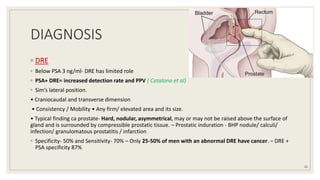
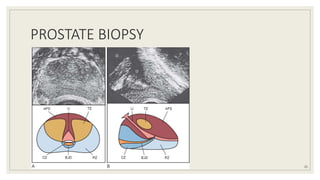
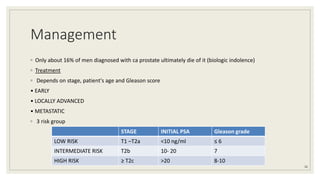
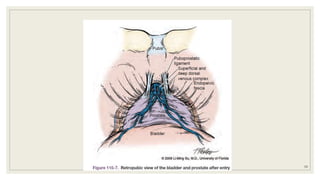
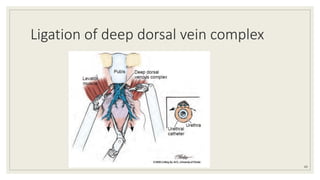
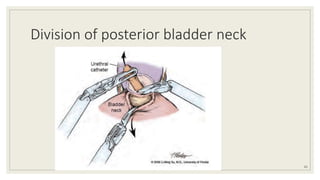
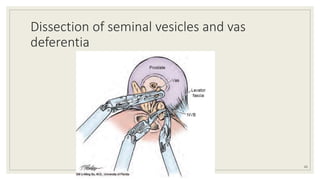
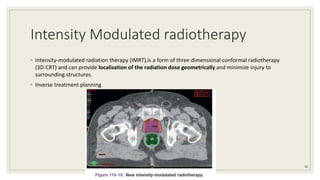
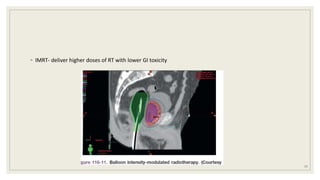
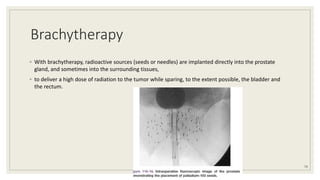
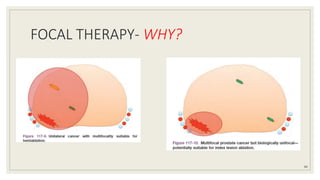
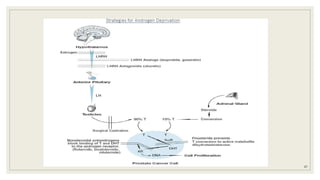
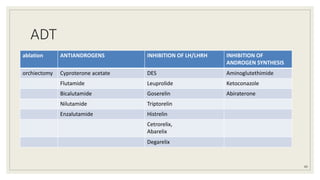
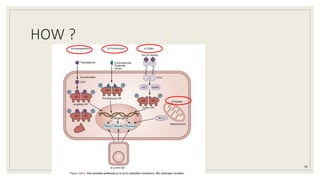
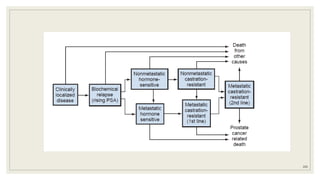
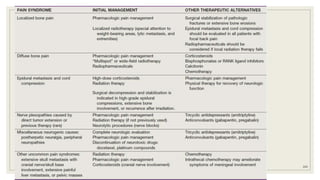
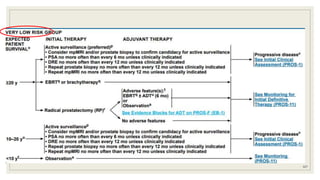
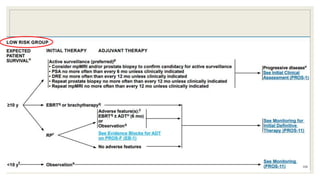
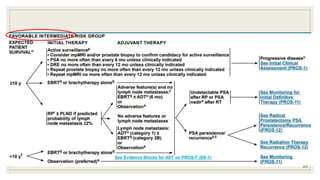
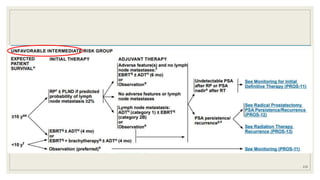
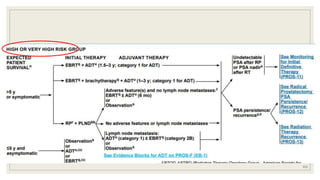
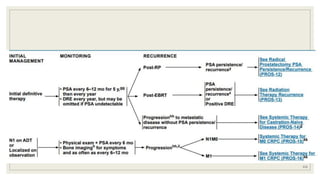
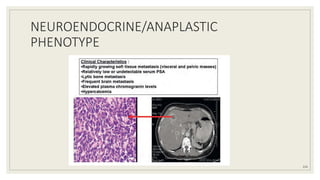
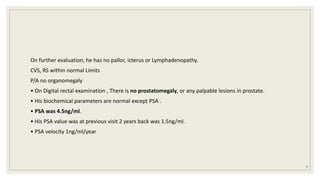
Dr. Arjun Singh, a 52-year-old male, presented for his annual health checkup. He has a family history of prostate cancer as his father had it. His PSA levels have been monitored every few years and were previously normal, but are now elevated at 4.5 ng/ml. A digital rectal exam found no abnormalities in the prostate. Given his rising PSA and family history, a prostate biopsy was recommended to evaluate for possible prostate cancer.






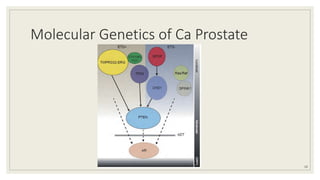
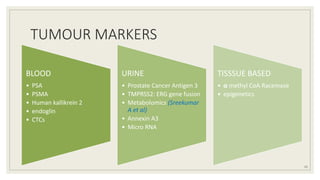
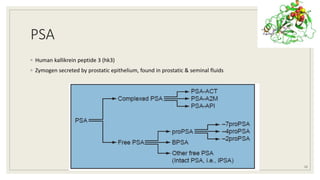
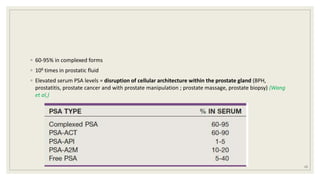



![◦ PHI:
◦ tPSA, f PSA, [-2] proPSA
◦ high-grade disease compared to either tPSA or %fPSA (Catalona et al,)
◦ 4K Pannel:
◦ likelihood of clinically significant prostate cancer (Carlsson et al,)
◦ Includes t PSA, fPSA, iPSA, hK2
◦ PSMA
◦ Increased tissue expression- worse prognosis after surgery
◦ 68Ga-PSMA PET- biochemical recurrence after primary therapy
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carcinomaprostate2-201012151730/85/carcinoma-prostate-19-320.jpg)