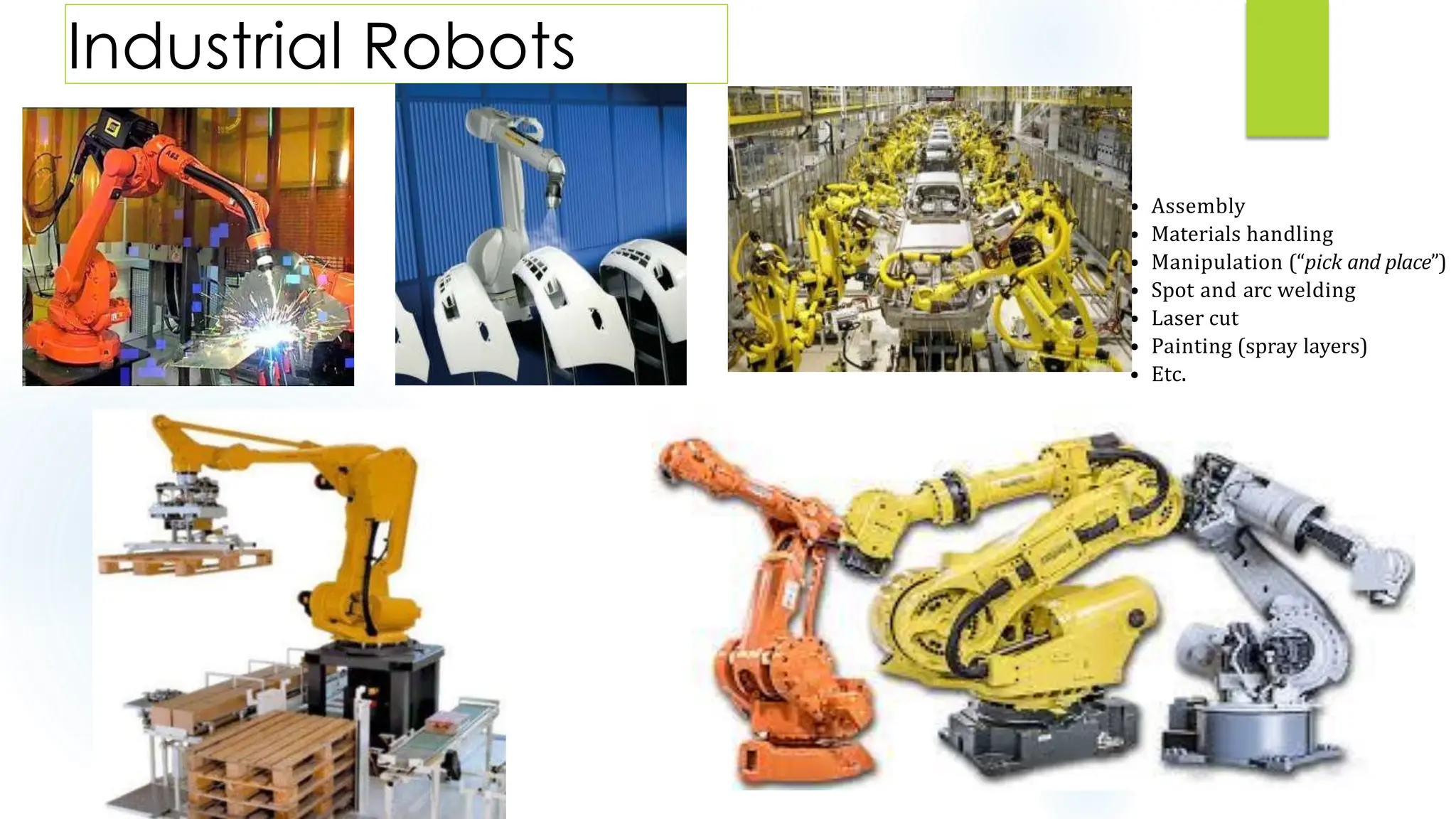
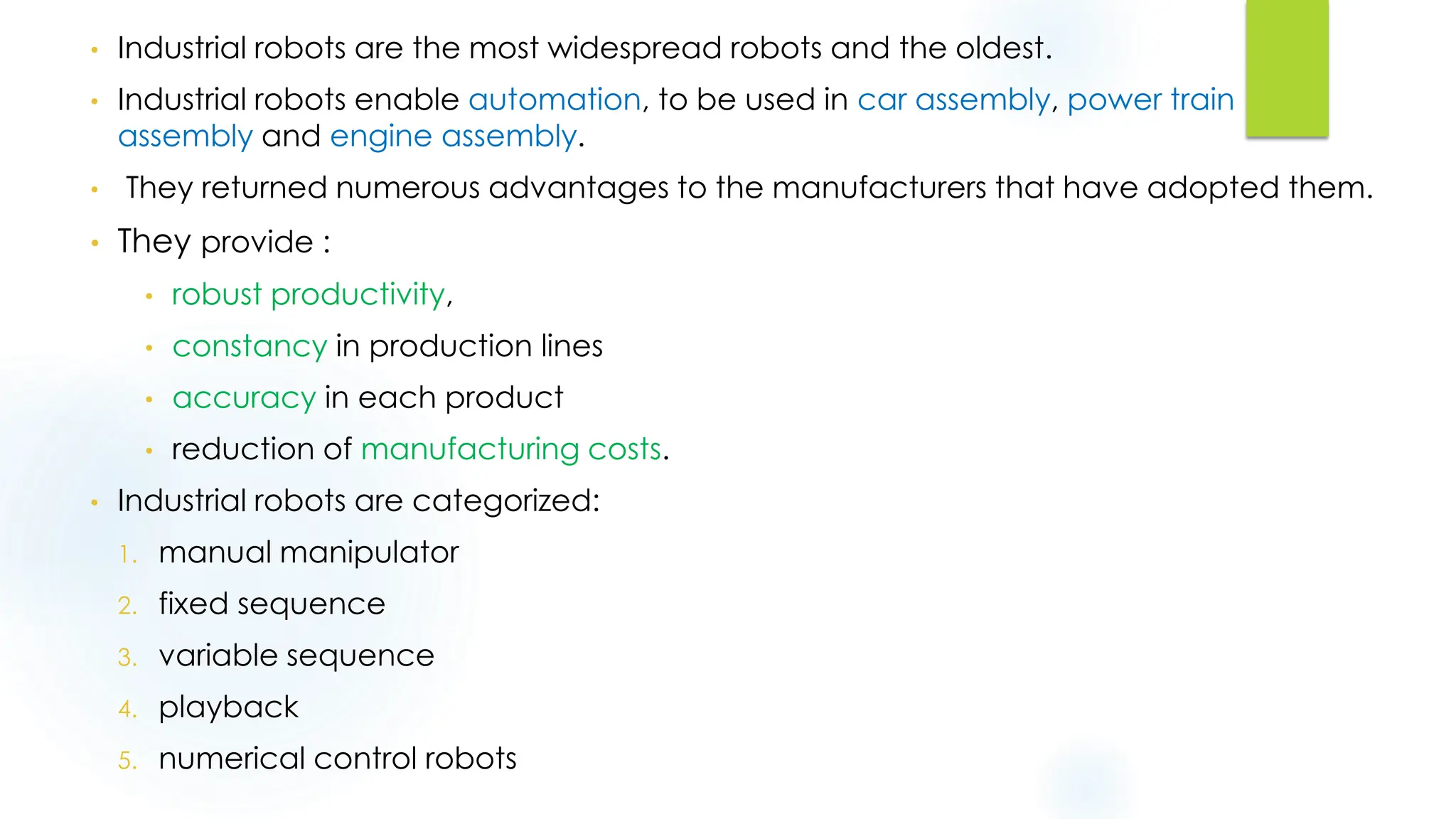
