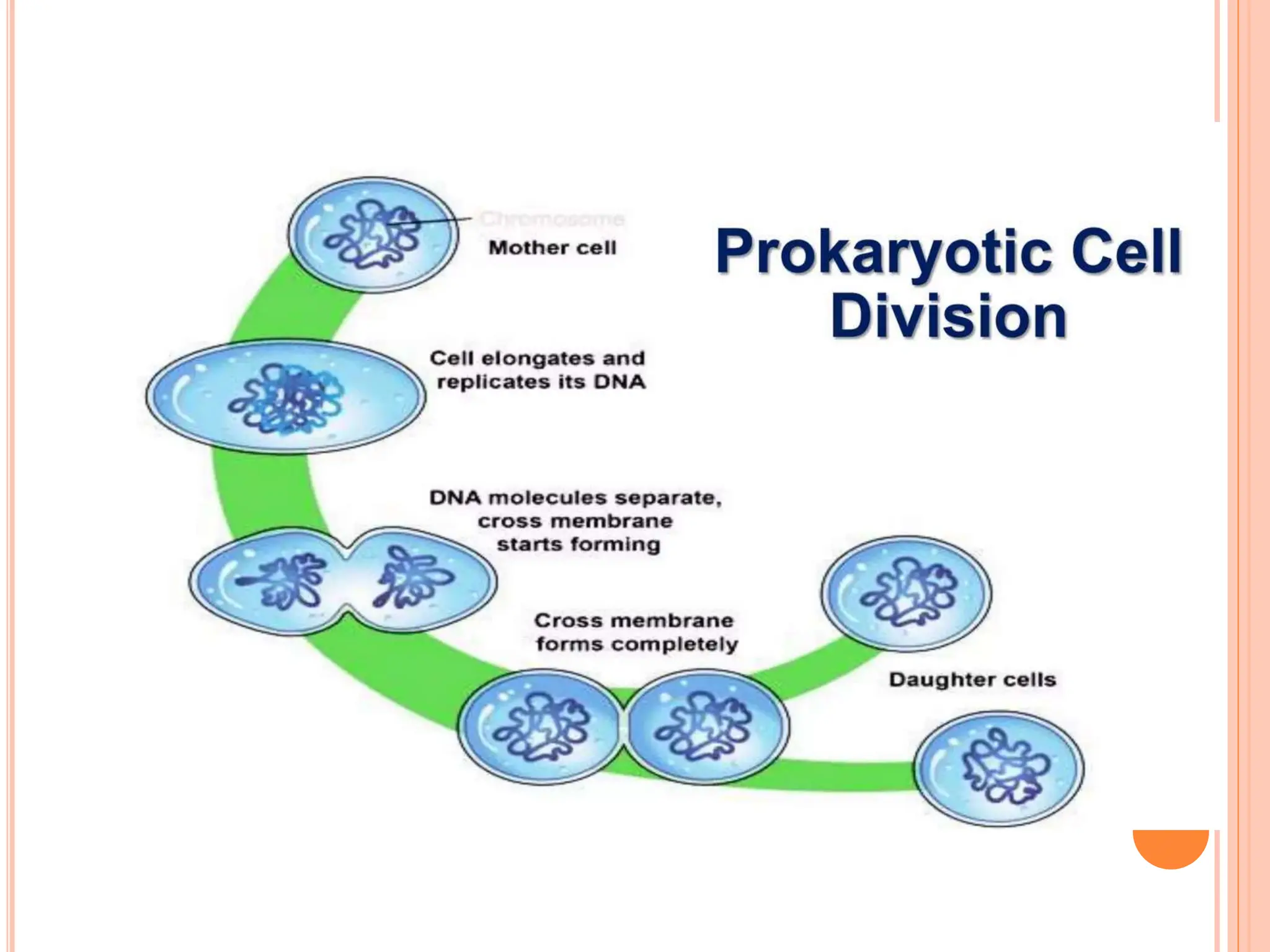
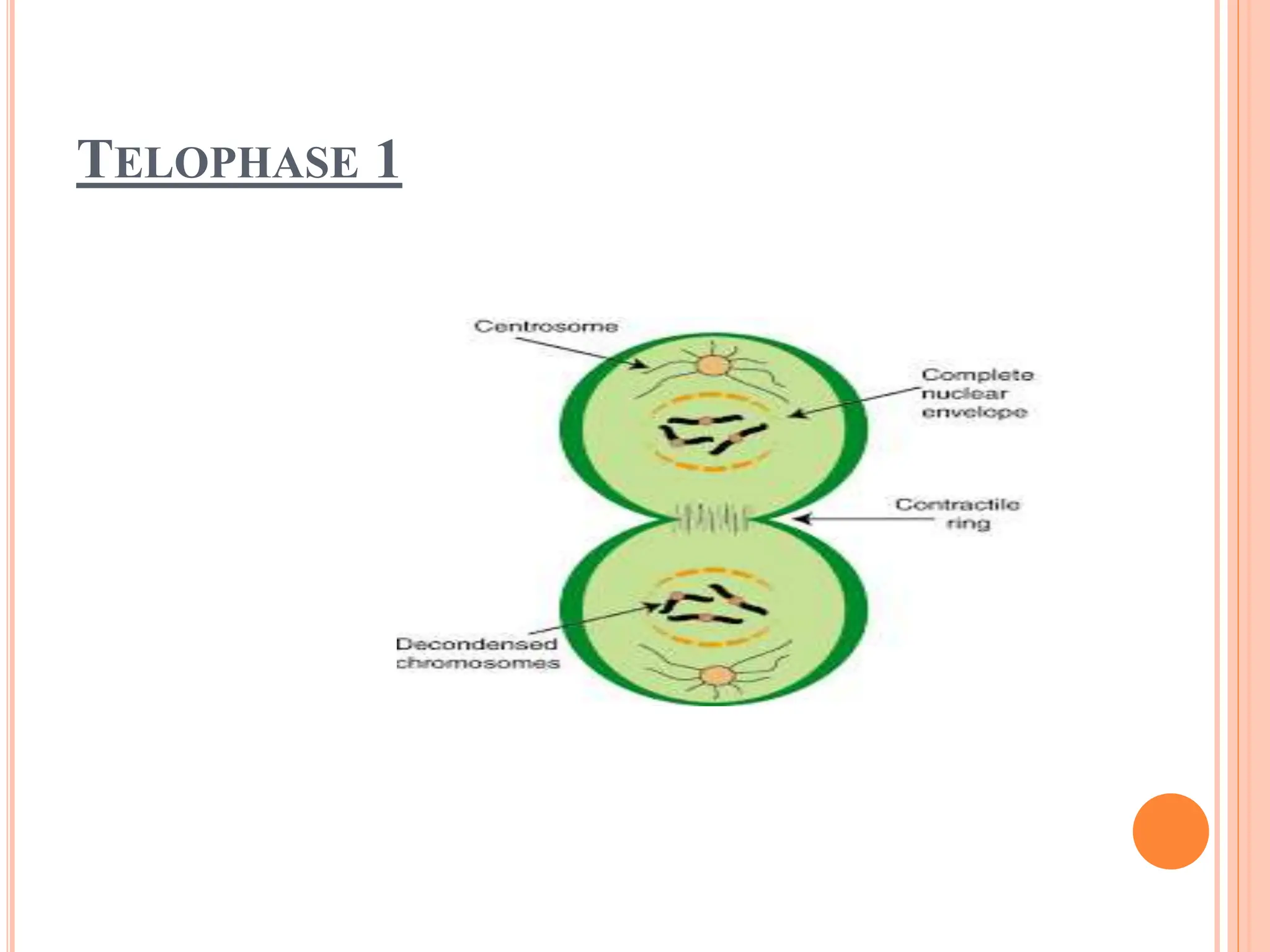
The document presents an overview of cell division and the cell cycle, emphasizing its importance in growth, development, and tissue repair. It details the two main types of cell division: mitosis, which results in two genetically identical daughter cells, and meiosis, which produces gametes with half the chromosome number. The cycle includes stages of growth and DNA replication, concluding with cell division, predominantly occurring during interphase.