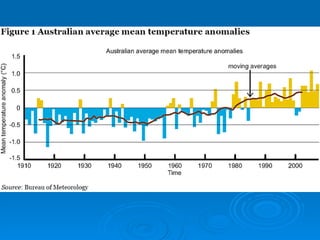
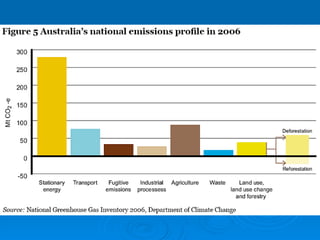
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is Australia's plan to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change. It aims to reduce Australia's emissions by 60% by 2050 through a cap-and-trade system. The scheme would cover 75% of Australia's national emissions and require the largest 1000 polluting firms to buy permits to emit carbon. It aims to reduce emissions in a cost-effective way while providing assistance to households, businesses, workers and regions most affected.