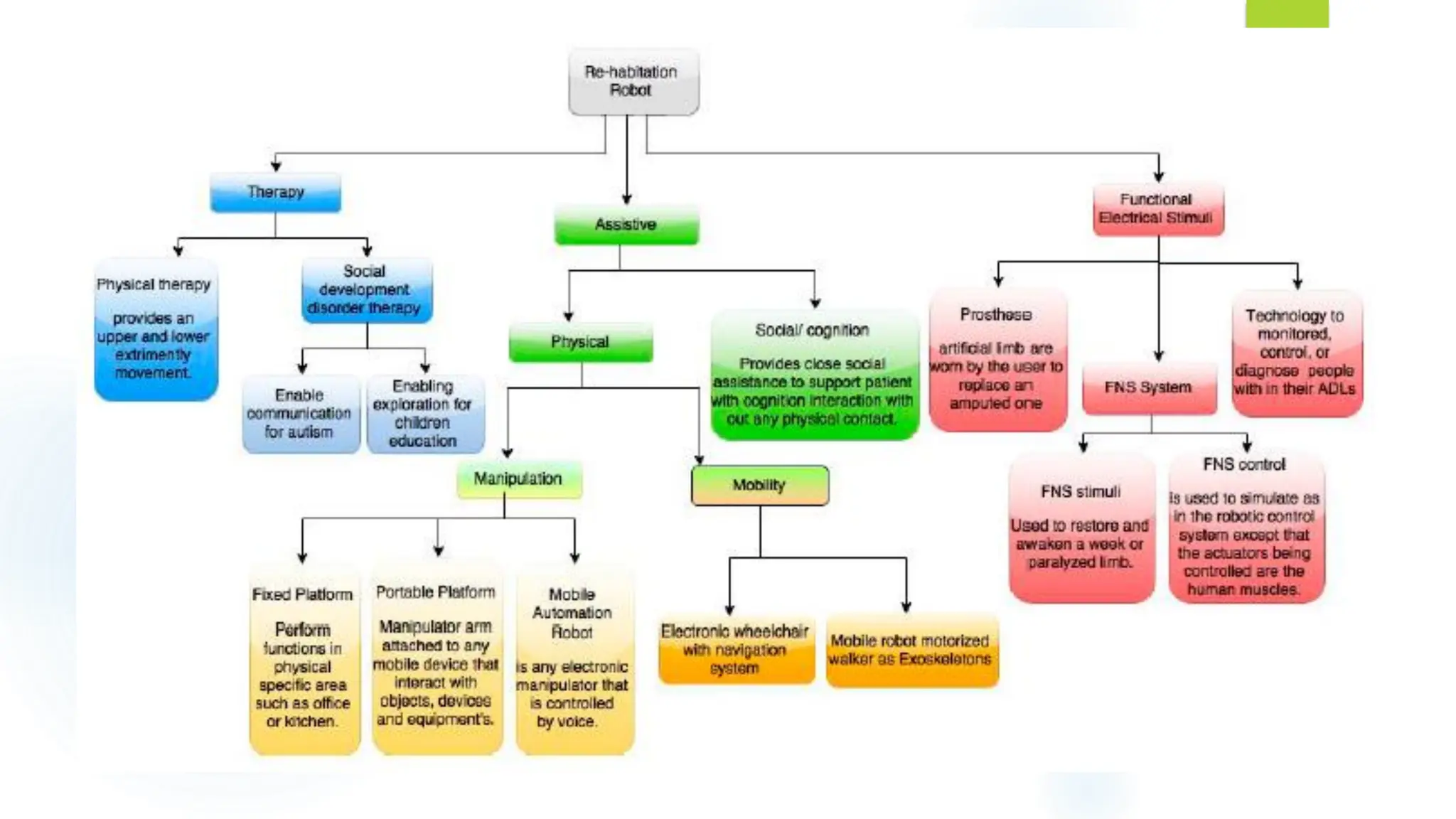
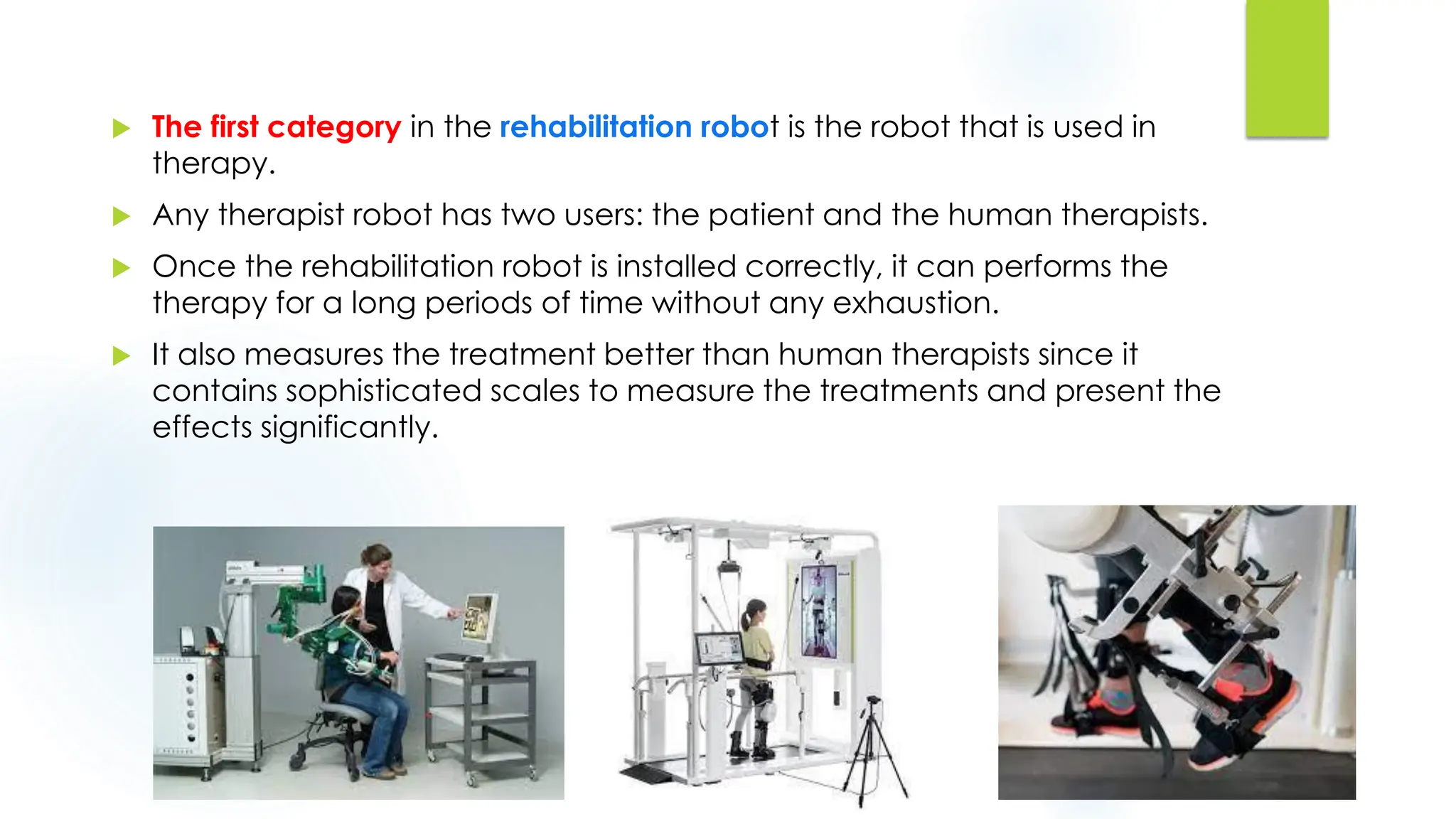
