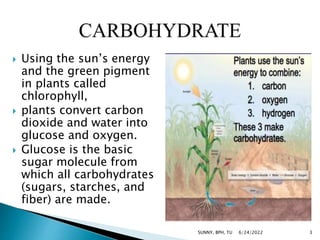
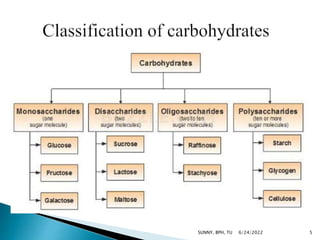
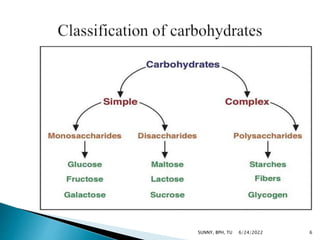
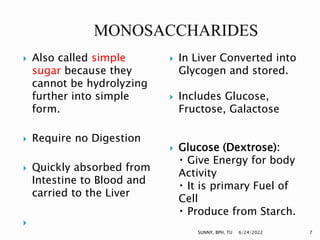
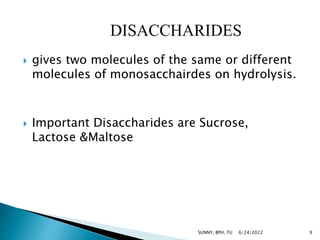
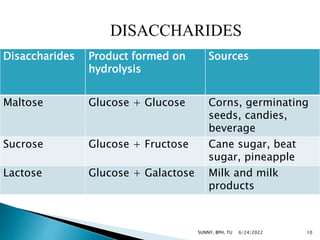
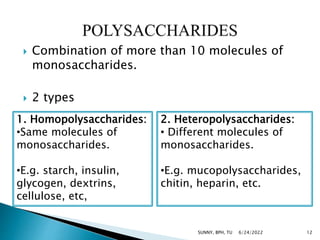
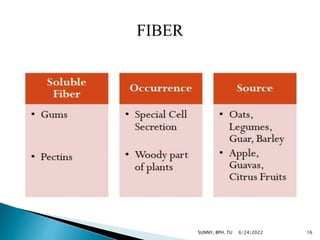
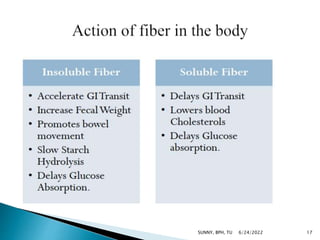
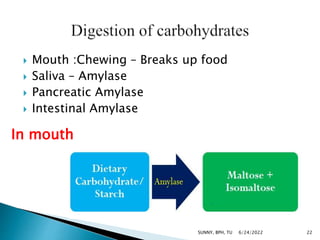
Carbohydrates are a major source of energy, providing 4 calories per gram. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Plants use photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which is the basic sugar molecule used to form carbohydrates like sugars, starches, and fiber. Carbohydrates provide energy for the body and are useful for fat oxidation, growth of bacteria, vitamin synthesis, mineral absorption, and more. Excess carbohydrates beyond 50-60% of daily calories can be converted to body fat.