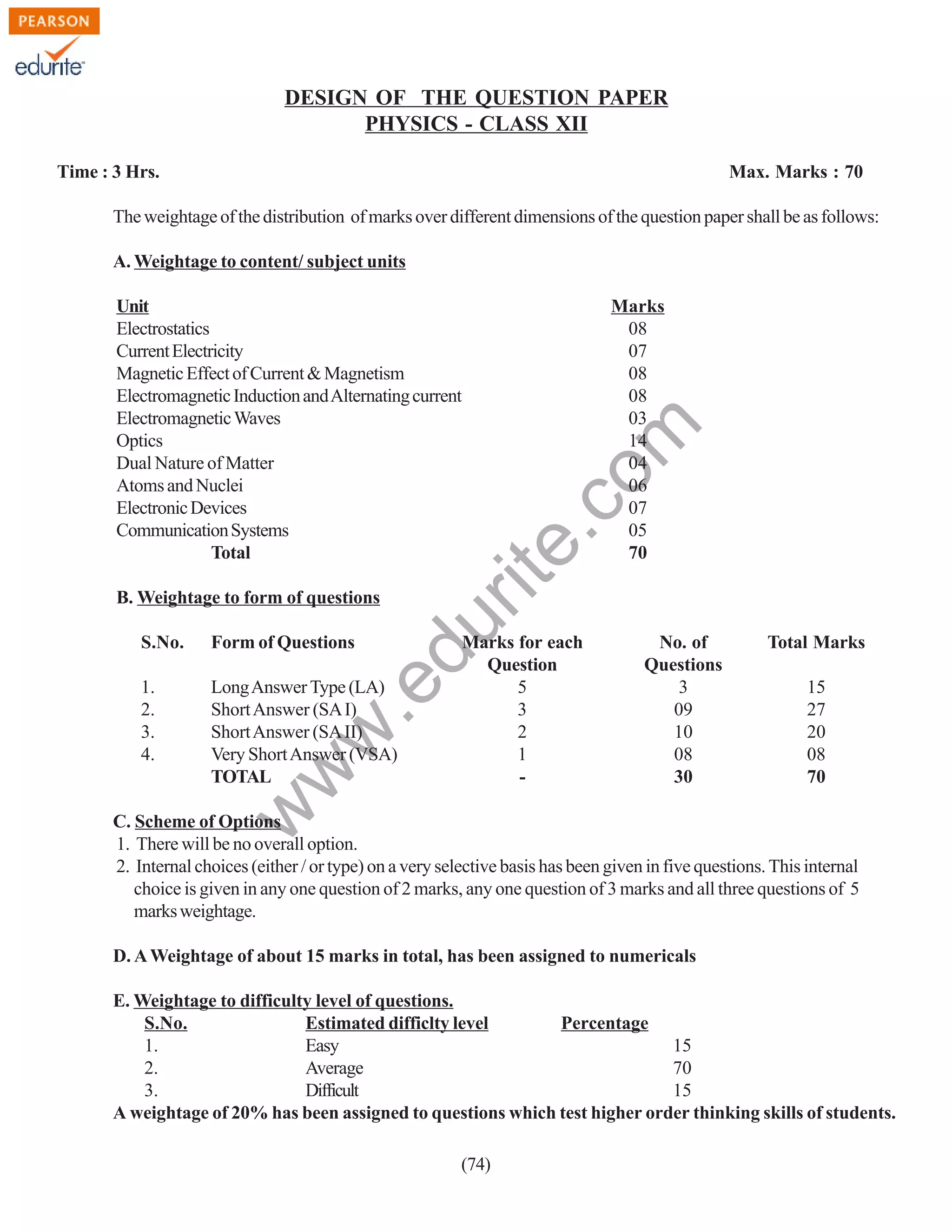
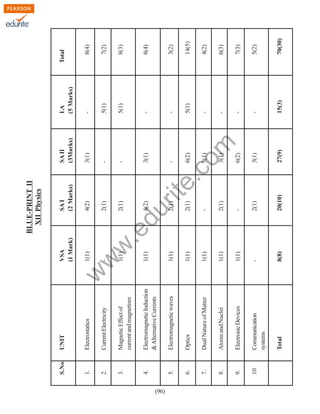
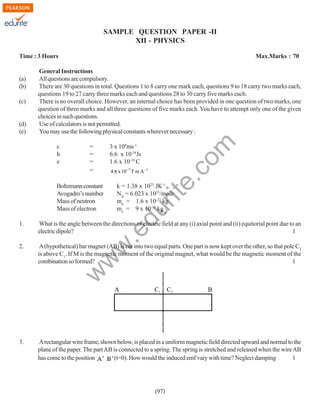
The document outlines the design of a Class XII Physics question paper with a total duration of 3 hours and a maximum score of 70 marks, detailing the distribution of marks across various types of questions including long answer, short answer, and very short answer questions. It includes weightage assigned to different units and levels of difficulty, as well as instructions for answering the questions, including the prohibition on the use of calculators. Additionally, it specifies the presence of internal choices for certain questions but no overall options.




![Q.No
Value Points
Marks
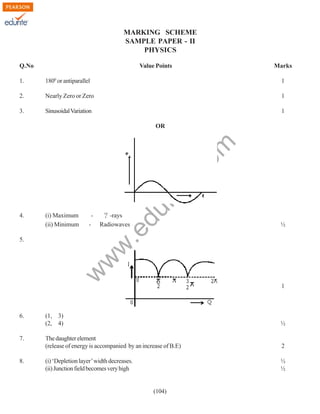
Change in energy stored
1
Output not symmetric for A, B = (0, 1) and
(1,0)
NOT gate in one input.
NOR gate
(i) has three zeros
1
Thus
1
(ii) has three one’s
OR gate
Thus
22.
The two main considerations
(i) Large light gathering power
(ii) Higher resolution (resolving power)
rit
e.
co
m
21.
1
½
½
.e
du
[Both these requirements are met better when an objective of large focal length as well as large aperture is used]
Ray diagram for normal adjustment.
½
Derivation of the expression for angular magnifying power
1
Derivation of the expression for the length of the telescope tube
½
w
w
w
23.
size of atom,
½
<<size of ball
1
24.
½
½
½
½
(108)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbse-class-12-physics-sample-paper-2010-model-2-140122062225-phpapp02/85/Cbse-12-Class-Physics-Sample-Paper-2010-Model-2-14-320.jpg)
![Q.No
Value Points
The term
Marks
is known as displacement current
This term has been used to modify and generalize Ampere’s Circuital law.
½
½
25.
½
Here
can take values
(Corresponding to n1 = 2, 3, 4, --------------
rit
e.
co
m
Let us take n2 = 1 (Lyman series of hydrogen spectrum)
)
, 1091Ao, 1034.6 Ao, ----------------------970Ao
½
½
Let us next take n2 = 2 (Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum)
.e
du
∴
λ
26.
½
½
of the given lines, cannot belong to the hydrogen atom
½
w
Hence
spectrum.
w
w
(Coresponding to n1 = 3, 4, 5--------------)
o
Possible values of
are 6984A , 5173. 3Ao, 4619Ao, -------3880Ao
½
Space wave : A space wave travels in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna : 1
Two ways : Line of sight communication and satellite communication]
½
½
We have
1
27.
Transfer characteristics
Brief discussion of ‘active region’
1
1½
(109)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbse-class-12-physics-sample-paper-2010-model-2-140122062225-phpapp02/85/Cbse-12-Class-Physics-Sample-Paper-2010-Model-2-15-320.jpg)