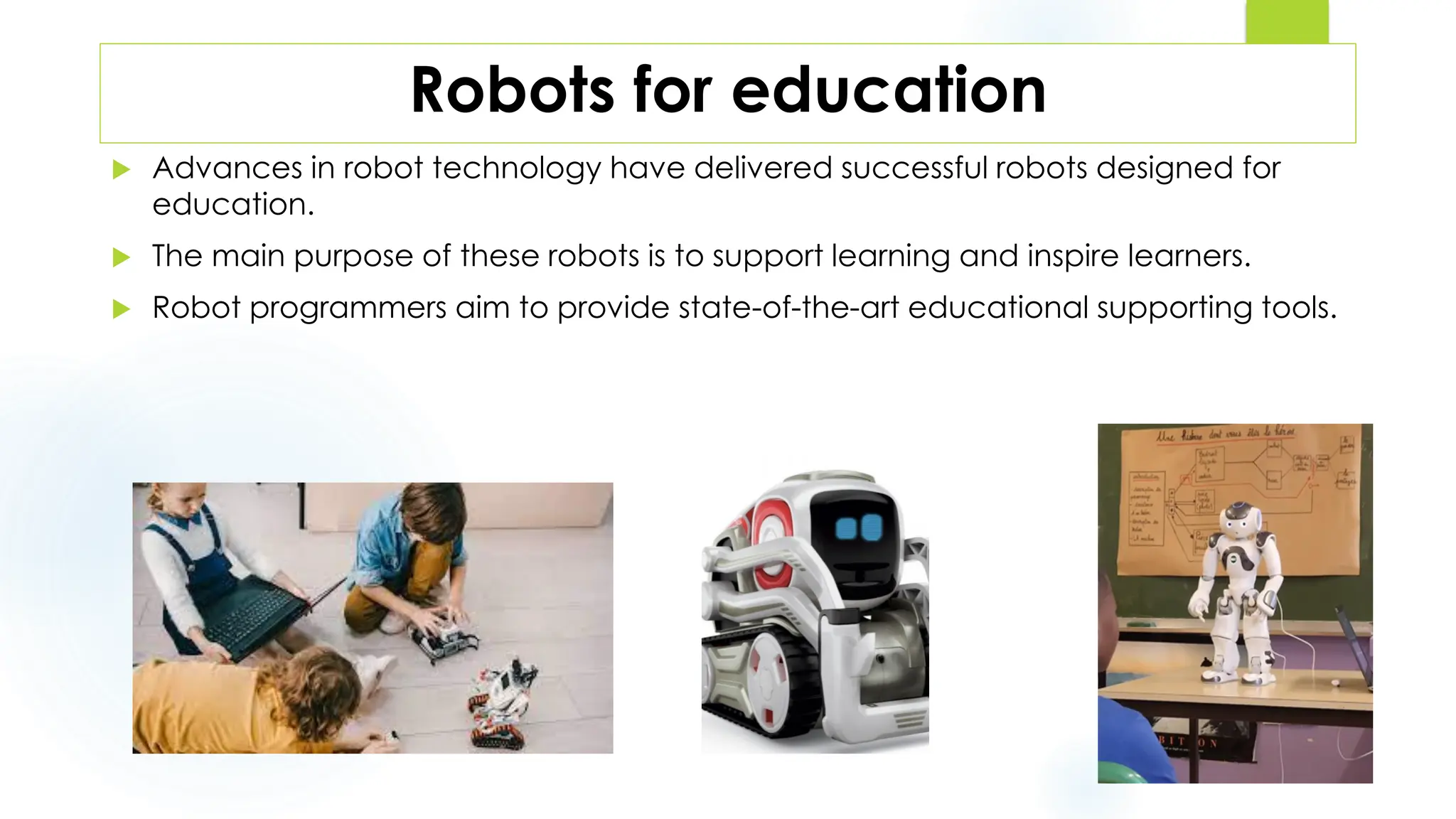
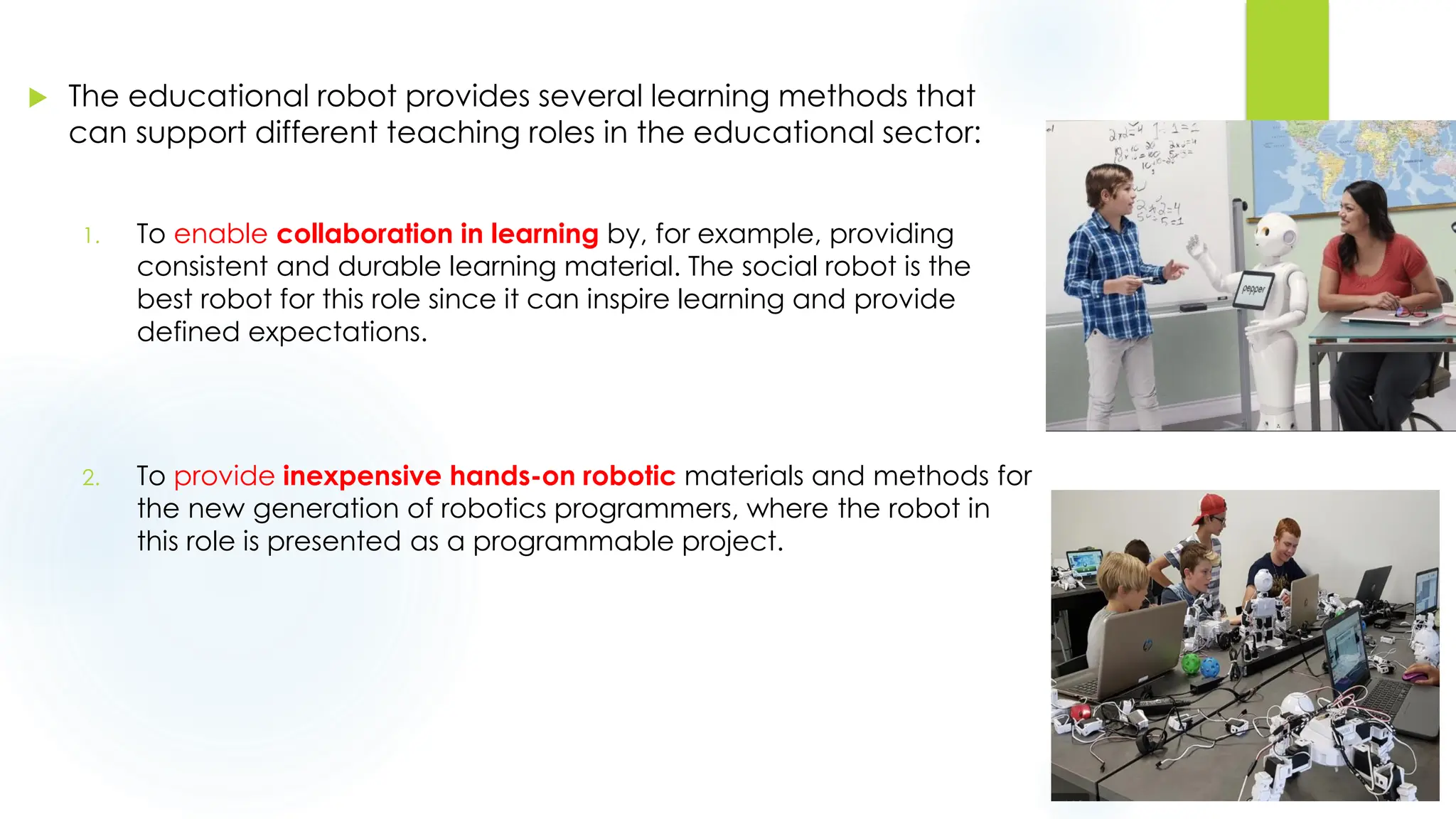
