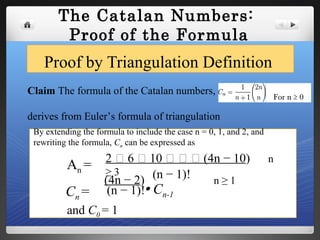
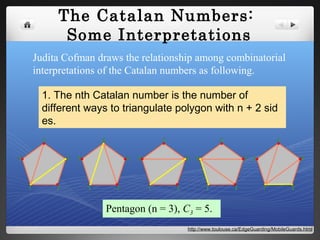
The document discusses Catalan numbers, which have various interpretations in combinatorics. Specifically:
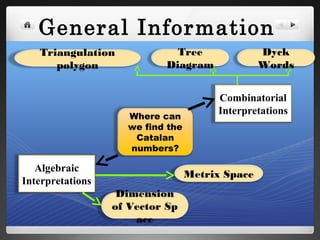
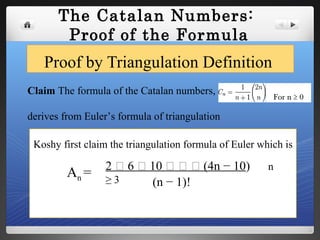
1) Catalan numbers count the number of ways to triangulate a polygon with n+2 sides.
2) They also count the number of possible tree diagrams that can be drawn with n+1 leaves.
3) Additionally, Catalan numbers represent the number of arrangements of Dyck words of length 2n.
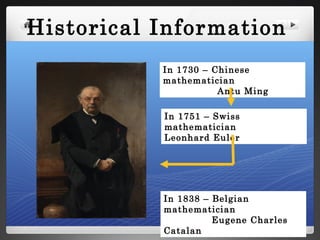
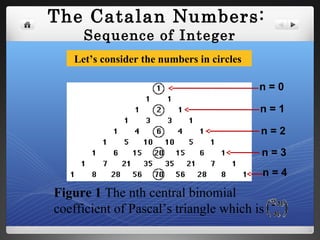
The document provides historical background on Catalan numbers and explores proofs and interpretations of the numbers in fields like triangulation, trees, Dyck words, and monotonic paths on grids.