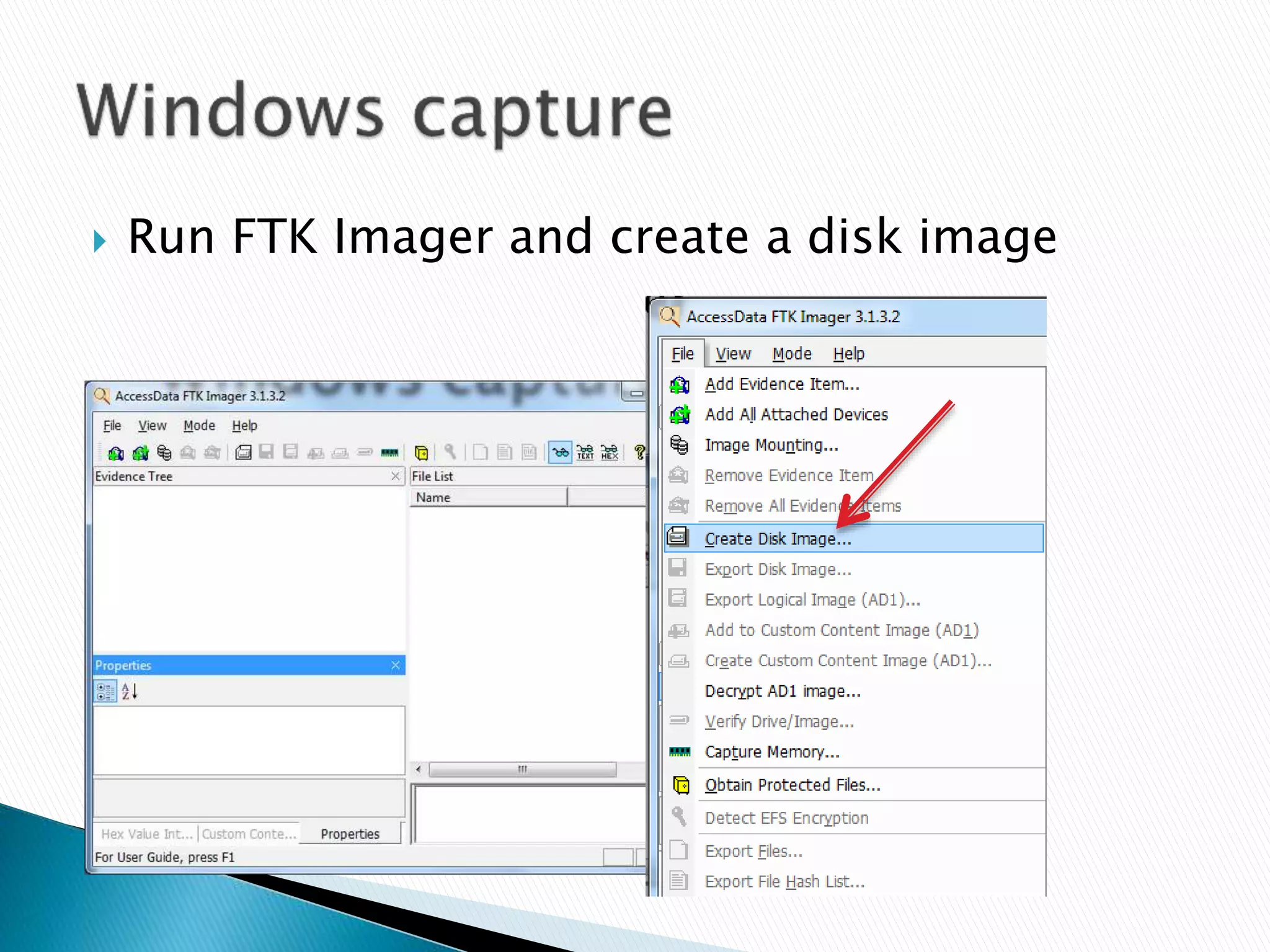
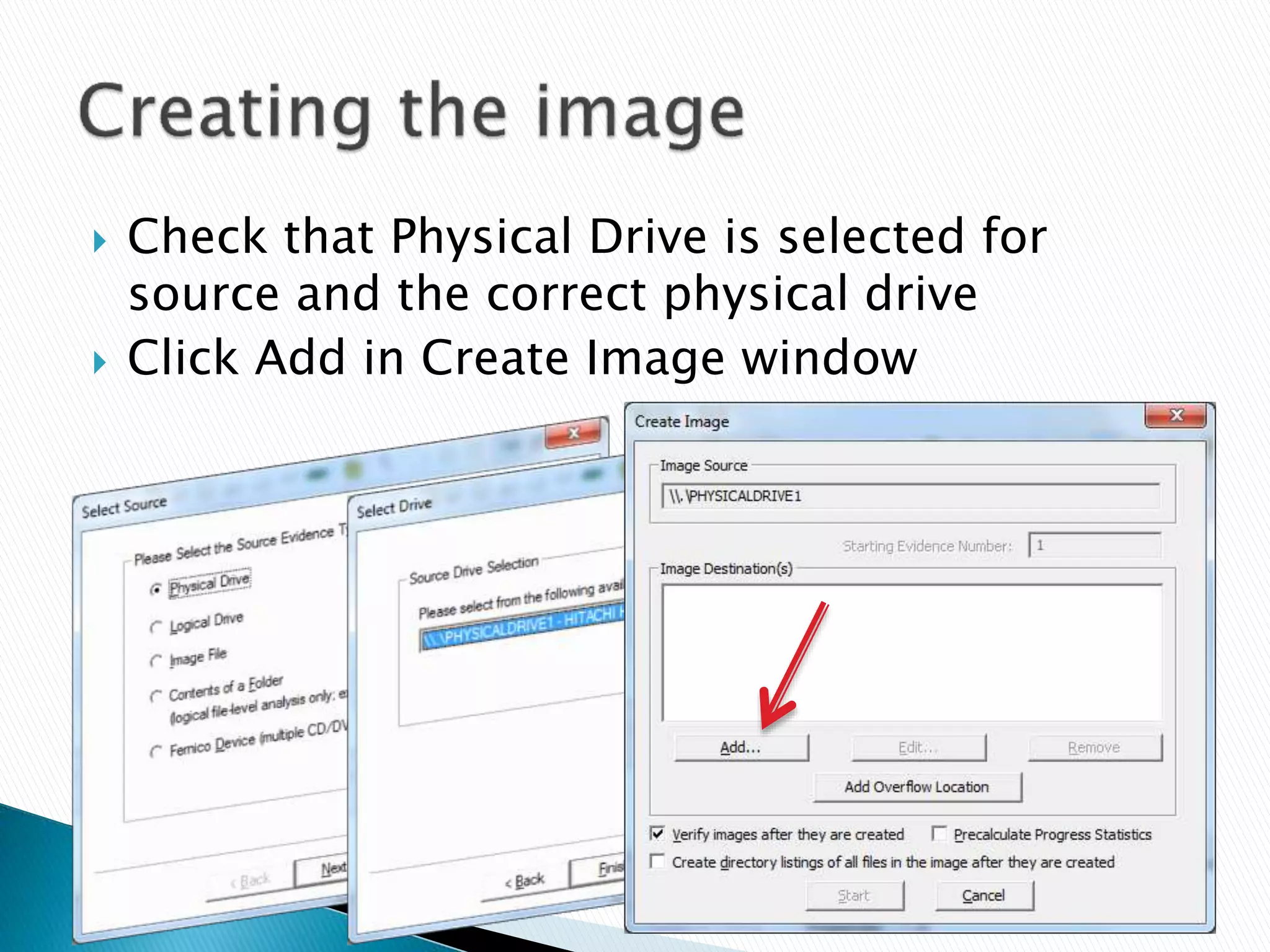
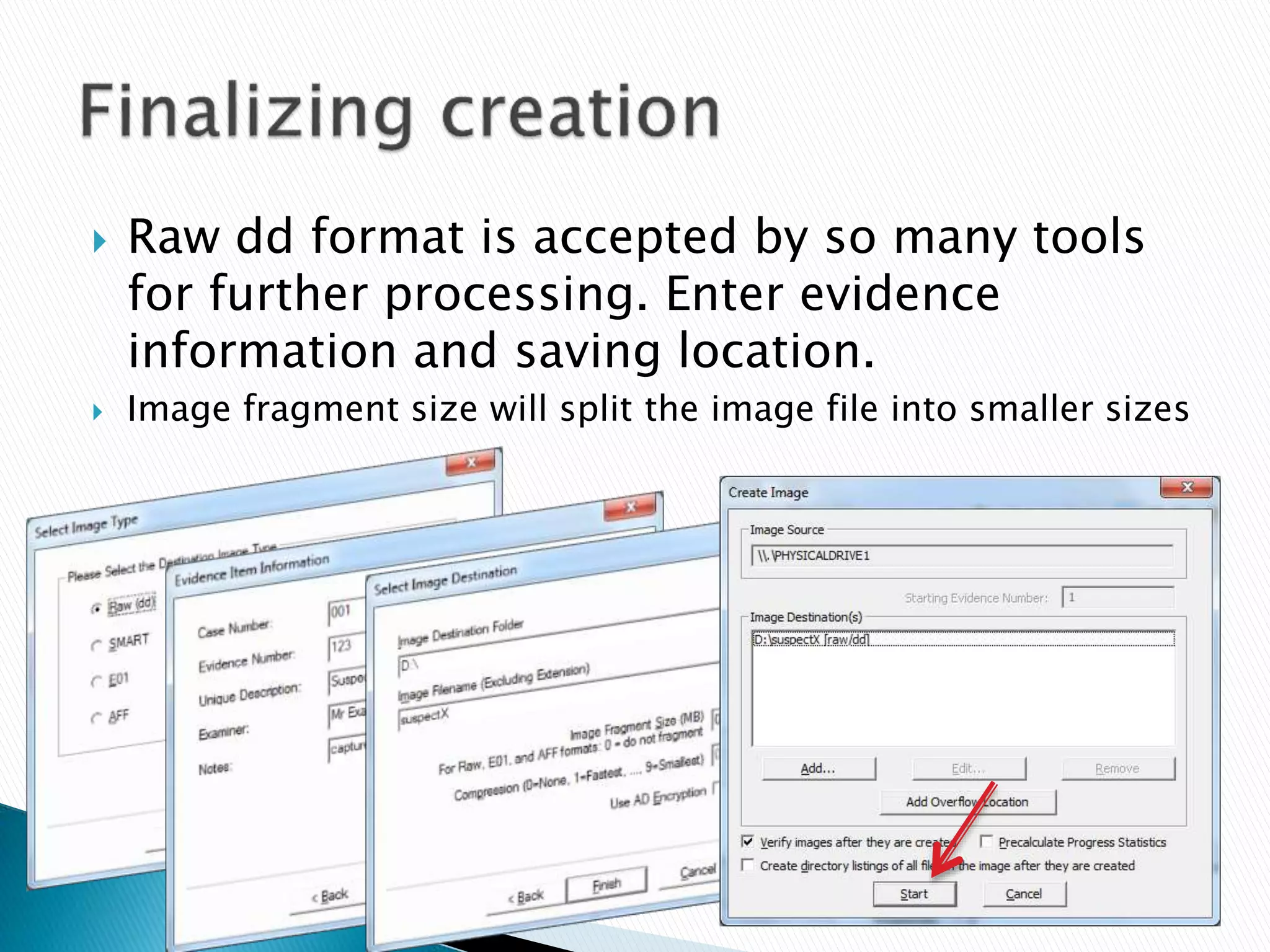
