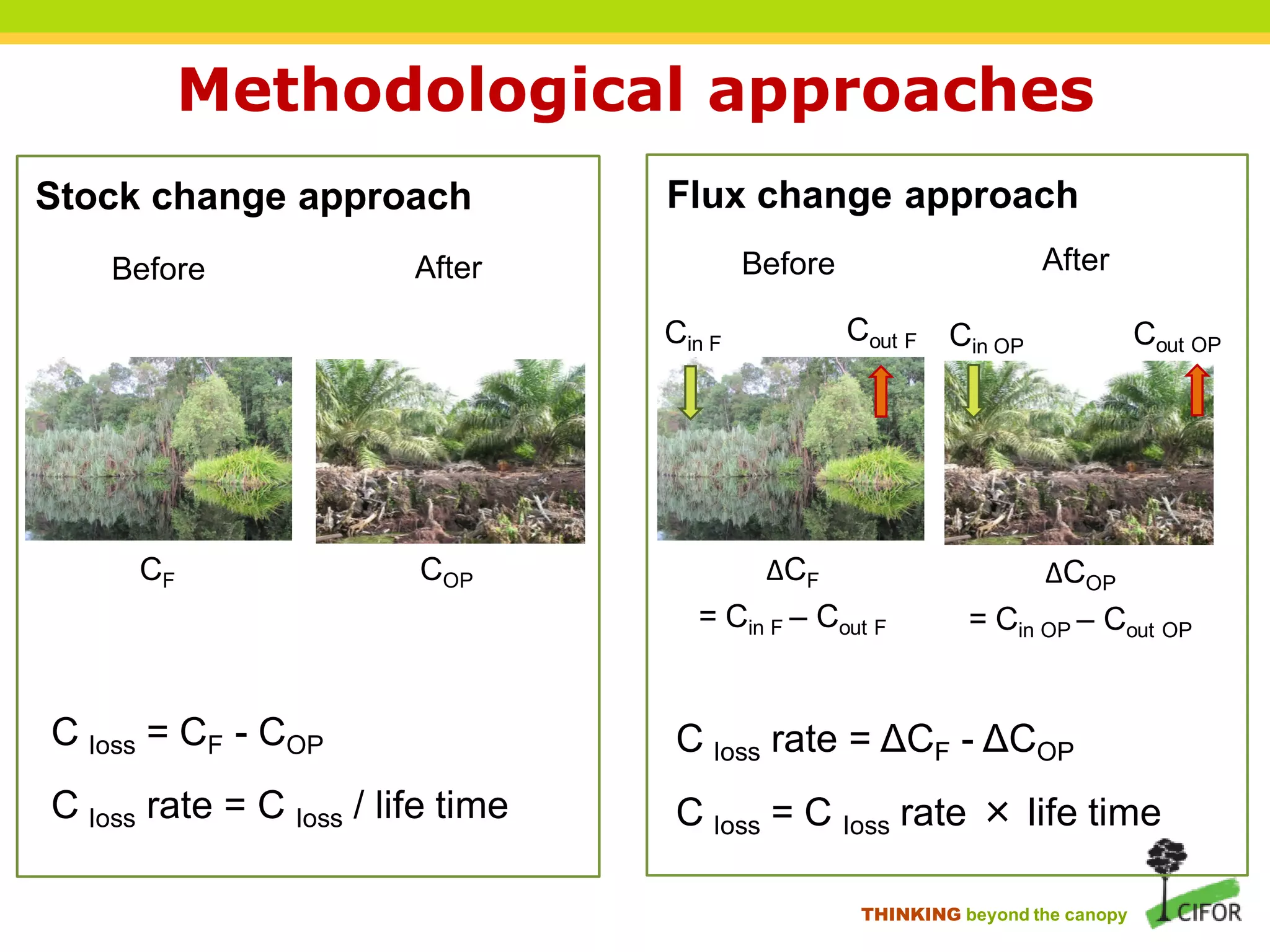
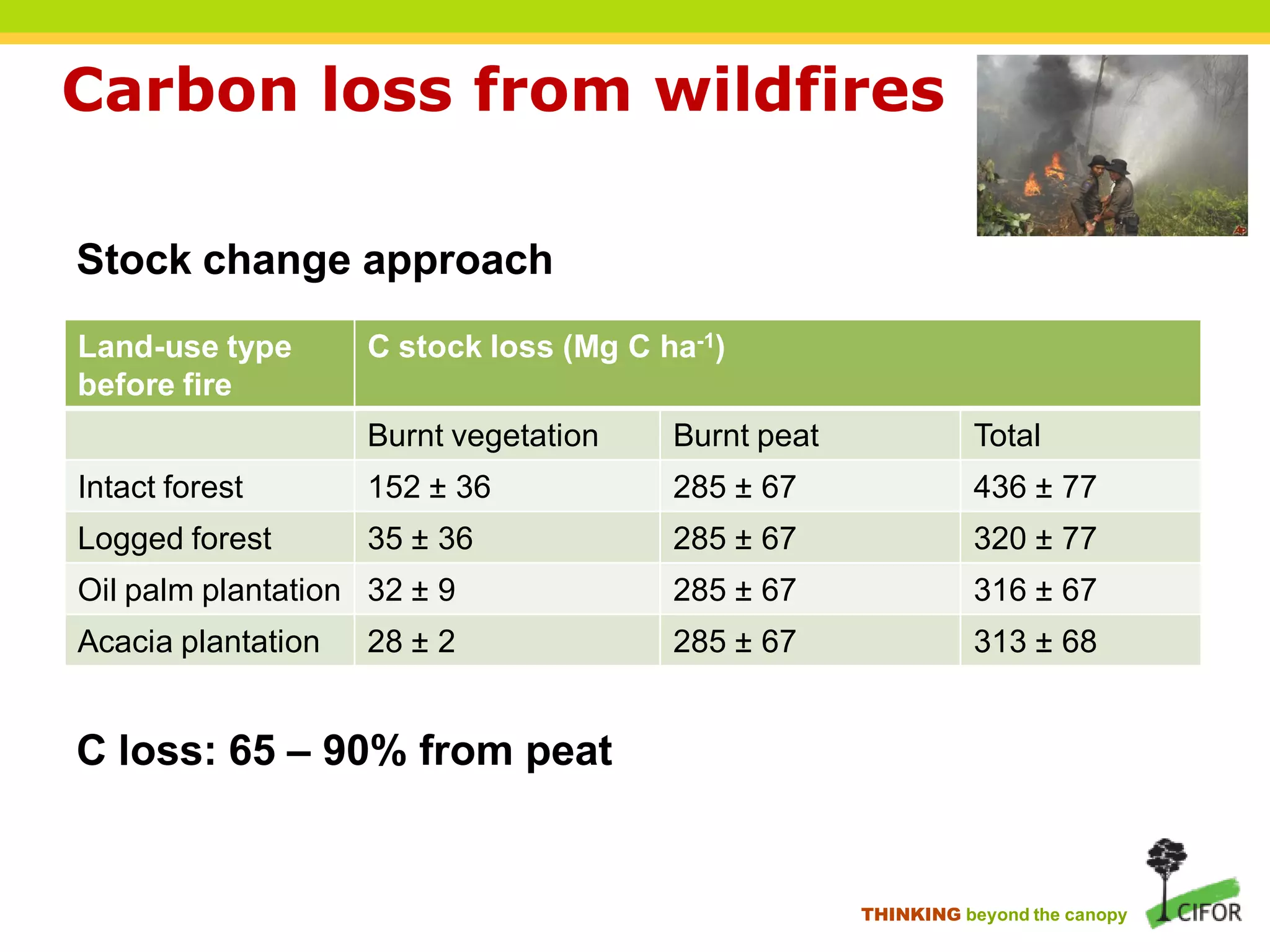
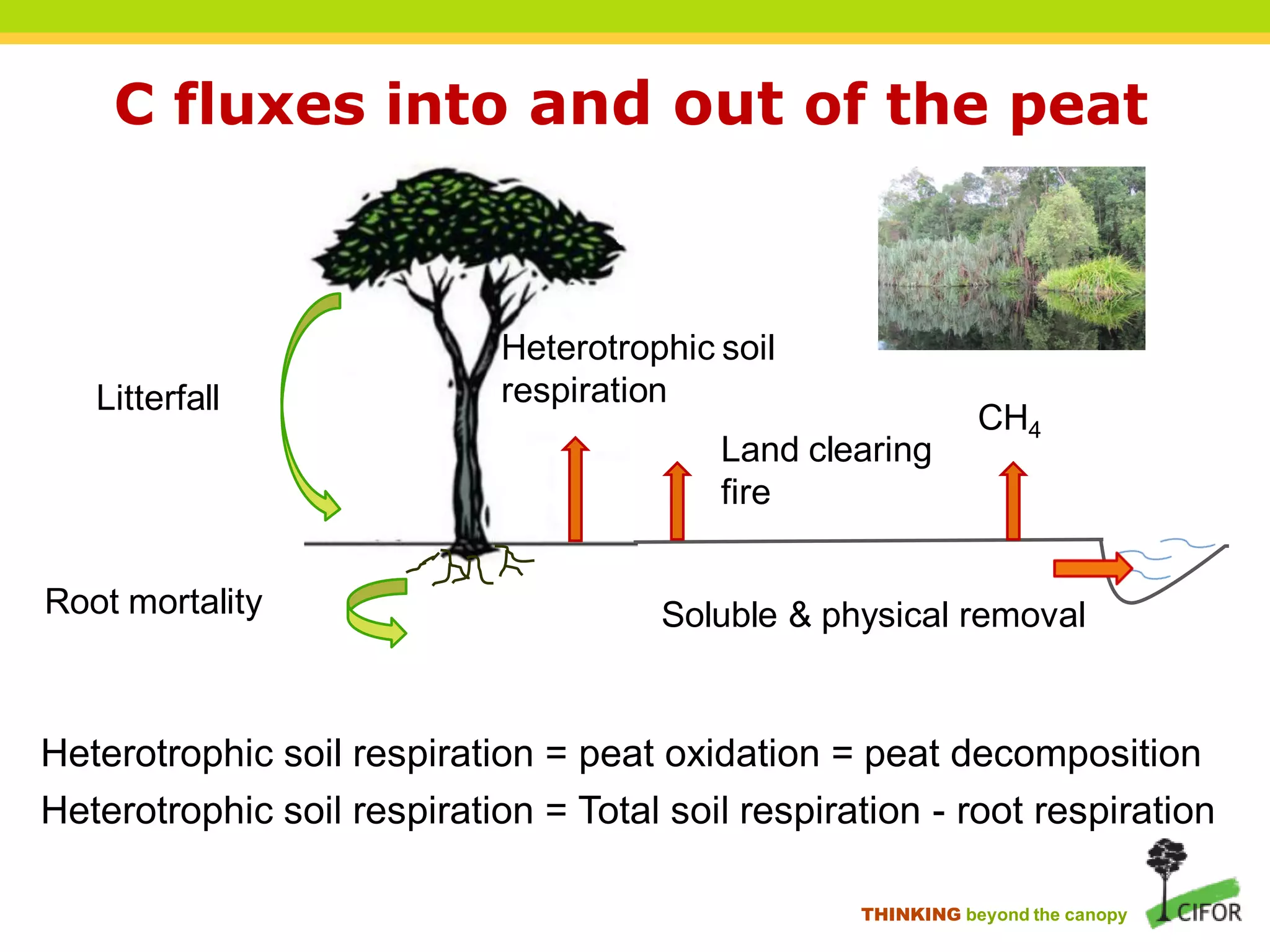
