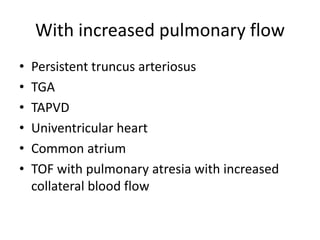
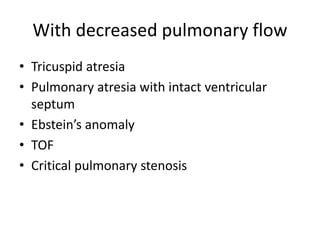
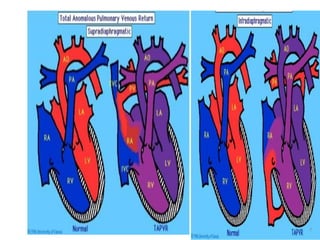
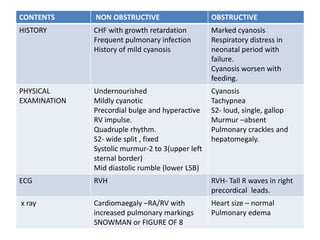
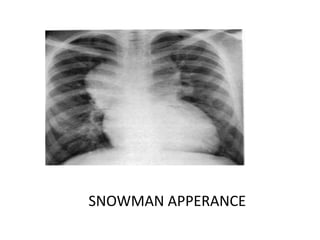
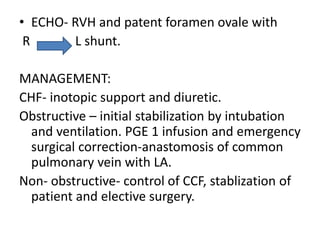
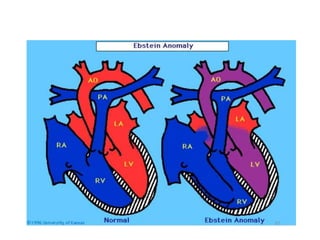
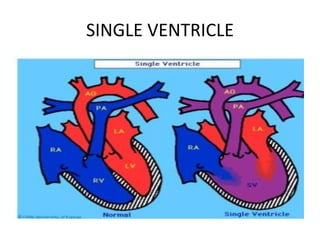
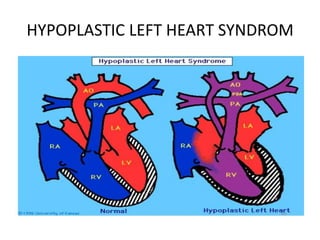
1. Congenital cyanotic heart disease refers to heart defects present at birth that result in low oxygen levels in the blood. They are classified as those with increased or decreased blood flow to the lungs.
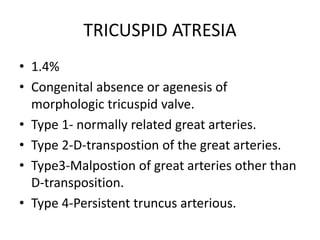
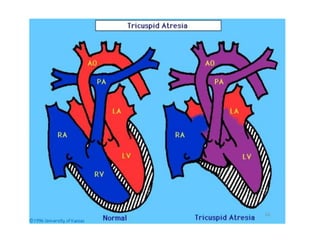
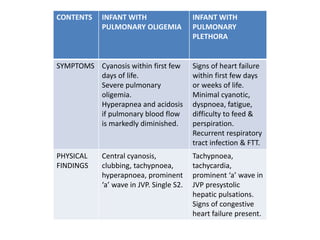
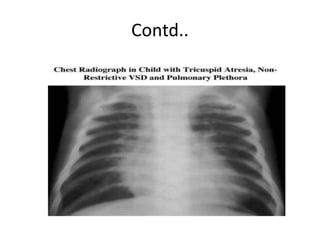
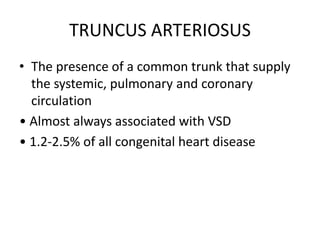
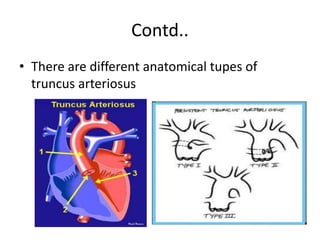
2. Common types with increased pulmonary blood flow include persistent truncus arteriosus and transposition of the great arteries (TGA). Common types with decreased pulmonary blood flow include tricuspid atresia and pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum.
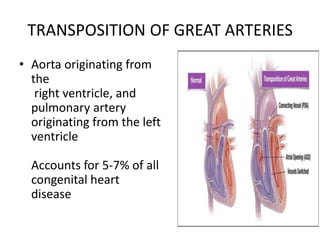
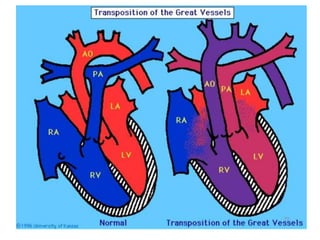
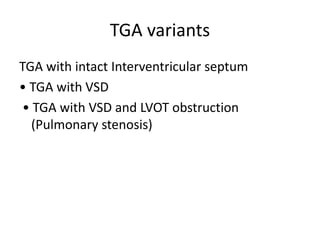
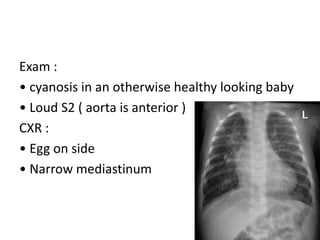
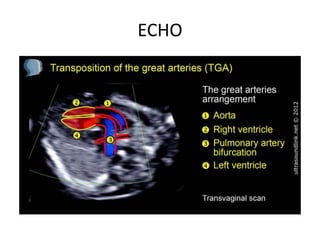
3. TGA accounts for 5-7% of congenital heart defects. It involves the aorta originating from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery originating from the left ventricle. It requires mixing of blood between the pulmonary and systemic