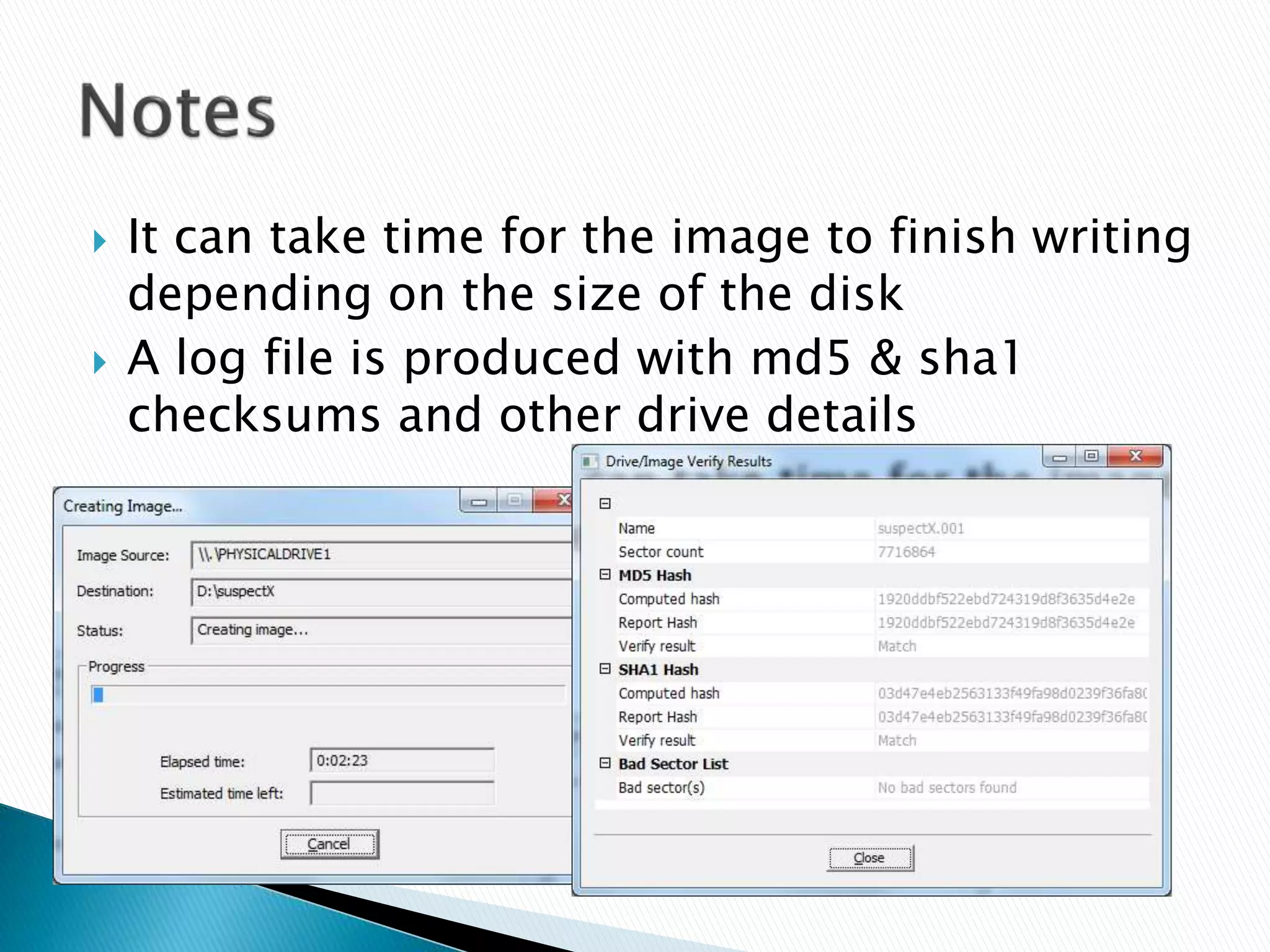
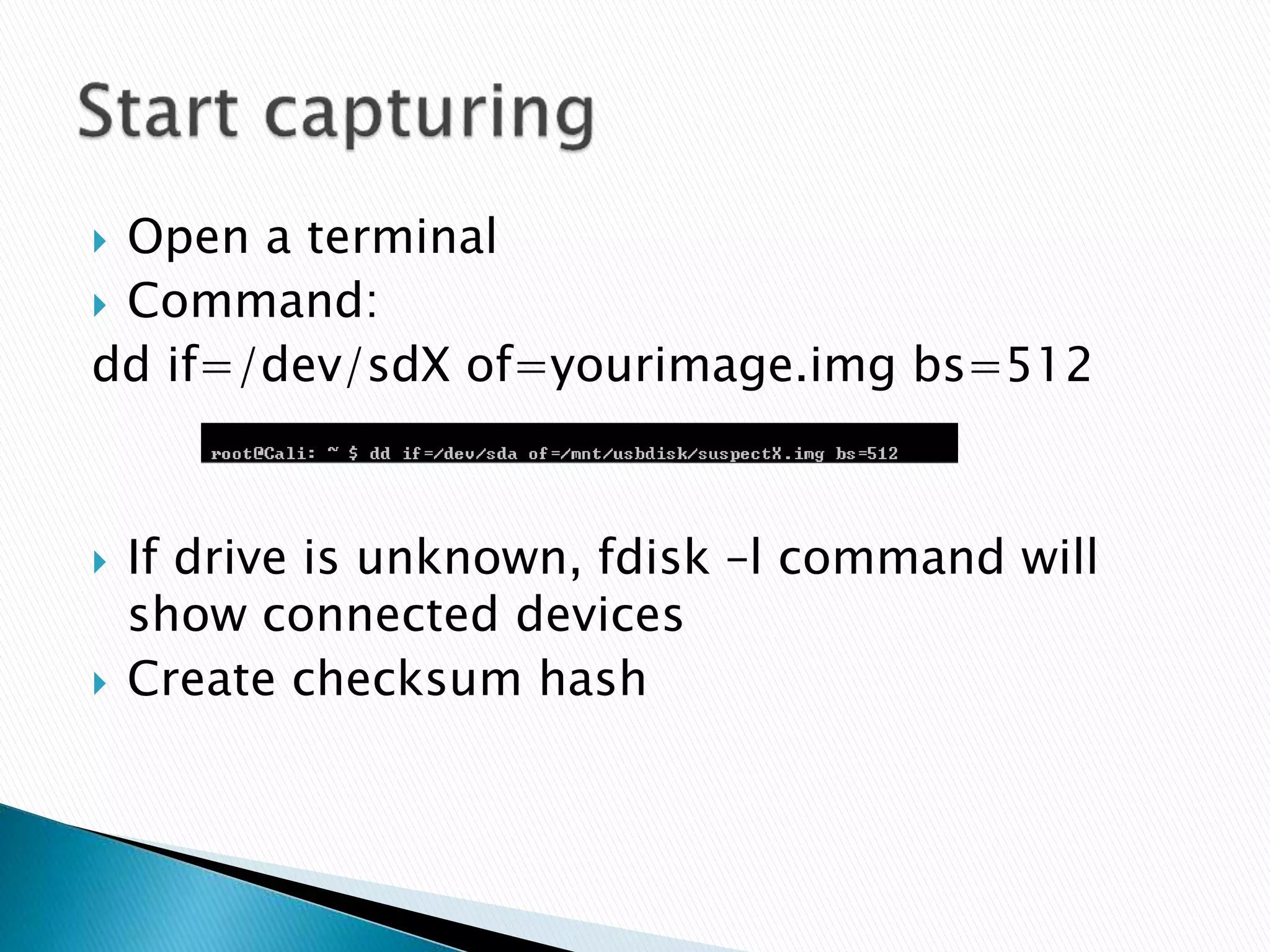
This document provides guidance on acquiring forensic images of digital evidence for investigation using either Windows or Linux tools. It outlines the necessary hardware requirements, recommended wiping of the destination drive, imaging software options like FTK Imager or dd, and technical procedures for capturing a disk image while avoiding modification of the original data. Checksums are generated to validate image integrity and documentation of all capture steps is emphasized.