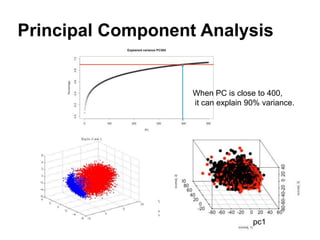
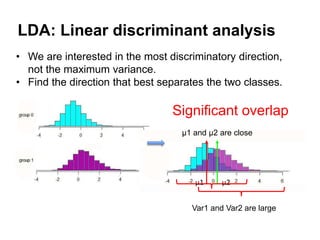
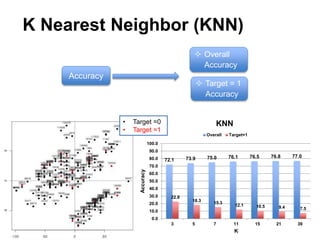
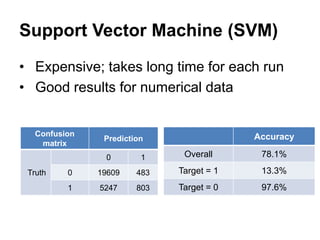
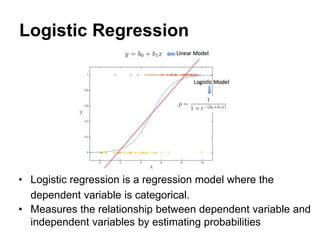
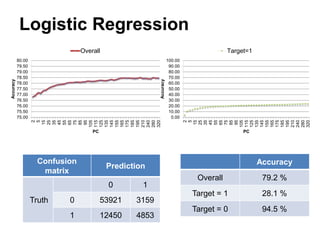
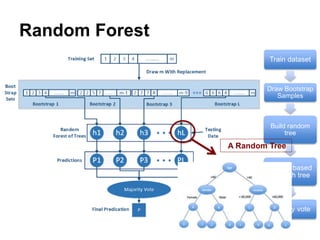
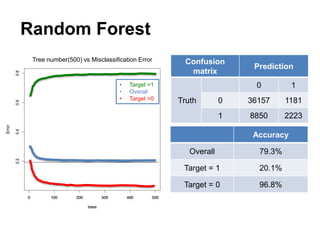
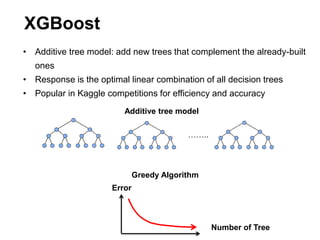
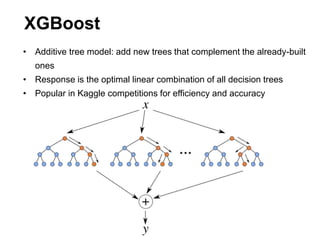
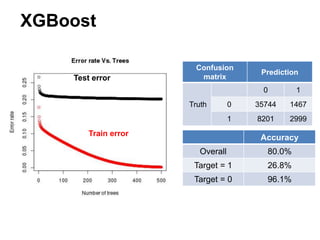
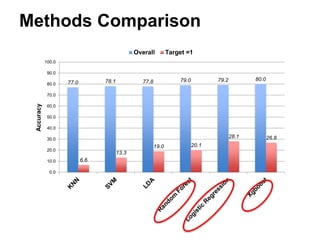
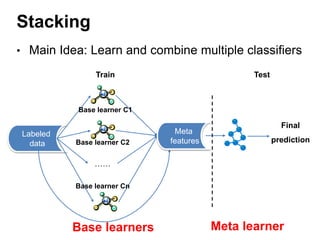
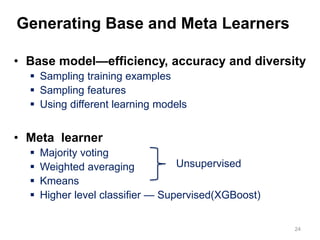
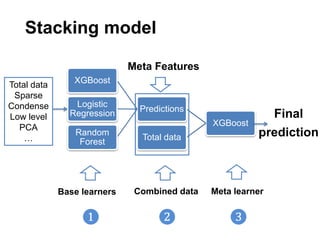
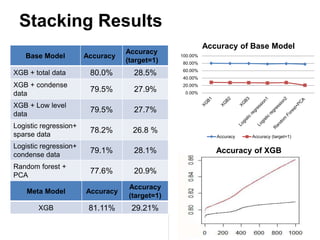
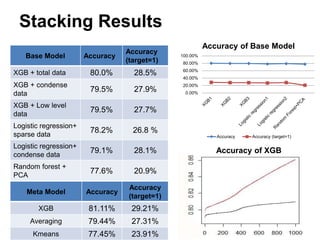
This document summarizes a team's analysis of the Springleaf lending dataset from a Kaggle competition. The team tested several classification methods including logistic regression, random forest, XGBoost, and stacking. Their best performing model was an XGBoost stacking ensemble that achieved an accuracy of 81.1% with 29.2% accuracy on the minority class. Through extensive data preprocessing and hyperparameter tuning, the team was able to improve on the winner's publicly reported accuracy of 80.4% despite their final result being 79.5%.



![Missing values
• “”, “NA”: 0.6%
• “[]”, -1: 2.0%
• -99999, 96, …, 999, …,
99999999: 24.9%
• 25.3% columns have
missing values 61.7%
Count of NAs in each column Count of NAs in each row](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcosfinalpresentationgroup2-230408203254-80f00851/85/CAMCOS_final-Presentation_Group2-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![Data preprocessing
Remove ID and target
Replace NA by median Replace NA randomly
Replace [] and -1 as NA
Remove duplicate cols
Replace character cols
Remove low variance cols
Regard NA as a new group
Normalize Log(1+|x|)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcosfinalpresentationgroup2-230408203254-80f00851/85/CAMCOS_final-Presentation_Group2-pptx-7-320.jpg)