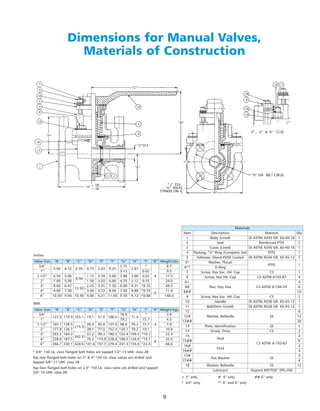
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Cam-Line® plastic lined trunnion ball valve, which is designed to address common issues in conventional valves by offering reliable sealing, reduced operating torque, and long service life. It highlights innovation in design, materials, and manufacturing processes, emphasizing the valve's suitability for various industries due to its durable construction and performance advantages. Additionally, the document includes technical specifications, options for actuators, and features such as venting and grounding devices.