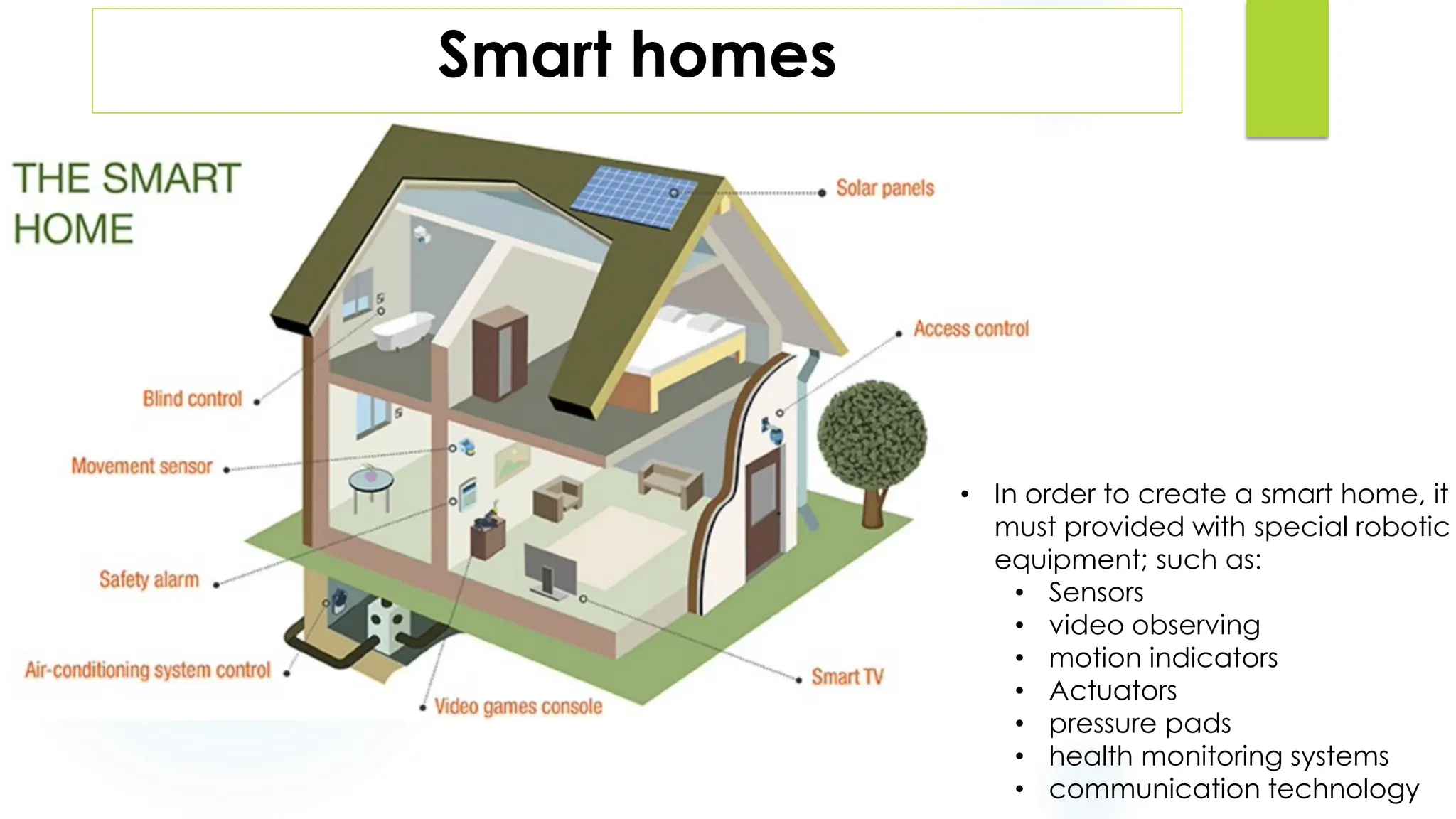
This document discusses krs and specifications for industrial robots.t provides details on each parameter, including defining major and minor axes, how load capacity depends on weight of the end effector, how speed is measured, differences between reach and stroke, and how tool orientation is determined by the robot's axes.