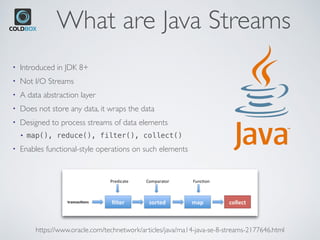
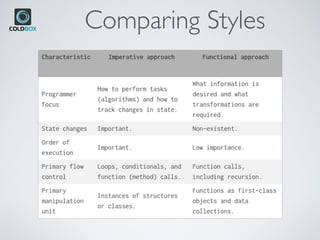
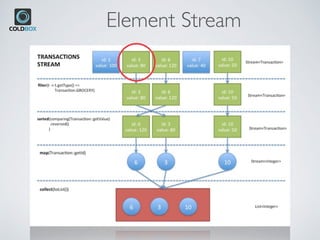
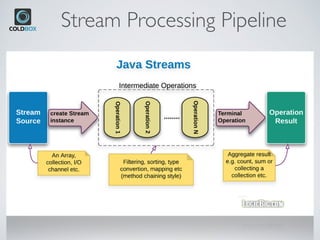
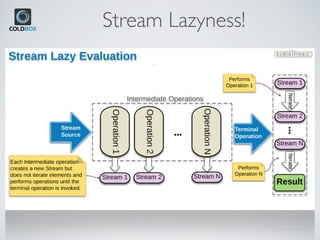
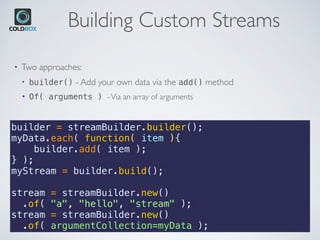
The document introduces CBStreams, a port of Java 8+ streams for CFML, emphasizing functional programming principles and stream functionalities like mapping, filtering, and collecting. It compares imperative and functional programming styles, highlights the lazy evaluation characteristic of streams, and provides examples of building and manipulating streams. Additionally, it covers advanced topics like parallel processing, collectors, and the usage of Java optionals in CFML.










![Streams Functional Heaven!
var errors = [];
var errorCount = 0;
var oFile = fileOpen( filename );
var thisLine = fileReadLine( oFile );
while( errorCount < 40 && !isNull( thisLine ) ){
if( line.startsWith( "ERROR" ) ){
errors.append( line );
errorCount++;
}
line = fileReadLine( oFile );
}
var errors = streamBuilder.ofFile( filePath )
.filter( line => line.startsWith( "ERROR" ) )
.limit( 40 )
.collect();
What if I
want to multi-
thread this?
.parallel()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbstreams-181127180145/85/CBStreams-Java-Streams-for-ColdFusion-CFML-13-320.jpg)


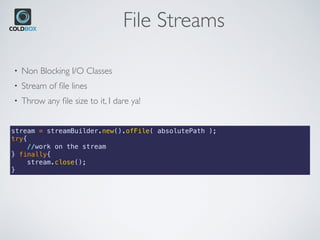
![Lazy Example
var empIds = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ];
var employee = streamBuilder.new( empIds )
// Convert ID's to Employee Objects, passing function reference
.map( employeeService.findByID )
// only valid employees
.filter( (employee) => !isNull( employee ) )
.filter( function( employee ){ return !isNull (employee); } )
// only salaries > 10000
.filter( (employee) => employee.getSalary() > 100000 )
// Find the first one
.findFirst()
// Return null
.orElse( null );
expect( employee.getSalary() ).toBe( 200000 );
• Stream performs the map and two filter operations, one element at a time.
• Since the salary of id 1 is not greater than 100000, the processing moves on to the next
element.
• Id 2 satisfies both of the filter predicates and hence the stream evaluates the terminal
operation findFirst() and returns the result.
• No operations are performed on id 3 and 4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbstreams-181127180145/85/CBStreams-Java-Streams-for-ColdFusion-CFML-19-320.jpg)






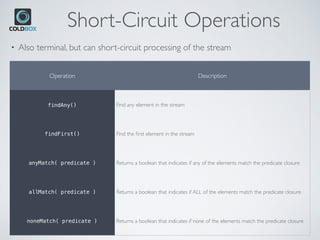
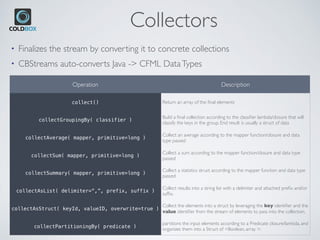
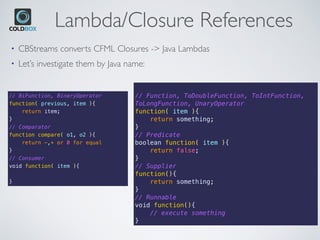
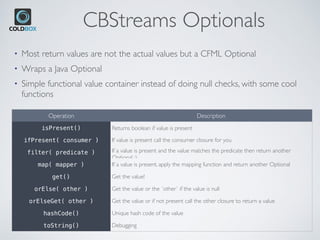
![Examples
myArray = [
"ddd2",
"aaa2",
"bbb1",
"aaa1",
"bbb3",
"ccc",
"bbb2",
"ddd1"
];
// Filtering
streamBuilder.new( myArray )
.filter( function( item ){
return item.startsWith( "a" );
} )
.forEach( function( item ){
writedump( item );
} );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbstreams-181127180145/85/CBStreams-Java-Streams-for-ColdFusion-CFML-33-320.jpg)


![Examples
// Partition stream to a struct of arrays according to even/odd
var isEven = streamBuilder.new( 2,4,5,6,8 )
.collectPartitioningBy( function(i){
return i % 2 == 0;
} );
expect( isEven[ "true" ].size() ).toBe( 4 );
expect( isEven[ "false" ].size() ).toBe( 1 );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbstreams-181127180145/85/CBStreams-Java-Streams-for-ColdFusion-CFML-36-320.jpg)