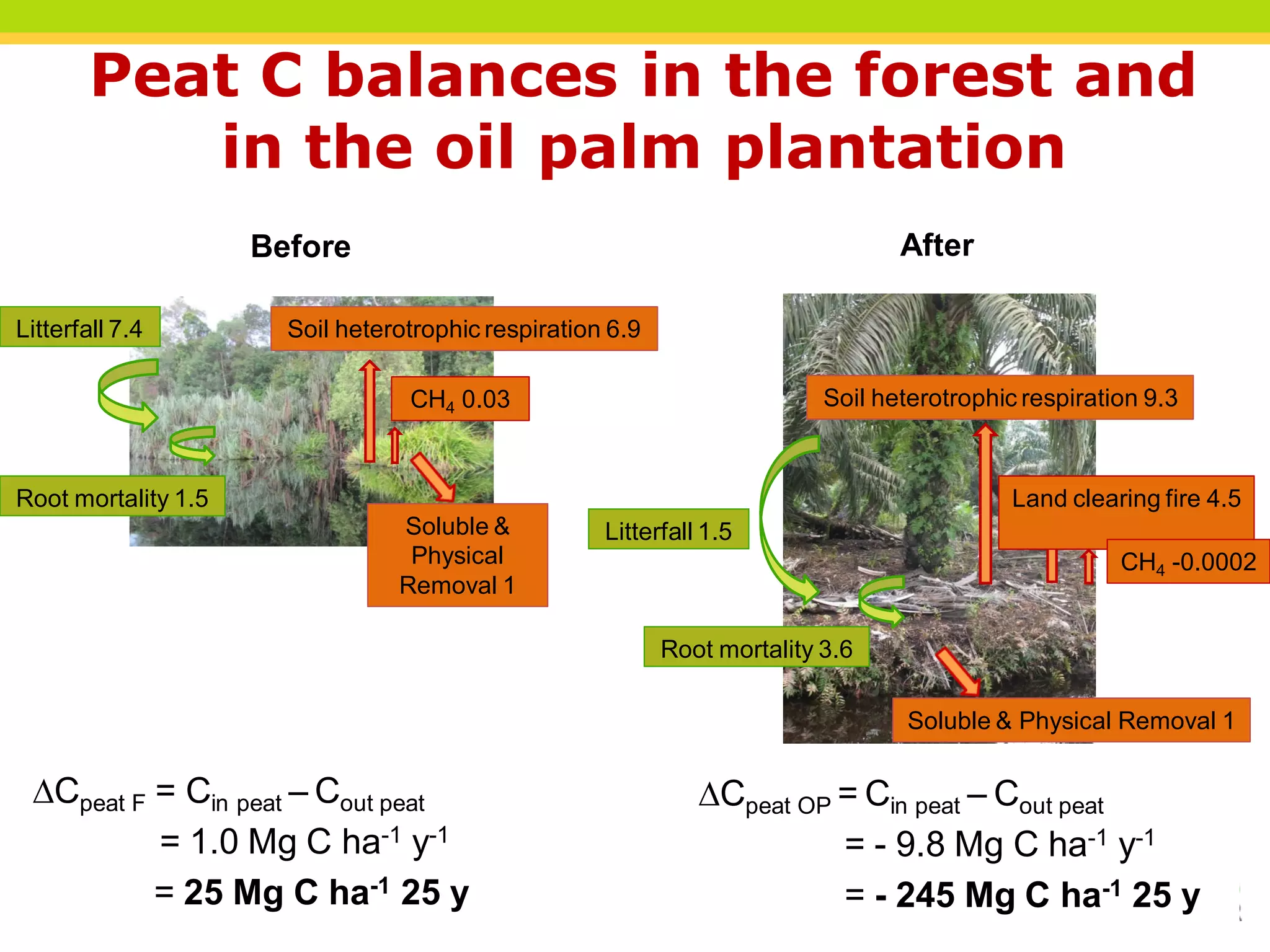
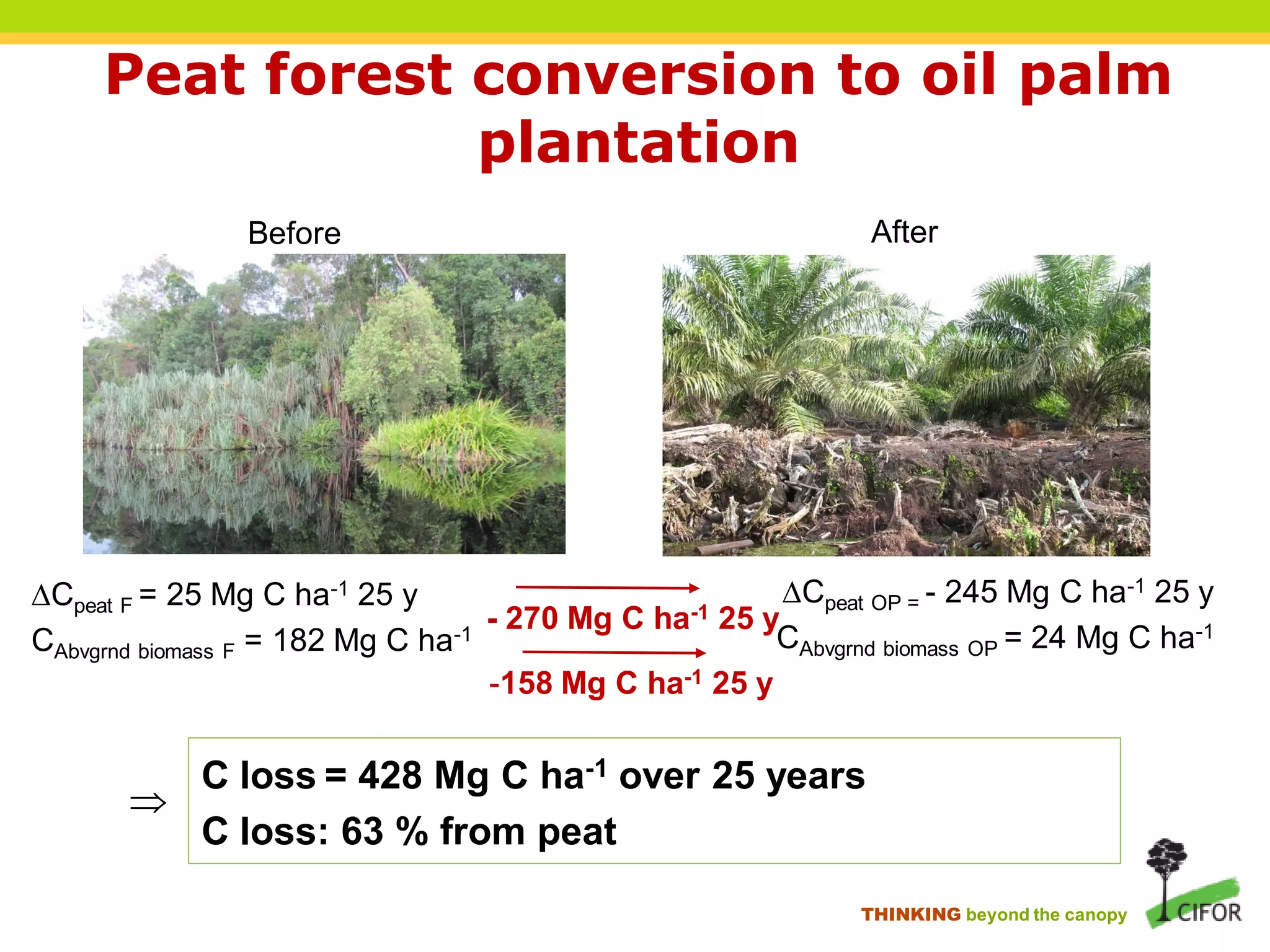
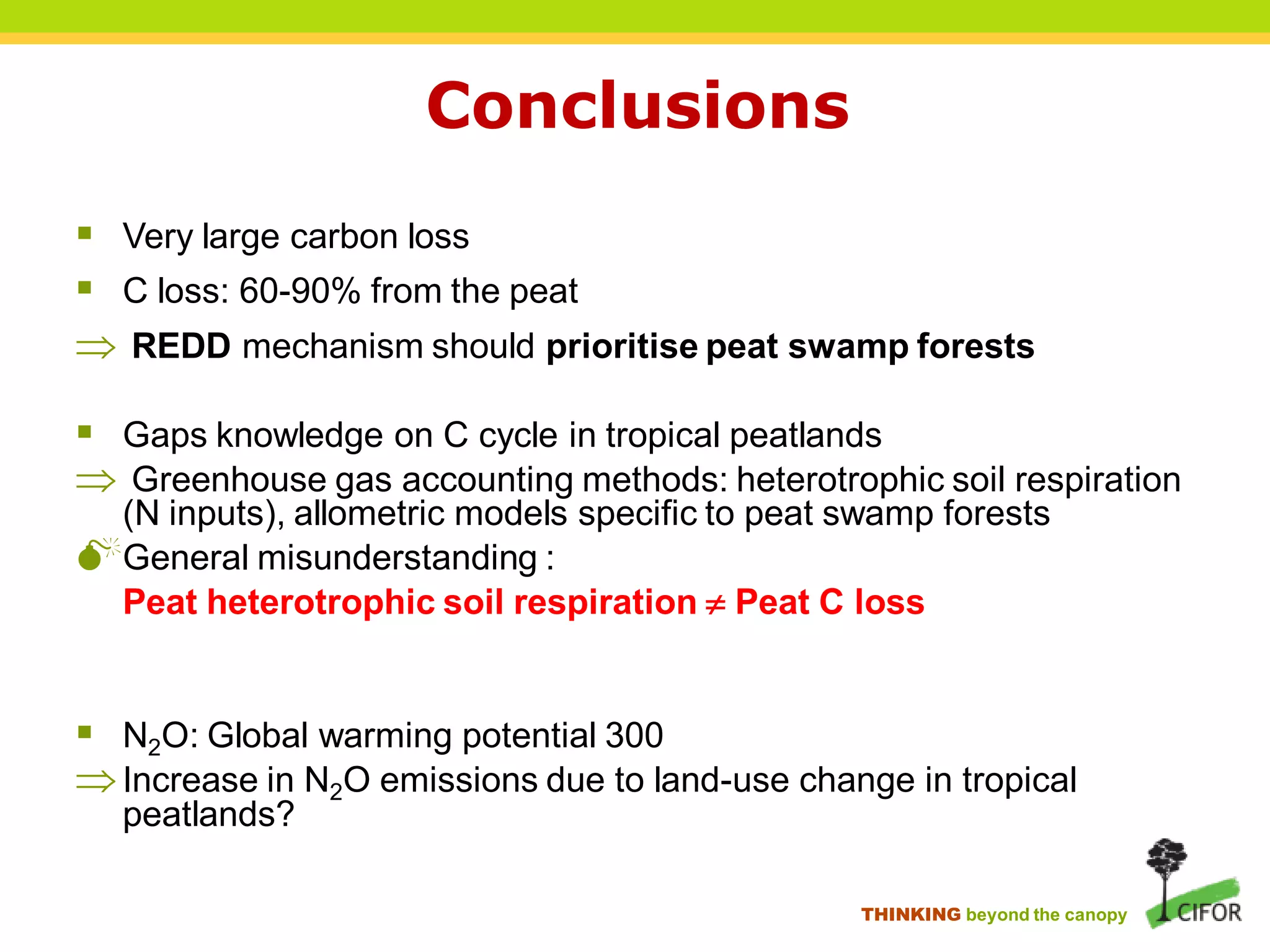
The document discusses carbon loss associated with land-use change in tropical peatlands, highlighting methodological approaches for estimating carbon stocks and fluxes. It reviews carbon loss data indicating that 60-90% of carbon loss primarily originates from peat, particularly during land-use changes such as conversion to oil palm plantations. The study emphasizes the need for improved greenhouse gas accounting methods specific to peat swamp forests and addresses gaps in understanding carbon cycling in these ecosystems.